Java 实现--时间片轮转 RR 进程调度算法
时间片轮转(Round-Robin)调度算法是操作系统一种比较公平的进程调度的方式,这种方式使得就绪队列上的所有进程在每次轮转时都可以运行相同的一个时间片。
基本原理
算法实现原理是,按进程到达顺序(FCFS 原则)将进程依次加入就绪队列当中,然后将 CPU 分配给位于队首的进程,确定一个时间片,让该进程执行一个时间片。当该进程执行时间到时,该进程可能已经执行完毕(可能在时间片未到时就以及执行完毕),或者未执行完毕,如果是前者只需将进程弹出队列即可,如果是后者则将该进程加入队尾,并将 CPU 分配给新的队首进程,如此循环。
进程切换时机
进程在执行时分为两种情况
- 在该时间片内进程执行完毕,这种情况调度程序将立即把该进程弹出队列,并把 CPU 分配给新的队首进程
- 在该时间片内进程未执行完毕,调度程序将立即中断该进程执行,把该进程加入队尾,并将 CPU 分配给新的队首进程
时间片大小的确定
在 RR 算法中,时间片的大小直接影响了系统的性能。
- 时间片过小,有利于短作业,但是会频繁地切换进程,增加了系统的开销,影响性能。
- 时间片过大,算法退化成 FCFS 算法,如果某个短作业进程之前的进程都是长作业,将导致后面的短作业进程长时间等待。
有关的计算
- 周转时间 = 进程完成时间 - 进程到达时间
- 带权周转时间 = 进程周转时间 / 进程实际运行时间
- 平均周转时间 = (进程1周转时间 + ... + 进程n周转时间)/ n
- 平均带权周转时间 = (进程1带权周转时间 + ... + 进程n带权周转时间)/ n

实现
package cn.vecrates.operatingSystem; import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; public class RR {
private int mProcessCount; //进程数
private Queue<Process> mReadyQueue; //就绪队列,存放“待运行的进程
private Queue<Process> mUnreachQueue; //存放“到达时间未到的进程”
private int mTimeSlice; //时间片 private Queue<Process> mExecutedQueue; //执行完毕的进程队列
private double mTotalWholeTime = 0.0;
private double mTotalWeightWholeTime = 0.0; private RR(int processCount, Queue<Process> processQueue, int timeSlice) {
this.mProcessCount = processCount;
this.mUnreachQueue = processQueue;
mReadyQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
this.mTimeSlice = timeSlice;
mExecutedQueue = new LinkedList<>();
} /**
* RR 算法实现
*/
public void RRAlgorithm() {
mReadyQueue.add(mUnreachQueue.poll());
Process currProcess = mReadyQueue.poll();
//第一个进程执行
int currTime = executeProcess(currProcess, 0); while(!mReadyQueue.isEmpty() || !mUnreachQueue.isEmpty()) {
//把所有“到达时间”达到的进程加入运行队列头部
while(!mUnreachQueue.isEmpty()) {
if(mUnreachQueue.peek().getArrivalTime() <= currTime) {
mReadyQueue.add(mUnreachQueue.poll());
} else {
break;
}
}java学习群669823128 if(currProcess.getRemainServiceTime() > 0) mReadyQueue.add(currProcess);
//运行队列不为空时
if(!mReadyQueue.isEmpty()) {
currProcess = mReadyQueue.poll();
currTime = executeProcess(currProcess, currTime);
} else {
//当前没有进程执行,但还有进程为到达,时间直接跳转到到达时间
currTime = mUnreachQueue.peek().getArrivalTime();
}
}
} private int executeProcess(Process currProcess, int currTime) {
if(currProcess.getRemainServiceTime() - mTimeSlice <= 0) {
//当前进程在这个时间片内能执行完毕
showExecuteMessage(currTime, currTime += currProcess.getRemainServiceTime(), currProcess.getName());
currProcess.setFinishTime(currTime);
currProcess.setRemainServiceTime(0);
//对周转时间等进行计算
calculeteWholeTime(currProcess);
calculateWeightWholeTime(currProcess);
mTotalWholeTime += currProcess.getWholeTime();
mTotalWeightWholeTime += currProcess.getWeightWholeTime();
mExecutedQueue.add(currProcess);
} else {
//不能执行完毕
showExecuteMessage(currTime, currTime += mTimeSlice, currProcess.getName());
currProcess.setRemainServiceTime(currProcess.getRemainServiceTime() - mTimeSlice);
}
return currTime;
} /**
* 计算周转时间
* @param process
*/
private void calculeteWholeTime(Process process) {
process.setWholeTime(process.getFinishTime() - process.getArrivalTime());
} /**
* 计算带权周转时间
* @param process
*/
private void calculateWeightWholeTime(Process process) {
process.setWeightWholeTime(process.getWholeTime() / (double)process.getServiceTime());
} private void showExecuteMessage(int startTime, int endTime, String name) {
System.out.println(startTime + "~" + endTime + ":【进程" + name + "】运行");
} public void showResult() {
System.out.print("进程名\t");
System.out.print("周转时间\t");
System.out.println("带权周转时间\t");
