Fire Net
Fire Net
Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 65536/32768K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 10 Accepted Submission(s) : 3
Font: Times New Roman | Verdana | Georgia
Font Size: ← →
Problem Description
A blockhouse is a small castle that has four openings through which to shoot. The four openings are facing North, East, South, and West, respectively. There will be one machine gun shooting through each opening.
Here we assume that a bullet is so powerful that it can run across any distance and destroy a blockhouse on its way. On the other hand, a wall is so strongly built that can stop the bullets.
The goal is to place as many blockhouses in a city as possible so that no two can destroy each other. A configuration of blockhouses is legal provided that no two blockhouses are on the same horizontal row or vertical column in a map unless there is at least one wall separating them. In this problem we will consider small square cities (at most 4x4) that contain walls through which bullets cannot run through.
The following image shows five pictures of the same board. The first picture is the empty board, the second and third pictures show legal configurations, and the fourth and fifth pictures show illegal configurations. For this board, the maximum number of blockhouses in a legal configuration is 5; the second picture shows one way to do it, but there are several other ways.
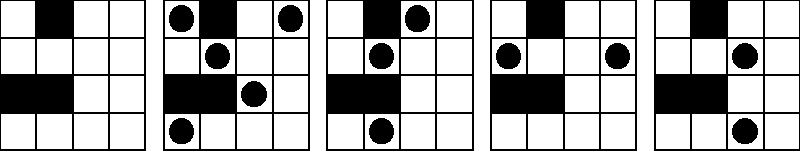
Your task is to write a program that, given a description of a map, calculates the maximum number of blockhouses that can be placed in the city in a legal configuration.
Input
Output
Sample Input
4
.X..
....
XX..
....
2
XX
.X
3
.X.
X.X
.X.
3
...
.XX
.XX
4
....
....
....
....
0
Sample Output
5
1
5
2
4
题意:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;/*
int cmp(const void *a,const void *b){
return *(int*)a-*(int*)b;
}*/
int count(int a[4][4],int row,int col,int n){/*数数,计算每个空位,十字架方向上所有能够放的,即会发生冲突的数目*/
int count1=0,i;/*注意四个方向,count计数,别忘了设初值为0*/
for(i=row-1;i>=0;i--){/*up*/
if(a[i][col]==2)/*碰到墙才会停止*/
break;
else
count1++;
}
for(i=row+1;i<n;i++){/*down*/
if(a[i][col]==2)
break;
else
count1++;
}
for(i=col-1;i>=0;i--){/*left*/
if(a[row][i]==2)
break;
else
count1++;
}
for(i=col+1;i<n;i++){/*right*/
if(a[row][i]==2)
break;
else
count1++;
}
return count1;
}
bool right(int a[4][4],int row,int col,int n){/*判断是否可以安置炮*/
int i;
for(i=row-1;i>=0;i--){/*用bool型*/
if(a[i][col]==1)/*十字架方向上碰到架炮的地方,就说明有冲突,即此处不可行*/
return false;
else if(a[i][col]==2)/*碰到墙停止*/
break;
}
//down
for(i=row+1;i<n;i++){/*仍旧是四个方向上检测*/
if(a[i][col]==1)
return false;
else if(a[i][col]==2)
break;
}
//left
for(i=col-1;i>=0;i--){
if(a[row][i]==2)
break;
else if(a[row][i]==1)
return false;
}
//right
for(i=col+1;i<n;i++){
if(a[row][i]==2)
break;
else if(a[row][i]==1)
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(){
int n,i,j,k,ans;
char c;
int map[4][4];
int cnt[4][4];
while(scanf("%d",&n),n){
k=0,ans=0;
memset(cnt,-1,sizeof(cnt));
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
// scanf("%c",&c);
cin>>c;
if(c=='.'){/*将字符型的图转化成数组型的*/
k++;/*顺表记录下总共有多少个空的位置,方便最后检测成不成功时的循环次数*/
map[i][j]=0;/*0表示可放的位置*/
}
else if(c=='X')/*X表示墙的位置*/
map[i][j]=2;
}
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++){/*计数,遇墙跳过,遇空地计数,并将地址与数目用二维数组cnt[i][j]保留下来*/
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
if(map[i][j]==2)
continue;
else
cnt[i][j]=count(map,i,j,n);
}
}
/*qsort(cnt,n*n,sizeof(cnt[0][0]),cmp);//!!!不能使用qsort直接对cnt排序,否则将会把位置给弄丢,所以应该使用冒泡排序*/
int min=7,mini,minj;/*最多只能是6,用题中的最大可能做最小箱的箱底*/
while(k--){/*有k个空位,即有k种可能性,每个位置都要判断下*/
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
if(cnt[i][j]==-1)
continue;
else if(cnt[i][j]<min){/*要先排排序,从最小的开始,使用贪心,因为周围的可能最少,该位成功的可能性最大*/
min=cnt[i][j];/*重置最小*/
mini=i;/*记录位置*/
minj=j;
}
}
}
if(right(map,mini,minj,n)){/*判断是否能够放*/
map[mini][minj]=1;/*可以的话,就将map中的该位置为1,标志为有炮,便于剩下位置的判断*/
ans++;/*成立计数加1*/
}
cnt[mini][minj]=-1;/*该位置不用再检测了,在cnt数组中标记下-1,直接跳过,检测第二个最小的位置*/
min=7;/*重置最小*/
}
/*“。”点表示可放东西,总计有多少个空,k个*/
/* for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
if(cnt[i][j]==-1)
continue;
else if(right(map,i,j,n)){
map[i][j]=1;
ans++;
}
}
}*/
printf("%d\n",ans);/*输出*/
}
return 0;
}
Fire Net的更多相关文章
- 关于SequeezeNet中的Fire Module
在论文<SQUEEZENET: ALEXNET-LEVEL ACCURACY WITH 50X FEWER PARAMETERS AND <0.5MB MODEL SIZE>中,作者 ...
