C++多线程编程二
1. 死锁与解锁:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex> using namespace std; //thread引用类型函数,模板,避免类型转换,尽量指针,引用
//锁住一个变量之后,尽快操作完解锁,不要再锁,否则互锁
#define COUNT 100000
mutex g_mutex1, g_mutex2;//互斥量 void add1(int *p1, int *p2)
{
for (int i = ; i < COUNT; i++)
{
/*g_mutex1.lock();
p1++;
g_mutex2.lock();
p2++;
g_mutex1.unlock();
g_mutex2.unlock();*/ g_mutex1.lock();
(*p1)++;
g_mutex1.unlock(); g_mutex2.lock();
(*p2)++;
g_mutex2.unlock();
}
}
void add2(int *p1, int *p2)
{
for (int i = ; i < COUNT; i++)
{
/*g_mutex2.lock();
g_mutex1.lock();
p1++;
g_mutex1.unlock();
p2++;
g_mutex2.unlock();*/ g_mutex2.lock();
(*p2)++;
g_mutex2.unlock(); g_mutex1.lock();
(*p1)++;
g_mutex1.unlock();
}
} void main()
{
int a = ;
int b = ; thread th1(add1, &a, &b);
thread th2(add2, &a, &b); th1.join();
th2.join(); while ()
{
cout << a << endl;
cout << b << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds()); } cin.get();
}
2. 迅雷面试题:
编写一个程序,开启3个线程,这3个线程的ID分别为A、B、C,每个线程将自己的ID在屏幕上打印10遍,
要求输出结果必须按ABC的顺序显示。如:ABCABC...,依次递推。
【参考答案】
//编写一个程序,开启3个线程,这3个线程的ID分别为A、B、C,每个线程将自己的ID在屏幕上打印10遍,
//要求输出结果必须按ABC的顺序显示。如:ABCABC...,依次递推。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable> using namespace std; int LOOP = ; //循环次数
int flag = ; //标识符 012012012012
mutex m;
condition_variable cv; void fun(int id)
{
for (int i = ; i < LOOP; i++)
{
unique_lock<mutex> ulk(m); //设定锁定
while ((id-) != flag)
{
cv.wait(ulk); //不是该出现的场合,就等待
}
cout << (char)id; //转换id flag = (flag + ) % ; //012,012,012,...
cv.notify_all(); //通知全部
}
} void main()
{
thread t1(fun, );
thread t2(fun, );
thread t3(fun, ); t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join(); cin.get();
}
运行结果:
【分析】若题目变为:4个线程,输出结果要求为: ABCDABCDABCD...又该如何做呢?
//编写一个程序,开启3个线程,这3个线程的ID分别为A、B、C,每个线程将自己的ID在屏幕上打印10遍,
//要求输出结果必须按ABC的顺序显示。如:ABCABC...,依次递推。 #include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable> using namespace std; int LOOP = ; //循环次数
int flag = ; //标识符 012012012012
mutex m;
condition_variable cv; void fun(int id)
{
for (int i = ; i < LOOP; i++)
{
unique_lock<mutex> ulk(m); //设定锁定
while ((id-) != flag)
{
cv.wait(ulk); //不是该出现的场合,就等待
}
cout << (char)id; //转换id flag = (flag + ) % ; //012,012,012,...
