Codeforces 526F Pudding Monsters - CDQ分治 - 桶排序
In this problem you will meet the simplified model of game Pudding Monsters.
An important process in developing any game is creating levels. A game field in Pudding Monsters is an n × n rectangular grid, n of its cells contain monsters and some other cells contain game objects. The gameplay is about moving the monsters around the field. When two monsters are touching each other, they glue together into a single big one (as they are from pudding, remember?).
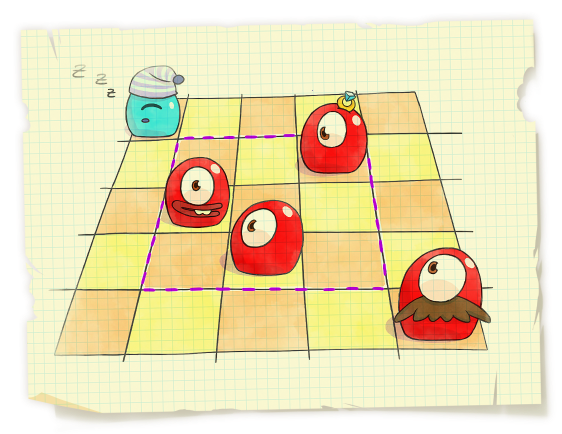
Statistics showed that the most interesting maps appear if initially each row and each column contains exactly one monster and the rest of map specifics is set up by the correct positioning of the other game objects.
A technique that's widely used to make the development process more efficient is reusing the available resources. For example, if there is a large n × n map, you can choose in it a smaller k × k square part, containing exactly k monsters and suggest it as a simplified version of the original map.
You wonder how many ways there are to choose in the initial map a k × k (1 ≤ k ≤ n) square fragment, containing exactly k pudding monsters. Calculate this number.
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3 × 105) — the size of the initial field.
Next n lines contain the coordinates of the cells initially containing monsters. The i-th of the next lines contains two numbers ri, ci(1 ≤ ri, ci ≤ n) — the row number and the column number of the cell that initially contains the i-th monster.
It is guaranteed that all ri are distinct numbers and all ci are distinct numbers.
Print the number of distinct square fragments of the original field that can form a new map.
5
1 1
4 3
3 2
2 4
5 5
10
题目大意 给定平面上有n个点,每行每列上只有一个点,问总共有多少个边长为k的矩形框住了k个点。
刚开学,好久(也就两周)都没搞OI,差点不知OI为何物了。qaq。有人把这道题改题面拿给我们考试,然后考试时没想出正解,暴力分段90分。。于是班上出现了一群优秀的魔(膜)法师。
显然,可以把它转化成序列上的问题(序列就是a[i]表示第i列上的点的纵坐标):有多少个长度为k的区间使得这一段的最大值和最小值之差等于k - 1。
然后上CDQ分治进行瞎搞。记当前分治区间为[l, r],分治中心为mid,统计经过分治中心的子区间,分四种情况讨论:
1)子区间的最大值和最小值同在左侧(相对于分治中心)
2)子区间的最小值在左侧,最大值在右侧
3)子区间的最大值和最小值同在右侧
4)子区间的最大值在左侧,最小值在右侧
由于情况1,3和2,4的做法类似,所以只考虑情况1,2
情况1:
记录左侧每个位置到分治中心的最大值和最小值。
枚举子区间的左端点,可以根据记录的数据计算出右端点,如果合法(在分治中心右侧,并且最大值和最小值满足在左侧)就将答案加1.
