Linux ip Command
Syntax
ip OBJECT COMMAND
ip [options] OBJECT COMMAND
ip OBJECT help
Understanding ip command OBJECTS syntax
OBJECTS can be any one of the following and may be written in full or abbreviated form:
|
Object |
Abbreviated form |
Purpose |
|
link |
l |
Network device. |
|
address |
a |
Protocol (IP or IPv6) address on a device. |
|
addrlabel |
addrl |
Label configuration for protocol address selection. |
|
neighbour |
n |
ARP or NDISC cache entry. |
|
route |
r |
Routing table entry. |
|
rule |
ru |
Rule in routing policy database. |
|
maddress |
m |
Multicast address. |
|
mroute |
mr |
Multicast routing cache entry. |
|
tunnel |
t |
Tunnel over IP. |
|
xfrm |
x |
Framework for IPsec protocol. |
To get information about each object use help command as follows:
ip OBJECT help
ip OBJECT h
ip a help
ip r help
Warning: The commands described below must be executed with care. If you make a mistake, you will loos connectivity to the server. You must take special care while working over the ssh based remote session.
Displays info about all network interfaces
Type the following command to list and show all ip address associated on on all network interfaces:
ip a
OR
ip addr
Sample outputs:
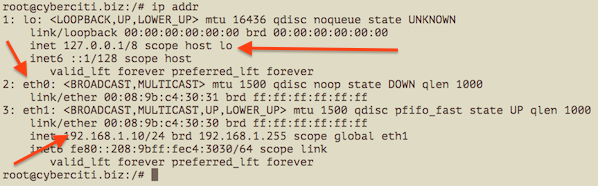
You can select between IPv4 and IPv6 using the following syntax:
### Only show TCP/IP IPv4 ## |
It is also possible to specify and list particular interface TCP/IP details:
### Only show eth0 interface ### |

Assigns the IP address to the interface
The syntax is as follows to add an IPv4/IPv6 address:
ip a add {ip_addr/mask} dev {interface}
To assign 192.168.1.200/255.255.255.0 to eth0, enter:
ip a add 192.168.1.200/255.255.255.0 dev eth0
OR
ip a add 192.168.1.200/24 dev eth0
ADDING THE BROADCAST ADDRESS ON THE INTERFACE
By default, the ip command does not set any broadcast address unless explicitly requested. So syntax is as follows to set broadcast ADDRESS:
ip addr add brd {ADDDRESS-HERE} dev {interface}
ip addr add broadcast {ADDDRESS-HERE} dev {interface}
ip addr add broadcast 172.20.10.255 dev dummy0
It is possible to use the special symbols such as + and - instead of the broadcast address by setting/resetting the host bits of the interface prex. In this example, add the address 192.168.1.50 with netmask 255.255.255.0 (/24) with standard broadcast and label “eth0Home” to the interface eth0:
ip addr add 192.168.1.50/24 brd + dev eth0 label eth0Home
You can set loopback address to the loopback device lo as follows:
ip addr add 127.0.0.1/8 dev lo brd + scope host
Remove / Delete the IP address from the interface
The syntax is as follows to remove an IPv4/IPv6 address:
ip a del {ipv6_addr_OR_ipv4_addr} dev {interface}
To delete 192.168.1.200/24 from eth0, enter:
ip a del 192.168.1.200/24 dev eth0
Flush the IP address from the interface
You can delete or remote an IPv4/IPv6 address one-by-one as described above. However, the flush command can remove as flush the IP address as per given condition. For example, you can delete all the IP addresses from the private network 192.168.2.0/24 using the following command:
ip -s -s a f to 192.168.2.0/24
Sample outputs:
2: eth0 inet 192.168.2.201/24 scope global secondary eth0
2: eth0 inet 192.168.2.200/24 scope global eth0 *** Round 1, deleting 2 addresses ***
*** Flush is complete after 1 round ***
You can disable IP address on all the ppp (Point-to-Point) interfaces:
ip -4 addr flush label "ppp*"
Here is another example for all the Ethernet interfaces:
ip -4 addr flush label "eth*"
How do I change the state of the device to UP or DOWN?
The syntax is as follows:
ip link set dev {DEVICE} {up|down}
To make the state of the device eth1 down, enter:
ip link set dev eth1 down
To make the state of the device eth1 up, enter:
ip link set dev eth1 up
How do I change the txqueuelen of the device?
You can set the length of the transmit queue of the device using ifconfig command or ip command as follows:
ip link set txqueuelen {NUMBER} dev {DEVICE}
In this example, change the default txqueuelen from 1000 to 10000 for the eth0:
ip link set txqueuelen 10000 dev eth0
ip a list eth0
How do I change the MTU of the device?