cv.notify_all(); //通知全部
}
} void main()
{
thread t1(fun, );
thread t2(fun, );
thread t3(fun, );
thread t4(fun, ); t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
t4.join(); cin.get();
}
运行结果:
3. 思考:上题中若变为开启5个线程,ID分别为1,2,3,4,5,每个线程将自己的ID在屏幕上打印10遍,要求输出结果为:12345,54321,12345,54321,...依此类推。
4. 线程交换 swap:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std; void main()
{
thread t1([]() {cout << "ZhangShan"<<endl; });
thread t2([]() {cout << "LiSi"<<endl; }); cout << "t1.get_id():" << t1.get_id() << " t2.get_id():" << t2.get_id() << endl; swap(t1, t2); //交换句柄 cout << "t1.get_id():" << t1.get_id() << " t2.get_id():" << t2.get_id() << endl; t1.join();
t2.join(); cin.get();
}
5. 线程移动 move:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <cstdlib> using namespace std; void main()
{
thread t1([]()
{
int i = ;
while ()
{
i++;
if (i > )
{
break;
}
}
cout << i << endl;
system("pause");
}); cout << "t1:" << t1.get_id() << endl; //6872
//t1.join();
thread t2 = move(t1);//线程移动,t2具备了t1的属性,t1挂了
cout << "t1:" << t1.get_id() << endl; //
cout << "t2:" << t2.get_id() << endl; // t2.join(); cin.get();
}
运行结果: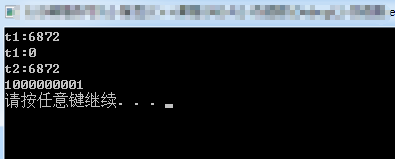
6. 线程自动加解锁:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex> using namespace std; #define N 10000000
mutex g_mutex;//全局互斥量 void add(int *p)
{
for (int i = ; i < N; i++)
{
unique_lock<mutex> ulk(g_mutex);
//没有mutex所有权,自动加锁自动解锁,根据块语句锁定
//根据mutex属性来决定,是否可以加锁 //lock_guard<mutex> lgd(g_mutex);
//拥有mutex所有权,自动加锁自动解锁
//读取mutex失败的情况下就会一直等待
(*p)++;
}
} void main()
{
int a = ; thread t1(add, &a);
thread t2(add, &a); t1.join();
t2.join(); cout << a << endl; cin.get();
}
7. 线程等待固定时间:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime> using namespace std; condition_variable cv;
mutex m;
bool done=false; void run()
{
auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); //当前时间
auto end = start + chrono::seconds(); unique_lock<mutex> ulk(m);
while (!done)
{
if (cv.wait_until(ulk, end) == cv_status::timeout)//超时
{
done = true;
break;
}
}
//this_thread::sleep_until(end); system("pause");
} void main1601()
{
thread th(run); cin.get();
} void main()
{
time_t t1, t2;
auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); //当前时间
t1 = time(&t1); double db = ;
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
db += i;
} auto end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); //当前时间
t2 = time(&t2); cout << (end - start).count() << endl; //10^-9秒(ns)
cout << difftime(t2, t1) << endl; cin.get();
}
8. 多线程实现生产者、消费者:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <array>
#include <vector> using namespace std; mutex m;
condition_variable isfull, isempty;//处理两种情况
bool flag = true;//标志,消费完了就退出
vector<int> myint();//开辟10个元素 void produce(int num) //生产
{
for (int i = ; i < num; i++)
{
unique_lock<mutex> lk(m); //锁定
while (myint.size()>=)
{
isempty.wait(lk); //满了一直等待
} myint.push_back(i);//插入
cout << "生产" << i << endl;
isfull.notify_all();//通知消费者 } this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds());//休眠5秒 flag = false;
} void consume() //消费
{
while (flag)
{
unique_lock<mutex> lk(m); //锁定
while (myint.size()==)
{
isfull.wait(lk);//等待
} if (flag)
{
cout << "消费" << myint[myint.size() - ] << " " << this_thread::get_id() << endl;
myint.pop_back();//剔除最后一个 isempty.notify_all();//通知生产者继续生产
}
}
} void main()
{
thread t1(consume); //消费者
thread t2(consume);
thread t3(consume); //produce(100);
thread s1(produce,);//消费者
thread s2(produce,); t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join(); cin.get();
}
C++多线程编程二的更多相关文章
- Linux系统编程@多线程编程(二)
线程的操作 线程标识 线程的ID表示数据类型:pthread_t (内核中的实现是unsigned long/unsigned int/指向pthread结构的指针(不可移植)几种类型) 1.对两个线 ...
