Tutorial: Triplet Loss Layer Design for CNN
Tutorial: Triplet Loss Layer Design for CNN
Xiao Wang 2016.05.02
Triplet Loss Layer could be a trick for further improving the accuracy of CNN. Today, I will introduce the whole process, and display the code for you. This tutorial mainly from the blog:
http://blog.csdn.net/tangwei2014/article/details/46812153
http://blog.csdn.net/tangwei2014/article/details/46788025
and the paper: <FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering>.
First, Let's talk about how to add the layer into caffe and make test this layer to check whether it works or not. And then, we will discuss the paper and introduce the process of how the triplet loss come from. In the new version of caffe framework, it mainly consists of these steps for add a new layer i.e.
step 1. add the paprameter message in the corresponding layer, which located in ./src/caffe/proto/caffe.proto ;
step 2. add the declaration information of the layer in ./include/caffe/***layers.hpp ;
step 3. add the corresponding .cpp and .cu files in ./src/caffe/layers/, realize the function of the new added layer;
step 4. add test code of new added layers in ./src/caffe/gtest/, test its foreward and back propagation and its computation speed.
Let's do it step by step.
First, we add triplet loss layer in caffe.proto file:
we could found that in line 101, it said: SolverParameter next available ID: 40 (last added: momentum2), thus we add the ID: 40 as the new added information :
message RankParameter {
optional uint32 neg_num = 1 [default = 1];
optional uint32 pair_size = 2 [default = 1];
optional float hard_ratio = 3;
optional float rand_ratio = 4;
optional float margin = 5 [default = 0.5];
}
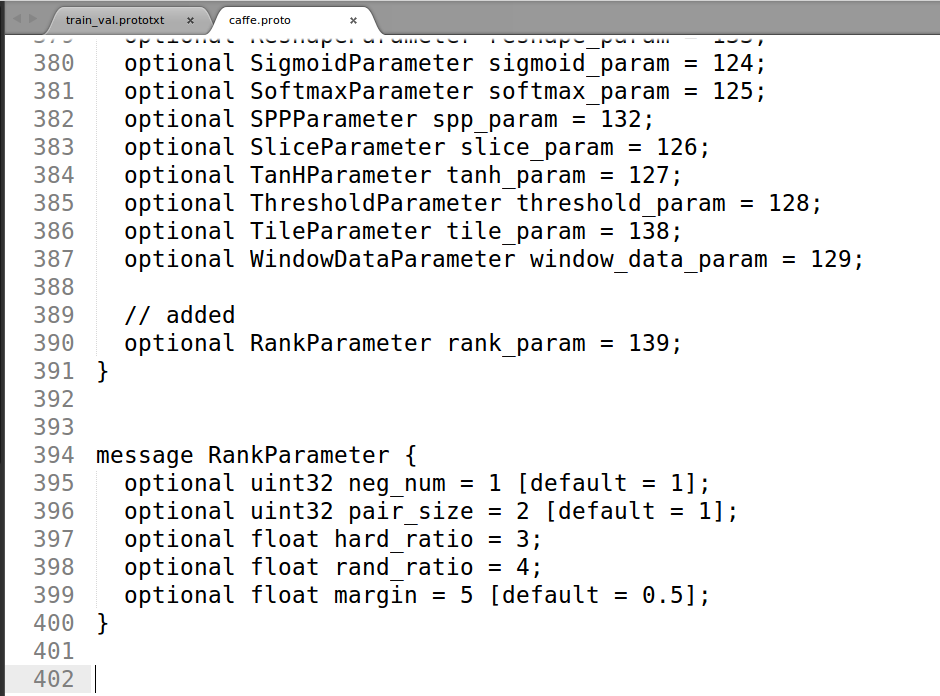
Second, we add the declearation information about triplet loss layer in ./include/caffe/TripletLoss_layers.hpp
Third, We compile the triplet loss layer of .cpp and .cu file
First of all is the .cpp file
#include <vector> #include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cfloat> #include "caffe/layer.hpp"
#include "caffe/util/io.hpp"
#include "caffe/util/math_functions.hpp"
#include "caffe/vision_layers.hpp" using std::max;
using namespace std;
using namespace cv; namespace caffe { int myrandom (int i) { return caffe_rng_rand()%i;} template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
LossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(bottom, top); diff_.ReshapeLike(*bottom[]);
dis_.Reshape(bottom[]->num(), bottom[]->num(), , );
mask_.Reshape(bottom[]->num(), bottom[]->num(), , );
} template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::set_mask(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom)
{ RankParameter rank_param = this->layer_param_.rank_param();
