hdu 2489(状态压缩+最小生成树)
Minimal Ratio Tree
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3899 Accepted Submission(s): 1196
Given
a complete graph of n nodes with all nodes and edges weighted, your
task is to find a tree, which is a sub-graph of the original graph, with
m nodes and whose ratio is the smallest among all the trees of m nodes
in the graph.
contains multiple test cases. The first line of each test case contains
two integers n (2<=n<=15) and m (2<=m<=n), which stands for
the number of nodes in the graph and the number of nodes in the minimal
ratio tree. Two zeros end the input. The next line contains n numbers
which stand for the weight of each node. The following n lines contain a
diagonally symmetrical n×n connectivity matrix with each element shows
the weight of the edge connecting one node with another. Of course, the
diagonal will be all 0, since there is no edge connecting a node with
itself.
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except
for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix) are integers and in the
range of [1, 100].
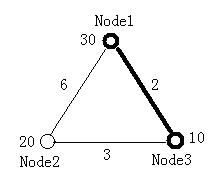
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form the minimal ratio tree.
each test case output one line contains a sequence of the m nodes which
constructs the minimal ratio tree. Nodes should be arranged in
ascending order. If there are several such sequences, pick the one which
has the smallest node number; if there's a tie, look at the second
smallest node number, etc. Please note that the nodes are numbered from 1
.
30 20 10
0 6 2
6 0 3
2 3 0
2 2
1 1
0 2
2 0
0 0
1 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = ;
const int INF = ;
int graph[N][N];
int weight[N];
int state[<<N];
int a[N],result[N];;
int n,m;
int vis[N],low[N];
void input(){
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&weight[i]);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=;j<=n;j++){
scanf("%d",&graph[i][j]);
}
}
}
bool check(int num){
int cnt =;
while(num){
if(num&) cnt++;
num = num>>;
}
if(cnt==m) return true;
return false;
}
void init(int &k){
for(int i=;i<(<<n);i++){
if(check(i)) state[k++]=i;
}
k--;
}
int prim(int n,int pos){
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
low[a[i]] = graph[pos][a[i]];
}
vis[pos] = true;
int cost = ;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
int Min = INF;
for(int j=;j<n;j++){
if(!vis[a[j]]&&low[a[j]]<Min){
pos = a[j];
Min = low[a[j]];
}
}
vis[pos] = true;
cost +=Min;
for(int j=;j<n;j++){
if(!vis[a[j]]&&low[a[j]]>graph[pos][a[j]]) low[a[j]] = graph[pos][a[j]];
}
}
return cost;
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF,n+m){
int k=;
init(k);
int min_id=N;
double _ratio = INF*1.0;
input(); for(int i=;i<=k;i++){
int num = state[i];
int t =,V=;
for(int j=;j<n;j++){
if((num>>j)&){ ///这里代表第j+1个点要选进去
a[t++] = j+;
V += weight[j+];
}
}
int cost = prim(t,a[]);
double temp1 = cost*1.0/V;
if(temp1<_ratio){
_ratio = temp1;
for(int i=;i<t;i++) result[i] = a[i];
}
}
for(int i=;i<m-;i++){
printf("%d ",result[i]);
}
printf("%d\n",result[m-]);
}
}
hdu 2489(状态压缩+最小生成树)的更多相关文章
- HDU 1074 (状态压缩DP)
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1074 题目大意:有N个作业(N<=15),每个作业需耗时,有一个截止期限.超期多少天就要扣多少 ...
- hdu 4739(状态压缩)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4739 思路:状态压缩. #include<iostream> #include<cs ...
- HDU 3341 状态压缩DP+AC自动机
题目大意: 调整基因的顺序,希望使得最后得到的基因包含有最多的匹配串基因,使得所能达到的智商最高 这里很明显要用状态压缩当前AC自动机上点使用了基因的情况所能达到的最优状态 我最开始对于状态的保存是, ...
- hdu 2167(状态压缩基础题)
题意:给你一个矩阵,让你在矩阵中找一些元素使它们加起来和最大,但是当你使用某一个元素时,那么这个元素周围的其它八个元素都不能取! 分析:这是一道比较基础的状态压缩题,也是我做的第三道状态压缩的题,但是 ...
- hdu 1565(状态压缩基础题)
题意:容易理解. 分析:这是我做的状态压缩第二题,一开始超内存了,因为数组开大了,后来超时了,因为能够成立的状态就那么多,所以你应该先把它抽出来!!总的来说还是比较简单的!! 代码实现: #inclu ...
- HDU 2553 状态压缩
N皇后问题 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
- hdu 3006(状态压缩)
The Number of set Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others ...
- hdu 4033 状态压缩枚举
/* 看别人的的思路 搜索搜不出来我太挫了 状态压缩枚举+好的位置 */ #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #define N 20 i ...
- hdu 2489(枚举 + 最小生成树)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2489 思路:由于N, M的范围比较少,直接枚举所有的可能情况,然后求MST判断即可. #include ...
随机推荐
- Eclipse 创建 Java 接口---Eclipse教程第11课
打开新建 Java 接口向导 新建 Java 接口向导可以创建新的 Java 接口.打开向导的方式有: 点击 File 菜单并选择 New > Interface 在 Package Explo ...
- Python 字符串换行的几种方式
第一种: x0 = '<?xml version="1.0"?>' \ '<ol>' \ ' <li><a href="/pyt ...
- linux->centos7设置tomcat开机自启
找到/etc/rc.d/文件下的rc.local,添加如下内容 export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_144export JRE_HOME=$JAVA_HOME/j ...
- mybatis批量添加、批量删除
<!-- 批量添加 --> <insert id="insertNameListSynHisBatch" parameterType="java.uti ...
- 牛客网暑期ACM多校训练营(第一场):J-Different Integers(分开区间不同数+树状数组)
链接:J-Different Integers 题意:给出序列a1, a2, ..., an和区间(l1, r1), (l2, r2), ..., (lq, rq),对每个区间求集合{a1, a2, ...
- JAVA相似算法的运用
今天要处理问题是把一个产品的名字按照其内容对比文档转换出它的中文名. 但是这个文档感觉不全,产品种类有多又杂. 如果像这样写的话 if(xxx.contains()) else if() ... 不知 ...
- docker 踩坑笔记之 psql: could not connect to server
最近在用docker跑rails,也遇到了一些坑,这里记录一下. 首先build项目: docker-compose build 然后就开始报错了: psql: could not connect t ...
- .Net MVC断点进不去
.Net MVC断点进不去 1.httpget httppost 2.启动项设为UI 3.基于页面没错误的情况下
- hdu 2141 Can you find it? (二分法)
Can you find it? Time Limit: 10000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/10000 K (Java/Others ...
- web项目报outmemory错误解决方案
因为数据问题内存不够出现错误,将参数加入到eclipse的run的配置文件中: