Determining if a point lies on the interior of a polygon
Determining if a point lies on the interior of a polygon
Written by Paul Bourke November 1987
Solution 1 (2D)
The following is a simple solution to the problem often encountered in computer graphics, determining whether or not a point (x,y) lies inside or outside a 2D polygonally bounded plane. This is necessary for example in applications such as polygon filling on raster devices, hatching in drafting software, and determining the intersection of multiple polygons.
Consider a polygon made up of N vertices (xi,yi) where i ranges from 0 to N-1. The last vertex (xN,yN) is assumed to be the same as the first vertex (x0,y0), that is, the polygon is closed. To determine the status of a point (xp,yp) consider a horizontal ray emanating from (xp,yp) and to the right. If the number of times this ray intersects the line segments making up the polygon is even then the point is outside the polygon. Whereas if the number of intersections is odd then the point (xp,yp) lies inside the polygon. The following shows the ray for some sample points and should make the technique clear.
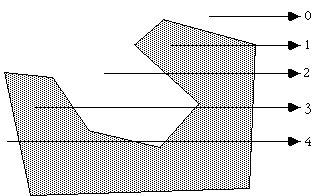
Note: for the purposes of this discussion 0 will be considered even, the test for even or odd will be based on modulus 2, that is, if the number of intersections modulus 2 is 0 then the number is even, if it is 1 then it is odd.
The only trick is what happens in the special cases when an edge or vertex of the polygon lies on the ray from (xp,yp). The possible situations are illustrated below.
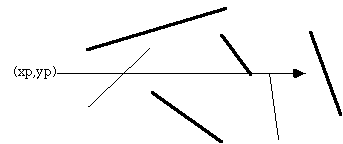
The thick lines above are not considered as valid intersections, the thin lines do count as intersections. Ignoring the case of an edge lying along the ray or an edge ending on the ray ensures that the endpoints are only counted once.
Note that this algorithm also works for polygons with holes as illustrated below
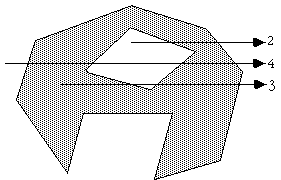
The following C function returns INSIDE or OUTSIDE indicating the status of a point P with respect to a polygon with N points.
#define MIN(x,y) (x < y ? x : y)
#define MAX(x,y) (x > y ? x : y)
#define INSIDE 0
#define OUTSIDE 1 typedef struct {
double x,y;
} Point; int InsidePolygon(Point *polygon,int N,Point p)
{
int counter = 0;
int i;
double xinters;
Point p1,p2; p1 = polygon[0];
for (i=1;i<=N;i++) {
p2 = polygon[i % N];
if (p.y > MIN(p1.y,p2.y)) {
if (p.y <= MAX(p1.y,p2.y)) {
if (p.x <= MAX(p1.x,p2.x)) {
if (p1.y != p2.y) {
xinters = (p.y-p1.y)*(p2.x-p1.x)/(p2.y-p1.y)+p1.x;
if (p1.x == p2.x || p.x <= xinters)
counter++;
}
}
}
}
p1 = p2;
} if (counter % 2 == 0)
return(OUTSIDE);
else
return(INSIDE);
}
The following code is by Randolph Franklin, it returns 1 for interior points and 0 for exterior points.