int neg_num = rank_param.neg_num();
int pair_size = rank_param.pair_size();
float hard_ratio = rank_param.hard_ratio();
float rand_ratio = rank_param.rand_ratio();
float margin = rank_param.margin(); int hard_num = neg_num * hard_ratio;
int rand_num = neg_num * rand_ratio; const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[]->cpu_data();
const Dtype* label = bottom[]->cpu_data();
int count = bottom[]->count();
int num = bottom[]->num();
int dim = bottom[]->count() / bottom[]->num();
Dtype* dis_data = dis_.mutable_cpu_data();
Dtype* mask_data = mask_.mutable_cpu_data(); for(int i = ; i < num * num; i ++)
{
dis_data[i] = ;
mask_data[i] = ;
} // calculate distance
for(int i = ; i < num; i ++)
{
for(int j = i + ; j < num; j ++)
{
const Dtype* fea1 = bottom_data + i * dim;
const Dtype* fea2 = bottom_data + j * dim;
Dtype ts = ;
for(int k = ; k < dim; k ++)
{
ts += (fea1[k] * fea2[k]) ;
}
dis_data[i * num + j] = -ts;
dis_data[j * num + i] = -ts;
}
} //select samples vector<pair<float, int> >negpairs;
vector<int> sid1;
vector<int> sid2; for(int i = ; i < num; i += pair_size)
{
negpairs.clear();
sid1.clear();
sid2.clear();
for(int j = ; j < num; j ++)
{
if(label[j] == label[i])
continue;
Dtype tloss = max(Dtype(), dis_data[i * num + i + ] - dis_data[i * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
if(tloss == ) continue; negpairs.push_back(make_pair(dis_data[i * num + j], j));
}
if(negpairs.size() <= neg_num)
{
for(int j = ; j < negpairs.size(); j ++)
{
int id = negpairs[j].second;
mask_data[i * num + id] = ;
}
continue;
}
sort(negpairs.begin(), negpairs.end()); for(int j = ; j < neg_num; j ++)
{
sid1.push_back(negpairs[j].second);
}
for(int j = neg_num; j < negpairs.size(); j ++)
{
sid2.push_back(negpairs[j].second);
}
std::random_shuffle(sid1.begin(), sid1.end(), myrandom);
for(int j = ; j < min(hard_num, (int)(sid1.size()) ); j ++)
{
mask_data[i * num + sid1[j]] = ;
}
for(int j = hard_num; j < sid1.size(); j++)
{
sid2.push_back(sid1[j]);
}
std::random_shuffle(sid2.begin(), sid2.end(), myrandom);
for(int j = ; j < min( rand_num, (int)(sid2.size()) ); j ++)
{
mask_data[i * num + sid2[j]] = ;
} } } template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) { const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[]->cpu_data();
const Dtype* label = bottom[]->cpu_data();
int count = bottom[]->count();
int num = bottom[]->num();
int dim = bottom[]->count() / bottom[]->num(); RankParameter rank_param = this->layer_param_.rank_param();
int neg_num = rank_param.neg_num(); //
int pair_size = rank_param.pair_size(); //
float hard_ratio = rank_param.hard_ratio();
float rand_ratio = rank_param.rand_ratio();
float margin = rank_param.margin();
Dtype* dis_data = dis_.mutable_cpu_data();