- java多线程编程(二)
1. wait 和 sleep 区别? 1.wait可以指定时间也可以不指定,sleep必须指定时间. 2.在同步中时,对cpu的执行权和锁的处理不同. wait:释放执行权,释放锁. sleep ...
- java多线程编程(二创建线程)
1.概念 因为java是完全面向对象的,所以在java中,我们说的线程,就是Thread类的一个实例对象.所以,一个线程就是一个对象,它有自己字段和方法. 2.创建线程 创建线程有 ...
- Android多线程编程<二>Handler异步消息处理机制之Message
Message(消息): 一. Message的字段: 在Android中,Message作为线程之间(主要是子线程和UI主线程之间)数据交换的载体,通过Handler去传递.它 ...
- C语言多线程编程二
一. 线程通信----事件: 1.一对一模式: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <Windows.h> ...
- Windows下多线程编程(二)
线程的分类 1. 有消息循环线程 MFC中有用户界面线程,从CWinThread派生出一个新的类作为UI线程类CUIThread,然后调用AfxBeginthread(RUNTIME_CLAS ...
- UNIX环境编程学习笔记(27)——多线程编程(二):控制线程属性
lienhua342014-11-09 1 线程属性概括 POSIX 线程的主要属性包括 scope 属性.detach 属性.堆栈地址.堆栈大小.优先级.在头文件 pthread.h 中定义了结构体 ...
- 多线程编程(二)-Exchanger的使用
Exchanger的介绍 类Exchanger的功能可以使两个线程之间传输数据. 方法exchange()的使用 package com.wjg.unit; import java.util.conc ...
- 多线程编程<二>
wait()与notify(): 1 public class ThreadComDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 try { 4 ...
随机推荐
- Kubernetes集群的安装部署
此文参照https://www.cnblogs.com/zhenyuyaodidiao/p/6500830.html,并根据实操过程略作修改. 1.环境介绍及准备: 1.1 物理机操作系统 物理机操作 ...
- redis在Web中的使用
redis是一个键值对数据库,用于缓存数据. redis是一个key-value存储系统.和Memcached数据库类似,它支持存储的value类型相对更多,包括string(字符串).list(链表 ...
- docker 容器创建参数错误记录
sudo docker ps -a -q sudo docker ps -a|cutawk '{print $1}' #删除前八条 sudo docker ps -a -q|head -n |xarg ...
- C#重启IIS
using System.Diagnostics; using System.ServiceProcess; //ServiceController sc1 = new ServiceControll ...
- 运行Junit单测时遇到的问题
现在有两个办法解决: 1.junit版本降到4.10 2.导入hamcrest-core-1.3.jar 官网:JUnit now uses the latest version of Hamcres ...
- for(var i=0;i<5;i++){ setTimeout(function() { console.log(i) }, 100);}
涉及异步.作用域.闭包 1.settimeout是异步执行,100ms后往任务队列里面添加一个任务 2.let不仅将i绑定到for循环块中,事实上它将其重新绑定到循环体的每一次迭代中 3.闭包 set ...
- jfinal框架教程
jfinal框架教程 下面通过一个小例子了解jfinal的结构和特点 1.建数据库(我用的是oracle数据库,其他的相对也差不多) -- Create table create table CLAS ...
- ASP.NET 4(和ASP.NET MVC 2)中输出HTML编码的新语法<%:%>
今天的文章介绍了ASP.NET 4中引入的一个小而且非常有用的新语法功能 - 这是在代码块中自动对输出进行HTML编码的功能.这有助于保护您的应用程序和站点免受跨站点脚本注入(XSS)和HTML注入攻 ...
- UVa 1614 Hell on the Markets (贪心+推理)
题意:给定一个长度为 n 的序列,满足 1 <= ai <= i,要求确实每一个的符号,使得它们和为0. 析:首先这一个贪心的题目,再首先不是我想出来的,是我猜的,但并不知道为什么,然后在 ...
- iOS隐藏导航条1px的底部横线
第二种方法:1)声明UIImageView变量,存储底部横线 @implementation MyViewController { UIImageView *navBarHairlineImageVi ...
