google地图的url参数
Google Maps Intents for Android
The Google Maps app for Android exposes several intents that you can use to launch Google Maps in display, search, navigation, or Street View modes. If you want to embed a map in your app, please refer to the Google Maps Android API Getting Started Guide.
Note: Maps URLs let you build a universal, cross-platform URL to launch Google Maps and perform searches, get directions, display map views, and display panoramic images. It is recommended that you use the cross-platform Maps URLs to launch Google Maps, since these universal URLs allow for broader handling of the maps requests no matter which platform the user is on. You should only use the Android-specific Maps Intents for features that may only be functional on a mobile platform (for example, turn-by-turn navigation).
Overview
Intents let you start an activity in another app by describing a simple action you'd like to perform (such as "display a map" or "show directions to the airport") in an Intent object. The Google Maps app for Android supports several different intents, allowing you to launch the Google Maps app and perform one of four actions:
- Display a map at a specified location and zoom level.
- Search for locations or places, and display them on a map.
- Request directions from one location to another. Directions can be returned for three modes of transportation: driving, walking, bicycling.
- Display panorama imagery in Google Street View.
This page describes the intents that you can use with Google Maps app for Android. For more information on Intents and Intent Filters, or Intents common to the Android platform, refer to the Android developer documentation.
Intent requests
In order to launch Google Maps with an intent you must first create an Intent object, specifying its action, URI and package.
- Action: All Google Maps intents are called as a View action —
ACTION_VIEW. - URI: Google Maps intents use URI encoded strings that specify a desired action, along with some data with which to perform the action.
- Package: Calling
setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")will ensure that the Google Maps app for Android handles the Intent. If the package isn't set, the system will determine which apps can handle theIntent. If multiple apps are available, the user may be asked which app they would like to use.
After creating the Intent, you can request that the system launch the related app in a number of ways. A common method is to pass the Intent to the startActivity() method. The system will launch the necessary app — in this case Google Maps — and start the corresponding Activity.
// Create a Uri from an intent string. Use the result to create an Intent.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.streetview:cbll=46.414382,10.013988");
// Create an Intent from gmmIntentUri. Set the action to ACTION_VIEW
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
// Make the Intent explicit by setting the Google Maps package
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
// Attempt to start an activity that can handle the Intent
startActivity(mapIntent);
If the system cannot identify an app that can respond to the intent, your app may crash. For this reason, you should first verify that a receiving application is installed before you present one of these intents to a user.
To verify that an app is available to receive the intent, call resolveActivity() on your Intent object. If the result is non-null, there is at least one app that can handle the intent and it's safe to call startActivity(). If the result is null, you should not use the intent and, if possible, you should disable the feature that invokes the intent.
if (mapIntent.resolveActivity(getPackageManager()) != null) {
...
}
For example, to display a map of San Francisco, you can use the following code:
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
if (mapIntent.resolveActivity(getPackageManager()) != null) {
startActivity(mapIntent);
}
URI encoded query strings
All strings passed to the Google Maps Intents must be URI encoded. For example, the string "1st & Pike, Seattle" should become 1st%20%26%20Pike%2C%20Seattle. Spaces in the string can be encoded with %20 or replaced with the plus sign (+).
You can use the android.net.Uri parse() method to encode your strings. For example:
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4192?q=" + Uri.encode("1st & Pike, Seattle"));
Display a map
Use the geo: intent to display a map at a specified location and zoom level.
geo:latitude,longitude?z=zoom
Parameters
latitudeandlongitudeset the center point of the map.zoptionally sets the initial zoom level of the map. Accepted values range from 0 (the whole world) to 21 (individual buildings). The upper limit can vary depending on the map data available at the selected location.
Examples
// Creates an Intent that will load a map of San Francisco
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Search for a location
Use this intent to display search queries within a specified viewport. When the query has a single result, you can use this intent to display a pin at a particular place or address, such as a landmark, business, geographic feature, or town.
geo:latitude,longitude?q=query
geo:0,0?q=my+street+address
geo:0,0?q=latitude,longitude(label)
Parameters
In addition to the parameters used to display a map, Search supports the following parameters:
qdefines the place(s) to highlight on the map. Theqparameter is required for all Search requests. It accepts a location as either a place name or address. The string should be URL-escaped, so an address such as "City Hall, New York, NY" should be converted to City+Hall,New+York,NY.labellets you set a custom label at a place identified on the map. Thelabelmust be specified as a String.
