【Java 8】Stream API
Java8的两个重大改变,一个是Lambda表达式,另一个就是本节要讲的Stream API表达式。Stream 是Java8中处理集合的关键抽象概念,它可以对集合进行非常复杂的查找、过滤、筛选等操作,在新版的JPA中,也已经加入了Stream。如:
@Query("select u from User u")
Stream<User> findAllByCustomQueryAndStream();
Stream<User> readAllByFirstnameNotNull();
@Query("select u from User u")
Stream<User> streamAllPaged(Pageable pageable);
Stream API给我们操作集合带来了强大的功用,同时Stream API操作简单,容易上手。
Stream的操作步骤
Stream有如下三个操作步骤:
一、创建Stream
从一个数据源,如集合、数组中获取流。
二、中间操作
一个操作的中间链,对数据源的数据进行操作。
三、终止操作
一个终止操作,执行中间操作链,并产生结果。
要注意的是,对流的操作完成后需要进行关闭操作(或者用JAVA7的try-with-resources)。
举个简单的例子:
假设有一个Person类和一个Person列表,现在有两个需求:1)找到年龄大于18岁的人并输出;2)找出所有中国人的数量。
@Data
class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String country;
private char sex;
public Person(String name, Integer age, String country, char sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.country = country;
this.sex = sex;
}
}
List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add(new Person("欧阳雪",18,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("Tom",24,"美国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("Harley",22,"英国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("向天笑",20,"中国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("李康",22,"中国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("小梅",20,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("何雪",21,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("李康",22,"中国",'M'));
在JDK8以前,我们可以通过遍历列表来完成。但是在有了Stream API后,可以这样来实现:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1)找到年龄大于18岁的人并输出;
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getAge() > 18).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
// 2)找出所有中国人的数量
long chinaPersonNum = personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getCountry().equals("中国")).count();
System.out.println("中国人有:" + chinaPersonNum + "个");
}
输出结果:
Person(name=Tom, age=24, country=美国, sex=M)
Person(name=Harley, age=22, country=英国, sex=F)
Person(name=向天笑, age=20, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=李康, age=22, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=小梅, age=20, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=何雪, age=21, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=李康, age=22, country=中国, sex=M)
\-------------------------------------------
中国人有:6
在这个例子中,personList.stream()是创建流,filter()属于中间操作,forEach、count()是终止操作。
Stream中间操作--筛选与切片
- filter:接收Lambda,从流中排除某些操作;
- limit:截断流,使其元素不超过给定对象
- skip(n):跳过元素,返回一个扔掉了前n个元素的流,若流中元素不足n个,则返回一个空流,与limit(n)互补
- distinct:筛选,通过流所生成元素的hashCode()和equals()去除重复元素。
limit举例
需求,从Person列表中取出两个女性。
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'F').limit(2).forEach(System.out::println);
输出结果为:
Person(name=欧阳雪, age=18, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=Harley, age=22, country=英国, sex=F)
skip举例
从Person列表中从第2个女性开始,取出所有的女性。
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'F').skip(1).forEach(System.out::println);
输出结果为:
Person(name=Harley, age=22, country=英国, sex=F)
Person(name=小梅, age=20, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=何雪, age=21, country=中国, sex=F)
distinct举例
1 personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'M').distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
输出结果为:
Person(name=Tom, age=24, country=美国, sex=M)
Person(name=向天笑, age=20, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=李康, age=22, country=中国, sex=M)
男性中有两个李康,去除掉了一个重复的。
Stream中间操作--映射
- map--接收Lambda,将元素转换成其他形式或提取信息。接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。
