jvm源码解读--09 创建oop对象,将static静态变量放置在oop的96 offset处 第二篇
先打断点systemDictionary.cpp 1915行
Universe::fixup_mirrors(CHECK);
进入
void Universe::fixup_mirrors(TRAPS) {
// Bootstrap problem: all classes gets a mirror (java.lang.Class instance) assigned eagerly,
// but we cannot do that for classes created before java.lang.Class is loaded. Here we simply
// walk over permanent objects created so far (mostly classes) and fixup their mirrors. Note
// that the number of objects allocated at this point is very small.
assert(SystemDictionary::Class_klass_loaded(), "java.lang.Class should be loaded");
HandleMark hm(THREAD);
// Cache the start of the static fields
InstanceMirrorKlass::init_offset_of_static_fields();
GrowableArray <Klass*>* list = java_lang_Class::fixup_mirror_list();
int list_length = list->length();
for (int i = 0; i < list_length; i++) {
Klass* k = list->at(i);
assert(k->is_klass(), "List should only hold classes");
EXCEPTION_MARK;
KlassHandle kh(THREAD, k);
java_lang_Class::fixup_mirror(kh, CATCH);
}
delete java_lang_Class::fixup_mirror_list();
java_lang_Class::set_fixup_mirror_list(NULL);
}
给红色打断点,当i=12的时候进入java.lang.String类的解析
void java_lang_Class::fixup_mirror(KlassHandle k, TRAPS) {
assert(InstanceMirrorKlass::offset_of_static_fields() != 0, "must have been computed already");
// If the offset was read from the shared archive, it was fixed up already
if (!k->is_shared()) {
if (k->oop_is_instance()) {
// During bootstrap, java.lang.Class wasn't loaded so static field
// offsets were computed without the size added it. Go back and
// update all the static field offsets to included the size.
for (JavaFieldStream fs(InstanceKlass::cast(k())); !fs.done(); fs.next()) {
if (fs.access_flags().is_static()) {
int real_offset = fs.offset() + InstanceMirrorKlass::offset_of_static_fields();
fs.set_offset(real_offset);
}
}
}
}
create_mirror(k, Handle(NULL), CHECK);
}
给紫色的构造器
JavaFieldStream(instanceKlassHandle k): FieldStreamBase(k->fields(), k->constants(), 0, k->java_fields_count()) {}
FieldStreamBase(Array<u2>* fields, constantPoolHandle constants, int start, int limit) {
_fields = fields;
_constants = constants;
_index = start;
int num_fields = init_generic_signature_start_slot();
if (limit < start) {
_limit = num_fields;
} else {
_limit = limit;
}
}
打印对象
(gdb) p fields
$25 = (Array<unsigned short> *) 0x7f28e0a03280
(gdb) x/36h fields
0x7f28e0a03280: 0x001f 0x0000 0x0012 0x0098 0x0099 0x0000 0x0031 0x0000
0x7f28e0a03290: 0x0002 0x009a 0x009b 0x0000 0x0041 0x0000 0x001a 0x009c
0x7f28e0a032a0: 0x009d 0x009f 0x0021 0x0000 0x001a 0x00a1 0x00a2 0x0000
0x7f28e0a032b0: 0x0001 0x0000 0x0819 0x00a3 0x00a4 0x0000 0x0011 0x0000
0x7f28e0a032c0: 0x00a6 0x0000 0x0000 0x0000
(gdb) p * this
$35 = {
<MetaspaceObj> = {<No data fields>},
members of Array<unsigned short>:
_length = 31,
_data = {18}
}
