【NLP】Conditional Language Modeling with Attention
Review: Conditional LMs
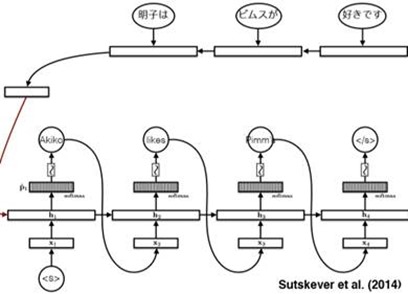
Note that, in the Encoder part, we reverse the input to the ‘RNN’ and it performs well.
And we use the Decoder network(also a RNN), and use the ‘beam search’ algorithm to generate the target statement word by word.
The above network is a translation model.But it still needs to optimizer.
A very essential part of the model is the [Attention mechanism].
Conditional LMs with Attention
First: talk about the [condition]
In last blog, we compress a lot of information in a finite-sized vector and use it as the condition. That is to say, in the ‘Decoder’, for each input we use this vector as the condition to predict the next word.
But is it really correct?
An obvious thing is that a finite-sized vector cannot contain all the information since the input sentence could have a very one length. And gradients have a long way to travl so even LSTMs could forget!
In Translation Question, we can solve the problem by this:
Represent a source sentence as a matrix whose size can be changeable.
Then Generate a target sentence from the matrix. (As the condition and the condition is transformed form that matrix)
So how does this do?
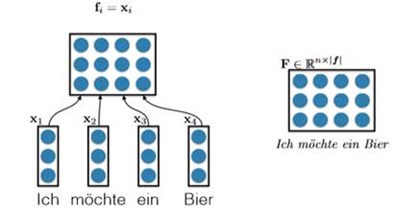
The very simpal way to fulfill that is [With Concatenation].
We have already known that the words can be represented by ‘embedding’ such as Word2Vec. And all the embeddings have the same size. For a sentence composed by n words, we can just put each word’s embedding together. So the matrix size is |vocabulary size|*n, which n is the length of sentence. That’s a really easy solution but it is useful. E.g.
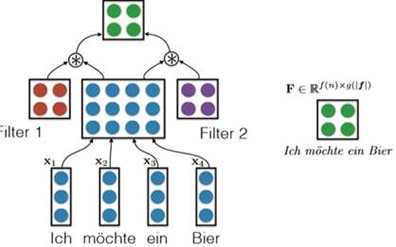
Another solution proposed by Gehring et al. (2016,FAIR) is [With Convolutional Nets].
It is to say, we use all embedding of the word from the sentence to form the concatenation matrix (just like the above method), and then we use a CNN to handle this matrix using some filters. And final we also generate a new matrix to represent the information. And in my opinion, this is a bit like extracting advanced features from image processing. E.g.
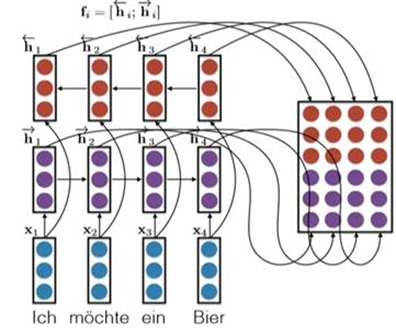
The most important method is [using the Bidirectional RNNs].
For one side, we use a RNN to handle the embedding, and we get n hidden layers which n is the length of the word.
For another side, we use another RNN to handle the embedding, but we reverse the input and finally we also get n hidden layers.
We put the 2n hidden layers together to generate the conditional matrix. E.g.
There are some other ways needed to be founded.
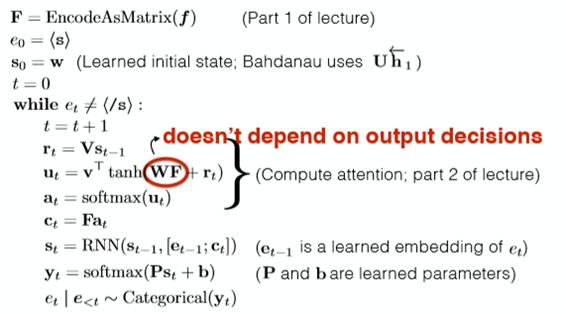
So next to the important part: how to use the ‘Attention model’ and use the attention to generate the condition vector form the condition matrix F.
Firstly, considering the decoder RNN:

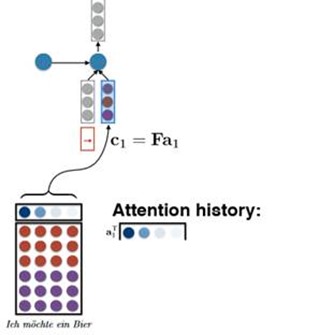
We have a ‘start hidden layer’ and then generate the next hidden layer using the input x and we still need a conditional vector.
Suppose we also had an attention vector a. We can generate the condition vector by doing this:
c = Fa. Where F is the matrix and a is the attention vector. This can be understood as weighting the conditional matrix so that we can pay more attention to the contents of a certain sentence.
E.g.