- flatMap--接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流
map举例
例1:比如,我们用一个PersonCountry类来接收所有的国家信息:
@Data
class PersonCountry {
private String country;
}
personList.stream().map((p) -> {
PersonCountry personName = new PersonCountry();
personName.setCountry(p.getCountry());
return personName;
}).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
输出结果为:
PersonName(country=中国)
PersonName(country=美国)
PersonName(country=英国)
例2:假如有一个字符列表,需要提出每一个字符
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd","ddd");
代码如下:
根据字符串获取字符方法:
public static Stream<Character> getCharacterByString(String str) {
List<Character> characterList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Character character : str.toCharArray()) {
characterList.add(character);
}
return characterList.stream();
}
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd","ddd");
final Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream
= list.stream().map(TestStreamAPI::getCharacterByString);
streamStream.forEach(System.out::println);
运行结果:
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@3f91beef
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@1a6c5a9e
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@37bba400
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@179d3b25
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@254989ff
从输出结果及返回结果类型(Stream<Stream>)可以看出这是一个流中流,要想打印出我们想要的结果,需要对流中的每个流进行打印:
streamStream.forEach(sm -> sm.forEach(System.out::print));
运行结果为:
aaabbbcccdddddd
但我们希望的是返回的是一个流,而不是一个包含了多个流的流,而flatMap可以帮助我们做到这一点。
flatMap举例
改写上面的方法,将map改成flatMap:
final Stream<Character> characterStream = list.stream().flatMap(TestStreamAPI::getCharacterByString);
characterStream.forEach(System.out::print);
运行结果为:
aaabbbcccdddddd
案例二:对给定单词列表 ["Hello","World"],你想返回列表["H","e","l","o","W","r","d"]
String[] words = new String[]{"Hello","World"};
List<String> a = Arrays.stream(words)
.map(word -> word.split(""))
.flatMap(Arrays::stream)
.distinct()
.collect(toList());
a.forEach(System.out::print);
map和flatMap的图解
map图解:
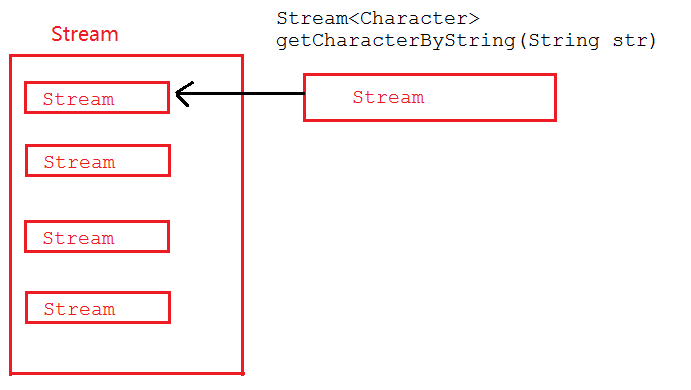
map在接收到流后,直接将Stream放入到一个Stream中,最终整体返回一个包含了多个Stream的Stream。
flatMap图解:
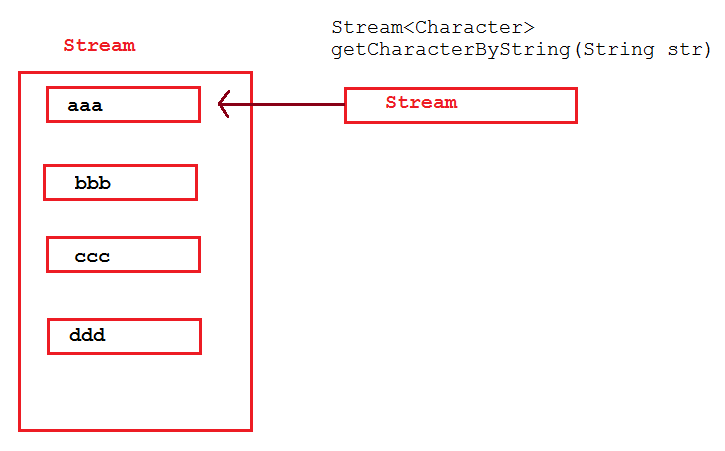
flatMap在接收到Stream后,会将接收到的Stream中的每个元素取出来放入一个Stream中,最后将一个包含多个元素的Stream返回。
ps:图画得丑,将就一下。
Stream中间操作--排序
- sorted()--自然排序(Comparable)
- sorted(Comparator com)--定制排序(Comparator)
自然排序比较好理解,这里只讲一下定制排序,对前面的personList按年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同,则再按姓名排序:
final Stream<Person> sorted = personList.stream().sorted((p1, p2) -> {
if (p1.getAge().equals(p2.getAge())) {
return p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());
} else {
return p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge());
}
});
sorted.forEach(System.out::println);
运行结果:
Person(name=欧阳雪, age=18, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=向天笑, age=20, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=小梅, age=20, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=何雪, age=21, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=Harley, age=22, country=英国, sex=F)
Person(name=李康, age=22, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=李康, age=22, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=Tom, age=24, country=美国, sex=M)
Stream中间操作--分流
partitioningBy 分流
public static <T>
Collector<T, ?, Map<Boolean, List<T>>> partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T> predicate) {
return partitioningBy(predicate, toList());
}
可以看出函数的参数一个Predicate接口,那么这个接口的返回值是boolean类型的,也只能是boolean类型,然后他的返回值是Map的key是boolean类型,也就是这个函数的返回值只能将数据分为两组也就是ture和false两组数据。
