What is a Database Trigger?
Link:
http://www.essentialsql.com/what-is-a-database-trigger/
Copy...
What is a Database Trigger?
A database trigger is special stored procedure that is run when specific actions occur within a database. Most triggers are defined to run when changes are made to a table’s data. Triggers can be defined to run instead of or after DML (Data Manipulation Language) actions such as INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
Triggers help the database designer ensure certain actions, such as maintaining an audit file, are completed regardless of which program or user makes changes to the data.
The programs are called triggers since an event, such as adding a record to a table, fires their execution.
Triggers and their implementations are specific to database vendors. In this article we’ll focus on Microsoft SQL server; however, the concepts are the same or similar in Oracle and MySQL.
Note: All the examples for this lesson are based on Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio and the AdventureWorks2012 database. You can get started using these free tools using my Guide Getting Started Using SQL Server.
Events
The triggers can occur AFTER or INSTEAD OF a DML action. Triggers are associated with the database DML actions INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. Triggers are defined to run when these actions are executed on a specific table.
AFTER triggers
Once the DML actions, such as an INSERT completes, the AFTER trigger executes. Here are some key characteristics of AFTER triggers:
- After triggers are run after a DML action, such as an INSERT statement and any ensuing referential cascade actions and constraint checks have run.
- You can’t cancel the database action using an AFTER trigger. This is because the action has already completed.
- One or more AFTER triggers per action can be defined on a table, but to keep things simple I recommend only defining one.
- You can’t define AFTER triggers on views.
INSTEAD OF triggers
INSTEAD OF triggers, as their name implies, run in place of the DML action which caused them to fire. Items to consider when using INSTEAD OF triggers include:
- An INSTEAD OF trigger overrides the triggering action. If an INSTEAD OF trigger is defined to execute on an INSERT statement, then once the INSERT statement attempt to run, control is immediately passed to the INSTEAD OF trigger.
- At most, one INSTEAD OF trigger can be defined per action for a table. This makes sense, as if you had to “INSTEAD OF” triggers for an insert, which one should run?
Special Database Objects
Triggers use two special database objects, INSERTED and DELETED, to access rows affected by the database actions. Within the scope of a trigger the INSERTED and DELETE objects have the same columns as the trigger’s table.
The INSERTED table contains all the new values; whereas, the DELETED table contains old values. Here is how the tables are used:
- INSERT – Use the INSERTED table to determine which rows were added to the table.
- DELETE – Use the DELETED table to see which rows were removed from the table.
- UPDATE – Use the INSERTED table to inspect the new or updated values and the DELETED table to see the values prior to update.
Definition
A trigger is defined for a specific table and one or more events. In most database management systems you can only define one trigger per table.
Below is an example trigger from the AdventureWorks2012 database.
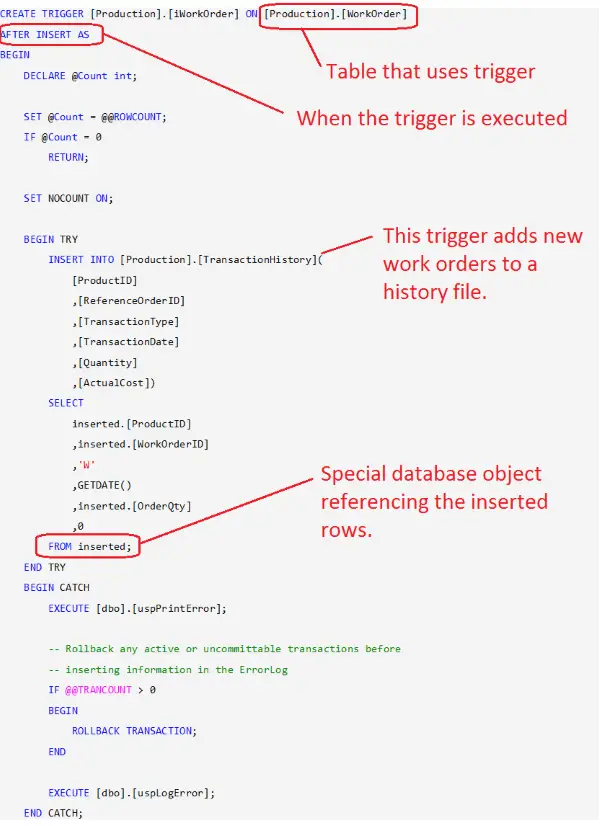
You’ll notice the syntax for a trigger is very similar to that of a stored procedure. In fact, the trigger uses the same language to implement its logic as do stored procedures. In MS SQL, this is T-SQL; whereas in Oracle it is PL/SQL.