(gdb) p this
$36 = (Array<unsigned short> * const) 0x7f28e0a03280
这个array类,前俩位是length,所以数数的时候从0x7f28e0a03284 开始数
看黄色的判断,判断访问表示符号是否是static static 是0x10
想进入的看的话可以简单的解释一下
AccessFlags access_flags() const {
AccessFlags flags;
flags.set_flags(field()->access_flags());
return flags;
}
//那么需要进入field(),这个就是获取字段信息
FieldInfo* field() const { return FieldInfo::from_field_array(_fields, _index); }
//在FieldInfo类中
static FieldInfo* from_field_array(Array<u2>* fields, int index) {
return ((FieldInfo*)fields->adr_at(index * field_slots));
}
//在Array类中
T at(int i) const { assert(i >= 0 && i< _length, err_msg("oob: 0 <= %d < %d", i, _length)); return _data[i]; }
这个array对象已经打印过,在上边贴的代码中
那么进入绿色的代码
int real_offset = fs.offset() + InstanceMirrorKlass::offset_of_static_fields();
int offset() const {
return field()->offset();
}
这个field()已经展示过了,获取field信息,不说了
u4 offset() const {
u2 lo = _shorts[low_packed_offset];
switch(lo & FIELDINFO_TAG_MASK) {
case FIELDINFO_TAG_OFFSET:
return build_int_from_shorts(_shorts[low_packed_offset], _shorts[high_packed_offset]) >> FIELDINFO_TAG_SIZE;
}
inline int build_int_from_shorts( jushort low, jushort high ) {
return ((int)((unsigned int)high << 16) | (unsigned int)low);
}
这打印下
(gdb) p _shorts
$44 = {26, 156, 157, 159, 33, 0}
这就很明确的,高位加低位的和 右移2位
// Packed field has the tag, and can be either of:
// hi bits <--------------------------- lo bits
// |---------high---------|---------low---------|
// ..........................................00 - blank
// [------------------offset----------------]01 - real field offset
// ......................[-------type-------]10 - plain field with type
// [--contention_group--][-------type-------]11 - contended field with type and contention group
enum FieldOffset {
access_flags_offset = 0,
name_index_offset = 1,
signature_index_offset = 2,
initval_index_offset = 3,
low_packed_offset = 4,
high_packed_offset = 5,
field_slots = 6
};
其中分支判断的宏
#define FIELDINFO_TAG_SIZE 2
#define FIELDINFO_TAG_BLANK 0
#define FIELDINFO_TAG_OFFSET 1
#define FIELDINFO_TAG_TYPE_PLAIN 2
#define FIELDINFO_TAG_TYPE_CONTENDED 3
#define FIELDINFO_TAG_MASK 3
这个向右移动2 就是这个宏定义的
那么这个结果就是高位 0x00 和低位 33 右移动2为,计算结果是8
还有就是后面的 InstanceMirrorKlass::offset_of_static_fields()
static int offset_of_static_fields() {
return _offset_of_static_fields;
}
//这是一个固定的值为96
那么real_offset就是96+8为104,
我们可以结合这个$44 = {26, 156, 157, 159, 33, 0}来查这个变量信息
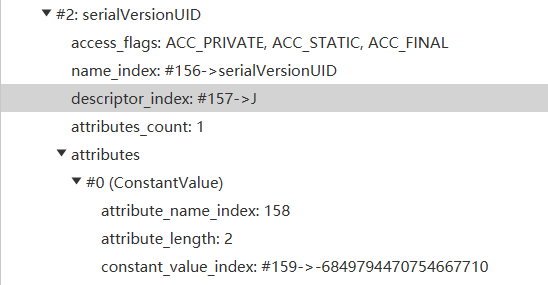
这个就对应上了
最后执行的是将真是偏移量放到field变量中
fs.set_offset(real_offset);
-->//field变量
void set_offset(int offset) {
field()->set_offset(offset);
}
-->
void set_offset(u4 val) {
val = val << FIELDINFO_TAG_SIZE; // make room for tag
_shorts[low_packed_offset] = extract_low_short_from_int(val) | FIELDINFO_TAG_OFFSET;
_shorts[high_packed_offset] = extract_high_short_from_int(val);
}
执行前打印信息
(gdb) p _shorts
$46 = {26, 156, 157, 159, 33, 0}