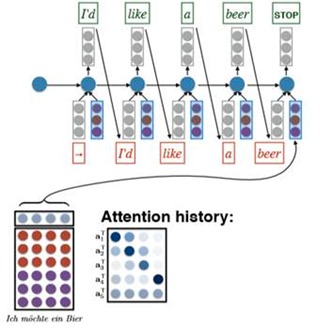
So How to generate the Attention Vector?
That is, how do we compute a.
We can do by the following method:
For the time t, we know the hidden layer Ht-1, and we do linear transformation to it to generate a vector r. ( r = VHt-1) V is the learned parameter. Then we take dot product with every column in the source matrix to compute the attention energy a. ( a = F.T*r). So we generate the attention vector a by using a softmax to Exponentiate and normalize it to 1.
That is a simplified version of Bahdanau et al.’s solution. Summary of it:
|
|
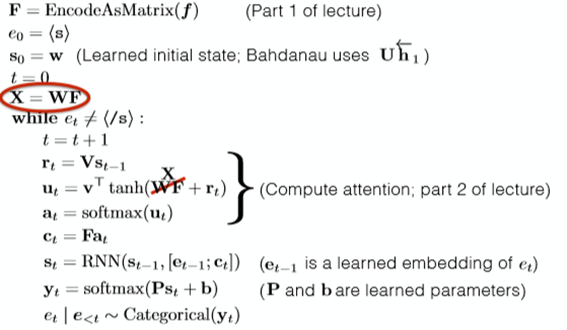
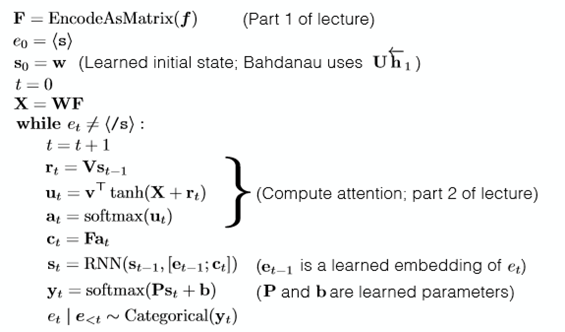
Another complex way to generate the attention vector is to use the [Nonlinear Attention-Energy Model].
Getting the r above, ( r = VHt-1) we generate a by: a = v.T * tanh(WF + r). Where v W and V is the learned parameter. How useful of the r is not to verify.
Summary
We put it all together and this is called the conditional LM with attention.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Attention in machine translation.
Add attention to seq2seq model translation: +11 BLEU.
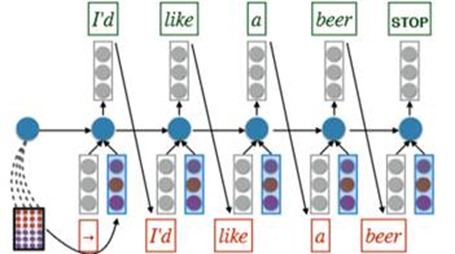
An improvement in computing:
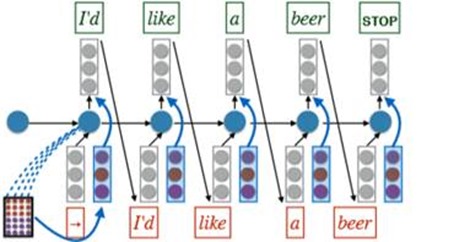
Note the difference form the above model. But whether it is useful is not sure.
About Gradients
We use the Gradient Descent.

Comprehension
Cho’s question: does a translator read and memorize the input sentence/document and then generate the output?
• Compressing the entire input sentence into a vector basically says “memorize the sentence”
• Common sense experience says translators refer back and forth to the input. (also backed up by eyetracking studies)
Image caption generation with attention: brief introduction
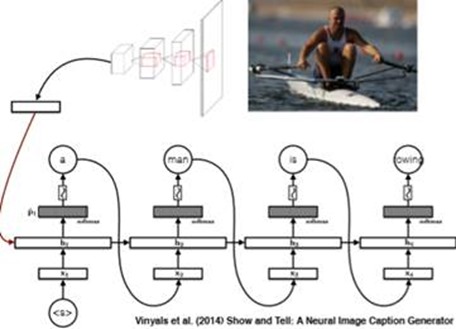
The main idea is that: we encode the picture to a matrix F and use it generate some attention and finally use the attention to generate the caption.
Generate matrix F:
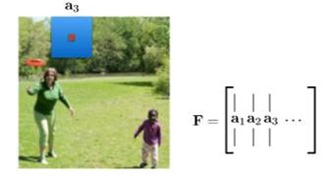
Attention “weights” (a) are computed using exactly the same technique as discussed above.
Other techinques: Stochastic hard attention(sampling matrix F idea and not like the weighting matrix F idea). Learning Hard Attention. To be honesty, I don't know much about this.
【NLP】Conditional Language Modeling with Attention的更多相关文章
- 【NLP】Conditional Language Models
Language Model estimates the probs that the sequences of words can be a sentence said by a human. Tr ...