Here are some important parts to a trigger:
- The CREATE Statement – It defines which table is associated with the trigger. In addition this statement is used to specify when the trigger executes (e.g. after insert).
- The actual program. In the example, this program runs whenever one or more rows are inserted into the WorkOrder table.
- Special database objects – Triggers use specially defined databases objects such as INSERTED, or DELETED to access records affected by the database action.
- In this example the trigger is using the INSERTED object to gain access to the newly created rows. The INSERT statement is used to table those rows and add them to a history table.
Uses for Triggers
Here are some common uses for triggers:
Complex Auditing
You can use triggers to track changes made to tables. In our example above, changes made to the WorkOrder table are recorded a TransactionHistory table.
Typically when creating audit trails, you’ll use AFTER triggers.
You may think this is redundant, as many changes are logged in the databases journals, but the logs are meant for database recovery and aren’t easily accessible by user programs. The TransactionHistory table is easily referenced and can be incorporated into end user reports.
Enforce Business Rules
Triggers can be used to inspect all data before a DML action is performed. You can use INSTEAD OF triggers to “intercept” the pending DML operation, apply any business rules, and ultimately complete the transaction.
An example business rule may be that a customer status is defined as:
- Gold – Purchases over $1,000,000 in the past 12 months.
- Silver – Purchase of $500,000 to $1,000,000 in the past 12 months.
- Bronze – All other purchase levels.
An INSTEAD OF trigger could be defined to check the customer status each time a customer record is added or modified. The status check would involve creating a sum of all the customers’ purchases and ensuring the new status corresponds with the sum of the last 12 months of purchases.
Derive Column Values
Triggers can be used to calculate column values. For instance, for each customer you may wish to maintain a TotalSales column on the customer record. Of course, for this to remain accurate, it would have to be update every time a sales was made.
This could be done using an AFTER trigger on INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements for the Sales table.
Triggers Are Tricky!
In general, my advice is to avoid using triggers unless absolutely necessary.
You should avoid using triggers in place of built in features. For instance, rather than rely on triggers to enforce referential integrity, you’re better off using relationships.
Here are some reasons why I shy away from them:
- They can be hard to troubleshoot.
- Triggers can cause other triggers to fire. Two Tables, A and B, both have an AFTER UPDATE trigger. If the AFTER UPDATE trigger on Table A updates Table B, then updating Table A causes it’s trigger and then B’s trigger to Fire.
- You have to be sure you don’t create a trigger storm! Can you imagine if Table B, for some reason, updated Table A? Now you have a circular reference… Boom!
- I try to move as much logic into Stored Procedures and have applications make changes to the database through them rather than straight up SQL statements.
What is a Database Trigger?的更多相关文章
- Oracle12c中多宿主环境(CDB&PDB)的数据库触发器(Database Trigger)
Oracle12c中可插拔数据库(PDBs)上的多宿主数据库触发器 随着多宿主选项的引入,数据库事件触发器可以在CDB和PDB范围内创建. 1. 触发器范围 为了在CDB中创建数据库事件触发器,需 ...
- [结]Oracle trigger(触发器)摘录
1.触发器: 是许多关系数据库系统都提供的一项技术.在ORACLE系统里,触发器类似过程和函数,都有声明,执行和异常处理过程的PL/SQL块. 触发器在数据库里以独立的对象存储,它与存储过程和函数不同 ...