Dtype* mask_data = mask_.mutable_cpu_data(); set_mask(bottom);
Dtype loss = ;
int cnt = neg_num * num / pair_size * ; for(int i = ; i < num; i += pair_size)
{
for(int j = ; j < num; j++)
{
if(mask_data[i * num + j] == )
continue;
Dtype tloss1 = max(Dtype(), dis_data[i * num + i + ] - dis_data[i * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
Dtype tloss2 = max(Dtype(), dis_data[i * num + i + ] - dis_data[(i + ) * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
loss += tloss1 + tloss2;
}
} loss = loss / cnt;
top[]->mutable_cpu_data()[] = loss;
} template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) { const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[]->cpu_data();
const Dtype* label = bottom[]->cpu_data();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[]->mutable_cpu_diff();
int count = bottom[]->count();
int num = bottom[]->num();
int dim = bottom[]->count() / bottom[]->num(); RankParameter rank_param = this->layer_param_.rank_param();
int neg_num = rank_param.neg_num();
int pair_size = rank_param.pair_size();
float hard_ratio = rank_param.hard_ratio();
float rand_ratio = rank_param.rand_ratio();
float margin = rank_param.margin(); Dtype* dis_data = dis_.mutable_cpu_data();
Dtype* mask_data = mask_.mutable_cpu_data(); for(int i = ; i < count; i ++ )
bottom_diff[i] = ; int cnt = neg_num * num / pair_size * ; for(int i = ; i < num; i += pair_size)
{
const Dtype* fori = bottom_data + i * dim;
const Dtype* fpos = bottom_data + (i + ) * dim; Dtype* fori_diff = bottom_diff + i * dim;
Dtype* fpos_diff = bottom_diff + (i + ) * dim;
for(int j = ; j < num; j ++)
{
if(mask_data[i * num + j] == ) continue;
Dtype tloss1 = max(Dtype(), dis_data[i * num + i + ] - dis_data[i * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
Dtype tloss2 = max(Dtype(), dis_data[i * num + i + ] - dis_data[(i + ) * num + j] + Dtype(margin)); const Dtype* fneg = bottom_data + j * dim;
Dtype* fneg_diff = bottom_diff + j * dim;
if(tloss1 > )
{
for(int k = ; k < dim; k ++)
{
fori_diff[k] += (fneg[k] - fpos[k]); // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
fpos_diff[k] += -fori[k]; // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
fneg_diff[k] += fori[k];
}
}
if(tloss2 > )
{
for(int k = ; k < dim; k ++)
{
fori_diff[k] += -fpos[k]; // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
fpos_diff[k] += fneg[k]-fori[k]; // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
fneg_diff[k] += fpos[k];
}
} }
} for (int i = ; i < count; i ++)
{
bottom_diff[i] = bottom_diff[i] / cnt;
} } #ifdef CPU_ONLY
STUB_GPU(RankHardLossLayer);
#endif INSTANTIATE_CLASS(RankHardLossLayer);
REGISTER_LAYER_CLASS(RankHardLoss); } // namespace caffe
and the .cu file
#include <vector> #include "caffe/layer.hpp"
