C++11学习之share_ptr和weak_ptr
一、shared_ptr学习
1.shared_ptr和weak_ptr 基础概念
- shared_ptr与weak_ptr智能指针均是C++ RAII的一种应用,可用于动态资源管理
- shared_ptr基于“引用计数”模型实现,多个shared_ptr可指向同一个动态对象,并维护了一个共享的引用计数器,记录了引用同一对象的shared_ptr实例的数量。当最后一个指向动态对象的shared_ptr销毁时,会自动销毁其所指对象(通过delete操作符)。
- shared_ptr的默认能力是管理动态内存,但支持自定义的Deleter以实现个性化的资源释放动作。
- weak_ptr用于解决“引用计数”模型循环依赖问题,weak_ptr指向一个对象,并不增减该对象的引用计数器
2.shared_ptr的基本操作
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
struct Foo {
Foo() { std::cout << "Foo...\n"; }
~Foo() { std::cout << "~Foo...\n"; }
};
struct D {
//删除p所指向的Foo对象
void operator()(Foo* p) const {
std::cout << "Call delete for Foo object...\n";
delete p;
}
};
int main()
{
// constructor with no managed object
std::shared_ptr<Foo> sh1;
// constructor with object
std::shared_ptr<Foo> sh2(new Foo);
std::shared_ptr<Foo> sh3(sh2);
std::cout << sh2.use_count() << '\n';
std::cout << sh3.use_count() << '\n';
//constructor with object and deleter
std::shared_ptr<Foo> sh4(new Foo, D());
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
构造方法:
1.通过make_shared函数构造
auto s_s = make_shared(“hello”);
2.通过原生指针构造
int* pNode = new int(5);
shared_ptr s_int(pNode);
//获取原生指针
int* pOrg = s_int.get();
3.通过赋值函数构造shared_ptr
4.重载的operator->, operator *,以及其他辅助操作如unique()、use_count(), get()等成员方法。
3 实验智能指针引用计数,增加和减少的规律
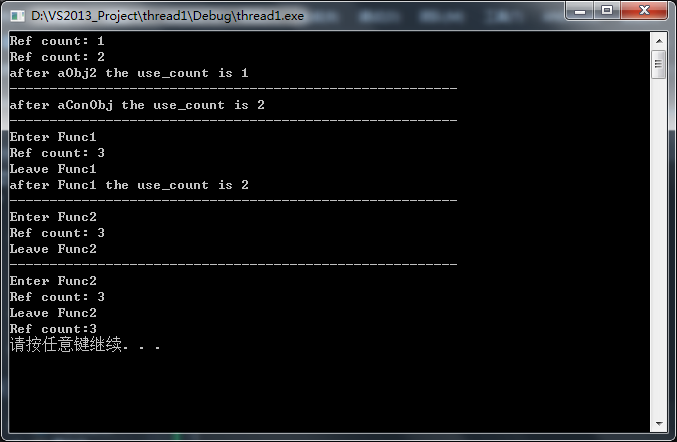
实验的主要内容有:
1.shared_ptr变量在生命周期中销毁后,引用计数是否减1?
2.shared_ptr作为函数参数,分为传值和传引用,引用计数如何变化?
2.函数返回值为shared_ptr类型时,引用计数是否会变化?
带着这几个问题,我们来看下代码.
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
void Func1(shared_ptr<int> a)
{
cout<<"Enter Func1"<<endl;
cout<<"Ref count: "<<a.use_count()<<endl;
cout<<"Leave Func1"<<endl;
}
shared_ptr<int> Func2(shared_ptr<int>& a)
{
cout<<"Enter Func2"<<endl;
cout<<"Ref count: "<<a.use_count()<<endl;
cout<<"Leave Func2"<<endl;
return a;
}
int main()
{
//构造一个指向int类型对象的指针aObj1,引用计数+1
shared_ptr<int> aObj1(new int(10));
cout<<"Ref count: "<<aObj1.use_count()<<endl;
{
//同aObj1,不过由于生存周期在括号内,所以aObj2会被销毁
shared_ptr<int> aObj2 = aObj1;
cout<<"Ref count: "<<aObj2.use_count()<<endl;//引用计数-1
}
//在调用函数时,参数为shared_ptr类型,参数为传值类型,智能指针引用计数+1
Func1(aObj1);
//在调用函数时,参数为shared_ptr类型,参数为传引用类型,智能指针引用计数不变
Func2(aObj1);
shared_ptr<int> aObj3 = Func2(aObj1);//引用计数+1
cout<<"Ref count:"<<aObj3.use_count()<<endl;
return 0;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
运行结果如下:
有效的掌握好智能指针的引用计数的变化规律,才能把程序写的更好.