int pnpoly(int npol, float *xp, float *yp, float x, float y)
{
int i, j, c = 0;
for (i = 0, j = npol-1; i < npol; j = i++) {
if ((((yp[i] <= y) && (y < yp[j])) ||
((yp[j] <= y) && (y < yp[i]))) &&
(x < (xp[j] - xp[i]) * (y - yp[i]) / (yp[j] - yp[i]) + xp[i]))
c = !c;
}
return c;
}
Contribution by Alexander Motrichuk:
//SOLUTION #1 (2D) - Redesigned #define MIN(x,y) (x < y ? x : y)
#define MAX(x,y) (x > y ? x : y) #define INSIDE 1
#define OUTSIDE 0 struct Point
{
Point() : x(.), y(.) {}; Point(double x1, double y1) : x(x1), y(y1) {}; bool operator==(const Point& _right)
{
return x == _right.x && y == _right.y;
}; double x, y;
}; //horizintal left cross over direction algorithm
//-----------------------------------------------
// bound | value that will be returned only if (p) lies on the bound or vertex
int InsidePolygon(Point* polygon, int N, Point p, int bound)
{
//cross points count of x
int __count = ; //neighbour bound vertices
Point p1, p2; //left vertex
p1 = polygon[]; //check all rays
for(int i = ; i <= N; ++i)
{
//point is an vertex
if(p == p1) return bound; //right vertex
p2 = polygon[i % N]; //ray is outside of our interests
if(p.y < MIN(p1.y, p2.y) || p.y > MAX(p1.y, p2.y))
{
//next ray left point
p1 = p2; continue;
} //ray is crossing over by the algorithm (common part of)
if(p.y > MIN(p1.y, p2.y) && p.y < MAX(p1.y, p2.y))
{
//x is before of ray
if(p.x <= MAX(p1.x, p2.x))
{
//overlies on a horizontal ray
if(p1.y == p2.y && p.x >= MIN(p1.x, p2.x)) return bound; //ray is vertical
if(p1.x == p2.x)
{
//overlies on a ray
if(p1.x == p.x) return bound;
//before ray
else ++__count;
} //cross point on the left side
else
{
//cross point of x
double xinters = (p.y - p1.y) * (p2.x - p1.x) / (p2.y - p1.y) + p1.x; //overlies on a ray
if(fabs(p.x - xinters) < __DBL_EPSILON__) return bound; //before ray
if(p.x < xinters) ++__count;
}
}
}
//special case when ray is crossing through the vertex
else
{
//p crossing over p2
if(p.y == p2.y && p.x <= p2.x)
{
//next vertex
const Point& p3 = polygon[(i+) % N]; //p.y lies between p1.y & p3.y
if(p.y >= MIN(p1.y, p3.y) && p.y <= MAX(p1.y, p3.y))
{
++__count;
}
else
{
__count += ;
}
}
} //next ray left point
p1 = p2;
} //EVEN
if(__count % == ) return(OUTSIDE);
//ODD
else return(INSIDE);
}
Quote: "For most of the algorithms above there is a pathological case if the point being queried lies exactly on a vertex. The easiest way to cope with this is to test that as a separate process and make your own decision as to whether you want to consider them inside or outside."
Contribution in VBA by Giuseppe Iaria:
'---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
'************************************ Function InsidePolygon *************************************
'---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
'VBA implementation of the theory provided by Paul Bourke (http://paulbourke.net/geometry/polygonmesh/)
'author: ing. Giuseppe Iaria - rev. 20/08/2014
'---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
'The function is based on Solution 1 (2D)
'The function determines if a point P lies inside or outside a Polygon, returning "True" or "False"
'The points are defined through the user-defined type "Point"
'The Polygon is an array of points, each being a user-defined type "Point"
'The Polygon is implemented assuming a "Base 1" condition, so the "Option Base 1" statement is required
'The optional argument "OnPolygonBorder" deals with these special cases:
' - P lies on a vertex of the Polygon
' - P lies on a line segment of the Polygon
'If omitted or passed as "False", and a special case occurs, then the function returns "False"