(gdb) p &_shorts
$47 = (unsigned short (*)[6]) 0x7f28e0a0329c
执行后打印信息
(gdb) p &_shorts
$48 = (unsigned short (*)[6]) 0x7f28e0a0329c
(gdb) p _shorts
$49 = {26, 156, 157, 159, 417, 0}
比如在看下一个变量的解析,执行前
(gdb) p &_shorts
$50 = (unsigned short (*)[6]) 0x7f28e0a032a8
(gdb) p _shorts
$51 = {26, 161, 162, 0, 1, 0}
我们同样分析一下这个变量
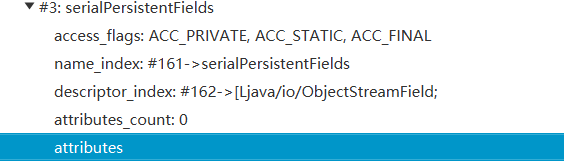
那么执行过程就是将96偏移量放了进去,执行后
(gdb) p _shorts
$52 = {26, 161, 162, 0, 385, 0}
那么还是进入create_mirror这个函数,之前解析过这个函数,不过那个时候解析的不带static变量,专门说下,static和其他不同的地方
Handle mirror = InstanceMirrorKlass::cast(SystemDictionary::Class_klass())->allocate_instance(k, CHECK_0);
-->
instanceOop InstanceMirrorKlass::allocate_instance(KlassHandle k, TRAPS) {
// Query before forming handle.
int size = instance_size(k);
KlassHandle h_k(THREAD, this);
instanceOop i = (instanceOop) CollectedHeap::Class_obj_allocate(h_k, size, k, CHECK_NULL);
return i;
}
-->
int InstanceMirrorKlass::instance_size(KlassHandle k) {
if (k() != NULL && k->oop_is_instance()) {
return align_object_size(size_helper() + InstanceKlass::cast(k())->static_field_size());
}
return size_helper();
}
看到了_static_field_size=2 那么就清楚了, 最终size=14
最后打印一下生成的对象
(gdb) p * mirror
$54 = {
_mark = 0x1,
_metadata = {
_klass = 0x200003e0,
_compressed_klass = 536871904
},
static _bs = 0x7f28dc01ea48
}
接着就是设置属性oop的便宜量定义了不同的信息OOP
| _protection_domain_offset | 52 |
| _init_lock_offset | 56 |
| _signers_offset | 60 |
| _klass_offset | 64 |
| _array_klass_offset | 72 |
| classRedefinedCount_offset | 80 |
| _oop_size_offset | 84 |
| _static_oop_field_count_offset | 88 |
| 静态变量1 | 96 |
| 静态变量2 | 104 |
| 静态变量2 | |
| 静态变量3 | |
| 静态变量n |
比如这个函数
void java_lang_Class::set_static_oop_field_count(oop java_class, int size) {
assert(_static_oop_field_count_offset != 0, "must be set");
java_class->int_field_put(_static_oop_field_count_offset, size);
}
就是在oop的88 偏移量设置了2
接着看
typeArrayOop r = oopFactory::new_typeArray(T_INT, 0, CHECK_NULL);
set_init_lock(mirror(), r); // Set protection domain also
set_protection_domain(mirror(), protection_domain());
这两个还是设置oop偏移量的 52 和 56的两个属性
// Initialize static fields
InstanceKlass::cast(k())->do_local_static_fields(&initialize_static_field, CHECK_NULL);
这个就是本篇的主旨,给静态变量赋值
typeArrayOop r = oopFactory::new_typeArray(T_INT, 0, CHECK_NULL);
set_init_lock(mirror(), r); // Set protection domain also
set_protection_domain(mirror(), protection_domain()); // Initialize static fields
InstanceKlass::cast(k())->do_local_static_fields(&initialize_static_field, CHECK_NULL);
然后
void InstanceKlass::do_local_static_fields(void f(fieldDescriptor*, TRAPS), TRAPS) {
instanceKlassHandle h_this(THREAD, this);
do_local_static_fields_impl(h_this, f, CHECK);
}
void InstanceKlass::do_local_static_fields_impl(instanceKlassHandle this_oop, void f(fieldDescriptor* fd, TRAPS), TRAPS) {
