pymongo 笔记(转)
1. 安装MongoDB并启动服务,安装PyMongo
2. 连接MongoDB,并指定连接数据库、集合
import pymongo client = pymongo.MongoClient(host='localhost', port=27017)
client = MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017/') db = client.test
db = client['test'] collection = db.students
collection = db['students']
3. 插入
student = {
'id': '20170101',
'name': 'Jordan',
'age': 20,
'gender': 'male'
}
'''
result = collection.insert(student)
print(result) #5932a68615c2606814c91f3d
result = collection.insert([student, student])
print(result) #[ObjectId('5932a80115c2606a59e8a048'), ObjectId('5932a80115c2606a59e8a049')]
'''
#PyMongo 3.x版本中推荐使用 insert_one、insert_many
result = collection.insert_one(student)
print(result.inserted_id)
result = collection.insert_many([student, student])
print(result.inserted_ids)
4. 查询
result = collection.find_one({'name': 'Mike'})
print(type(result)) #<class 'dict'>
print(result)
from bson.objectid import ObjectId
result = collection.find_one({'_id': ObjectId('593278c115c2602667ec6bae')}) #查询指定id结果
print(result)
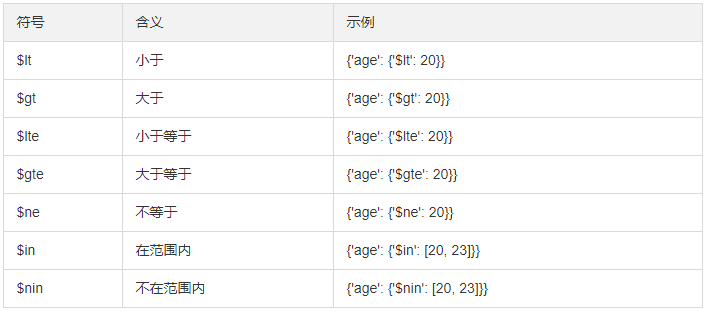
results = collection.find({'age': 20}) #等值查询
results = collection.find({'age': {'$gt': 20}}) #大于20
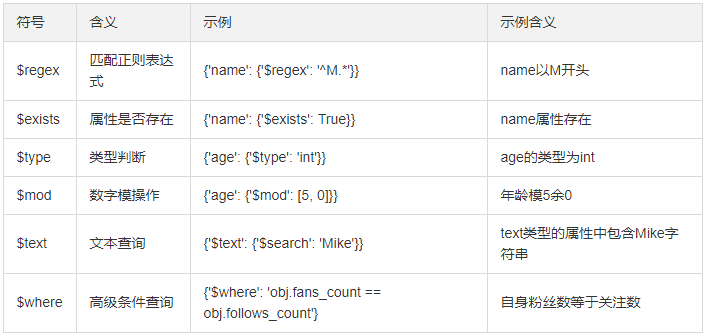
results = collection.find({'name': {'$regex': '^M.*'}}) #正则,M开头
print(results) #cursor对象,相当于生成器
for result in results:
print(result)
5. 计数
count = collection.find().count()
count = collection.find({'age': 20}).count()
print(count)
6. 排序
results = collection.find().sort('name', pymongo.ASCENDING) #DESCENDING
print([result['name'] for result in results])
7. 偏移
''' 忽略前N个元素,取几条
注意:在数据库数量非常庞大的时候,如千万、亿级别,最好不要使用大的偏移量来查询数据,
因为这样很可能导致内存溢出。最好记录上次_id用条件查询
'''
results = collection.find().sort('name', pymongo.ASCENDING).skip(2)
results = collection.find().sort('name', pymongo.ASCENDING).skip(2).limit(2)
print([result['name'] for result in results])
8. 更新
'''
首先指定查询条件,然后将数据查询出来,修改年龄后调用update()方法将原条件和修改后的数据传入。
condition = {'name': 'Kevin'}
student = collection.find_one(condition)
student['age'] = 25
result = collection.update(condition, student)
print(result) #{'ok': 1, 'nModified': 1, 'n': 1, 'updatedExisting': True} 这样可以只更新student字典内存在的字段。如果原先还有其他字段,则不会更新,也不会删除。
而如果不用$set的话,则会把之前的数据全部用student字典替换;如果原本存在其他字段,则会被删除。
result = collection.update(condition, {'$set': student})
''' # 推荐使用
condition = {'name': 'Kevin'}
student = collection.find_one(condition)
student['age'] = 26
result = collection.update_one(condition, {'$set': student}) condition = {'age': {'$gt': 20}}
result = collection.update_one(condition, {'$inc': {'age': 1}}) #年龄+1
#result = collection.update_many(condition, {'$inc': {'age': 1}})
print(result)
print(result.matched_count, result.modified_count)
9. 删除
'''result = collection.remove({'name': 'Kevin'}) #符合条件的所有记录'''
#推荐使用
result = collection.delete_one({'name': 'Kevin'})
result = collection.delete_many({'age': {'$lt': 25}})
print(result)
print(result.deleted_count)
10. 其他组合方法
create_index、create_indexes、drop_index
find_one_and_delete、find_one_and_replace、find_one_and_update
参考链接:
pymongo 笔记(转)的更多相关文章
- Pymongo 笔记
Pymongo 1.MongoDB概念 MongoDB是一种非关系型数据库(NoSQL),MongoDB数据存储于内存,内存不足则将热度低数据写回磁盘.存储的数据结构为文档.每个数据库包含若干集合(c ...
