java自学-常用api
API(Application Programming Interface),应用程序编程接口。Java API是JDK中提供给我们使用的类的说明文档。即jdk包里边写好的类,这些类将底层的代码实现封装了起来,我们不需要关心这些类是如何实现的,只需要学习这些类如何使用即可。所以我们可以通过查询API的方式,来学习Java提供的类,并得知如何使用它们。
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList就是一个常用集合类,我们可以调用调用这个类的方法来进行业务操作,不需要我们自己去实现一个集合功能。下面介绍一些常用的类。
1.String类
String s1 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1);
String s1 = "abc";
s1 += "d";
System.out.println(s1); // "abcd"
// 值不变,不是说变量s1不能变,是字符串"abc"不变,内存中有"abc","abcd"两个对象,s1从指向"abc",改变指向,指向了"abcd"。 String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "abc"; // 内存中只有一个"abc"对象被创建,同时被s1和s2共享。
java.lang包下的类不需要导入,可直接使用。创建String对象时,根据具体需要,调用构造方法创建
构造方法:
// 无参构造
String str = new String();
// 通过字符数组构造
char chars[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str2 = new String(chars);
// 通过字节数组构造
byte bytes[] = { 97, 98, 99 };
String str3 = new String(bytes);
public class String_Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建字符串对象
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = "HELLO";
// boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同 System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); // false
System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐");
//boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); // true
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3)); // true
}
}
public class String_Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建字符串对象
String s = "helloworld";
// int length():获取字符串的长度,其实也就是字符个数
System.out.println(s.length());
System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐");
// String concat (String str):将将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾.
String s = "helloworld";
String s2 = s.concat("**hello");
System.out.println(s2);// helloworld**hello
// char charAt(int index):获取指定索引处的字符
System.out.println(s.charAt(0));
System.out.println(s.charAt(1));
System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐");
// int indexOf(String str):获取str在字符串对象中第一次出现的索引,没有返回‐1
System.out.println(s.indexOf("l"));
System.out.println(s.indexOf("owo"));
System.out.println(s.indexOf("ak"));
System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐");
// String substring(int start):从start开始截取字符串到字符串结尾
System.out.println(s.substring(0));
System.out.println(s.substring(5));
System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐");
// String substring(int start,int end):从start到end截取字符串。含start,不含end。
System.out.println(s.substring(0, s.length()));
System.out.println(s.substring(3,8));
}
}
public class String_Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建字符串对象
String s = "abcde";
// char[] toCharArray():把字符串转换为字符数组
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
for(int x = 0; x < chs.length; x++) {
System.out.println(chs[x]);
}
System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐");
// byte[] getBytes ():把字符串转换为字节数组
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
for(int x = 0; x < bytes.length; x++) {
System.out.println(bytes[x]);
}
System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐");
// 替换字母it为大写IT
String str = "itcast";
String replace = str.replace("it", "IT");
System.out.println(replace); // ITcast
}
}
public class String_Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建字符串对象
String s = "aa|bb|cc";
String[] strArray = s.split("|"); // ["aa","bb","cc"]
for(int x = 0; x < strArray.length; x++) {
System.out.println(strArray[x]); // aa bb cc
}
}
}
2.Arrays类
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义int 数组
int[] arr = {2,34,35,4,657,8,69,9};
// 打印数组,输出地址值
System.out.println(arr); // [I@2ac1fdc4
// 数组内容转为字符串
String s = Arrays.toString(arr);
// 打印字符串,输出内容
System.out.println(s); // [2, 34, 35, 4, 657, 8, 69, 9]
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义int 数组
int[] arr = {24, 7, 5, 48, 4, 46, 35, 11, 6, 2};
System.out.println("排序前:"+ Arrays.toString(arr)); // 排序前:[24, 7, 5, 48, 4, 46, 35, 11, 6, 2]
// 升序排序
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println("排序后:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));// 排序后:[2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 11, 24, 35, 46, 48]
}
3.ArrayList类
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
public class Demo01ArrayListMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
//添加元素
list.add("hello");
list.add("world");
list.add("java");
//public E get(int index):返回指定索引处的元素
System.out.println("get:"+list.get(0));
System.out.println("get:"+list.get(1));
System.out.println("get:"+list.get(2));
//public int size():返回集合中的元素的个数
System.out.println("size:"+list.size());
//public E remove(int index):删除指定索引处的元素,返回被删除的元素
System.out.println("remove:"+list.remove(0));
//遍历输出
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
4.基本类型包装类
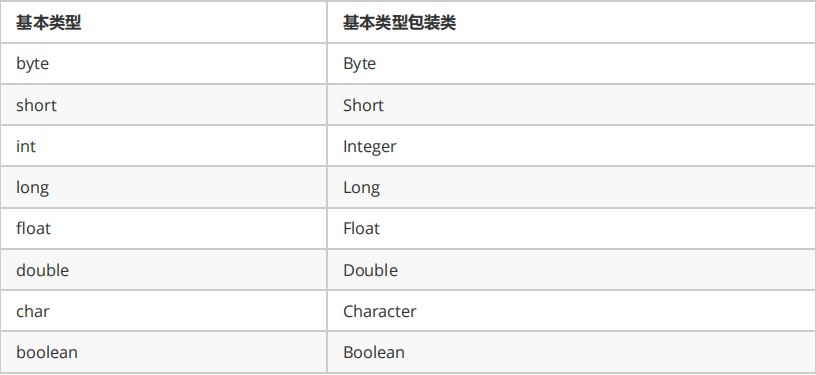
5.Random类
构造方法
Random r = new Random();
//1. 导包
import java.util.Random;
public class Demo01_Random {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//2. 创建键盘录入数据的对象
Random r = new Random();
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
//3. 随机生成一个数据
int number = r.nextInt(10);
//4. 输出数据
System.out.println("number:"+ number);
}
}
}
6.Math类
double d1 = Math.abs(‐5); //d1的值为5
double d1 = Math.ceil(3.3); //d1的值为 4.0
double d1 = Math.floor(3.3); //d1的值为3.0
long d1 = Math.round(5.5); //d1的值为6.0
java自学-常用api的更多相关文章
- Java 之常用API(一)
常用API 1 API概述 2 Scanner类与String类 3 StringBuilder类 NO.one API概述 1.1 API概述 API(Application Programm ...