Categorical search
If you pass a general search term, Google Maps will attempt to find a location near the lat/lng you specified that matches your criteria. If no location is specified, Google Maps will try to find nearby listings. For example:
// Search for restaurants nearby
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=restaurants");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
// Search for restaurants in San Francisco
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194?q=restaurants");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
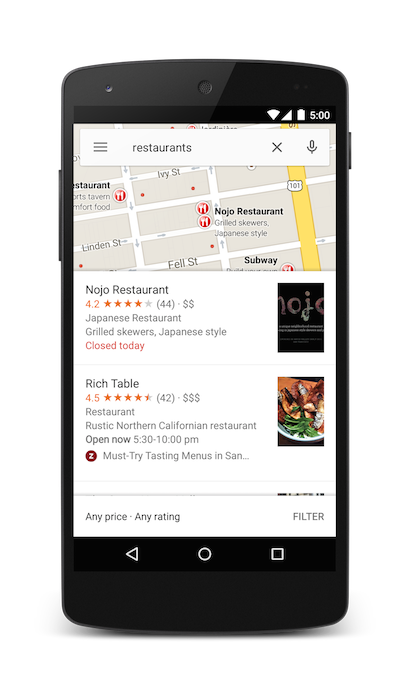
You can further bias the search results by specifying a zoom parameter along with the query string. In the below example, adding a zoom of 10 will attempt to find restaurants at a city level instead of nearby.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194?z=10&q=restaurants");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Location search
Searching for a specific address will display a pin at that location.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain+View, California");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
The above example sets a lat/lng of 0,0, but passes an address as a query string. When searching for a very specific location, the latitude and longitude are not required. However, if you do not know the exact address, you can attempt to bias the results of the search by specifying a coordinate. For example, performing an address search for 'Main Street' will return too many results.
// Searching for 'Main Street' will return too many results
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=101+main+street");
Adding a lat/lng to the intent URI will bias the results towards a particular area:
// Searches for 'Main Street' near San Francisco
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194?q=101+main+street");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
When you know your search will return a single value, you may wish to pass an optional label. Labels must be specified as a String, and will appear under the map marker. Note that labels are only available when q is specified as a lat/lng coordinate.
// Display a label at the location of Google's Sydney office
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=-33.8666,151.1957(Google+Sydney)");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
As an alternative to a street address or a latitude/longitude, you can display a pin at a known location using a plus code.
// Display the location of Google, San Francisco using a global plus code.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("http://plus.codes/849VQJQ5+XX");
// Equivalently, define the same location using a local plus code
gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("https://plus.codes/QJQ5+XX,San%20Francisco");
// Construct and use the Intent as in the examples above
Launch turn-by-turn navigation
Use this intent to launch Google Maps navigation with turn-by-turn directions to the address or coordinate specified. Directions are always given from the users current location.
google.navigation:q=a+street+address
google.navigation:q=latitude,longitude
Parameters
q: Sets the end point for navigation searches. This can be a latitude,longitude or a query formatted address. If it is a query string that returns more than one result, the first result will be selected.modesets the method of transportation. Mode is optional, defaults to driving, and can be set to one of:dfor drivingwfor walkingbfor bicycling
avoidsets features the route should try to avoid. Avoid is optional and can be set to one or more of:tfor tollshfor highwaysffor ferries
Examples
The below Intent will request turn-by-turn navigation to Taronga Zoo, in Sydney Australia:
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Taronga+Zoo,+Sydney+Australia");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
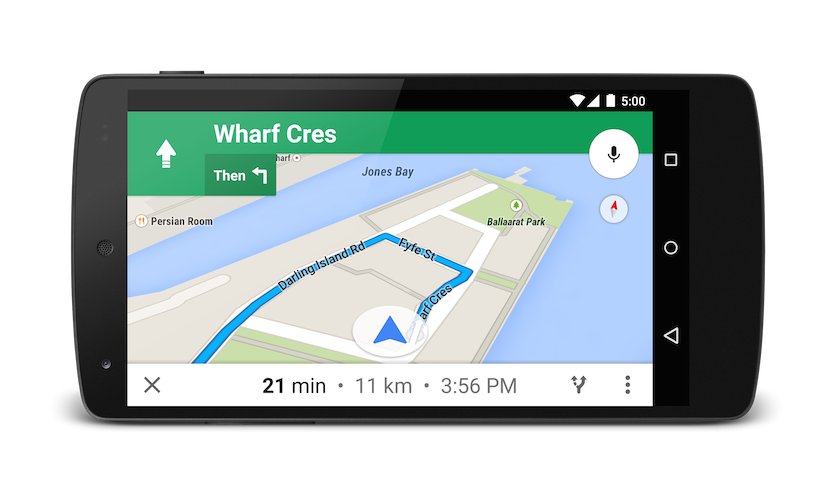
If you prefer not to pay tolls or ride a ferry, you can request routing that tries to avoid those things.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Taronga+Zoo,+Sydney+Australia&avoid=tf");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
If you'd prefer a bit of exercise, you can request bicycling directions instead.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Taronga+Zoo,+Sydney+Australia&mode=b");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Display a Street View panorama
Use the google.streetview intent to launch Google Street View. Google Street View provides panoramic views from designated locations throughout its coverage area. User contributed Photospheres, and Street View special collectionsare also available.