- pymongo 3.3 使用笔记
#首先安装pymongo sudo pip install pymongo || sudo easy_install pymongo #demo均在交互解释器下进行 from pymongo impo ...
- MongoDB学习笔记六:进阶指南
[数据库命令]『命令的工作原理』MongoDB中的命令其实是作为一种特殊类型的查询来实现的,这些查询针对$cmd集合来执行.runCommand仅仅是接受命令文档,执行等价查询,因此,> db. ...
- 《Python 数据科学实践指南》读书笔记
文章提纲 全书总评 C01.Python 介绍 Python 版本 Python 解释器 Python 之禅 C02.Python 基础知识 基础知识 流程控制: 函数及异常 函数: 异常 字符串 获 ...
- 学习笔记:python3,PIP安装第三方库(2017)
https://pip.pypa.io/en/latest/quickstart/ pip的使用文档 http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/ .whl ...
- python高级编程读书笔记(一)
python高级编程读书笔记(一) python 高级编程读书笔记,记录一下基础和高级用法 python2和python3兼容处理 使用sys模块使程序python2和python3兼容 import ...
- python学习笔记比较全
注:本笔记基于python2.6而编辑,尽量的偏向3.x的语法 Python的特色 1.简单 2.易学 3.免费.开源 4.高层语言: 封装内存管理等 5.可移植性: 程序如果避免使用依赖于系统的特性 ...
- 笔记-python lib-pymongo
笔记-python lib-pymongo 1. 开始 pymongo是python版的连接库,最新版为3.7.2. 文档地址:https://pypi.org/project/pymong ...
- Scrapy笔记06- Item Pipeline
Scrapy笔记06- Item Pipeline 当一个item被蜘蛛爬取到之后会被发送给Item Pipeline,然后多个组件按照顺序处理这个item. 每个Item Pipeline组件其实就 ...
随机推荐
- 剑指Offer-28.数组中出现次数超过一半的数字(C++/Java)
题目: 数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字.例如输入一个长度为9的数组{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}.由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2.如 ...
- docker修改系统时间总结
最近弄docker烦躁的一笔,时区问题踩了不少坑,为了以后再遇到类似问题再花时间查资料,特记录一下... Ubuntu: echo "Asia/Shanghai" > /et ...
- 【LOJ2402】「THUPC 2017」天天爱射击 / Shooting(整体二分)
点此看题面 大致题意: 有\(n\)个区间,每个区间有一个权值,当权值变成\(0\)时消失.每个时刻将覆盖某一位置的所有区间权值减\(1\),求每个时刻有多少个区间在这一刻消失. 前言 整体二分裸题啊 ...
- 【Sublime】Sublime 常用插件
1.sublime设置默认浏览器及打开网页的快捷键设置插件 名称:SideBarEnhancements 地址:https://github.com/titoBouzout/SideBarEnhanc ...
- centos6和centos7的防火墙基本命令
一.centos6: 1.firewall的基本启动/停止/重启命令 $查看防火墙状态: service iptables status (/etc/init.d/iptables status) $ ...
- python写文件时,使用代码强制刷新文件
一.实验环境 1.Windows10x64 2.anaconda4.6.9 + python3.7.1(anaconda集成,不需单独安装) 3.pyinstaller3.5 二.任务需求 三.问题描 ...
- vue的基础概念和语法01
vue的特点和web开发中的常见高级功能 解耦视图和数据 可复用的组件 前端路由技术 状态管理 虚拟DOM 数据响应式 不是所有元素操作都Vue都会监听并实现数据响应式 //push方法:追加 thi ...
- ES5提取公共变量
在ES5中,请求地址前缀等需要作为公共变量提出. 则需在common.js写上 Object.defineProperty(window,'base',{ value:"http://xx. ...
- PostgreSQL 12 YUM安装
目录 1.创建postgres用户 2.查看操作系统版本 3.配置yum源(对应CentOS 6) 4.安装客户端包 5.安装服务器端包 6.初始化数据库和设置自启动服务 7.postgres用户的b ...
- SLB外部端口非80时---》转发到nginx---》URL跳转丢失端口的解决方案
配置nginx反向代理时遇到一个问题,当设置nginx监听80端口时转发请求没有问题.但一旦设置为监听其他端口,就一直跳转不正常: 如,访问欢迎页面时应该是重定向到登录页面,在这个重定向的过程中端口丢 ...