例如:有一组人名,包含中文和英文,在 JDK8 中可以通过 partitioningBy 收集器将其区分开来。
// 创建一个包含人名称的流(英文名和中文名)
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("Alen", "Hebe", "Zebe", "张成瑶", "钟其林");
// 通过判断人名称的首字母是否为英文字母,将其分为两个不同流
final Map<Boolean, List<String>> map = stream.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> {
// 如果是英文字母,则将其划分到英文人名,否则划分到中文人名
int code = s.codePointAt(0);
return (code >= 65 && code <= 90) || (code >= 97 && code <= 122);
}));
// 输出分组结果
map.forEach((isEnglishName, names) -> {
if (isEnglishName) {
System.out.println("英文名称如下:");
} else {
System.out.println("中文名称如下:");
}
names.forEach(name -> System.out.println("\t" + name));
});
groupingBy 分流
groupingBy 生成一个拥有分组功能的Collector,有三个重载方法。
需要一个参数:按照该参数进行分组。结果返回一个Map集合,每个Map的key默认是分组参数的类型,value是一个List集合。
public void test1() {
Map <String,List < User >> collect = users.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User: :getEdu));
}
需要两个参数:第二参数是Collector类型,可以对value进行处理。
可以对结果进行映射
public void test2() {
Map <String,List <Integer>> collect = users.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User: :getEdu,
//第二个参数对Map的value进行处理(映射)
Collectors.mapping(User: :getId, Collectors.toList())));
}
可以对结果进行求和
public static void test3() {
Map <String,Double> collect = users.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User: :getEdu,
//对参数进行累计求和
Collectors.summingDouble(User: :getPrice)));
System.out.println(collect);
}
对结果的统计
public static void test4() {
Map < String,Long > collect = users.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User: :getEdu,
//获取count数量
Collectors.counting()));
System.out.println(collect);
}
需要三个参数,第二个参数添加了对结果Map的生成方式,默认是HashMap
public static void test3() {
Map <String,Double > collect = users.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User: :getEdu,
//决定map的生成方式,使用TreeMap
TreeMap: :new,
//对参数进行累计求和
Collectors.summingDouble(User: :getPrice)));
System.out.println(collect);
}
如果k,v是唯一对应的,可以使用Collectors.toMap来实现。
终止操作--查找与匹配
- allMatch--检查是否匹配所有元素
- anyMatch--检查是否至少匹配一个元素
- noneMatch--检查是否没有匹配所有元素
- findFirst--返回第一个元素
- findAny--返回当前流中的任意元素
- count--返回流中元素的总个数
- max--返回流中最大值
- min--返回流中最小值
这些方面在Stream类中都有说明,这里不一一举例,只对allMatch、max各举一例进行说明。
allMatch
判断personList中的人是否都是成年人:
final boolean adult = personList.stream().allMatch(p -> p.getAge() >= 18);
System.out.println("是否都是成年人:" + adult);
final boolean chinaese = personList.stream().allMatch(p -> p.getCountry().equals("中国"));
System.out.println("是否都是中国人:" + chinaese);
运行结果:
是否都是成年人:true
是否都是中国人:false
max min
final Optional<Person> maxAge = personList.stream().max((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("年龄最大的人信息:" + maxAge.get());
final Optional<Person> minAge = personList.stream().min((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("年龄最小的人信息:" + minAge.get());
运行结果:
年龄最大的人信息:Person(name=Tom, age=24, country=美国, sex=M)
年龄最小的人信息:Person(name=欧阳雪, age=18, country=中国, sex=F)
findAny()
用findAny()寻找List中符合要求的数据
这段代码如果找不到数据就会抛异常。
A a = bList().stream().filter(b -> "test".equals(b.getName())).findAny().get();
这段代码如果找不到数据会返回null。orElse()是设置找不到数据后的默认值。
A a =bList().stream().filter(b->"test".equals(b.getName())).findAny().orElse(null);
注意orElse()和orElseGet()
如下代码:
return Stream.of(getObjectAttributeValue(product, matchCriteria.getFieldName()))
.map(o -> isIngredientRestricted(matchCriteria, (List<String>) o))
.filter(Boolean::valueOf)
.findAny().orElse(isCommercialHierarchyInfoRestricted(product, matchCriteria));
所期望的是,如果第一个地图发出布尔值false,那么它将被过滤,因此findAny将找不到任何可选项,因此将调用orElse.