情况2:
从分治中心向左枚举左端点i,考虑先使最值的条件合法。
考虑到前后缀最大值和最小值都有不增或不减的单调性。所以设置两个"指针",r1和r2。
r1是第一个使最大值在右侧的位置,r2是第一个使最小值不在左边的位置。那么左端点为i,右端点在整数区间[r1, r2)内的子区间都满足最值的限制。
现在考虑如何统计答案。临时约定max[l, r]表示a[l],a[l + 1], ..., a[r]的最大值,同理定义min[l, r]。
显然

移一下项得到
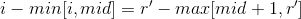
所以在挪动"指针"的时候把右边的一坨东东扔进某个桶里面就好了。挪动完成后根据当前枚举的左端点i,首先判断是否合法(比如什么r1大于等于r2的时候就continue就好了,如果合法的话就加上对应桶里的计数就好了。
这种情况搞定了之后,不要忘记清空桶,由于桶可能很大,所以不要memset或者fill,for数组a就好了。
Code
/**
* Codeforces
* Problem#526F
* Accepted
* Time: 140ms
* Memory: 8200k
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#ifndef WIN32
#define Auto "%lld"
#else
#define Auto "%I64d"
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
#define clra(a) memset(a, false, sizeof(a))
const signed int inf = ((~0u) >> );
#define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b)
#define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b)
#define LL long long const int N = 3e5; int n;
int *arr;
int *pmin, *pmax, *rmin, *rmax;
int bucket[(N << ) + ]; inline void init() {
scanf("%d", &n);
arr = new int[(n + )];
pmin = new int[(n + )];
pmax = new int[(n + )];
rmin = new int[(n + )];
rmax = new int[(n + )];
for(int i = , x, y; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
arr[x] = y;
}
} LL CDQDividing(int l, int r) {
if(l == r) return ; int mid = (l + r) >> ;
LL rt = ;
pmin[mid] = arr[mid], pmax[mid] = arr[mid], rmin[mid + ] = arr[mid + ], rmax[mid + ] = arr[mid + ];
for(int i = mid - ; i >= l; i--)
pmin[i] = min(pmin[i + ], arr[i]), pmax[i] = max(pmax[i + ], arr[i]);
for(int i = mid + ; i <= r; i++)
rmin[i] = min(rmin[i - ], arr[i]), rmax[i] = max(rmax[i - ], arr[i]); for(int i = l, rg; i <= mid; i++) {
rg = i + pmax[i] - pmin[i];
rt += rg > mid && rg <= r && rmax[rg] < pmax[i] && rmin[rg] > pmin[i];
}
for(int i = mid + , lf; i <= r; i++) {
lf = i - rmax[i] + rmin[i];
rt += lf <= mid && lf >= l && pmax[lf] < rmax[i] && pmin[lf] > rmin[i];
}
for(int i = mid, r1 = mid + , r2 = mid + ; i >= l && r1 <= r; i--) { // The min num is on the left.
while(r2 <= r && rmin[r2] > pmin[i]) bucket[r2 - rmax[r2] + N]++, r2++;
while(r1 <= r && rmax[r1] < pmax[i]) bucket[r1 - rmax[r1] + N]--, r1++;
if(r1 < r2) rt += bucket[i - pmin[i] + N];
}
for(int i = mid + ; i <= r; i++)
bucket[i - rmax[i] + N] = ;
// cout << rt << endl;
for(int i = mid + , l1 = mid, l2 = mid; i <= r && l2 >= l; i++) { // The min num is on the right.
while(l1 >= l && pmin[l1] > rmin[i]) bucket[l1 + pmax[l1]]++, l1--;
while(l2 >= l && pmax[l2] < rmax[i]) bucket[l2 + pmax[l2]]--, l2--;
if(l1 < l2) rt += bucket[i + rmin[i]];
}
for(int i = l; i <= mid; i++)
bucket[i + pmax[i]] = ; return rt + CDQDividing(l, mid) + CDQDividing(mid + , r);
} inline void solve() {
printf(Auto, CDQDividing(, n));
} int main() {
init();
solve();
return ;
}
Codeforces 526F Pudding Monsters - CDQ分治 - 桶排序的更多相关文章
- 【CF526F】Pudding Monsters cdq分治
[CF526F]Pudding Monsters 题意:给你一个排列$p_i$,问你有对少个区间的值域段是连续的. $n\le 3\times 10^5$ 题解:bzoj3745 Norma 的弱化版 ...
- 奇袭 CodeForces 526F Pudding Monsters 题解
考场上没有认真审题,没有看到该题目的特殊之处: 保证每一行和每一列都恰有一只军队,即每一个Xi和每一个Yi都是不一样 的. 于是无论如何也想不到复杂度小于$O(n^3)$的算法, 只好打一个二维前缀和 ...
- Codeforces 526F Pudding Monsters
先把题目抽象一下: 有一个静态的数组,求有多少个区间[i,j]满足:j-i==max{ai,...,aj}-min{ai,...,aj} 也就是要求max-min+i-j==0的区间数 所以肿么做呢? ...