Process process ;
while(!mExecutedQueue.isEmpty()) {
process = mExecutedQueue.poll();
System.out.print("进程" + process.getName() + "\t");
System.out.print("\t" + process.getWholeTime() + "\t");
System.out.println("\t" + process.getWeightWholeTime() + "\t");
}
System.out.println("平均周转时间:" + mTotalWholeTime / (double) mProcessCount);
System.out.println("平均带权周转时间:" + mTotalWeightWholeTime / (double) mProcessCount);
} public static void printAll(Queue<Process> queue) {
System.out.print("进程名\t");
System.out.print("到达时间\t");
System.out.println("服务时间\t");
Process process = null;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
process = queue.poll();
System.out.print("进程" + process.getName() + "\t");
System.out.print("\t" + process.getArrivalTime() + "\t");
System.out.println("\t" + process.getServiceTime() + "\t");
}
} public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入进程个数:");
int processCount = scanner.nextInt();
if(processCount < 1) return;
Queue<Process> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
System.out.println("依次输入每个进程的到达时间(按到达顺序):");
for(int i=0; i<processCount; i++) {
Process process = new Process((char)(i + 65) + "");
process.setArrivalTime(scanner.nextInt());
queue.add(process);
}
System.out.println("依次输入每个进程的服务时间(按到达顺序):");
for(int i=0; i<processCount; i++) {
Process process = queue.poll();
int time = scanner.nextInt();
process.setServiceTime(time);
process.setRemainServiceTime(time);
queue.add(process);
} System.out.println("输入时间片大小");
int timeSlice = scanner.nextInt(); RR rr = new RR(processCount, queue, timeSlice); System.err.println("*******************进程情况*****************");
Thread.sleep(1000);
printAll(new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(queue));
Thread.sleep(1000); System.err.println("******************运行过程*****************");
Thread.sleep(1000);
rr.RRAlgorithm();
Thread.sleep(1000); System.err.println("*******************运行结果*****************");
Thread.sleep(1000);
rr.showResult();
} } //进程
class Process {
private String name;
private int arrivalTime; //到达时间
private int serviceTime; //服务时间
private int remainServiceTime; //还需要服务的时间
private int finishTime; //完成时间
private int wholeTime; //周转时间
private double weightWholeTime; //带权周转时间 public int getRemainServiceTime() {
return remainServiceTime;
} public void setRemainServiceTime(int remainServiceTime) {
this.remainServiceTime = remainServiceTime;
} public Process(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getArrivalTime() {
return arrivalTime;
} public void setArrivalTime(int arrivalTime) {
this.arrivalTime = arrivalTime;
} public int getServiceTime() {
return serviceTime;
} public void setServiceTime(int serviceTime) {
this.serviceTime = serviceTime;
} public int getFinishTime() {
return finishTime;
} public void setFinishTime(int finishTime) {
this.finishTime = finishTime;
} public int getWholeTime() {
return wholeTime;
} public void setWholeTime(int wholeTime) {
this.wholeTime = wholeTime;
} public double getWeightWholeTime() {
return weightWholeTime;
} public void setWeightWholeTime(double weightWholeTime) {
this.weightWholeTime = weightWholeTime;
}
}
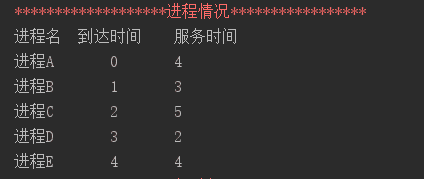
运行结果当时间片为 1 时:

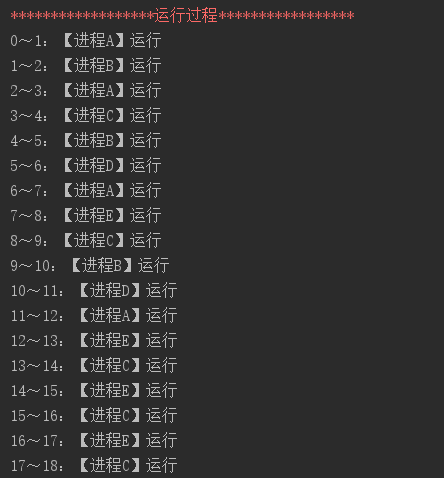

时间片为 4 时:

java学习群669823128
Java 实现--时间片轮转 RR 进程调度算法的更多相关文章
- 《操作系统_时间片轮转RR进程调度算法》
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/houchaoqun_xmu/article/details/55540250 时间片轮转RR进程调度算法 一.概念介绍和案例解析时间片轮转法 - 基 ...