For gigabit networks you can set maximum transmission units (MTU) sizes (JumboFrames) for better network performance. The syntax is:
ip link set mtu {NUMBER} dev {DEVICE}
To change the MTU of the device eth0 to 9000, enter:
ip link set mtu 9000 dev eth0
ip a list eth0
Sample outputs:
2: eth0: <broadcast,multicast,up,lower_up> mtu 9000 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:08:9b:c4:30:30 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.10/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global eth1
inet6 fe80::208:9bff:fec4:3030/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Display neighbour/arp cache
The syntax is:
ip n show
ip neigh show
Sample outputs (note: I masked out some data with alphabets):
74.xx.yy.zz dev eth1 lladdr 00:30:48:yy:zz:ww REACHABLE
10.10.29.66 dev eth0 lladdr 00:30:48:c6:0a:d8 REACHABLE
74.ww.yyy.xxx dev eth1 lladdr 00:1a:30:yy:zz:ww REACHABLE
10.10.29.68 dev eth0 lladdr 00:30:48:33:bc:32 REACHABLE
74.fff.uu.cc dev eth1 lladdr 00:30:48:yy:zz:ww STALE
74.rr.ww.fff dev eth1 lladdr 00:30:48:yy:zz:ww DELAY
10.10.29.65 dev eth0 lladdr 00:1a:30:38:a8:00 REACHABLE
10.10.29.74 dev eth0 lladdr 00:30:48:8e:31:ac REACHABLE
The last field show the the state of the “neighbour unreachability detection” machine for this entry:
- STALE – The neighbour is valid, but is probably already unreachable, so the kernel will try to check it at the first transmission.
- DELAY – A packet has been sent to the stale neighbour and the kernel is waiting for confirmation.
- REACHABLE – The neighbour is valid and apparently reachable.
Add a new ARP entry
The syntax is:
ip neigh add {IP-HERE} lladdr {MAC/LLADDRESS} dev {DEVICE} nud {STATE}
In this example, add a permanent ARP entry for the neighbour 192.168.1.5 on the device eth0:
ip neigh add 192.168.1.5 lladdr 00:1a:30:38:a8:00 dev eth0 nud perm
Where,
| neighbour state (nud) | meaning |
| permanent | The neighbour entry is valid forever and can be only be removed administratively |
| noarp | The neighbour entry is valid. No attempts to validate this entry will be made but it can be removed when its lifetime expires. |
| stale | The neighbour entry is valid but suspicious. This option to ip neigh does not change the neighbour state if it was valid and the address is not changed by this command. |
| reachable | The neighbour entry is valid until the reachability timeout expires. |
Delete a ARP entry
The syntax to invalidate or delete an ARP entry for the neighbour 192.168.1.5 on the device eth1 is as follows.
ip neigh del {IPAddress} dev {DEVICE}
ip neigh del 192.168.1.5 dev eth1
CHANGE ARE STATE TO REACHABLE FOR THE NEIGHBOUR 192.168.1.100 ON THE DEVICE ETH1
ip neigh chg 192.168.1.100 dev eth1 nud reachable
Flush ARP entry
This flush or f command flushes neighbour/arp tables, by specifying some condition. The syntax is:
ip -s -s n f {IPAddress}
In this example, flush neighbour/arp table
ip -s -s n f 192.168.1.5
OR
ip -s -s n flush 192.168.1.5
ip route: Routing table management commands
Use the following command to manage or manipulate the kernel routing table.
Show routing table
To display the contents of the routing tables:
ip r
ip r list
ip route list
ip r list [options]
ip route
Sample outputs:
default via 192.168.1.254 dev eth1 |
Display routing for 192.168.1.0/24:
ip r list 192.168.1.0/24
Sample outputs:
192.168.1.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.10
Add a new route
The syntax is:
ip route add {NETWORK/MASK} via {GATEWAYIP}
ip route add {NETWORK/MASK} dev {DEVICE}
ip route add default {NETWORK/MASK} dev {DEVICE}
ip route add default {NETWORK/MASK} via {GATEWAYIP}
Add a plain route to network 192.168.1.0/24 via gateway 192.168.1.254:ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.1.254
To route all traffic via 192.168.1.254 gateway connected via eth0 network interface:ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0
Delete a route
The syntax is as follows to delete default gateway:
ip route del default
In this example, delete the route created in previous subsection:
ip route del 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0
How to change MAC address on Linux
he MAC address of a Linux network interface card (NIC) can be changed as follows:NIC="eno1" ## <-- My NIC name ##
ip link show $NIC
ip link set dev $NIC down
## set new MAC address ##
ip link set dev $NIC address XX:YY:ZZ:AA:BB:CC
ip link set dev $NIC up
Old vs. new tool
Deprecated Linux command and their replacement cheat sheet:
| Old command (Deprecated) | New command |
|---|---|
| ifconfig -a | ip a |
| ifconfig enp6s0 down | ip link set enp6s0 down |
| ifconfig enp6s0 up | ip link set enp6s0 up |
| ifconfig enp6s0 192.168.2.24 | ip addr add 192.168.2.24/24 dev enp6s0 |
| ifconfig enp6s0 netmask 255.255.255.0 | ip addr add 192.168.1.1/24 dev enp6s0 |
| ifconfig enp6s0 mtu 9000 | ip link set enp6s0 mtu 9000 |
| ifconfig enp6s0:0 192.168.2.25 | ip addr add 192.168.2.25/24 dev enp6s0 |
| netstat | ss |
| netstat -tulpn | ss -tulpn |
| netstat -neopa | ss -neopa |
| netstat -g | ip maddr |
| route | ip r |
| route add -net 192.168.2.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 dev enp6s0 | ip route add 192.168.2.0/24 dev enp6s0 |
| route add default gw 192.168.2.254 | ip route add default via 192.168.2.254 |
| arp -a | ip neigh |
| arp -v | ip -s neigh |
| arp -s 192.168.2.33 1:2:3:4:5:6 | ip neigh add 192.168.3.33 lladdr 1:2:3:4:5:6 dev enp6s0 |
| arp -i enp6s0 -d 192.168.2.254 | ip neigh del 192.168.2.254 dev wlp7s0 |
|
Linux ip Command的更多相关文章
- 第一种SUSE Linux IP设置方法
第一种SUSE Linux IP设置方法ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.22 netmask 255.255.255.0 uproute add default gw 192.168. ...