- ORACLE DB TRIGGER详解
本篇主要内容如下: 8.1 触发器类型 8.1.1 DML触发器 8.1.2 替代触发器 8.1.3 系统触发器 8.2 创建触发器 8.2.1 触发器触发次序 8.2.2 创建DML触发器 8.2. ...
- 使用Server Trigger保护重要的数据库对象
一 .Server Trigger的简单介绍 在SQL Server数据库中,Server Trigger 是一种特殊类型的存储过程,它可以对特定表.视图或存储中的必然事件自动响应,不由用户调用.创建 ...
- 【Oracle】详解ORACLE中的trigger(触发器)
本篇主要内容如下: 8.1 触发器类型 8.1.1 DML触发器 8.1.2 替代触发器 8.1.3 系统触发器 8.2 创建触发器 8.2.1 触发器触发次序 8.2.2 创建DML触发器 8.2. ...
- 16Oracle Database 系统权限和对象权限
Oracle Database 系统权限和对象权限 Oracle中的系统权限和对象权限 DCL 数据控制语言 -- 查看对象的权限 grant / revoke 查看登录用户 Show user 查看 ...
- 从AdventureWorks学习数据库建模——实体分析
最近打算写写数据库建模的文章,所以打算分析微软官方提供的SQL Server示例数据库AdventureWorks,看看这个数据库中有哪些值得学习的地方. 首先我们需要下载安装一个SQL Server ...
- Oracle触发器原理、创建、修改、删除
本篇主要内容如下: 8.1 触发器类型 8.1.1 DML触发器 8.1.2 替代触发器 8.1.3 系统触发器 8.2 创建触发器 8.2.1 触发器触发次序 8.2.2 创建DML触发器 8.2. ...
- linux 安装 ArcSDE10.1
实验仍未成功,步骤仅供参考. 1:首先检查一下在Linux操作系统下Oracle数据库是否能启动,是否能连通等 [oracle@localhost ~]$ sqlplus SQL*Plus: Rele ...
随机推荐
- maven install时报错Failed to execute goal org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:2.3.2:compile
首先检查父项目,子项目的jdk版本是否一致,编码格式是否一致我的问题就错在了编码格式上,父项目用的是UTF-8,子项目新建的,默认GBK这时,使用maven install命令出错 提示:[INFO] ...
- 关于使用 no-js (Modernizr)
最近有些朋友问到:为什么我的网页 code 有 class="no-js" ? <!DOCTYPE html> <html dir="ltr" ...
- 1 web.xml配置详解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http:// ...
- IK分词器 整合solr4.7 含同义词、切分词、停止词
转载请注明出处! IK分词器如果配置成 <fieldType name="text_ik" class="solr.TextField"> < ...
- CSS3 时钟
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- Authcode()
加密解密函数Authcode(): 1. // 参数解释 2. // $string: 明文 或 密文 3. // $operation:DECODE表示解密,其它表示加密 4. // ...
- Mac Pro 软件安装/个性化配置 汇总
苹果产品维修 一.Spotlight 搜索程序和文档 Spotlight是最最常用的东西, 类似Windows开始菜单中的搜索. 可以用来搜索文档,也可以搜索本机的程序, 这样可以快速启动. 点击右 ...
- PhpStorm 2016.3 For Mac 重大里程碑更新 -- 终于解决了不能输入中文标点符号的重大bug
PhpStorm 2016.3 For Mac 重大里程碑更新 1.[终于解决了]不能输入中文标点符号的重大bug,如 逗号“,”.“.”: 2.可以在一个窗体中,同时打开多个项目: 3.其他... ...
- 摄像头视频捕捉(简单通用--通过IsampleGrabberCB实现)
前言 DirectShow是微软公司提供的一套在Windows平台上进行流媒体处理的开发包,与DirectX开发包一起发布.DirectShow为多媒体流的捕捉和回放提供了强有力的支持.用Direct ...
- opencv的图片的灰度处理‘
#include "stdafx.h" //实现将彩色图片转换成灰度图 int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]){ IplImage *image; ...