- FZU 2150 Fire Game
Fire Game Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Submit St ...
- Fire
Fire 分析: 首先,明确题意:b1,b2,--,bn 交换为b2,--,bn,b1,但这并不是意味着只能从b1开始交换,(这点从样例中可以看出),并且也不意味着交换的必须是连续的一串,可以是几个单 ...
- Android 轻量级输入校验库:Fire Eye
Fire Eye是一款轻量级简单易用的Android校验库. FireEye 2.0 在 1.0 的基础上,全部重写了代码,并优化了架构,性能上和逻辑上都大大提升.只需要几行代码,即可验证用户输入,并 ...
- ACM: FZU 2150 Fire Game - DFS+BFS+枝剪 或者 纯BFS+枝剪
FZU 2150 Fire Game Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u ...
- UVA 11624 Fire!(广度优先搜索)
题目大意:在一个N*M的迷宫内,J代表某人(只有一个),F代表火(可能不只一个),#代表墙,火每分钟会向四周除了墙以外的地方扩散一层,问人能否在没被火烧到 之前逃出迷宫,若能逃出输出最短时间.很明显的 ...
- Amazon的Fire Phone之于Android开发者
在上周Amazon也耐不住加入了手机竞争行列之中,发布了自己的Fire Phone,于是Android家族又多了一位变种成员,Android系统的碎片化程度也进一步加剧.因为工作的关系,我有幸在上个月 ...
- Fire!(BFS)
Fire! Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:0KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu Submit Status Descr ...
- FZU Problem 2150 Fire Game
Problem 2150 Fire Game Accept: 145 Submit: 542 Time Limit: 1000 mSec Memory Limit : 32768 KB P ...
- hdu 1045:Fire Net(DFS经典题)
Fire Net Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
随机推荐
- CentOS6.5安装telnet
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhongshengzhen/ 1.检查是否已经安装telnet [root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa | grep teln ...
- Oracle中遍历Ref Cursor示例
示例编写环境 数据库:Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Release 12.1.0.1.0 - 64bit Production 登陆用户:Scott O ...
- 数组和集合List的相互转化
一.数组转为List 调用Arrays类的静态方法asList static void convertArray2List() { String[] strs = new String[]{" ...
- 在Entity Framework中重用现有的数据库连接字符串
本文转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/dudu/archive/2011/01/29/entity_framework_connection_string.html 如果EF在使用实 ...
- Android 访问权限设置记录-存档留着有用!
Android开发应用程序时,如果应用程序需要访问网络权限,需要在 AndroidManifest.xml 中加入以下代码: <uses-permission android:name=”and ...
- [原创]oracle 顺序号生成函数。仿Sequence
问题提出自项目中的老代码:一个Bill表,存储所有的表单信息,比如:员工入职单,离职单等等.(别喷,我知道要分多个表.但领导的意愿你是没办法违背的)表单的单据号是以四个字母+年月日+数字顺序号来表示. ...
- Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments) 类数组转成真正的数组
Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments) 我们知道,Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments)能将具有length属性的对象转成数 ...
- 信号之kill和raise函数
kill函数将信号发送给进程或进程组.raise函数则允许进程向自身发送信号. #include <signal.h> int kill(pid_t pid, int signo); in ...
- Vmware中为Mac Os安装vmtools
成功方法: 1. 在VMWare中点击edit this virtual machine 2. 添加CD/DVD,使用iso,找到那个darwin.iso 3. 在setting里面,点击CD/DVD ...
- 【转】Android开发之Bitmap的内存优化详解
本文来源:转载自: http://mobile.51cto.com/abased-410796.htm 在Android应用里,最耗费内存的就是图片资源.而且在Android系统中,读取位图Bitma ...