'If passed as "True", and a special case occurs, then the function returns "True"
'Auxiliary functions used:
' - DistancePointSegment: determines the distance between a point and a line segment
' - Distance2Point: determines the distance between two points
'Both the auxiliary functions have been developed on:
' - the theory by Paul Bourke (http://paulbourke.net/geometry/pointlineplane/)
' - an original VBA code by Brandon Crosby (http://paulbourke.net/geometry/pointlineplane/source.vba)
'--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Option Base Public Type Point
x As Double
y As Double
End Type Public Function InsidePolygon(Polygon() As Point, P As Point, Optional ByVal OnPolygonBorder As Boolean) As Boolean
Dim counter As Integer, i As Integer, ip1 As Integer
Dim xInters As Double, dist As Double
Const EPS As Single = 0.0001
'Check if the point lies on a polygon's vertex or line segment
For i = To UBound(Polygon)
ip1 = i Mod UBound(Polygon) +
dist = DistancePointSegment(P, Polygon(i), Polygon(ip1))
If dist < EPS Then
If OnPolygonBorder Then
InsidePolygon = True
Else
InsidePolygon = False
End If
Exit Function
End If
Next i
'Determine the numbers of intersection between the orizzontal ray from point and polygon
For i = To UBound(Polygon)
ip1 = i Mod UBound(Polygon) +
If P.y > IIf(Polygon(i).y < Polygon(ip1).y, Polygon(i).y, Polygon(ip1).y) Then
If P.y <= IIf(Polygon(i).y > Polygon(ip1).y, Polygon(i).y, Polygon(ip1).y) Then
If P.x <= IIf(Polygon(i).x > Polygon(ip1).x, Polygon(i).x, Polygon(ip1).x) Then
If Polygon(i).y <> Polygon(ip1).y Then
xInters = Polygon(i).x + (Polygon(ip1).x - Polygon(i).x) * (P.y - Polygon(i).y) / (Polygon(ip1).y - Polygon(i).y)
If (Polygon(i).x = Polygon(ip1).x) Or (P.x <= xInters) Then counter = counter +
End If
End If
End If
End If
Next i
If counter Mod = Then InsidePolygon = False Else InsidePolygon = True
End Function Private Function DistancePointSegment(P As Point, P1 As Point, P2 As Point) As Double
Dim LineMag As Double, u As Double
Dim d1 As Double, d2 As Double
Dim Pint As Point
Const EPS As Single = 0.0001
LineMag = Distance2Point(P1, P2)
If LineMag < EPS Then Exit Function
u = (((P.x - P1.x) * (P2.x - P1.x)) + ((P.y - P1.y) * (P2.y - P1.y))) / LineMag ^
If u < Or u > Then
d1 = Distance2Point(P, P1)
d2 = Distance2Point(P, P2)
If d1 > d2 Then DistancePointSegment = d2 Else DistancePointSegment = d1
Else
Pint.x = P1.x + u * (P2.x - P1.x)
Pint.y = P1.y + u * (P2.y - P1.y)
DistancePointSegment = Distance2Point(P, Pint)
End If
End Function Private Function Distance2Point(P1 As Point, P2 As Point) As Double
Distance2Point = Sqr((P2.x - P1.x) ^ + (P2.y - P1.y) ^ )
End Function
Contribution written in c# by Jerry Knauss:
public static bool Contains( Point[] points, Point p )
{
bool result = false; for( int i = ; i < points.Length - ; i++ )
{
if( ( ( ( points[ i + ].Y <= p.Y ) && ( p.Y < points[ i ].Y ) ) || ( ( points[ i ].Y <= p.Y ) && ( p.Y < points[ i + ].Y ) ) ) && ( p.X < ( points[ i ].X - points[ i + ].X ) * ( p.Y - points[ i + ].Y ) / ( points[ i ].Y - points[ i + ].Y ) + points[ i + ].X ) )
{
result = !result;
}
}
return result;
}
Solution 2 (2D)
Another solution forwarded by Philippe Reverdy is to compute the sum of the angles made between the test point and each pair of points making up the polygon. If this sum is 2pi then the point is an interior point, if 0 then the point is an exterior point. This also works for polygons with holes given the polygon is defined with a path made up of coincident edges into and out of the hole as is common practice in many CAD packages.