但即使在过滤器中有一个true,也会调用isCommercialHierarchyInfoRestricted.
这是因为使用orElse(表达式)总是在调用方法orElse之前导致表达式的评估,而您必须使用orElseGet(() – > expression)来推迟表达式的求值.
此外,这是不必要的Stream API使用.如果要评估单个项目,则不需要创建单个元素流,只是为了之后调用findAny.可以在第一时间创建一个Optional:
return Optional.of(getObjectAttributeValue(product, matchCriteria.getFieldName()))
.map(o -> isIngredientRestricted(matchCriteria, (List<String>)o))
.filter(b -> b)
.orElseGet(() -> isCommercialHierarchyInfoRestricted(product, matchCriteria));
allMatch, anyMatch, noneMatch
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
boolean allMatch = list.stream().allMatch(e -> e.equals("a"));
boolean anyMatch = list.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.equals("a"));
boolean noneMatch = list.stream().noneMatch(e -> e.equals("a"));
System.out.println(allMatch);// true
System.out.println(anyMatch);// false
System.out.println(noneMatch);// true
}
注意 boolean allMatch = list.stream().allMatch(e -> e.equals("a"));
当list的为空集合时候,这个返回默认为true;
归约
Stream API的归约操作可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值,有:
Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
<U> U reduce(U identity,
BiFunction<U, ? super T, U> accumulator,
BinaryOperator<U> combiner);
求一个1到100的和
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>(100);
for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++) {
integerList.add(i);
}
final Integer reduce = integerList.stream().reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y);
System.out.println("结果为:" + reduce);
结果为:5050
这个例子用到了reduce第二个方法:T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator accumulator)
把这个动作拆解一下,其运算步骤模拟如下:
0 (1,2) -> 1 + 2 + 0
3 (3,4) -> 3 + 4 + 3
10 (5,6) -> 5 + 6 + 10
.
.
.