4. shared_ptr的应用场景以及使用注意事项
4.1 对象之间“共享数据”,对象创建与销毁“分离”
4.2 放入容器中的动态对象,使用shared_ptr包装,比unique_ptr更合适
4.3 管理“动态数组”时,需要制定Deleter以使用delete[]操作符销毁内存,因为shared_ptr并没有针对数组的特化版本(unique_ptr有针对数组的特化版本)
5.shared_ptr的线程安全问题
- 同一个shared_ptr被多个线程读,是线程安全的;
- 同一个shared_ptr被多个线程写,不是 线程安全的;
- 共享引用计数的不同的shared_ptr被多个线程写,是线程安全的。
对于第三点,我们一般采用:
对于线程中传入的外部shared_ptr对象,在线程内部进行一次新的构造,例如: sharedptr AObjTmp = outerSharedptrObj;
二、weak_ptr学习
我们先搞清楚,weak_ptr为什么出现,或者说它是为了解决什么问题而存在的(存在即合理),哈哈
class Parent
{
public:
shared_ptr<Child> child;
};
class Child
{
public:
shared_ptr<Parent> parent;
};
shared_ptr<Parent> pA(new Parent);
shared_ptr<Child> pB(new Child);
pA->child = pB;
pB->parent = pA;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
在Parent类中存储了指向Child类对象的智能指针成员变量,而在Child类中也存储了指向Parent类对象的智能指针成员变量,如此就会造成环形引用,这个成因在C++中很好解释.
要解决环形引用的问题,没有特别好的办法,一般都是在可能出现环形引用的地方使用weak_ptr来代替shared_ptr。说到了weak_ptr,那下面就接着总结weak_ptr吧。
下面我们来一起学习下weak_ptr这个东东
weak_ptr指向shared_ptr指针指向的对象的内存,却并不拥有该内存。
但是,使用weak_ptr成员lock,则可返回其指向内存的一个shared_ptr对象,且在所指对象内存已经无效时,返回指针空值(nullptr)。由于weak_ptr是指向shared_ptr所指向的内存的,所以,weak_ptr并不能独立存在。
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
void Check(weak_ptr<int> &wp)
{
shared_ptr<int> sp = wp.lock(); // 重新获得shared_ptr对象
if (sp != nullptr)
{
cout << "The value is " << *sp << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Pointer is invalid." << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
shared_ptr<int> sp1(new int(10));
shared_ptr<int> sp2 = sp1;
weak_ptr<int> wp = sp1; // 指向sp1所指向的内存
cout << *sp1 << endl;
cout << *sp2 << endl;
Check(wp);
sp1.reset();
cout << *sp2 << endl;
Check(wp);
sp2.reset();
Check(wp);
system("pause");
return 0;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
学习编程最好的方式就是一步步的跟踪去调试.
借鉴上面的代码,我们在使用weak_ptr时也要当心,时刻需要判断weak_ptr对应的shared_ptr是否为空,weak_ptr并不会增加shared_ptr的引用计数.
另附一篇地址,讲解为何不同的shared_ptr对象可以被多线程同时修改(即使这些shared_ptr对象管理着同一个对象的指针)
https://blog.csdn.net/jiangfuqiang/article/details/8292906
C++11学习之share_ptr和weak_ptr的更多相关文章
- C++11智能指针 share_ptr,unique_ptr,weak_ptr用法
0x01 智能指针简介 所谓智能指针(smart pointer)就是智能/自动化的管理指针所指向的动态资源的释放.它是存储指向动态分配(堆)对象指针的类,用于生存期控制,能够确保自动正确的销毁动 ...
- C++11 学习笔记 std::function和bind绑定器
C++11 学习笔记 std::function和bind绑定器 一.std::function C++中的可调用对象虽然具有比较统一操作形式(除了类成员指针之外,都是后面加括号进行调用),但定义方法 ...
