hdu 4444 Walk (离散化+建图+bfs+三维判重 好题)
Walk
What’s the minimum number of turns Biaoge need to make?
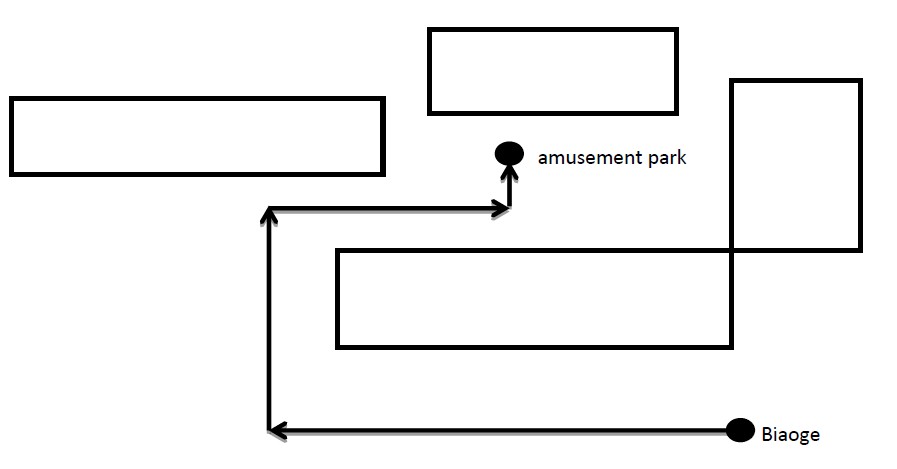
As the figure above shows, there are 4 buildings and Biaoge need to make at least 3 turns to reach the amusement park(Before walking he can chose a direction freely). It is guaranteed that all the buildings are parallel to the coordination axis. Buildings may contact but overlapping is impossible. The amusement park and Biaoge’s initial positions will not contact or inside any building.
Each test case contains several lines.
The first line contains 4 integers x1, y1, x2, y2 indicating the coordinate of Biaoge and amusement park.
The second line contains one integer N(0≤N≤50), indicating the number of buildings.
Then N lines follows, each contains 4 integer x1, y1, x2, y2, indicating the coordinates of two opposite vertices of the building.
Input ends with 0 0 0 0, you should not process it.
All numbers in the input range from -10
8 to 10
8.
1
0 5 5 8
0 0 0 10
2
0 5 5 8
-2 1 0 5
0 0 0 0
2
In the first case, Biaoge can walk along the side of building, and no turn needed.
In the second case, two buildings block the direct way and Biaoge need to make 2 turns at least.
 早上开始研究一个人的代码(很简洁,风格很好),研究了一个早上,思想都懂了,然后下午开始自己写,写出来后测别人贴的数据,发现最后一组数据怎么也过不了,又仔细研究了一会,发现这种思路就是错的。
早上开始研究一个人的代码(很简洁,风格很好),研究了一个早上,思想都懂了,然后下午开始自己写,写出来后测别人贴的数据,发现最后一组数据怎么也过不了,又仔细研究了一会,发现这种思路就是错的。
 我 X_X ,当时就有砸电脑的冲动了,白白浪费我我这么长时间。
我 X_X ,当时就有砸电脑的冲动了,白白浪费我我这么长时间。 ps:这题区域赛时数据水了,所以有些代码页就水过了,所以提供的解题报告有些就是错的。然后下午又重新开始搞,看了一个人的思路觉得很正确,然后晚上就开始按照这种思路写,写出来了也是各种debug,各种改代码,最后终于AC了,那叫一个爽呀!
ps:这题区域赛时数据水了,所以有些代码页就水过了,所以提供的解题报告有些就是错的。然后下午又重新开始搞,看了一个人的思路觉得很正确,然后晚上就开始按照这种思路写,写出来了也是各种debug,各种改代码,最后终于AC了,那叫一个爽呀!