The inside/outside test might then be defined in C as
typedef struct {
int h,v;
} Point;
int InsidePolygon(Point *polygon,int n,Point p)
{
int i;
double angle=0;
Point p1,p2;
for (i=0;i<n;i++) {
p1.h = polygon[i].h - p.h;
p1.v = polygon[i].v - p.v;
p2.h = polygon[(i+1)%n].h - p.h;
p2.v = polygon[(i+1)%n].v - p.v;
angle += Angle2D(p1.h,p1.v,p2.h,p2.v);
}
if (ABS(angle) < PI)
return(FALSE);
else
return(TRUE);
}
/*
Return the angle between two vectors on a plane
The angle is from vector 1 to vector 2, positive anticlockwise
The result is between -pi -> pi
*/
double Angle2D(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2)
{
double dtheta,theta1,theta2;
theta1 = atan2(y1,x1);
theta2 = atan2(y2,x2);
dtheta = theta2 - theta1;
while (dtheta > PI)
dtheta -= TWOPI;
while (dtheta < -PI)
dtheta += TWOPI;
return(dtheta);
}
Solution 3 (2D)
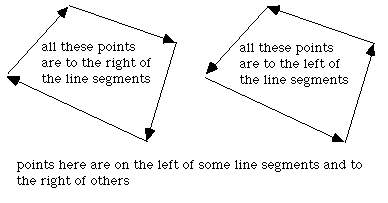
There are other solutions to this problem for polygons with special attributes. If the polygon is convex then one can consider the polygon as a "path" from the first vertex. A point is on the interior of this polygons if it is always on the same side of all the line segments making up the path.
Given a line segment between P0 (x0,y0) and P1 (x1,y1), another point P (x,y) has the following relationship to the line segment.
Compute
(y - y0) (x1 - x0) - (x - x0) (y1 - y0)
if it is less than 0 then P is to the right of the line segment, if greater than 0 it is to the left, if equal to 0 then it lies on the line segment.
Solution 4 (3D)
|
This solution was motivated by solution 2 and correspondence with Reinier van Vliet and Remco Lam. To determine whether a point is on the interior of a convex polygon in 3D one might be tempted to first determine whether the point is on the plane, then determine it's interior status. Both of these can be accomplished at once by computing the sum of the angles between the test point (q below) and every pair of edge points p[i]->p[i+1]. This sum will only be 2pi if both the point is on the plane of the polygon AND on the interior. The angle sum will tend to 0 the further away from the polygon point q becomes. |
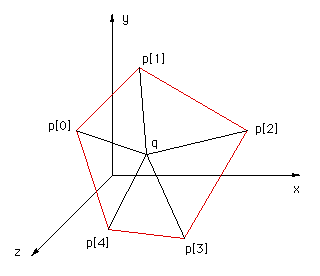 |
The following code snippet returns the angle sum between the test point q and all the vertex pairs. Note that the angle sum is returned in radians.
typedef struct {
double x,y,z;
} XYZ;
#define EPSILON 0.0000001
#define MODULUS(p) (sqrt(p.x*p.x + p.y*p.y + p.z*p.z))
#define TWOPI 6.283185307179586476925287
#define RTOD 57.2957795
double CalcAngleSum(XYZ q,XYZ *p,int n)
{
int i;
double m1,m2;
double anglesum=0,costheta;
XYZ p1,p2;
for (i=0;i<n;i++) {
p1.x = p[i].x - q.x;
p1.y = p[i].y - q.y;
p1.z = p[i].z - q.z;
p2.x = p[(i+1)%n].x - q.x;
p2.y = p[(i+1)%n].y - q.y;
p2.z = p[(i+1)%n].z - q.z;
m1 = MODULUS(p1);
m2 = MODULUS(p2);
if (m1*m2 <= EPSILON)
return(TWOPI); /* We are on a node, consider this inside */
else
costheta = (p1.x*p2.x + p1.y*p2.y + p1.z*p2.z) / (m1*m2);
anglesum += acos(costheta);
}
return(anglesum);
}
Note
For most of the algorithms above there is a pathological case if the point being queries lies exactly on a vertex. The easiest way to cope with this is to test that as a separate process and make your own decision as to whether you want to consider them inside or outside.
Determining if a point lies on the interior of a polygon的更多相关文章
- [算法]A General Polygon Clipping Library
A General Polygon Clipping Library Version 2.32 http://www.cs.man.ac.uk/~toby/alan/software/gpc.h ...
