Booksort POJ - 3460 (IDA*)
Description
The Leiden University Library has millions of books. When a student wants to borrow a certain book, he usually submits an online loan form. If the book is available, then the next day the student can go and get it at the loan counter. This is the modern way of borrowing books at the library.
There is one department in the library, full of bookcases, where still the old way of borrowing is in use. Students can simply walk around there, pick out the books they like and, after registration, take them home for at most three weeks.
Quite often, however, it happens that a student takes a book from the shelf, takes a closer look at it, decides that he does not want to read it, and puts it back. Unfortunately, not all students are very careful with this last step. Although each book has a unique identification code, by which the books are sorted in the bookcase, some students put back the books they have considered at the wrong place. They do put it back onto the right shelf. However, not at the right position on the shelf.
Other students use the unique identification code (which they can find in an online catalogue) to find the books they want to borrow. For them, it is important that the books are really sorted on this code. Also for the librarian, it is important that the books are sorted. It makes it much easier to check if perhaps some books are stolen: not borrowed, but yet missing.
Therefore, every week, the librarian makes a round through the department and sorts the books on every shelf. Sorting one shelf is doable, but still quite some work. The librarian has considered several algorithms for it, and decided that the easiest way for him to sort the books on a shelf, is by sorting by transpositions: as long as the books are not sorted,
- take out a block of books (a number of books standing next to each other),
- shift another block of books from the left or the right of the resulting ‘hole’, into this hole,
- and put back the first block of books into the hole left open by the second block.
One such sequence of steps is called a transposition.
The following picture may clarify the steps of the algorithm, where X denotes the first block of books, and Y denotes the second block.
| Original situation: |  |
| After step 1: |  |
| After step 2: |  |
| After step 3: |  |
Of course, the librarian wants to minimize the work he has to do. That is, for every bookshelf, he wants to minimize the number of transpositions he must carry out to sort the books. In particular, he wants to know if the books on the shelf can be sorted by at most 4 transpositions. Can you tell him?
Input
The first line of the input file contains a single number: the number of test cases to follow. Each test case has the following format:
- One line with one integer n with 1 ≤ n ≤ 15: the number of books on a certain shelf.
- One line with the n integers 1, 2, …, n in some order, separated by single spaces: the unique identification codes of the n books in their current order on the shelf.
Output
For every test case in the input file, the output should contain a single line, containing:
- if the minimal number of transpositions to sort the books on their unique identification codes (in increasing order) is T ≤ 4, then this minimal number T;
- if at least 5 transpositions are needed to sort the books, then the message "5 or more".
Sample Input
3
6
1 3 4 6 2 5
5
5 4 3 2 1
10
6 8 5 3 4 7 2 9 1 10
Sample Output
2
3
5 or more
题意:给n本书,每次可以选取其中一段移动到另外的位置,使得书的编号变成1~n,如果步数超过4,就输出5 or more,反则输出步数。
思路:抽取书同一长度的书,有n-len+1种选择,有n-len个位置可以插入,并且因为一位置len长度后移等于后面位置前移
Σ(n-len)*(n-len+1)/2 <= (15*14+14*13+...+2*1)/2 == 560 ,因为只用判断是否步数<=4,不同搜索(560)4,时间复杂度过大。
通过IDA*(迭代加深+A*)
迭代加深:因为我们确定答案会在5之前收到
A*:评估函数,因为一次移动,最多可以使得3本书后面的书籍编号改变,所以该状态到达终态的至少步数f = ⌈错误后继/3⌉
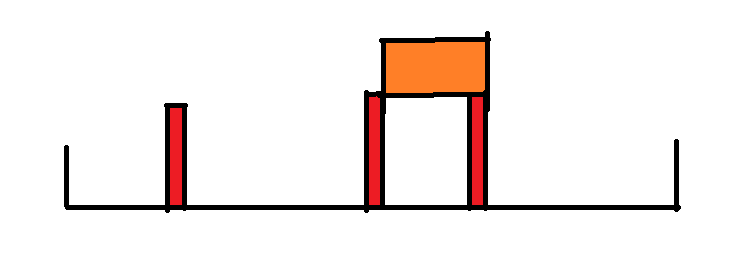
(红色为三本书,是一次移动种最多改变的三本,橙色区域代表移动的区域,移动至第一个红色书的后面,那么第二个和第三个红色书的后继都改变了)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath> using namespace std; const int maxn = ;
int t;
int n; struct Node
{
int s[maxn];
}; bool check(int s[])
{
for(int i=; i<n; i++)
if(s[i] + != s[i+])
return ;
return ;
} Node change(Node x,int l,int r,int len)
{
Node tmp = x;
for(int i=l; i<l+len; i++)
x.s[r-len-l+i+] = tmp.s[i];
for(int i=l+len; i<=r; i++)
x.s[i-len] = tmp.s[i];
return x;
} int cal(int s[])
{
int ans = ;
for(int i=; i<n; i++)
if(s[i] + != s[i+])
ans++;
return ceil(ans/3.0);
} bool dfs(Node x,int now,int lim)
{
if(now + cal(x.s) > lim)
return ;
if(check(x.s))return ;
for(int len=; len<n; len++)
{
for(int i=; i+len- <=n; i++)
{
for(int j=i+len; j<=n; j++)
{
if(dfs(change(x,i,j,len),now+,lim))return ;
}
}
}
return ;
} int main()
{
scanf("%d",&t);
Node start;
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
scanf("%d",&start.s[i]);
for(int i=; i<; i++)
{
if(dfs(start,,i))
{
printf("%d\n",i);
break;
}
else if(i == )printf("5 or more\n"); }
}
}
Booksort POJ - 3460 (IDA*)的更多相关文章
- POJ题目(转)
http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/07/29/2120667.html 初期:一.基本算法: (1)枚举. (poj1753,poj29 ...