#include "caffe/util/io.hpp"
#include "caffe/util/math_functions.hpp"
#include "caffe/vision_layers.hpp" namespace caffe { template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
Forward_cpu(bottom, top);
} template <typename Dtype>
void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
Backward_cpu(top, propagate_down, bottom);
} INSTANTIATE_LAYER_GPU_FUNCS(RankHardLossLayer); } // namespace caffe
Finally, we make the caffe file and check whether have some mistakes about it.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
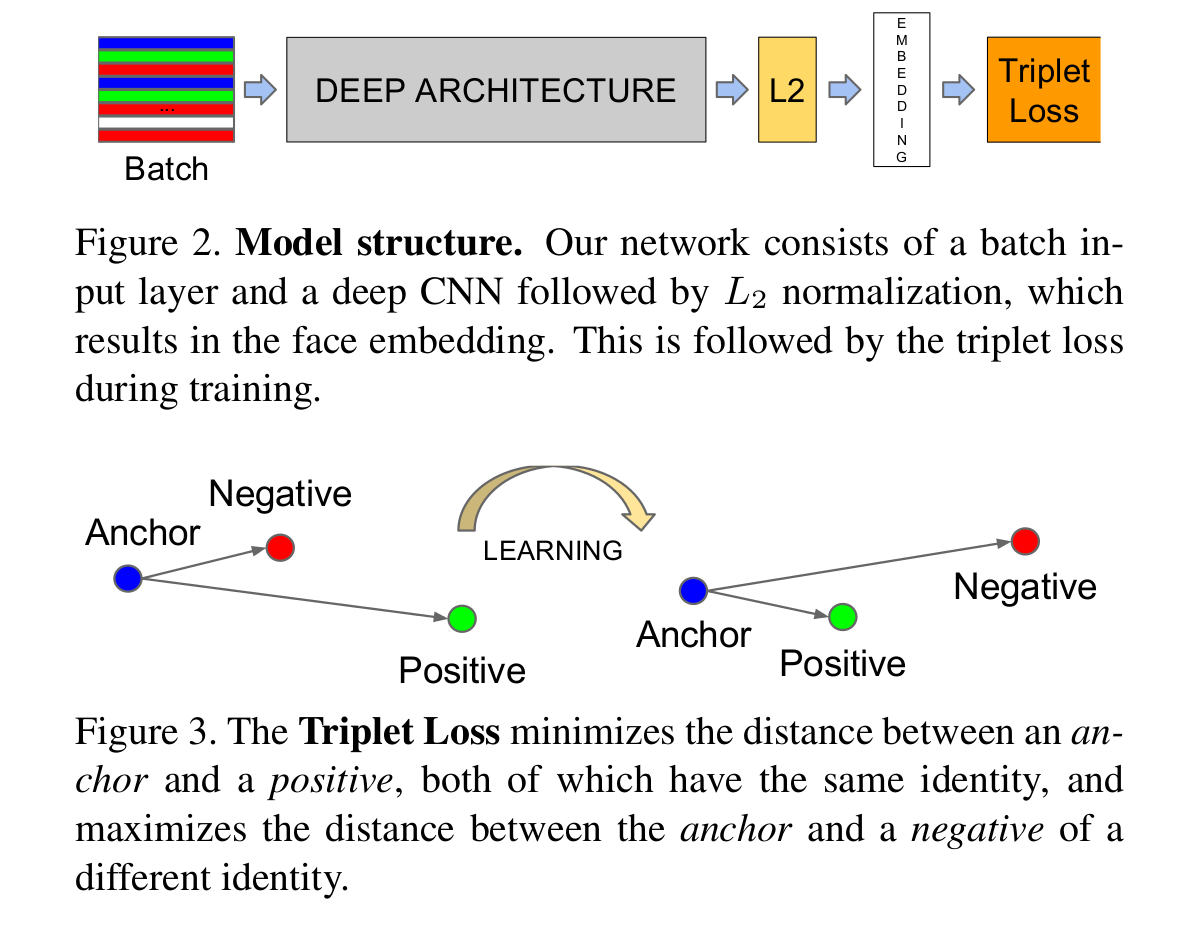
Let's continue to talk about the triplet loss:
Just like the above figure showns, the triplet loss usually have three components, i.e. the anchors, the positive, and the negative. What we are going to do is try to reduce the distance between the archor and the same, and push the different from the anchors.
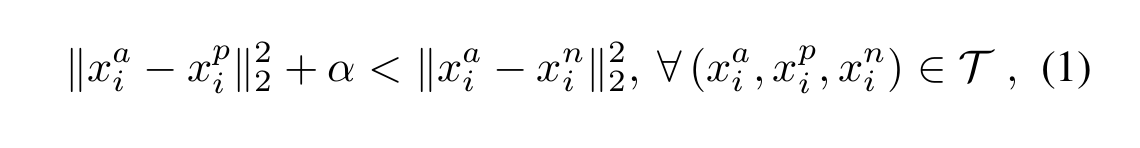
Thus, the whole loss could be described as following:
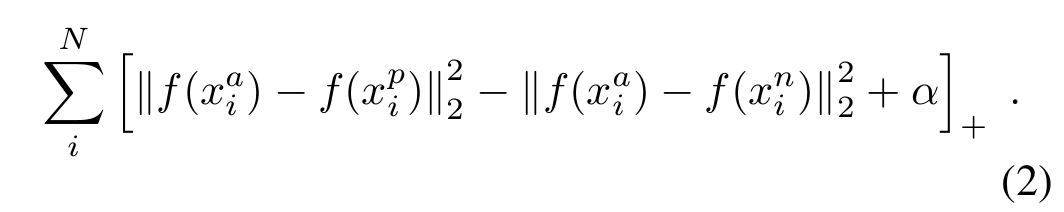
Only select triplets randomly may lead to slow converage of the network, and we need to find those hard triplets, that are active and can therefore contribute to improving the model. The following section will give you an explanination about the approach.
Triplet Selection:
There are two appproaches for generate triplets, i.e.
1. Generate triplets offline every n steps, using the most recent newwork checkpoint and computing the argmin and argmax on a subset of the data.
2. Generate the triplets online. This can be done by selecting the hard positive/negative exemplars form within a mini-batch.
This paper use all anchor-positive pairs in a mini-batch while still selecting the hard negatives. the all anchor-positive method was more stable and converaged slightly faster at the begining of training.
The code could refer the github page: https://github.com/wangxiao5791509/caffe-video_triplet
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "RankHardLoss"
rank_param{
neg_num: 4
pair_size: 2
hard_ratio: 0.5
rand_ratio: 0.5
margin: 1
}
bottom: "norml2"
bottom: "label"
}Triplet Loss Implementation using Pytorch:
the following document comes from: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#tripletmarginloss
Creates a criterion that measures the triplet loss given an input tensors x1, x2, x3 and a margin with a value greater than 0. This is used for measuring a relative similarity between samples. A triplet is composed by a, p and n: anchor, positive examples and negative example respectively. The shapes of all input tensors should be (N,D)(N,D).
The distance swap is described in detail in the paper Learning shallow convolutional feature descriptors with triplet losses by V. Balntas, E. Riba et al.