其运算步骤是,每次将列表的两个元素相加,并将结果与前一次的两个元素的相加结果进行累加,因此,在开始时,将identity设为0,因为第1个元素和第2个元素在相加的时候,前面还没有元素操作过。
求所有人的年龄之和
final Optional<Integer> reduce = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge).reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println("年龄总和:" + reduce);
年龄总和:169
收集
collect:将流转换为其他形式,接收一个Collector接口实现 ,用于给Stream中汇总的方法
<R, A> R collect(Collector<? super T, A, R> collector);
<R> R collect(Supplier<R> supplier,
BiConsumer<R, ? super T> accumulator,
BiConsumer<R, R> combiner);
collect不光可以将流转换成其他集合等形式,还可以进行归约等操作,具体实现也很简单,主要是与Collectors类搭配使用。
改写map举例中的的例子,将国家收集起来转换成List
final List<String> collect = personList.stream().map(p -> p.getCountry()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
输出结果:
[中国, 美国, 英国]
计算出平均年龄
final Double collect1 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(p -> p.getAge()));
System.out.println("平均年龄为:" + collect1);
输出结果:
平均年龄为:21.125
找出最小年龄、最大年龄
final Optional<Integer> maxAge2 = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println(maxAge2.get());
最小年龄类似。
还有其他很操作,可以参考java.util.stream.Collectors。
注意流的关闭
try(final Stream<Integer> integerStream = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge)) {
final Optional<Integer> minAge = integerStream.collect(Collectors.minBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println(minAge.get());
}
最好将流的操作放到try-with-resources,本章前面内容为了方便,没有放到try-with-resources中。
完整测试代码
iimport lombok.Data;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class TestStreamAPI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add(new Person("欧阳雪",18,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("Tom",24,"美国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("Harley",22,"英国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("向天笑",20,"中国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("李康",22,"中国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("小梅",20,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("何雪",21,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("李康",22,"中国",'M'));
// 1)找到年龄大于18岁的人并输出;
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getAge() > 18).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
// 2)找出所有中国人的数量
long chinaPersonNum = personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getCountry().equals("中国")).count();
System.out.println("中国人有:" + chinaPersonNum);
// limit
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'F').limit(2).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// skip
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'F').skip(1).forEach(System.out::println);
// distinct
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'M').distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
// map
personList.stream().map((p) -> {
PersonCountry personName = new PersonCountry();
personName.setCountry(p.getCountry());
return personName;
}).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
// map2
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd","ddd");
final Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream
= list.stream().map(TestStreamAPI::getCharacterByString);
// streamStream.forEach(System.out::println);
streamStream.forEach(sm -> sm.forEach(System.out::print));
// flatMap
final Stream<Character> characterStream = list.stream().flatMap(TestStreamAPI::getCharacterByString);
characterStream.forEach(System.out::print);
// sort
final Stream<Person> sorted = personList.stream().sorted((p1, p2) -> {
if (p1.getAge().equals(p2.getAge())) {
return p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());
} else {
return p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge());
}
});
sorted.forEach(System.out::println);
// allMatch
final Stream<Person> stream = personList.stream();
final boolean adult = stream.allMatch(p -> p.getAge() >= 18);
System.out.println("是否都是成年人:" + adult);
final boolean chinaese = personList.stream().allMatch(p -> p.getCountry().equals("中国"));
System.out.println("是否都是中国人:" + chinaese);
// max min
final Optional<Person> maxAge = personList.stream().max((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("年龄最大的人信息:" + maxAge.get());
final Optional<Person> minAge = personList.stream().min((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("年龄最小的人信息:" + minAge.get());
// reduce
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>(100);
for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++) {
integerList.add(i);
}
final Integer reduce = integerList.stream().reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y);
System.out.println("结果为:" + reduce);
final Optional<Integer> totalAge = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge).reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println("年龄总和:" + totalAge);
// collect
final List<String> collect = personList.stream().map(p -> p.getCountry()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
final Double collect1 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(p -> p.getAge()));
System.out.println("平均年龄为:" + collect1);
final Optional<Integer> maxAge2 = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println(maxAge2.get());
try(final Stream<Integer> integerStream = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge)) {
final Optional<Integer> minAge2 = integerStream.collect(Collectors.minBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println(minAge2.get());
}
}
public static Stream<Character> getCharacterByString(String str) {
List<Character> characterList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Character character : str.toCharArray()) {
characterList.add(character);
}
return characterList.stream();
}
}
@Data
class PersonCountry {
private String country;
}
@Data
class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String country;
private char sex;
public Person(String name, Integer age, String country, char sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.country = country;
this.sex = sex;
}
}
【Java 8】Stream API的更多相关文章
- 【Java 8】Stream中的Pipeline理解
基于下面一段代码: public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = Arrays.asList("123 ...
- 【Java 8】Stream.distinct() 列表去重示例
在这篇文章里,我们将提供Java8 Stream distinct()示例. distinct()返回由该流的不同元素组成的流.distinct()是Stream接口的方法. distinct()使用 ...
- 【Java 8】Stream中flatMap方法
在java 8 Stream中,flatMap方法是一个维度升降的方法 举例说明 给 定 单 词 列 表["Hello","World"] ,要返回列表 [&q ...