- Linux常见的进程调度算法
进程调度:在操作系统中调度是指一种资源分配. 调度算法是指: 根据系统的资源分配策略所规定的资源分配算法. 操作系统管理了系统的有限资源,当有多个进程(或多个进程发出的请求)要使用这些资源时,因为资源 ...
- 进程调度算法Linux进程调度算法
这次介绍一下操作系统的进程调度算法 操作系统的调度分为三种:1.远程调度(创建新进程):2.中程调度(交换功能的一部分):3.短程调度(下次执行哪个进程) 这次讲述的就是短程调度,可以简单的看作咱们平 ...
- Linux 常见的进程调度算法
1.在介绍进程调度之前,先对进程的状态的概念应该有所了解,下面是关于进程状态的一些基本概念:进程的状态分为三种,分别为: 1).运行态:该状态表明进程在实际占用CPU 2).就绪态: 该状态下进程可以 ...
- os的进程调度算法(抄袭的)
package me.letterwish.test; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.FileInputStream; impo ...
- 2016-2017-2 《Java程序设计》教学进程
2016-2017-2 <Java程序设计>教学进程 目录 考核方式 课前准备 教学进程 第00周学习任务和要求 第01周学习任务和要求 第02周学习任务和要求 第03周学习任务和要求 第 ...
- Java并发编程:进程和线程之由来
Java多线程基础:进程和线程之由来 在前面,已经介绍了Java的基础知识,现在我们来讨论一点稍微难一点的问题:Java并发编程.当然,Java并发编程涉及到很多方面的内容,不是一朝一夕就能够融会贯通 ...
- 2015-2016-2 《Java程序设计》教学进程
2015-2016-2 <Java程序设计>教学进程 目录 考核方式 寒假准备 教学进程 第00周学习任务和要求 第01周学习任务和要求 第02周学习任务和要求 第03周学习任务和要求 第 ...
- Java多线程基础:进程和线程之由来
转载: Java多线程基础:进程和线程之由来 在前面,已经介绍了Java的基础知识,现在我们来讨论一点稍微难一点的问题:Java并发编程.当然,Java并发编程涉及到很多方面的内容,不是一朝一夕就能够 ...
随机推荐
- redis的一些命令
字符串操作 EX在设置值的时候设置过期时间,ttl查看过期时间 expire能单独设置过期时间 查看所有的key key * 列表操作 lpush从列表左边添加值,rpush从列表右边添加值 lran ...
- 第一课Linux系统安装知识(2)
接着上节课单击Finish按钮之后,虚拟机将会启动进入安装界面. 根据提示按回车选择图形界面安装. 这里选择Skip跳过媒介检查. 选择安装语言为简体中文,键盘鼠标默认项即可. 这里安装类型选择是定制 ...
- powerdesign初级入门教程
首先我们需要创建一个测试数据库,为了简单,我们在这个数据库中只创建一个Student表和一个Major表.其表结构和关系如下所示. 看看怎样用PowerDesigner快速的创建出这个数据库吧. 1. ...
- 微软名人数据集 ms_celeb_1m 处理(MsCelebV1-Faces-Aligned.tsv)python脚本
本文主要介绍了如何对MsCelebV1-Faces-Aligned.tsv文件进行提取 原创by南山南北秋悲 欢迎引用!请注明原地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/hwd9654/p/ ...
- 20145219 《Java程序设计》实验一 Java开发环境的熟悉(Linux + Eclipse)实验报告
20145219 <Java程序设计>实验一 Java开发环境的熟悉(Windws + IDEA)实验报告 实验内容 1.使用JDK编译.运行简单的Java程序: 2.使用IDEA 编辑. ...
- Facebook力推导航库:React Navigation使用详解
本文来自Songlcy投稿:文章地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u013718120/article/details/72357698 一.开源库介绍 今年1月份,新开源的react- ...
- iOS开发进阶 - 日志输出框架CocoaLumberjack与XcodeColors插件的简单使用(swift版)
CocoaLumberjack是Mac和iOS上一个集快捷.简单.强大和灵活于一身的日志框架.XcodeColors是用于控制台着色的工具,配合着CocoaLumberjack用有更好的效果,不废话, ...
- PHP练习题二
1.抓取远程图片到本地,你会用什么函数? fsockopen, A 2.用最少的代码写一个求3值最大值的函数. function($a,$b,$c){* W0 z* u6 k+ e. L a: }5 ...
- 记一次如何解决低版本jar包里面的bug,不适宜替换成高版本的经历
背景:目前正在迭代开发的项目,应用户要求新增一个电子文档转换的功能,即将不标准的excel文件转换为标准的excel文件(标准模板). 选择:pio ,本项目里面本来就有poi的jar包 问题:项目里 ...
- Java中的条件运算符
条件运算符( ? : )也称为 “三元运算符”. 语法形式:布尔表达式 ? 表达式1 :表达式2 运算过程:如果布尔表达式的值为 true ,则返回 表达式1 的值,否则返回 表达式2 的值 例如: ...