- 【NLP】Tika 文本预处理:抽取各种格式文件内容
Tika常见格式文件抽取内容并做预处理 作者 白宁超 2016年3月30日18:57:08 摘要:本文主要针对自然语言处理(NLP)过程中,重要基础部分抽取文本内容的预处理.首先我们要意识到预处理的重 ...
- [转]【NLP】干货!Python NLTK结合stanford NLP工具包进行文本处理 阅读目录
[NLP]干货!Python NLTK结合stanford NLP工具包进行文本处理 原贴: https://www.cnblogs.com/baiboy/p/nltk1.html 阅读目录 目 ...
- 【NLP】前戏:一起走进条件随机场(一)
前戏:一起走进条件随机场 作者:白宁超 2016年8月2日13:59:46 [摘要]:条件随机场用于序列标注,数据分割等自然语言处理中,表现出很好的效果.在中文分词.中文人名识别和歧义消解等任务中都有 ...
- 【NLP】基于自然语言处理角度谈谈CRF(二)
基于自然语言处理角度谈谈CRF 作者:白宁超 2016年8月2日21:25:35 [摘要]:条件随机场用于序列标注,数据分割等自然语言处理中,表现出很好的效果.在中文分词.中文人名识别和歧义消解等任务 ...
- 【NLP】基于机器学习角度谈谈CRF(三)
基于机器学习角度谈谈CRF 作者:白宁超 2016年8月3日08:39:14 [摘要]:条件随机场用于序列标注,数据分割等自然语言处理中,表现出很好的效果.在中文分词.中文人名识别和歧义消解等任务中都 ...
- 【NLP】基于统计学习方法角度谈谈CRF(四)
基于统计学习方法角度谈谈CRF 作者:白宁超 2016年8月2日13:59:46 [摘要]:条件随机场用于序列标注,数据分割等自然语言处理中,表现出很好的效果.在中文分词.中文人名识别和歧义消解等任务 ...
- 【NLP】条件随机场知识扩展延伸(五)
条件随机场知识扩展延伸 作者:白宁超 2016年8月3日19:47:55 [摘要]:条件随机场用于序列标注,数据分割等自然语言处理中,表现出很好的效果.在中文分词.中文人名识别和歧义消解等任务中都有应 ...
- 【NLP】Attention Model(注意力模型)学习总结
最近一直在研究深度语义匹配算法,搭建了个模型,跑起来效果并不是很理想,在分析原因的过程中,发现注意力模型在解决这个问题上还是很有帮助的,所以花了两天研究了一下. 此文大部分参考深度学习中的注意力机制( ...
随机推荐
- 【代码笔记】Web-CSS-CSS样式列表(url)
一,效果图. 二,代码. <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> ...
- ios手机录屏软件哪个好
苹果手机中的airplay镜像,是苹果手机系统的一大特色,可以轻松把手机屏幕投射电脑,这个功能使苹果手机相较安卓手机投屏会更加轻松,那么如何实现苹果手机投射电脑屏幕?下面小编便来分享ios手机录屏软件 ...
- ps -ef |grep java
一.ps -ef |grep java 查看包含“java”的所有进程 二.涉及命令详解 ps命令将某个进程显示出来(是LINUX下最常用的也是非常强大的进程查看命令) grep命令是查找(是一种强大 ...
- LEDAPS1.3.0版本移植到windows平台----HuPm参数初始化模块
这个是2012年左右放在百度空间的,谁知百度空间关闭...转移到博客园. 最近项目用到3.1.2版本的LEDAPS,新版本的使用情况会在后续文章中慢慢丰富. LEDAPS的调用顺序是:HuPm--&g ...
- asp.net core webapi/website+Azure DevOps+GitHub+Docker
asp.net core webapi/website+Azure DevOps+GitHub+Docker 新春开篇作,主要写一下关于asp.net core web/api 2.2 项目借助dev ...
- Xshell工具使用--连接VMware虚拟机
假设有这样的场景,开发者用的是Windows系统,且系统的存储资源和内存有限,在运行VMware虚拟机中做一些测试时,通常会碍于电脑的VMWare客户端图形界面的响应速度太慢.而在Xshell中对虚拟 ...
- ES6常用
ECMAScript 6(以下简称ES6)是JavaScript语言的下一代标准. 因为当前版本的ES6是在2015年发布的,所以又称ECMAScript 2015(简称ES2015).虽然浏览器在不 ...
- 浅析Springboot自动配置
首先我们先来看springboot的主程序类,主程序类中使用@SpringBootApplication注解来标记说明这是一个springboot应用,查看该注解源码如下图: 图中的@EnableAu ...
- centos7 安装java运行环境
1.检测是否存在相关历史版本 shell:java-version 1.1.存在相关OpenJDK和其他版本SDK则需要删除,如图. 查看详细信息,命令窗口输入,shell:rpm -qa | gre ...
- Spark之Pipeline处理模式
一.简介 Pipeline管道计算模式:只是一种计算思想,在数据处理的整个流程中,就想水从管道流过一下,是顺序执行的. 二.特点 1.数据一直在管道中,只有在对RDD进行持久化[cache,persi ...