- Java之常用API
API概述 什么是API API (Application Programming Interface) :应用程序编程接口 java中的API 指的就是 JDK 中提供的各种功能的 Java类,这些 ...
- Java 基础 常用API (Object类,String类,StringBuffer类)
Java API Java 的API(API: Application(应用) Programming(程序) Interface(接口)) Java API就是JDK中提供给我们使用的类,这些类将底 ...
- Java 之常用API(二)
Object类 & System类 日期相关类 包装类 & 正则表达式 Object类 & System类 1.1 Object类 1.1.1 概述 Object类是Java语 ...
- java selenium常用API(WebElement、iFrame、select、alert、浏览器窗口、事件、js) 一
WebElement相关方法 1.点击操作 WebElement button = driver.findElement(By.id("login")); button.clic ...
- Java的常用API
Object类 1.toString方法在我们直接使用输出语句输出对象的时候,其实通过该对象调用了其toString()方法. 2.equals方法方法摘要:类默认继承了Object类,所以可以使用O ...
- Java的常用API之System类简介
Syetem类 java.lang.System类中提供了大量的静态方法,可以获取与系统相关的信息或系统级操作,在System类的API文档中,常用的方法有: public static long c ...
- java selenium常用API汇总
(WebElement.iFrame.select.alert.浏览器窗口.事件.js) 一 WebElement相关方法 1.点击操作 WebElement button = driver. ...
- Java 基础 常用API (System类,Math类,Arrays, BigInteger,)
基本类型包装类 基本类型包装类概述 在实际程序使用中,程序界面上用户输入的数据都是以字符串类型进行存储的.而程序开发中,我们需要把字符串数据,根据需求转换成指定的基本数据类型,如年龄需要转换成int类 ...
随机推荐
- centos 6.x 系统基础优化简版
Centos 6.x 系统基础优化 1.更换国内yum源 删除系统带的centos官方yum源 rm -rf /etc/yum.repos.d/* 使用国内阿里云源 curl -o /etc/yum. ...
- JSON.parse() 报错和一些解决方法
js 报错 Unexpected end of JSON input,Unexpected token u in JSON at position 0 JSON 通常用于与服务端交换数据. 在接收服务 ...
- python_regex
正则表达动机(目的): 1.处理文本成为计算机主要工作之一 2.根据文本内容进行固定搜索是文本处理的常见工作 3.为了快速方便的处理上述问题,正则表达式技术诞生,逐渐发展为一种单独技 ...
- springboot+微信小程序实现微信支付【统一下单】
说明: 1)微信支付必须有营业执照才可以申请 2)微信支付官方api是全套的,我这是抽取其中的统一下单api,做了一个简单的封装 首先看看微信支付 商户系统和微信支付系统主要交互: 1.小程序内调用登 ...
- 一文看尽Java-并发编程知识点
一.前言 从7月份开始一直加班比较多,一直到双11结束,博客没跟上写,接下来写一点总结性的东西,比如Java并发编程总结.Mybatis源码总结.Spring源码和基础知识总结,首先来看下并发 ...
- 华为云DevCloud为开发者提供高效智能的可信开发环境
在HUAWEI CONNECT 2019期间,在华为云云服务开发者分论坛上,华为云布道师做了<CloudIDE:开发者的高效.智能的可信开发环境>专题演讲,主要介绍了华为云DevCloud ...
- Too many open files的四种解决办法
[摘要] Too many open files有四种可能:一 单个进程打开文件句柄数过多,二 操作系统打开的文件句柄数过多,三 systemd对该进程进行了限制,四 inotify达到上限. 领导见 ...
- Leader 让我做 CMS 帮助中心的技术选型,我撸了 VuePress 和 GitBook,然后选择...
前言 因为自己平时经常写博客,也有博客网站,所以 Leader 叫我做一个 CMS 的帮助中心的技术选型,CMS 的帮助中心的功能:是通过文章来教用户如何使用我们的项目. 所以笔者要做一个静态网站的技 ...
- [TimLinux] JavaScript 面向对象程序设计
1. 面向对象 面向对象语言有一个标志:都有类的概念.通过类可以创建任意多个具有相同属性和方法的对象.ECMAScript中没有类的概念,因此JavaScript中的对象夜雨基于类的语言中的面向对象有 ...
- django学习01-建project和app
按装完成后,执行命令 django-admin startproject mysite 建一个名字为mysite的工程.运行 python manage.py runserver 启动网络服务器,然后 ...
