C++ 双链表基本操作
上一篇博客主要总结了单向链表,这次再总结一下双向链表.
1.概念
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。一般我们都构造双向循环链表。
结构图如下所示:
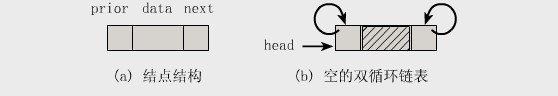
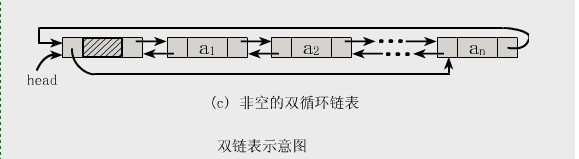
2.基本操作实例
DoubleList.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "DoubleList.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
DoubleList::DoubleList()
{
pDoubleListNode pDouList = NULL;
// 创建双链表
CreateDouList(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 打印逆序链表
PrintDouReverseList(pDouList);
// 节点后插入节点
InsertNodeAfter(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 节点前插入节点
InsertNodeBefore(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 删除节点
DeleteNode(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 删除链表
DeleteDouList(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
system("PAUSE");
}
DoubleList::~DoubleList()
{
}
//创建双向链表
void DoubleList::CreateDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
char x; // 定义成char型是用于输入'q'时可以退出,其实定义成int也能退出
pDoubleListNode p, s;
head = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
head->next = NULL;
head->prior = NULL; // 构造头结点p
p = head;
printf("\n输入双向链表的元素,每输入一个元素后按回车,输入q表示结束.\n");
fflush(stdin); //清空输入缓冲区
x = getchar();
while (x != 'q')
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = x - ''; // 得到的是输入字符的ASCII码,减去30H就变成想要的数字
s->next = NULL;
s->prior = p;
p->next = s;
p = s;
fflush(stdin);
x = getchar();
}
if (x == 'q')
{
printf("双向链表构造完毕!\n");
}
}
//打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
pDoubleListNode p;
printf("\n打印出双向链表数据为:\n");
if (!IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
p = head->next;
while (p)
{
printf("%d\n", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
}
//逆序打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouReverseList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
pDoubleListNode p;
printf("\n打印出逆序双向链表数据为:\n");
if (!IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
p = head->next;
while (p->next)
{
p = p->next;
}
while (p->prior)
{
printf("%d \n", p->data);
p = p->prior;
}
}
}
//求链表长度
int DoubleList::GetDouListLength(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int length = ;
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else
{
pDoubleListNode p = head->next;
while (p)
{
length++;
p = p->next;
}
}
return length;
}
//判断链表是否为空
bool DoubleList::IsDouListEmpty(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
return true;
}
else if (head->next == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空!\n");
return true;
} return false;
}
//把双向链表置空
void DoubleList::ClearDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else
{
pDoubleListNode p, q;
p = q = head->next; //是p、q指向第一个元素
head->next = NULL;
while (p) //逐个释放元素所占内存
{
p = p->next;
free(q);
q = p;
}
}
}
// 删除双向链表
void DoubleList::DeleteDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
printf("\n删除双向链表\n");
ClearDouList(head);
free(head);
head = NULL;
}
// 在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素
void DoubleList::InsertNodeAfter(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int data, pos;
pDoubleListNode p, s;
p = head;
int i = ;
printf("\n在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素\n");
printf("请输入要插入的元素和位置:\n");
scanf_s("%d%d", &data, &pos, );
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else if (head->next == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空,插入第一个元素!\n");
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = NULL;
s->next = NULL;
head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后
}
else if (pos< || pos>GetDouListLength(head) + )