- Linux:-bash: ***: command not found
Linux:-bash: ***: command not found,系统很多命令都用不了,均提示没有此命令. 突然之间linux很多命令都用不了,均提示没有此命令. 这应该是系统环境变量出现了问题 ...
- 12 Linux Which Command, Whatis Command, Whereis Command Examples
This Linux tutorial will explain the three "W" commands. The three "W"s are what ...
- Linux ip forward
Linux 默认带有 ip forward 功能,只不过因为各种原因,默认的配置把该功能关闭了.本文通过 demo 来演示 Linux 的 ip forward 功能,具体场景为:开启 Linux 的 ...
- 【Linux】-NO.8.Linux.4.Command.1.001-【Common Command】-
1.0.0 Summary Tittle:[Linux]-NO.8.Linux.4.Command.1.001-[Common Command]- Style:Linux Series:Command ...
- linux ip白名单、防火墙白名单 设置
http://blog.csdn.net/catoop/article/details/50476099 登录信息在 /var/log/secure linux ip白名单 配置文件:/etc/hos ...
- learn Linux sed command
learn Linux sed command 一.参考文档: . sed命令详解 http://qifuguang.me/2015/09/21/sed%E5%91%BD%E4%BB%A4%E8%AF ...
- linux IP动态变动之后 , 需要做的杂项操作
linux的动态ip经常变来变去,目前还没找到固定它不变化的方法.所以每次变动之后都需要做以下的操作,极其麻烦.(必须找到让linux IP 固定的方法) 1.先找到变化之后的动态ip地址 ifcon ...
- VMware下配置Linux IP,解决Linux ping不通
因为安装好VMware8.0后,把VMware服务都设成手动的了,导致有些功能不好使,费了半天劲, 如果安装Linux时选择DHCP自动分配IP,需要启动服务: VMware DHCP service ...
随机推荐
- canvas的常用功能(电脑版)
前言: canvas可以单独算为前端的一大知识模块, 今天就研究一下. 先做下前文铺垫: ①创建canvas <canvas id="myCanvas" width=&quo ...
- 从webkit内核简单看css样式和css规则优先级(权重)
目录 webkit中样式相关类及类间关系 样式规则匹配 权重(优先级)计算 权重相同时的覆盖原则 webkit中样式相关类及类间关系 资料来源: <webkit技术内幕> 结构相关类: 1 ...
- vue -全局组件和局部组件
1.全局组件:Vue.component('标签名', 构造器名) Vue.component('mycpn', cpnC) 注:这种注册组件的方式是全局组件,可以在多个Vue实例中使用. 2.局部组 ...
- 【DB_MySQL】MySQL日志分析
MySQL数据库常见的日志有:错误日志(log_error).慢查询日志(slow_query_log).二进制日志(bin_log).通用日志(general_log) 开启慢查询日志并分析 开启慢 ...
- rhel7学习第一天
今天是在线学习刘遄老师<Linux就该这么学>的第一天,对Linux的发展和优越性有了进一步的了解.
- Arbitrage POJ - 2240
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-2240 思路:判正环,Bellman-ford和SPFA,floyd都可以,有正环就可以套利. 这里用SPFA,就是个板子题吧 ...
- 09-webpack--配置less
<!-- cnpm i less-loader less -D 要下载两个 在入口文件main.js文件中引入 import './css/index.less' webpack.config. ...
- IDEA结合Maven的profile构建不同开发环境(SpringBoot)
一.概述 在开发过程中,我们的项目会存在不同的开发环境,比如开发环境.生产环境.测试环境,而我们的项目在不同的环境中有些配置也是不一样的,比如数据源配置.日志文件配置等,假如我们每次将软件部署到不同的 ...
- 莫烦TensorFlow_03 Variable加法
import tensorflow as tf ## 定义变量 state = tf.Variable(0, name = 'counter') #print(state.name) one = tf ...
- Exception in createBlockOutputStream
Exception in createBlockOutputStream 出现这个问题,可能是端口没打开,把异常往下拉,就可以看到哪个端口,在centos 打开端口