- 【Java 8】Stream通过reduce()方法合并流为一条数据示例
在本页中,我们将提供 Java 8 Stream reduce()示例. Stream reduce()对流的元素执行缩减.它使用恒等式和累加器函数进行归约. 在并行处理中,我们可以将合并器函数作为附 ...
- 【Java面试】基础知识篇
[Java面试]基础知识篇 Java基础知识总结,主要包括数据类型,string类,集合,线程,时间,正则,流,jdk5--8各个版本的新特性,等等.不足的地方,欢迎大家补充.源码分享见个人公告.Ja ...
- 【Java面试】1、基础知识篇
[Java面试]基础知识篇 Java基础知识总结,主要包括数据类型,string类,集合,线程,时间,正则,流,jdk5--8各个版本的新特性,等等.不足的地方,欢迎大家补充. 源码分享:https: ...
- 【java爬虫】---爬虫+基于接口的网络爬虫
爬虫+基于接口的网络爬虫 上一篇讲了[java爬虫]---爬虫+jsoup轻松爬博客,该方式有个很大的局限性,就是你通过jsoup爬虫只适合爬静态网页,所以只能爬当前页面的所有新闻.如果需要爬一个网站 ...
- 【java爬虫】---爬虫+jsoup轻松爬博客
爬虫+jsoup轻松爬博客 最近的开发任务主要是爬虫爬新闻信息,这里主要用到技术就是jsoup,jsoup 是一款 Java的HTML解析器,可直接解析某个URL地址.HTML文本内容.它提供了一套非 ...
- 【JAVA系列】Google爬虫如何抓取JavaScript的?
公众号:SAP Technical 本文作者:matinal 原文出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/SAPmatinal/ 原文链接:[JAVA系列]Google爬虫如何抓取Java ...
随机推荐
- linux磁盘空间查看
du -h --max-depth=1 du -sh df -h
- vite2 + vite.config.js 比较坑的环境变量,vite2模式的使用
想在vite.config.js 里面判断一下环境,看看是不是开发环境,查了一下官网(https://cn.vitejs.dev/guide/env-and-mode.html),说是 可以使用 im ...
- [luogu7417]Minimizing Edges P
令$e_{G}(a)$和$o_{G}(a)$分别表示在图$G$中从1到$a$的长度为奇数/偶数的最短路(若该类最短路不存在则为$\infty$),不难得到有以下结论--$f_{G}(a,b)=\beg ...
- [loj3276]遗迹
假设已知$a_{i}$,通过以下方式确定$b_{i}$:从后往前枚举每一个数$i$,先令$b_{i}=a_{i}$,再将$b_{i}$不断减1直至不存在$j>i$且$b_{i}=b_{j}$或$ ...
- bean注解
1.beans.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi=&qu ...
- .NET 开源免费图表组件库,Winform,WPF 通用
大家好, 我是等天黑, 今天给大家介绍一个功能完善, 性能强悍的图表组件库 ScottPlot, 当我第一次在 github 上看到这个库, 我看不懂,但我大受震撼, 这么好的项目当然要分享出来了. ...
- 关于postman的接口登录验证问题
1.shiro的接口登录问题 碰到需要接口登录验证的:访问项目接口地址login,找到cookie将Cookie数据放入postman的headers 中. 2.碰到 security的项目.首先把相 ...
- C# Pechkin初始化一次后被锁住的问题
Pechkin.dll可用于pdf的生成,常规用法网上都有介绍:https://www.cnblogs.com/felixnet/p/5143934.html 但是当在一个页面上执行过一次之后,再次就 ...
- 6.K8s集群升级、etcd备份和恢复、资源对象及其yaml文件使用总结、常用维护命令
1.K8s集群升级 集群升级有一定的风险,需充分测试验证后实施 集群升级需要停止服务,可以采用逐个节点滚动升级的方式 1.1 准备新版本二进制文件 查看现在的版本 root@k8-master1:~# ...
- 【2020五校联考NOIP #4】今天的你依旧闪耀
题面传送门 题意: 对于一个长度为 \(n\)(\(n\) 为偶数)的排列 \(p\),定义一次"变换"后得到的排列 \(p'\) 为: \(p'_i=\begin{cases}p ...