The loss function for each sample in the mini-batch is:
where d(xi,yi)=∥xi−yi∥pd(xi,yi)=‖xi−yi‖p.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
- Shape:
-
- Input: (N,D)(N,D) where D is the vector dimension.
- Output: scalar. If reduce is False, then (N).
>>> triplet_loss = nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0, p=2)
>>> input1 = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
>>> input2 = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
>>> input3 = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
>>> output = triplet_loss(input1, input2, input3)
>>> output.backward()
Example:
import torch.nn as nn
triplet_loss = nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.2, p=2)
# 计算特征向量
anchor = model.forward(data[0])
positive = model.forward(data[1])
negative = model.forward(data[2])
# 计算三元组loss
loss = triplet_loss.forward(anchor, positive, negative)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
Tutorial: Triplet Loss Layer Design for CNN的更多相关文章
- 怎样在caffe中添加layer以及caffe中triplet loss layer的实现
关于triplet loss的原理.目标函数和梯度推导在上一篇博客中已经讲过了.详细见:triplet loss原理以及梯度推导.这篇博文主要是讲caffe下实现triplet loss.编程菜鸟.假 ...
- 论文笔记之: Person Re-Identification by Multi-Channel Parts-Based CNN with Improved Triplet Loss Function
Person Re-Identification by Multi-Channel Parts-Based CNN with Improved Triplet Loss Function CVPR 2 ...
- Paper Reading: In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification
In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification 2017-07-02 14:04:20 This blog comes ...
- Re-ID with Triplet Loss
一篇讲Person Re-ID的论文,与人脸识别(认证)有非常多相通的地方. 文章链接: <In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identi ...
- triplet loss 在深度学习中主要应用在什么地方?有什么明显的优势?
作者:罗浩.ZJU链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/62486208/answer/199117070来源:知乎著作权归作者所有.商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转 ...
- Facenet Triplet Loss
Triplet Loss 在人脸识别中,Triplet loss被用来进行人脸嵌入的训练.如果你对triplet loss很陌生,可以看一下吴恩达关于这一块的课程.Triplet loss实现起来并不 ...
- triplet loss
因为待遇低,因为工作不开心,已经严重影响了自己的工作积极性和工作效率,这几天发觉这样对自己实在是一种损失,决定提高工作效率,减少工作时间. 说说最近做的tracking, multi-object t ...
- Triplet Loss(转)
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u013082989/article/details/83537370 作用:用于对差异较小的类别进行区分
- Caffe的loss layer(转)
英文可查:地址 1.SoftmaxWithLoss 对一对多的分类任务计算多项逻辑斯蒂损失,并通过softmax传递预测值,来获得各类的概率分布.该层可以分解为SoftmaxLayer+Multino ...
随机推荐
- 跨域请求之jQuery的ajax jsonp的使用解惑
前天在项目中写的一个ajax jsonp的使用,出现了问题:可以成功获得请求结果,但没有执行success方法,直接执行了error方法提示错误——ajax jsonp之前并没有用过,对其的理解为跟普 ...
- HTML--3css样式表
CSS(Cascading Style Sheet,叠层样式表),作用是美化HTML网页. /*注释区域*/ 此为注释语法 一.样式表 (一)样式表的分类 1.内联样式表 和HTML联合显示,控 ...
- 如何为Eclipse设置代理
看图,不解释:
- leetcode 229 Majority Element II
这题用到的基本算法是Boyer–Moore majority vote algorithm wiki里有示例代码 1 import java.util.*; 2 public class Majori ...
- UIImageView异步加载网络图片
在iOS开发过程中,经常会遇到使用UIImageView展现来自网络的图片的情况,最简单的做法如下: 去下载https://github.com/rs/SDWebImage放进你的工程里,加入头文件# ...
- jQuery轮播图
yii2 轮播 样式: <style type="text/css"> *{margin:0;padding:0} body{margin:50px} li{list- ...
- JS回车键处理
HTML <input type="text" id="keyword" name="keyword" autocomplete=&q ...
- How to migrate from VMware and Hyper-V to OpenStack
Introduction I migrated >120 VMware virtual machines (Linux and Windows) from VMware ESXi to Open ...
- strong和b
strong和b标签都是很久以前遗留下来的标签,b标签用来加粗字体,strong用来强调,通常浏览器会把强调的语句加粗,所以二者效果比较近似.语义化愈发受重视以后,b标签退出大众视野,strong依然 ...
- Java-->实现群聊功能(C/S模式--TCP协议)
--> Java 对TCP协议的支持: --> java.net包中定义了两个类ServerSocket 和Socket ,分别用来实现双向连接的server 端和client 端. -- ...