{
printf("插入位置错误!\n");
}
else
{
while (i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if (i == GetDouListLength(head)) //如果在最后一个元素后面插入data
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->next = NULL;
s->prior = p;
p->next = s;
}
else
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = s;
p->next = s;
s->prior = p;
}
}
}
// 在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素
void DoubleList::InsertNodeBefore(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int data, pos;
pDoubleListNode p, s;
p = head;
int i = ;
printf("\n在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素\n");
printf("请输入要插入的元素和位置:\n");
scanf_s("%d%d", &data, &pos, );
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else if (head->next == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空,插入第一个元素!\n");
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = NULL;
s->next = NULL;
head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后
}
else if (pos< || pos>GetDouListLength(head) + )
{
printf("插入位置错误!\n");
}
else
{
while (i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if (i == ) // 如果在第一个元素前面插入data
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后
s->prior = head; // 新结点的前结点指向头结点
s->next = p; // 新结点的后结点指向原head的后结点
p->prior = s ; // 原第一个结点的前结点指向新结点
}
else
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = p->prior;
s->next = p;
p->prior->next = s;
p->prior = s;
}
}
}
//删除双向链表中的第i个元素
void DoubleList::DeleteNode(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int pos;
int i = ;
pDoubleListNode p = head;
printf("\n在双向链表中删除第i个位置的元素\n");
printf("请输入要删除的位置:");
scanf_s("%d", &pos, ); if (IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
return;
}
else if (pos< || pos>GetDouListLength(head))
{
printf("删除的位置不存在!\n");
}
else
{
while (i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if (i == GetDouListLength(head))
{
p->prior->next = NULL;
free(p);
}
else
{
p->prior->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = p->prior;
free(p);
}
}
}
DoubleList.h
#pragma once
typedef struct DoubleListNode
{
int data; //数据
struct DoubleListNode *prior; //前驱
struct DoubleListNode *next; //后继
}DoubleListNode, *pDoubleListNode;
class DoubleList
{
public:
DoubleList();
~DoubleList();
//初始化双向链表
void DoubleList::CreateDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//逆序打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouReverseList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//求链表长度
int DoubleList::GetDouListLength(pDoubleListNode &head);
//判断链表是否为空
bool DoubleList::IsDouListEmpty(pDoubleListNode &head);
//把双向链表置空
void DoubleList::ClearDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//删除双向链表
void DoubleList::DeleteDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素m
void DoubleList::InsertNodeAfter(pDoubleListNode &head);
// 在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素
void DoubleList::InsertNodeBefore(pDoubleListNode &head);
//删除双向链表中的第i个元素
void DoubleList::DeleteNode(pDoubleListNode &head);
};
3.对链表插入节点的理解
例如在节点i前插入一个新的节点(即上面代码中的InsertNodeBefore函数):
链表结构体为:
假设该链表由五个节点构成,分别为A,B,C,D,E
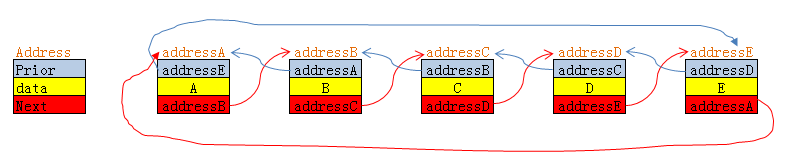
图中假设了A,B,C,D,E的地址分别为:addressA,addressB,addressC,addressD,addressE。
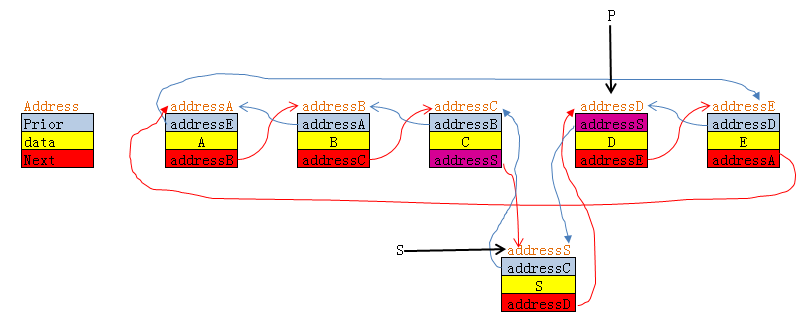
下面将分析链表的前插的例子:
双链表的前插,下面这是在节点"D"前插入一个新的节点"S"的代码和分析
C++ 双链表基本操作的更多相关文章
- c语言实现双链表的基本操作—增删改查
//初始化 Node*InitList() { Node*head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); if(NULL==head) { printf("内存分配失败! ...
- [C++11][数据结构]自己的双链表实现
这个双链表,是我模仿stl的list制作的,只实现了一些基本功能,像merge,transfer这些就没有实现,用户可以用基本操作来自己做外部实现. 我没有选用stl的[begin,end)迭代器模式 ...