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#define maxn 350
using namespace std; int n,m,ans;
int sx,sy,ex,ey;
int x[maxn],y[maxn];
int xx[maxn],yy[maxn];
int mp[maxn][maxn];
int up[maxn][maxn],down[maxn][maxn];
int le[maxn][maxn],ri[maxn][maxn];
int dx[]= {-3,3,0,0};
int dy[]= {0,0,-3,3};
bool vis[maxn][maxn][4]; // 三维判重 x+y+方向
struct Node
{
int l,d,r,u;
} rect[maxn];
struct node
{
int mx,my;
int d,cnt; // 方向 转向次数
} cur,now,q[maxn*maxn]; void showxxyy() // 输出离散化后的x y
{
int i,j;
printf("xx:\n");
for(i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
printf("%d ",xx[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("yy:\n");
for(i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
printf("%d ",yy[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void showmap() // 输出地图
{
int i,j;
printf("showmap:\n");
printf(" 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 \n");
for(i=1; i<=3*xx[m]; i++)
{
printf("%3d: ",i);
for(j=1; j<=3*yy[m]; j++)
{
printf("%d",mp[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void disc() // 离散化
{
int i,j;
m=2*n+2;
sort(x+1,x+m+1);
xx[1]=1;
for(i=2; i<=m; i++)
{
if(x[i]==x[i-1]) xx[i]=xx[i-1];
else xx[i]=xx[i-1]+1;
}
sort(y+1,y+m+1);
yy[1]=1;
for(i=2; i<=m; i++)
{
if(y[i]==y[i-1]) yy[i]=yy[i-1];
else yy[i]=yy[i-1]+1;
}
// showxxyy();
}
int find(int v,int k) // 找到离散化对应的点
{
int i,j;
if(k)
{
for(i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
if(y[i]==v) return yy[i];
}
}
else
{
for(i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
if(x[i]==v) return xx[i];
}
}
}
void buildgraph() // 将1*1的方格转化为3*3的方格后建图
{
int i,j,ni,nj,k,l,d,r,u;
memset(mp,0,sizeof(mp));
memset(up,1,sizeof(up));
memset(down,1,sizeof(down));
memset(le,1,sizeof(le));
memset(ri,1,sizeof(ri));
for(k=1; k<=n; k++) // 将矩形在地图上涂黑
{
l=3*find(rect[k].l,0)+1;
d=3*find(rect[k].d,1)+1;
r=3*find(rect[k].r,0)-1;
u=3*find(rect[k].u,1)-1;
// printf("l:%d d:%d r:%d u:%d\n",l,d,r,u);
for(i=l; i<=r; i++)
{
for(j=d; j<=u; j++)
{
mp[i][j]=1;
}
}
}
for(i=1; i<=xx[m]; i++) // 记录是否能走 是否是‘L’型区域
{
for(j=1; j<=yy[m]; j++)
{
ni=3*i;
nj=3*j;
if(mp[ni-1][nj-1]&&mp[ni+1][nj+1])
{
up[ni][nj]=down[ni][nj]=le[ni][nj]=ri[ni][nj]=-1;
}
else if(mp[ni+1][nj-1]&&mp[ni-1][nj+1]) up[ni][nj]=down[ni][nj]=le[ni][nj]=ri[ni][nj]=-2;
if(mp[ni-1][nj-1]&&mp[ni-1][nj+1]) up[ni][nj]=0;
if(mp[ni+1][nj-1]&&mp[ni+1][nj+1]) down[ni][nj]=0;
if(mp[ni-1][nj-1]&&mp[ni+1][nj-1]) le[ni][nj]=0;
if(mp[ni-1][nj+1]&&mp[ni+1][nj+1]) ri[ni][nj]=0;
}
}
// showmap();
}
bool bfs() // 图建好了 就是简单的bfs了
{
int i,j,nx,ny,nd,ncnt,tx,ty;
int head=0,tail=-1;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
sx=3*find(sx,0);
sy=3*find(sy,1);