for (JavaFieldStream fs(this_oop()); !fs.done(); fs.next()) {
if (fs.access_flags().is_static()) {
fieldDescriptor& fd = fs.field_descriptor();
f(&fd, CHECK);
}
}
}
进入
static void initialize_static_field(fieldDescriptor* fd, TRAPS) {
Handle mirror (THREAD, fd->field_holder()->java_mirror());
assert(mirror.not_null() && fd->is_static(), "just checking");
if (fd->has_initial_value()) {
BasicType t = fd->field_type();
switch (t) {
case T_BYTE:
mirror()->byte_field_put(fd->offset(), fd->int_initial_value());
break;
case T_BOOLEAN:
mirror()->bool_field_put(fd->offset(), fd->int_initial_value());
break;
case T_CHAR:
mirror()->char_field_put(fd->offset(), fd->int_initial_value());
break;
case T_SHORT:
mirror()->short_field_put(fd->offset(), fd->int_initial_value());
break;
case T_INT:
mirror()->int_field_put(fd->offset(), fd->int_initial_value());
break;
case T_FLOAT:
mirror()->float_field_put(fd->offset(), fd->float_initial_value());
break;
case T_DOUBLE:
mirror()->double_field_put(fd->offset(), fd->double_initial_value());
break;
case T_LONG:
mirror()->long_field_put(fd->offset(), fd->long_initial_value());
break;
case T_OBJECT:
{
#ifdef ASSERT
TempNewSymbol sym = SymbolTable::new_symbol("Ljava/lang/String;", CHECK);
assert(fd->signature() == sym, "just checking");
#endif
oop string = fd->string_initial_value(CHECK);
mirror()->obj_field_put(fd->offset(), string);
}
break;
default:
THROW_MSG(vmSymbols::java_lang_ClassFormatError(),
"Illegal ConstantValue attribute in class file");
}
}
}
开始
(gdb) p * fd
$56 = {
_access_flags = {
_flags = 26
},
_index = 2,
_cp = {
<StackObj> = {
<AllocatedObj> = {
_vptr.AllocatedObj = 0x7f28e4a90390 <vtable for constantPoolHandle+16>
}, <No data fields>},
members of constantPoolHandle:
_value = 0x7f28e0a01100,
_thread = 0x7f28dc00b800
}
}
条件判断
bool has_initial_value() const { return field()->initval_index() != 0; }
initval_index_offset = 3,
这获取了初始值,就是变量的 值,比如说 private static final long serialVersionUID = -6849794470754667710L; 值就是-6849794470754667710L,
意思就是如果你有值就给oop的96偏移量后面的static变量赋值
看这个
BasicType t = fd->field_type();
BasicType field_type() const { return FieldType::basic_type(signature()); }
Symbol* signature() const {
return field()->signature(_cp);
}
Symbol* signature(constantPoolHandle cp) const {
int index = signature_index(); --> u2 signature_index() const { return _shorts[signature_index_offset]; } //off=2 //index =157
if (is_internal()) {
return lookup_symbol(index);
}
return cp->symbol_at(index);
}
BasicType FieldType::basic_type(Symbol* signature) {
return char2type(signature->byte_at(0));
}
BasicType t = fd->field_type(); t:T_LONG
就是解析出来了 t 是T_LONG
case T_LONG:
mirror()->long_field_put(fd->offset(), fd->long_initial_value());
这个fd->offset是oop偏移量
jlong fieldDescriptor::long_initial_value() const {
return constants()->long_at(initial_value_index());
}
这个就是