- C++11学习笔记
C++11 1.long long新类型 2.列表初始化 int t=0; int t={0}; int t(0); int t{0}; 注意:如果我们使用列表初始化有丢失信息的风险,则编译器报错 l ...
- C++ 11 学习1:类型自动推导 auto和decltype
Cocos 3.x 用了大量的C++ 11 的东西,所以作为一个C++忠实粉丝,有必要对C++ 11进行一个系统的学习. 使用C++11之前,一定要注意自己使用的编译器对C++11的支持情况,有些编译 ...
- C++ 11 创建和使用共享 weak_ptr
1.为什么需要weak_ptr? 在正式介绍weak_ptr之前,我们先来回忆一下shared_ptr的一些知识.我们知道shared_ptr是采用引用计数的智能指针,多个shared_ptr实例可以 ...
- C++11学习
转自: https://www.cnblogs.com/llguanli/p/8732481.html Boost教程: http://zh.highscore.de/cpp/boost/ 本章目的: ...
- Linux0.11学习
Linux 0.11虽然不是什么“珠穆朗玛峰”,但它肯定还是“华山”或“泰山”.虽然有路但你还是需要最基本的努力和花费一定的代价才能“攀登”上去.1. PC兼容机硬件工作原理(比如8259A,8253 ...
- C++ 11学习和掌握 ——《深入理解C++ 11:C++11新特性解析和应用》读书笔记(一)
因为偶然的机会,在图书馆看到<深入理解C++ 11:C++11新特性解析和应用>这本书,大致扫下,受益匪浅,就果断借出来,对于其中的部分内容进行详读并亲自编程测试相关代码,也就有了整理写出 ...
- C++ 11学习(1):lambda表达式
转载请注明,来自:http://blog.csdn.net/skymanwu #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include &l ...
随机推荐
- springboot项目更改代码后实时刷新问题
在spring boot使用的过程中, 发现我修改了静态文件, 前台刷新后, 没有任何变化, 必须重新启动, 才能看到, 这简直不能让人接受. 那有什么方法来解决这个问题呢. Baidu之后, 得到了 ...
- Java中子类覆盖父类方法所必须满足的条件
因为太喜欢,所以转来,侵删! 参考自:http://www.it165.net/pro/html/201504/39284.html 一.描述 子类重写(覆盖)父类的方法必须满足的条件:1.父类中的方 ...
- Go语言备忘录(1):基本数据结构
本文内容是本人对Go语言的变量.常量.数组.切片.映射.结构体的备忘录,记录了关键的相关知识点,以供翻查. 文中如有错误的地方请大家指出,以免误导!转摘本文也请注明出处:Go语言备忘录(1):基本数据 ...
- JavaScript中Undefined 和 Null的区别
Undefined 这个值表示变量不含有值. 可以通过将变量的值设置为 null 来清空变量. 例如: <script> var person; var car="Volvo&q ...
- Map.Entry遍历集合中的元素
Entry是Map中的一个内部累,map.entrySet()可以得到key和value的视图给你一个比较简单的小事例public static void main(String[] args) { ...
- Java反射获取当前项目下所有类,支持Servlet
反射在很多时候要用,尤其自己编写框架时,那么如何获得当前项目下所有类呢!以下是本人封装的一个比较简洁的方法: [功能代码] //通过loader加载所有类 private List<Class& ...
- 深入浅出ConcurrentHashMap1.8
转载:https://www.jianshu.com/p/c0642afe03e0 好文 关于文章中的疑问:为什么要构造一个反序链表,放在nextTable的i+n的位置上呢,在<深入分析Con ...
- Js的核心:找到DOM
掌握 JavaScript 的核心之一:DOM,能够熟悉DOM相关操作,了解JavaScript事件机制 一.使用getElementById().getElementsByTagName().chi ...
- Echarts按需引入后没有显示图例问题
因为Echarts官网的例子都是引入整个Echarts.js.如果使用按需引入对应模块就要记得引入legend模块,才能显示出图例. 例如这样: require("echarts/lib/c ...
- 使用JS完成首页轮播图效果
获取document.getElementById("id名称"); 事件onload 定时操作setInterval("changeImg()",3000); ...