ex=3*find(ex,0);
ey=3*find(ey,1);
// printf("sx:%d sy:%d ex:%d ey:%d\n",sx/3,sy/3,ex/3,ey/3);
cur.mx=sx;
cur.my=sy;
cur.d=-1;
cur.cnt=0;
vis[sx][sy][0]=vis[sx][sy][1]=vis[sx][sy][2]=vis[sx][sy][3]=1;
q[++tail]=cur;
while(head<=tail)
{
now=q[head];
head++;
nx=now.mx;
ny=now.my;
nd=now.d;
ncnt=now.cnt;
// printf("nx:%d ny:%d nd:%d ncnt:%d\n",nx/3,ny/3,nd,ncnt);
if(nx==ex&&ny==ey)
{
ans=ncnt;
return true ;
}
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
{
if(i==0&&!up[nx][ny]||i==1&&!down[nx][ny]||i==2&&!le[nx][ny]||i==3&&!ri[nx][ny]) continue ; // 判断是否能往这个方向走
if(up[nx][ny]==-1) // 对‘L’型区域特判
{
if(i==0&&(nd==0||nd==3)) continue ;
else if(i==1&&(nd==1||nd==2)) continue ;
else if(i==2&&(nd==2||nd==1)) continue ;
else if(i==3&&(nd==3||nd==0)) continue ;
}
else if(up[nx][ny]==-2)
{
if(i==0&&(nd==0||nd==2)) continue ;
else if(i==1&&(nd==1||nd==3)) continue ;
else if(i==2&&(nd==2||nd==0)) continue ;
else if(i==3&&(nd==3||nd==1)) continue ;
}
tx=nx+dx[i];
ty=ny+dy[i];
while(tx>=1&&tx<=3*xx[m]&&ty>=1&&ty<=3*yy[m]&&!mp[tx][ty]) // 每次向一个方向搜索
{
if(!vis[tx][ty][i])
{
vis[tx][ty][i]=1;
cur.mx=tx;
cur.my=ty;
cur.d=i;
cur.cnt=ncnt;
if(cur.d!=nd&&nd!=-1) cur.cnt++;
q[++tail]=cur;
}
if(i==0&&!up[tx][ty]||i==1&&!down[tx][ty]||i==2&&!le[tx][ty]||i==3&&!ri[tx][ty]) break ;
if(up[tx][ty]==-1||up[tx][ty]==-2) break ;
tx+=dx[i];
ty+=dy[i];
}
}
}
return false ;
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
int x1,y1,x2,y2,l,d,r,u;
while(scanf("%d%d%d%d",&sx,&sy,&ex,&ey),sx||sy||ex||ey)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
l=min(x1,x2);
r=max(x1,x2);
d=min(y1,y2);
u=max(y1,y2);
x[i]=rect[i].l=l;
x[i+n]=rect[i].r=r;
y[i]=rect[i].d=d;
y[i+n]=rect[i].u=u;
}
x[2*n+1]=sx;
x[2*n+2]=ex;
y[2*n+1]=sy;
y[2*n+2]=ey;
disc();
buildgraph();
if(bfs()) printf("%d\n",ans);
else printf("-1\n");
}
return 0;
}
/* // 绕路 2
1 1 1 4
1
0 2 2 3 // 直走 0
1 1 1 4
1
3 3 4 5 // 沿着边直走 0
0 1 0 7
2
0 2 2 3
-1 4 0 5 // 沿着边直走 0
0 1 0 7
2
0 2 2 3
0 3 2 4 // 无法穿过缝隙,绕路 2
0 1 0 7
2
0 2 2 3
-1 3 0 5 // 无法到达 -1
0 0 5 5
4
-1 1 1 2
1 -1 2 1
-1 -1 1 -2
-1 1 -2 -1 // 同点经过两次。 5
1 3 4 1
10
-1 -1 3 2
3 -1 7 0
7 -1 11 3
9 3 11 7
-1 7 11 9
0 5 4 7
-1 2 0 7
2 2 4 3
4 3 5 4
5 4 8 6
*/
hdu 4444 Walk (离散化+建图+bfs+三维判重 好题)的更多相关文章
- HDU 4444 Walk (离散化建图+BFS+记忆化搜索) 绝对经典
题目地址:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4444 题意:给你一些n个矩形,给你一个起点,一个终点,要你求从起点到终点最少需要转多少个弯 题解:因为 ...
- BZOJ_3073_[Pa2011]Journeys_线段树优化建图+BFS
BZOJ_3073_[Pa2011]Journeys_线段树优化建图+BFS Description Seter建造了一个很大的星球,他准备建造N个国家和无数双向道路.N个国家很快建造好了,用1..N ...
- HDU 4292 Food (建图思维 + 最大流)
(点击此处查看原题) 题目分析 题意:某个餐馆出售f种食物,d种饮料,其中,第i种食物有fi份,第i种饮料有di份:此时有n个人来餐馆吃饭,这n个人必须有一份食物和一份饮料才会留下来吃饭,否则,他将离 ...
- Eliminate the Conflict HDU - 4115(2-sat 建图 hhh)
题意: 石头剪刀布 分别为1.2.3,有n轮,给出了小A这n轮出什么,然后m行,每行三个数a b k,如果k为0 表示小B必须在第a轮和第b轮的策略一样,如果k为1 表示小B在第a轮和第b轮的策略不一 ...
- Meeting HDU - 5521 虚点建图
Problem Description Bessie and her friend Elsie decide to have a meeting. However, after Farmer John ...
- 逃生 HDU 4857(反向建图 + 拓扑排序)
逃生 链接 Problem Description 糟糕的事情发生啦,现在大家都忙着逃命.但是逃命的通道很窄,大家只能排成一行. 现在有n个人,从1标号到n.同时有一些奇怪的约束条件,每个都形如:a必 ...
- hdu 1226 bfs+余数判重+大数取余
题目: 超级密码 Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- poj 1465 Multiple(bfs+余数判重)
题意:给出m个数字,要求组合成能够被n整除的最小十进制数. 分析:用到了余数判重,在这里我详细的解释了.其它就没有什么了. #include<cstdio> #include<cma ...
- Keyboarding (bfs+预处理+判重优化)
# #10030. 「一本通 1.4 练习 2」Keyboarding [题目描述] 给定一个 $r$ 行 $c$ 列的在电视上的"虚拟键盘",通过「上,下,左,右,选择」共 $5 ...
随机推荐
- javascript (二) 事件
<script></script> 函数写法: function fun_name(){ x=docment.getElementById("demo") ...
- TCP、UDP数据包大小的限制(UDP数据包一次发送多大为好)——数据帧的物理特性决定的,每层都有一个自己的数据头,层层递减
1.概述 首先要看TCP/IP协议,涉及到四层:链路层,网络层,传输层,应用层. 其中以太网(Ethernet)的数据帧在链路层 IP包在网络层 TCP或UDP包在传输层 TCP或UDP中的数据(Da ...
- 彻底搞定c指针
第一篇 变量的内存实质 一.先来理解C语言中变量的实质 要理解C指针,我认为一定要理解C中“变量”的存储实质,所以我就从“变量”这个东西开始讲起吧! 先来理解理解内存空间吧!请看下图: 内存地址→ ...
- c语言实现动态指针数组Dynamic arrays
c语言实现动态数组.其它c的数据结构实现,hashTable參考点击打开链接 treeStruct參考点击打开链接 基本原理:事先准备好一个固定长度的数组. 假设长度不够的时候.realloc一块区域 ...
- 利用未公开API获取终端会话闲置时间(Idle Time)和登入时间(Logon Time)
利用未公开API获取终端会话闲置时间(Idle Time)和登入时间(Logon Time)作者:Tuuzed(土仔) 发表于:2008年3月3日23:12:38 版权声明:可以任意转载,转载时请 ...
- phpc.sinaapp.com 加密的解密方法
原文:phpc.sinaapp.com 加密的解密方法 很简单,用类似phpjm的解密方式,替换掉_inc.php中最后一个return中的eval为print就出来了.
- Android开发周报:反编译对抗研究、动手制作智能镜子
新闻 <Android Wear落地中国 谷歌增强安卓生态控制力> :9月8日,由摩托罗拉推出的智能手表Moto 360二代作为国内发售的第一款搭载官方Android Wear的设备,正式 ...
- nginx 源码安装
安装环境: 操作系统:Ubuntu 12.04 Nginx: V1.4.2 PCRE: V8.33 zlib: V1.2.8 下载上述源包到当前用户主目录(本机:/hom ...
- cocos2dx游戏开发学习笔记3-lua面向对象分析
在lua中,能够通过元表来实现类.对象.继承等.与元表相关的方法有setmetatable().__index.getmetatable().__newindex. 详细什么是元表在这里就不细说了,网 ...
- Linux 挂载NTFS文件系统
步骤如下: 1.安装ntfs-3g包 [root@CS-1 pub]# yum install ntfs-3g 2.创建挂载目录 [root@CS-1 pub]# mkdir /data 3.挂载NT ...