- Repeater POJ - 3768 (分形)
Repeater POJ - 3768 Harmony is indispensible in our daily life and no one can live without it----may ...
- UVA - 10384 The Wall Pusher(推门游戏)(IDA*)
题意:从起点出发,可向东南西北4个方向走,如果前面没有墙则可走:如果前面只有一堵墙,则可将墙向前推一格,其余情况不可推动,且不能推动游戏区域边界上的墙.问走出迷宫的最少步数,输出任意一个移动序列. 分 ...
- Radar Installation POJ - 1328(贪心)
Assume the coasting is an infinite straight line. Land is in one side of coasting, sea in the other. ...
- Best Cow Fences POJ - 2018 (二分)
Farmer John's farm consists of a long row of N (1 <= N <= 100,000)fields. Each field contains ...
- E - The Balance POJ - 2142 (欧几里德)
题意:有两种砝码m1, m2和一个物体G,m1的个数x1, m2的个数为x2, 问令x1+x2最小,并且将天平保持平衡 !输出 x1 和 x2 题解:这是欧几里德拓展的一个应用,欧几里德求不定方程 ...
- 人类即将进入互联网梦境时代(IDA)
在电影<盗梦空间>中,男主角科布和妻子在梦境中生活了50年,从楼宇.商铺.到河流浅滩.一草一木.这两位造梦师用意念建造了属于自己的梦境空间.你或许并不会想到,在不久未来,这看似科幻的情节将 ...
- POJ - 2286 - The Rotation Game (IDA*)
IDA*算法,即迭代加深的A*算法.实际上就是迭代加深+DFS+估价函数 题目传送:The Rotation Game AC代码: #include <map> #include < ...
- POJ3460 Booksort(IDA*)
POJ3460 Booksort 题意:给定一个长度为n的序列,每次可以取出其中的一段数,插入任意一个位置,问最少需要几次操作才能使整个序列变为1~n 思路:IDA*+迭代加深搜索 小技巧:将一段数插 ...
随机推荐
- Confluence 6 启用远程 API
XML-RPC 和 SOAP 远程 API 从 Confluence 5.5 开始已经废弃了.我们推荐你使用完全支持的Confluence Server REST API. 希望启用 XML-RPC ...
- Confluence 6 影响语言的其他设置
一个独立的用户可以在 Confluence 中选择应用到界面文字和消息中的语言.请注意,支持的语言类型基于在 Confluence 中安装的语言包. 你登录使用 Confluence 回话的语言基于下 ...
- 将Maven项目打包成可执行jar文件(引用第三方jar)
方法一. mvn assembly 或 mvn package (一个jar包) 把依赖包和自己项目的文件打包如同一个jar包(这种方式对spring的项目不支持) <build> ...
- 【git】提交代码到远程仓库
看完不用,就是一个字:忘! 之前学了两天git结果今天要用的时候,啥也想不起来.... 场景: 已有远程仓库: git@192.168.1.1:test/test.git 要提交代码到远程仓库的新分支 ...
- Java 并发类
java.util.concurrent包里 提供了一批线程安全的类 一. java.util.concurrent.atomic java.util.concurrent.atomic包里的原子处理 ...
- java常用实用类
1.String类概念 java程序中默认导入java.lang包的,像java.lang.String等String类属于final类,用户不能扩展String类,String 类没有子类.Stri ...
- Python函数之递归函数
递归函数的定义:在这个函数里再调用这个函数本身 最大递归深度默认是997或者998,python从内存角度做的限制 优点:代码变简单 缺点:占内存 一:推导年龄 问a的值是多少: a 比 b 小2,b ...
- Python杂写1
一:编程及编程语言介绍 编程的目的:人把自己的思想流程表达出来,让计算机按照这种思想去做事,把人给解放出来. 编程语言:简单的说就是一种语言,是人和计算机沟通的语言. 编程:例如Python,利用Py ...
- 使用Docker方式运行Mysql(MariaDB)
两者差不多.我使用的是MariaDB. 下面的docker命令,挂了数据,配置,映射了端口,指定了root密码,服务端编码. 蛮快的! docker run \ --name mariadb \ -v ...
- Node 杂技
1.关于require 当文件夹a中含有index.js时,在b.js中如果有require("文件夹a的路径"),则将会自动执行index.js的语句