google.streetview:cbll=latitude,longitude&cbp=0,bearing,0,zoom,tilt
google.streetview:panoid=id&cbp=0,bearing,0,zoom,tilt
Parameters
All google.streetview URIs must include either a cbll or a panoid parameter.
cbllaccepts a latitude and a longitude as comma-separated values (46.414382,10.013988). The app will display the panorama photographed closest to this location. Because Street View imagery is periodically refreshed, and photographs may be taken from slightly different positions each time, it's possible that your location may snap to a different panorama when imagery is updated.panoidis a specific panorama ID. Google Maps will use the panorama ID if both apanoidand acbllare specified. Panorama IDs are available to an Android app from theStreetViewPanoramaLocationobject.cbpis an optional parameter that adjusts the initial orientation of the camera. Thecbpparameter takes 5 comma-separated values, all of which are optional. The most significant values are the second, fourth and fifth which set the bearing, zoom and tilt respectively. The first and third values are not supported, and should be set to0.bearing: indicates the compass heading of the camera in degrees clockwise from North. True north is 0, east is 90, south is 180, west is 270. Values passed to bearing will wrap; that is, 0°, 360° and 720° all point in the same direction. Bearing is defined as the second of five comma-separated values.zoom: Sets the zoom level of the camera. The default zoom level is set at 0. A zoom of 1 would double the magnification. The zoom is clamped between 0 and the maximum zoom level for the current panorama. This means that any value falling outside this range will be set to the closest extreme that falls within the range. For example, a value of -1 will be set to 0. Zoom is the fourth of five comma-separated values.tilt: specifies the angle, up or down, of the camera. The range is -90 through 0 to 90, with 90 looking straight down, 0 centered on the horizon, and -90 looking straight up.
Examples
Below are some examples of using the Street View intent.
// Displays an image of the Swiss Alps
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.streetview:cbll=46.414382,10.013988");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
// Uses a PanoID to show an image from Maroubra beach in Sydney, Australia
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.streetview:panoid=Iaa2JyfIggYAAAQfCZU9KQ");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
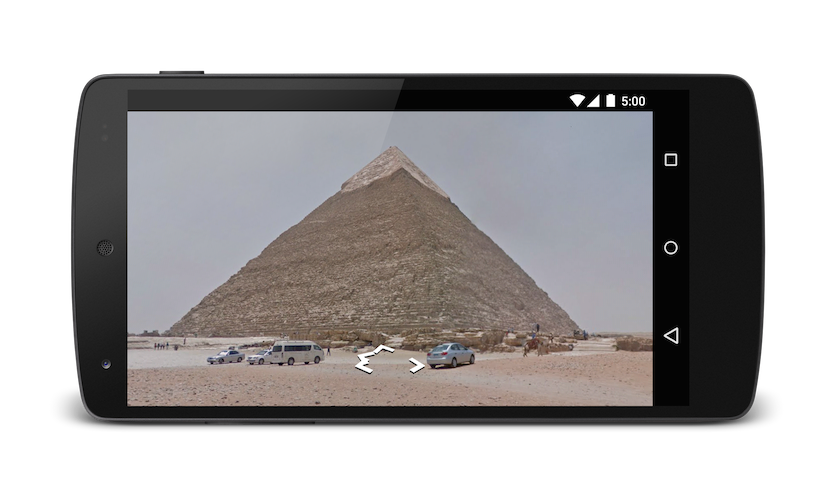
// Opens Street View between two Pyramids in Giza. The values passed to the
// cbp parameter will angle the camera slightly up, and towards the east.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.streetview:cbll=29.9774614,31.1329645&cbp=0,30,0,0,-15");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
google地图的url参数的更多相关文章
- Google 地图切片URL地址解析
一.Google地图切片的投影方式及瓦片索引机制 1.地图投影 Google地图采用的是Web墨卡托投影(如下图),为了方便忽略了两极变形较大的地区,把世界地图做成了一个边长等于赤道周长的正方形(赤道 ...
- JavaScript一个google地图获取
<script type="text/javascript"> /** * 返回一个新创建的<img>元素,该元素用于在获取到地理位置信息后,显示一张Goo ...
