HDU 1688 Sightseeing&HDU 3191 How Many Paths Are There(Dijkstra变形求次短路条数)
Sightseeing
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1023 Accepted Submission(s): 444
Different groups of tourists may have different preferences for the sights they want to see, and thus for the route to be taken from S to F. Therefore, Your Personal Holiday wants to offer its clients a choice from many different routes. As hotels have been booked in advance, the starting city S and the final city F, though, are fixed. Two routes from S to F are considered different if there is at least one road from a city A to a city B which is part of one route, but not of the other route.
There is a restriction on the routes that the tourists may choose from. To leave enough time for the sightseeing at the stops (and to avoid using too much fuel), the bus has to take a short route from S to F. It has to be either a route with minimal distance, or a route which is one distance unit longer than the minimal distance. Indeed, by allowing routes that are one distance unit longer, the tourists may have more choice than by restricting them to exactly the minimal routes. This enhances the impression of a personal holiday.
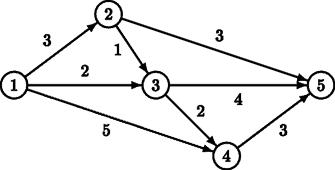
For example, for the above road map, there are two minimal routes from S = 1 to F = 5: 1 → 2 → 5 and 1 → 3 → 5, both of length 6. There is one route that is one distance unit longer: 1 → 3 → 4 → 5, of length 7.
Now, given a (partial) road map of the Benelux and two cities S and F, tour operator Your Personal Holiday likes to know how many different routes it can offer to its clients, under the above restriction on the route length.
One line with two integers N and M, separated by a single space, with 2 ≤ N ≤ 1,000 and 1 ≤ M ≤ 10, 000: the number of cities and the number of roads in the road map.
M lines, each with three integers A, B and L, separated by single spaces, with 1 ≤ A, B ≤ N, A ≠ B and 1 ≤ L ≤ 1,000, describing a road from city A to city B with length L.
The roads are unidirectional. Hence, if there is a road from A to B, then there is not necessarily also a road from B to A. There may be different roads from a city A to a city B.
One line with two integers S and F, separated by a single space, with 1 ≤ S, F ≤ N and S ≠ F: the starting city and the final city of the route.
There will be at least one route from S to F.
2
题目链接:HDU 1688
后一题原理一模一样,就不放题面了,题目要分别求最短路和次短路两者的条数与长度,若次短路长度刚好比最短路长1,则答案加上最短路的……
这题简直搞的无语,由于以前只会SPFA模版,并不知道Dij的思路,然而搜到的都是用朴素Dij做的,于是重新看了下离散数学和数据结构的最短路求法——每一次找一个不在S中且离源点最近的点进行拓展,按照这样的顺序得到一系列长度递增(感觉应该是不减的序列)的顺序序列D{i},然后这题怎么套呢。
就分四种情况,比最短路短,跟最短路一样长,比次短路短,跟次短路一样长,第一种情况下要先更新次短再更新最短,然后就是一个比较不复杂的Dij,不过网上的题解都是说循环2*n-1次,但是我觉得是2*n次,因为普通的Dij确实是n-1次因为初始化的时候直接对邻接S起点的点进行了拓展然后让vis[s]=1,但是这题可以不进行拓展只要vis[s]保持0即可,就是让S这个集合初始化为空,起点s的初始化也直接让下面的循环去更新,以前用A*什么的直接爆炸超时……too naive啊,毕竟另外一题范围是10^9,相信数据不会这么友好……
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define CLR(arr,val) memset(arr,val,sizeof(arr))
#define LC(x) (x<<1)
#define RC(x) ((x<<1)+1)
#define MID(x,y) ((x+y)>>1)
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long LL;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const int N=1010;
const int M=10010;
struct edge
{
int to;
int pre;
int w;
}; edge E[M];
int head[N],tot,n,m;
int d[N][2],way[N][2];
int vis[N][2]; void init()
{
CLR(head,-1);
tot=0;
CLR(d,INF);
CLR(way,0);
CLR(vis,0);
}
inline void add(int s,int t,int w)
{
E[tot].to=t;
E[tot].w=w;
E[tot].pre=head[s];
head[s]=tot++;
}
void Dij(int s)
{
d[s][0]=0;
way[s][0]=1;
for (int i=0; i<2*n; ++i)
{
int cur=-1;
int minm=INF;
int flag=0;
for (int j=1; j<=n; ++j)
{
if(!vis[j][0]&&minm>d[j][0])
{
flag=0;
minm=d[j][0];
cur=j;
}
else if(!vis[j][1]&&minm>d[j][1])
{
flag=1;
minm=d[j][1];
cur=j;
}
}
if(cur==-1)
break;
vis[cur][flag]=1;
for (int j=head[cur]; ~j; j=E[j].pre)
{
int v=E[j].to;
int w=E[j].w;
if(d[v][0]>d[cur][flag]+w)
{
d[v][1]=d[v][0];
way[v][1]=way[v][0]; d[v][0]=d[cur][flag]+w;
way[v][0]=way[cur][flag];
}
else if(d[v][0]==d[cur][flag]+w)
way[v][0]+=way[cur][flag]; else if(d[v][1]>d[cur][flag]+w)
{
d[v][1]=d[cur][flag]+w;
way[v][1]=way[cur][flag];
} else if(d[v][1]==d[cur][flag]+w)
way[v][1]+=way[cur][flag];
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
int tcase,a,b,w,s,t,i;
scanf("%d",&tcase);
while (tcase--)
{
init();
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for (i=0; i<m; ++i)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&w);
add(a,b,w);
}
scanf("%d%d",&s,&t);
Dij(s);
int ans=way[t][0];
if(d[t][0]+1==d[t][1])
ans+=way[t][1];
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
HDU 1688 Sightseeing&HDU 3191 How Many Paths Are There(Dijkstra变形求次短路条数)的更多相关文章
- HDU 1688 Sightseeing 【输出最短路+次短路条数】
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1688 题目大意:给n个点,m条有向边.再给出起点s, 终点t.求出s到t的最短路条数+次短路条数. 思 ...