- Codeforces 1045G AI robots [CDQ分治]
洛谷 Codeforces 简单的CDQ分治题. 由于对话要求互相看见,无法简单地用树套树切掉,考虑CDQ分治. 按视野从大到小排序,这样只要右边能看见左边就可以保证互相看见. 发现\(K\)固定,那 ...
- Codeforces 848C Goodbye Souvenir [CDQ分治,二维数点]
洛谷 Codeforces 这题我写了四种做法-- 思路 不管做法怎样,思路都是一样的. 好吧,其实不一样,有细微的差别. 第一种 考虑位置\(x\)对区间\([l,r]\)有\(\pm x\)的贡献 ...
- CodeForces526F:Pudding Monsters (分治)
In this problem you will meet the simplified model of game Pudding Monsters. An important process in ...
- [Codeforce526F]:Pudding Monsters(分治)
题目传送门 题目描述 由于各种原因,桐人现在被困在Under World(以下简称UW)中,而UW马上要迎来最终的压力测试——魔界入侵.唯一一个神一般存在的Administrator被消灭了,靠原本的 ...
- Codeforces 436D - Pudding Monsters(dp)
Codeforces 题目传送门 & 洛谷题目传送门 u1s1 这题数据范围有点迷惑啊--乍一看 \(\mathcal O(nm)\) 过不去,还以为是正解是 \(\mathcal O(n+m ...
- Codeforces 436D Pudding Monsters
题意简述 开始有无限长的一段格子,有n个格子种有布丁怪兽,一开始连续的布丁怪兽算一个布丁怪兽. 每回合你可以将一个布丁怪兽向左或右移动,他会在碰到第一个布丁怪兽时停下,并与其合并. 有m个特殊格子,询 ...
随机推荐
- is_readable() 函数检查指定的文件是否可读。
定义和用法 is_readable() 函数判断指定文件名是否可读. 语法 is_readable(file) 参数 描述 file 必需.规定要检查的文件. 说明 如果由 file 指定的文件或目录 ...
- Cf Round #403 B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed(二分答案)
The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed 我发现我最近越来越zz了,md 连调程序都不会了,首先要有想法,之后输出如果和期望的不一样就从输入开始一步一步地调啊,tmd现在 ...
- LeetCode110.平衡二叉树
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1. 示例 1: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7 返回 true . 示例 ...
- 使用spring的特殊bean完成分散配置
1.在使用分散配置时,spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml中写法如下: <!-- 引入db.properties文件, --> <context:pro ...
- 爬取笔下wenxue小说
import urllib.request from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import re def gethtml(url): page=urllib.request. ...
- C++的类型转换
一.类型转换名称和语法 1.C风格的强制类型转换(Type Cast)很简单,不管什么类型的转换统统是: TYPE b = (TYPE)a 2.C++风格的类型转换提供了4种类型转换操作符来应对 ...
- sitecore系统教程之媒体库
您可以管理媒体库中的所有媒体项目,例如要嵌入网页的图像或供访问者下载的图像.媒体库包含所有媒体项目,例如图像,文档,视频和音频文件. 在媒体库中,您可以: 将所有媒体文件保存在一个位置,并将其组织在与 ...
- 【转】通过Excel生成批量SQL语句,处理大量数据
经常会遇到这样的要求:用户给发过来一些数据,要我们直接给存放到数据库里面,有的是Insert,有的是Update等等,少量的数据我们可以采取最原始的办法,也就是在SQL里面用Insert into来实 ...
- 使用Hive读取ElasticSearch中的数据
本文将介绍如何通过Hive来读取ElasticSearch中的数据,然后我们可以像操作其他正常Hive表一样,使用Hive来直接操作ElasticSearch中的数据,将极大的方便开发人员.本文使用的 ...
- 创建一个简单的WCF程序2——手动开启/关闭WCF服务与动态调用WCF地址
一.创建WCF服务器 1.创建WCF服务器的窗体应用程序 打开VS2010,选择文件→新建→项目菜单项,在打开的新建项目对话框中,依次选择Visual C#→Windows→Windows窗体应用程序 ...