- postgis几何操作函数集
管理操作函数 AddGeometryColumn - Adds a geometry column to an existing table of attributes. By default use ...
- linux tcp调优
Linux TCP Performance Tuning News Linux Performance Tuning Recommended Books Recommended Links Linux ...
- simplestyle
simplestyle-spec A simple specification for styling GeoJSON data. Versions 1.1.0 Adds properties to ...
- MySQL所有函数及操作符
参考:Function and Operator Reference Name Description ABS() Return the absolute value ACOS() Return th ...
- OpenGL ES 正反面设置指令
在OpenGL ES 中,仅有一种表面网格表示方式,那就是三角形. 三角形的三个顶点,可以组几个面?有答 1 的没有?有!那就是还不懂OpenGL ES 的我. 事实上,一张纸是有正反面的,那么一个三 ...
- GDI+ Tutorial for Beginners
原文 GDI+ Tutorial for Beginners GDI+ is next evolution of GDI. Using GDI objects in earlier versions ...
- Extensions for Spatial Data
http://dev.mysql.com/worklog/task/?spm=5176.100239.blogcont4270.8.j3asa7&id=6609 前文: 这两天因为项目原因看了 ...
- mysql 函数表
Name Description ABS() Return the absolute value ACOS() Return the arc cosine ADDDATE() Add time val ...
随机推荐
- select 练习4
21.查询score中选学多门课程的同学中分数不是所有成绩中最高分成绩的记录. select * from score where cno in(select cno from score grou ...
- shell语法快速入门(1)
#得到绝对路径 DIR=$(cd `dirname $0`;pwd) $DIR/file.txt #去掉#注释 egrep -v "(#|^$)" /etc/zabbix/zabb ...
- SkyDrive 中Office 的版本控制功能
之前看到了这么个图片,然后想着自己过一年后也要写毕业论文… 总不能也这个样子吧,这种版本到底知道哪个是最终版啊,不用版本号也就算了……还……(据说这是张内涵图) 当年的Word 没有版本控制也就算了, ...
- 在Openfire中使用自己的数据表之修改系统属性
通过修改Openfire安装目录的conf/openfire目录下是openfire.xml文件可以使用我们自定义的认证集成以及用户数据集成.其实仔细观察之后,在修改完配置文件再次启动openfire ...
- 如何卸除SDL TRADOS中的自开发插件
去年学着用SDL的例子编译了一个名为SimpleText的插件,每次打开TRADOS 2014时都要提示三次加载插件,很是烦人.但我想卸掉时,却无从下手,不知道怎么办.这个问题纠缠了我很久,今晨心性比 ...
- PayPal贝宝集成
今天在集成PayPal贝宝在线支付功能时,遇到了一些小挫折,费了不少功夫才最终解决(贝宝的技术支持确实让我很想吐槽).现在记录下来,供后来者参考.根据集成说明文档,我们写的测试demo如下: < ...
- 重装Eclipse、离线安装ADT、Android SDK
由于最新的ADT.Android SDK需要最新版本的Eclipse才能使用,我无奈的只好升级Eclipse.看看自己的Eclipse已经两年没有升级了,也是时候升级了.升级前,有很多的顾虑.因为像这 ...
- 读《你必须知道的.NET》继承本质论 Bird bird=new Chicken()
我们创建如下的三层继承层次类. public abstract class Animal { public abstract void ShowType(); } public class Bird ...
- 微软发布手机版 Sample Browser。7000多示例代码一手掌握
今天早上,Sample Browser发布其全新的Windows Phone版本.至此,自2012年相继推出Desktop版.Visual Studio版,以及2013年推出Windows Store ...
- 基于D3JS绘制中国地图
仿照D3JS官网上的美国地图制作了一个中国版的地图. D3JS官网上的版本: http://bl.ocks.org/NPashaP/a74faf20b492ad377312 中国版的地图效果: 如要制 ...