int initial_value_index() const { return field()->initval_index(); }
(gdb) p initial_value_index()
$59 = 159
然后从常量池中找到这个159的符号
jlong long_at(int which) {
assert(tag_at(which).is_long(), "Corrupted constant pool");
// return *long_at_addr(which);
u8 tmp = Bytes::get_native_u8((address)&base()[which]);
return *((jlong*)&tmp);
}
具体在说一边这个fd->offset()
==> int offset() const { return field()->offset(); }
==>
FieldInfo* field() const {
InstanceKlass* ik = field_holder();
return ik->field(_index);
}
==>
InstanceKlass* field_holder() const { return _cp->pool_holder(); }
这就得到了Field这个6个成员的数组变量_short
让后就是调用Field->offset()函数
u4 offset() const {
u2 lo = _shorts[low_packed_offset];
switch(lo & FIELDINFO_TAG_MASK) {
case FIELDINFO_TAG_OFFSET:
return build_int_from_shorts(_shorts[low_packed_offset], _shorts[high_packed_offset]) >> FIELDINFO_TAG_SIZE;
}
查到这个便宜量
(gdb) p fd->offset()
$60 = 104
接着就是赋值
inline void oopDesc::long_field_put(int offset, jlong contents) { *long_field_addr(offset) = contents; }
offset=104 值为求出来的常数 -6849794470754667710L
inline jlong* oopDesc::long_field_addr(int offset) const { return (jlong*) field_base(offset); }
inline void* oopDesc::field_base(int offset) const { return (void*)&((char*)this)[offset]; }
this 就是oop对象
那么这样子就给oop赋值了一个static 的常量
打印内存
(gdb) x/14xg 0xd7580830
0xd7580830: 0x0000000000000001 0x00000000200003e0
0xd7580840: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0xd7580850: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0xd7580860: 0x0000000000000000 0x00000000d75808a0
0xd7580870: 0x00000001000016d8 0x0000000000000000
0xd7580880: 0x0000000e00000000 0x0000000000000002
0xd7580890: 0x0000000000000000 0xa0f0a4387a3bb342
能看到了这个常数0xa0f0a4387a3bb342
到此就结束了static 变量的赋值
重要的也是证明了,static 静态变量放到了oop对象offset=96的便宜量位置
这个是instanceklass的的field的数据,其中,其中分析过
enum FieldOffset {
access_flags_offset = 0,
name_index_offset = 1,
signature_index_offset = 2,
initval_index_offset = 3,
low_packed_offset = 4,
high_packed_offset = 5,
field_slots = 6
};
(gdb) x/36h _data
0x7f28e0a03284:
0x0012 0x0098 0x0099 0x0000 0x0031 0x0000
0x0002 0x009a 0x009b 0x0000 0x0041 0x0000
0x001a 0x009c 0x009d 0x009f 0x0021 0x0000
0x001a 0x00a1 0x00a2 0x0000 0x0001 0x0000
0x0819 0x00a3 0x00a4 0x0000 0x0011 0x0000
0x00a6 0x0000 0x0000 0x0000 0x005e 0x0000
重点看序号为3的第4个,用来判断是否有 has_initial_value,那么所有变量了就只有一个0x9f,其他变量没有
,那么其他变量如何赋值呢?这又是另一个知识点了
jvm源码解读--09 创建oop对象,将static静态变量放置在oop的96 offset处 第二篇的更多相关文章
- jvm源码解读--08 创建oop对象,将static静态变量放置在oop的96 offset处
之前分析的已经加载的.Class文件中都没有Static 静态变量,所以也就没这部分的解析,自己也是不懂hotspot 将静态变量放哪里去了,追踪源码之后,看清楚了整个套路,总体上来说,可以举例来说对 ...
- jvm源码解读--07 创建 fixup_mirrors
通过前面的分析,创建的insttanceKlass 都没放入了java_lang_Class::fixup_mirror_list()这里类的数组里面了,所有的instance列举如下 ------- ...
- JVM 源码解读之 CMS 何时会进行 Full GC
t点击上方"涤生的博客",关注我 转载请注明原创出处,谢谢!如果读完觉得有收获的话,欢迎点赞加关注. 前言 本文内容是基于 JDK 8 在文章 JVM 源码解读之 CMS GC 触 ...