- 如何使用google地图的api(整理)
如何使用google地图的api(整理) 一.总结 一句话总结:直接用script标签引google地图api即可. 1.如何使用google地图的api? 页面引用javascript文件<s ...
- Blazor组件自做五 : 使用JS隔离封装Google地图
Blazor组件自做五: 使用JS隔离封装Google地图 运行截图 演示地址 正式开始 1. 谷歌地图API 谷歌开发文档 开始学习 Maps JavaScript API 的最简单方法是查看一个简 ...
- Google地图开发总结
我们经常使用地图查位置.看公交.看街景,同时地图还开放第三方的API给开发者.利用这些API进行地图的个性化的展示和控制,例如北京被水淹了,开发一个网页显示北京被淹的地图,地图上面标志被水淹的位置.严 ...
- Google 地图 API V3 使用入门
Google官方教程: Google 地图 API V3 使用入门 Google 地图 API V3 针对移动设备进行开发 Google 地图 API V3 之事件 Google 地图 API V3 ...
- Google 地图 API V3 针对移动设备进行开发
Google官方教程: Google 地图 API V3 使用入门 Google 地图 API V3 针对移动设备进行开发 Google 地图 API V3 之事件 Google 地图 API V3 ...
- Google 地图 API V3 之事件
Google官方教程: Google 地图 API V3 使用入门 Google 地图 API V3 针对移动设备进行开发 Google 地图 API V3 之事件 Google 地图 API V3 ...
- Google 地图 API V3 之 叠加层
Google官方教程: Google 地图 API V3 使用入门 Google 地图 API V3 针对移动设备进行开发 Google 地图 API V3 之事件 Google 地图 API V3 ...
随机推荐
- hexo d 报错‘fatal: could not read Username for 'https://github.com': No error’
问题描述 今天早上,一如往常的往在github上创建的hexo博客上传文章,结果报错 'fatal: could not read Username for 'https://github.com': ...
- 【跨域】jsonp跨域实现方法
封装原生jsonp: 以跨域调取豆瓣电影最热榜单为例: function $jsonp(url,data,callback){ var funcName = 'jsonp_cb' + Math.ran ...
- 深入理解ajax系列第六篇——头部信息
前面的话 每个HTTP请求和响应都会带有相应的头部信息,其中有的对开发人员有用.XHR对象提供了操作头部信息的方法.本文将详细介绍HTTP的头部信息 默认信息 默认情况下,在发送XHR请求的同时,还会 ...
- P2704 [NOI2001]炮兵阵地
题目描述 司令部的将军们打算在N*M的网格地图上部署他们的炮兵部队.一个N*M的地图由N行M列组成,地图的每一格可能是山地(用“H” 表示),也可能是平原(用“P”表示),如下图.在每一格平原地形上最 ...
- Tyvj1038 忠诚 (线段树)
[Tyvj1038]忠诚 线段树 题目描述 老管家是一个聪明能干的人.他为财主工作了整整10年,财主为了让自已账目更加清楚.要求管家每天记k次账,由于管家聪明能干,因而管家总是让财主十分满意.但是 ...
- 洛谷P3703 [SDOI2017]树点涂色(LCT,dfn序,线段树,倍增LCA)
洛谷题目传送门 闲话 这是所有LCT题目中的一个异类. 之所以认为是LCT题目,是因为本题思路的瓶颈就在于如何去维护同颜色的点的集合. 只不过做着做着,感觉后来的思路(dfn序,线段树,LCA)似乎要 ...
- sql server 小技巧(6) Cannot resolve the collation conflict between "Latin1_General_CI_AI" and "Chinese_PRC_CI_AS" in the equal to operation
今天查询二个db,出现这个错误,二种方法,一种是把db里的collation改成一样的:如果不方便可以直接在sql语句后面转一下: select * from table where crm_mscr ...
- 【bzoj2877】 Noi2012—魔幻棋盘
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2877 (题目链接) 题意 一个${n*m}$的矩阵,维护两个操作:给任意子矩阵${+val}$:问某 ...
- windows2008设置IIS服务器定时自动重启的方法
我们在使用windows2008下IIS服务器时会经常出现资源耗尽的现象,运行一段时间下来就会出现访问服务器上的网站时提示数据库连接出错,重启IIS后网站又能正常访问了,这个问题可能困扰了很多站长朋友 ...
- linux中awk工具的使用(转载)
awk是一个非常好用的数据处理工具.相较于sed常常一整行处理,awk则比较倾向于一行当中分成数个“字段”处理,awk处理方式如下: $ awk '条件类型1{动作1} 条件类型2{动作2} ...' ...