- HDU 1688 Sightseeing
题目链接:Sightseeing 题意:求最短路和比最短路长度+1的所有路径条数. 附代码:用数组记录最短和次短路径的长度和条数,一次更新,直到没有边可以更新. #include <stdio. ...
- hdu 1688 Sightseeing (最短路径)
Sightseeing Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- 【最短路】HDU 1688 Sightseeing
题目大意 给出一个有向图(可能存在重边),求从\(S\)到\(F\)最短路的条数,如果次短路的长度仅比最短路的长度多1,那么再加上次短路的条数. 输入格式 第一行是数据组数\(T\). 对于魅族数据, ...
- poj 3463 Sightseeing(次短路+条数统计)
/* 对dij的再一次理解 每个点依旧永久标记 只不过这里多搞一维 0 1 表示最短路还是次短路 然后更新次数相当于原来的两倍 更新的时候搞一下就好了 */ #include<iostream& ...
- hdu 3191 How Many Paths Are There (次短路径数)
How Many Paths Are There Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java ...
- hdu 3191 How Many Paths Are There
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3191 这道题求次短路经和路径数 #include <cstdio> #include <cst ...
- poj 3463/hdu 1688 求次短路和最短路个数
http://poj.org/problem?id=3463 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1688 求出最短路的条数比最短路大1的次短路的条数和 ...
- HDU 3416 Marriage Match IV (求最短路的条数,最大流)
Marriage Match IV 题目链接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/122685#problem/Q Description Do not si ...
随机推荐
- HDU 3833 YY's new problem ()
YY's new problem Time Limit: 12000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others ...
- EZ的间谍网络(codevs 4093)
由于外国间谍的大量渗入,学校安全正处于高度的危机之中.YJY决定挺身而作出反抗.如果A间谍手中掌握着关于B间谍的犯罪证据,则称A可以揭发B.有些间谍收受贿赂,只要给他们一定数量的美元,他们就愿意交出手 ...
- Find them, Catch them(poj 1703)
题目大意: 在这个城市里有两个黑帮团伙,现在给出N个人,问任意两个人他们是否在同一个团伙输入D x y代表x于y不在一个团伙里输入A x y要输出x与y是否在同一团伙或者不确定他们在同一个团伙里 思路 ...
- SpringMVC详细示例实战
一.SpringMVC基础入门,创建一个HelloWorld程序 1.首先,导入SpringMVC需要的jar包. 2.添加Web.xml配置文件中关于SpringMVC的配置 1 2 3 4 5 6 ...
- Linux时间子系统之六:高精度定时器(HRTIMER)的原理和实现
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/droidphone/article/details/8074892 上一篇文章,我介绍了传统的低分辨率定时器的实现原理.而随着内核的不断演进,大牛们已 ...
- jquery之别踩白块游戏的实现
转载请注明出处http://www.cnblogs.com/Wxtrkbc/p/5687112.html 前端学习要告一段落了,也没机会写什么像样的东西,然后无意中想起某人以前给我玩了一下别踩白块的游 ...
- [杂]SQL Server 之 Service Broker
由于某些原因,我们的缓存依赖于数据库,而数据库反向通知需要依赖和使用ServiceBroker, 由于Deploy的人往往不是很清楚这个SB需要如何部署,特此记录. 判断数据库是否启用了Service ...
- php 解决和避免form表单重复提交的方法
在提交表单的时候,可能遇到网速等导致页面突然加载变慢,用户重复地点击提交按钮,将在数据库产生多条数据,导致不可控情况. 比如下面的情况就会导致表单重复提交: 点击提交按钮两次. 点击刷新按钮. 使用浏 ...
- poj 2019 二维rmq *
题目大意:给出一个N*N矩形,每个格子上有一个价值.询问一个b*b的矩形在左上角的位置(x,y),(x+b-1,y+b-1)这一部分的最大值-最小值是多少. 模板题 #include <stdi ...
- Java中如何使封装自己的类,建立并使用自己的类库?
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/luoweifu/article/details/7281494 随着自己的编程经历的积累会发现往往自己在一些项目中写的类在别的项目中也会有多次用到.你 ...