- jvm源码解读--17 Java的wait()、notify()学习
write and debug by 张艳涛 wait()和notify()的通常用法 A线程取得锁,执行wait(),释放锁; B线程取得锁,完成业务后执行notify(),再释放锁; B线程释放锁 ...
- jvm源码解读--15 oop对象详解
(gdb) p obj $15 = (oopDesc *) 0xf3885d08 (gdb) p * obj $16 = { _mark = 0x70dea4e01, _metadata = { _k ...
- jvm源码解读--13 gc_root中的栈中oop的mark 和copy 过程分析
粘贴源码 package com.test; import java.util.Random; public class Test { static int number=12; private in ...
- jvm源码解读--12 invokspecial指令的解读
先看代码 package com.zyt.jvmbook; public class Girl extends Person{ public Girl() { int a; } @Override p ...
- jvm源码解读--11 ldc指令的解读
写一个java文件 public static void main(String[] args) { String str1="abc"; String str2 ="a ...
- jvm源码解读--06 Method 方法解析
进入 // Methods bool has_final_method = false; AccessFlags promoted_flags; promoted_flags.set_flags(0) ...
随机推荐
- Java第二次博客作业
Java第二次博客作业 时间过的很快啊,在不知不觉中这门课程的学习也就快要过去一半了,现在就来总结一下在这个第二个月的学习当中存在的问题以及得到的心得. 1.前言 第四次题目集和第五次题目集给我的感觉 ...
- Git操作文档
Git 操作文档 Git 是一个十分流行的版本控制系统,Git 和 SVN 区别在于,SVN使用增量文件系统,存储每次提交之间的差异.而 git 使用全量文件系统,存储每次提交的文件的全部内容(sna ...
- MySQL的自增ID用完了,怎么办?
既然这块知识点不清楚,那回头就自己动手实践下. 首先,创建一个最简单的表,只包含一个自增id,并插入一条数据. create table t0(id int unsigned auto_increme ...
- 管中窥豹-ssh链接过多的问题分析及复盘
缘起 某一天,产品侧同事联系过来,反馈话单传输程序报错,现象如下: 实际上,该节点仅提供了一个sftp服务,供产品侧传输话单过来进行临时存储,由计费部门取走而已. 分析 于是找运维同事上服务器看了下情 ...
- javascript之一切都是对象
在学习的过程中,我们常常能听到这样一句话:一切皆是对象.那么这句话该如何理解呢?首先,我们要明确对象的概念.要明白除了基本数据类型都是对象. typeof操作符是大家经常使用的,我们常用它来检测给定变 ...
- 海量数据Excel报表利器——EasyExcel(开场篇)
EasyExcel 简介篇 互联网的精髓就是共享,可以共享技术.共享经验.共享情感.共享快乐~ 很多年前就有这个想法了,从事IT行业时间也不短了,应该把自己工作和业余所学习的东西记录并分享出来,和有缘 ...
- Kubernetes架构原理
1.了解架构 在研究Kubernetes如何实现其功能之前,先具体了解下Kubernetes集群有哪些组件.Kubernetes集群分为两部分: Kubernetes控制平面 (工作)节点 具体看下这 ...
- 『无为则无心』Python序列 — 19、Python列表的其他操作(切片和遍历)
目录 1.通过切片对列表的操作 (1)通过切片对列表进行修改 (2)通过切片对列表进行删除 (3)注意 2.列表的循环遍历 (1)while循环遍历 (2)for循环遍历 3.列表嵌套 4.综合示例 ...
- layui table 列宽百分比显示
var layer = layui.layer, form = layui.form, table = layui.table; var $ = layui.$; /*select gysmc,zyz ...
- POJ 1584 A Round Peg in a Ground Hole 判断凸多边形 点到线段距离 点在多边形内
首先判断是不是凸多边形 然后判断圆是否在凸多边形内 不知道给出的点是顺时针还是逆时针,所以用判断是否在多边形内的模板,不用是否在凸多边形内的模板 POJ 1584 A Round Peg in a G ...