- 双链表【参照redis链表结构】
参照了Redis里面的双链表结构,可以说是完全复制粘贴,redis的双链表还是写的很通俗易懂的,没有什么花里胡哨的东西,但是redis还有个iter迭代器的结构来遍历链表.我这里就没有实现了,只是实现 ...
- python-实现双链表
双链表和单链表进行比较的优点与不同 节点多了一个前驱指针域 在很多基本操作上,多了一种选择,因为双链表可以向前进行移动寻位 如果给每个节点添加一个对应的下标,那么在寻找节点时,我们可以使用二分发来进行 ...
- JAVA 链表操作:单链表和双链表
主要讲述几点: 一.链表的简介 二.链表实现原理和必要性 三.单链表示例 四.双链表示例 一.链表的简介 链表是一种比较常用的数据结构,链表虽然保存比较复杂,但是在查询时候比较便捷,在多种计算机语言都 ...
- java实现双链表(差点没写吐系列...)
刚才把单链表写完了,现在又把双链表写了,双链表和单链表的区别就是每个节点有prior和next两个指针,不同于单链表的一个next指针,而且,正是因为有这两个指针,所以双链表可以前后两个方向去移动指针 ...
- 数据结构图文解析之:数组、单链表、双链表介绍及C++模板实现
0. 数据结构图文解析系列 数据结构系列文章 数据结构图文解析之:数组.单链表.双链表介绍及C++模板实现 数据结构图文解析之:栈的简介及C++模板实现 数据结构图文解析之:队列详解与C++模板实现 ...
- C和指针 第十二章 使用结构和指针 双链表和语句提炼
双链表中每个节点包含指向当前和之后节点的指针,插入节点到双链表中需要考虑四种情况: 1.插入到链表头部 2.插入到链表尾部 3.插入到空链表中 4.插入到链表内部 #include <stdio ...
- C#双链表
单链表允许从一个结点直接访问它的后继结点,所以, 找直接后继结点的时间复杂度是 O(1).但是,要找某个结点的直接前驱结点,只能从表的头引用开始遍历各结点.如果某个结点的 Next 等于该结点,那么, ...
随机推荐
- Windows下编译openssl
依赖工具: 1.VS 2.perl 编译方法: release: :\> 切换到openssl目录 :\> perl Configure VC-WIN32 no-asm --prefix= ...
- mysql 参数read_rnd_buffer_size的真正含义
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/order-by-optimization.html http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/ ...
- 第三方Push服务:Urban Airship
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/kmyhy/article/details/7355756 关于推送通知,除了苹果的APNs之外,我们还有其它选择. Urban Airship就是其中 ...
- 使用@media实现IE hack的方法
文章简介:众所周知,有些时候为了实现IE下的某些效果与现代浏览器一致,我们不得不使用一些hack手段来实现目的.比如说使用“\0”,“\”和“\9”来仅让IE某些版本识别,而对于现代浏览器来说,他会直 ...
- CBM-业务组件模型
- (Android学习系列)一,用按钮实现时间的显示
我们先用AndroidStudio新建一个项目,选择空白模板,然后像其中拖入两个Button,将他们的id分别命名为btDate(显示日期),btTime(显示时间),他的模板XML代码很简单 < ...
- uva 327 Evaluating Simple C Expressions 简易C表达式计算 stl模拟
由于没有括号,只有+,-,++,--,优先级简单,所以处理起来很简单. 题目要求计算表达式的值以及涉及到的变量的值. 我这题使用stl的string进行实现,随便进行练手,用string的erase删 ...
- 重构10-Extract Method(提取方法)
我们要介绍的重构是提取方法.这个重构极其简单但却大有裨益.首先,将逻辑置于命名良好的方法内有助于提高代码的可读性.当方法的名称可以很好地描述这部分代码的功能时,可以有效地减少其他开发者的研究时间.假设 ...
- VS2013 支持python和nodejs
一.在VS2013中,安装python的支持 1. http://pytools.codeplex.com/下载插件 2. https://www.python.org/download/下载Pyth ...
- WebStrom9 体验nodejs
之前就有体验过 WebStrom8.0.3 版本,确实不错. 最喜欢的是集成了Terminal 很方便的使用NPM,今天装上发现 Terminal 死活打不上字.什么原因! WebStrom9 在wi ...
