使用yocs_velocity_smoother对机器人速度进行限制
yocs_velocity_smoother是一个速度、加速度限制器,用来防止robot navigation的速度/转速过快,加速度/快减速过大。Bound incoming velocity messages according to robot velocity and acceleration limits. The velocity smoother nodelet runs together with the kobuki_node to apply robot's velocity and acceleration limits to the incoming commands before resending them to the robot. It will however also work for any other generic ros mobile base driver.
输入下面命令安装yocs_velocity_smoother或者从GitHub上下载源代码进行编译。
sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-yocs-velocity-smoother
订阅的话题
- raw_cmd_vel:Input velocity commands. 原始速度指令
- odometry:We compare the output velocity commands to measured velocity to ensure we don't create very big jumps in the velocity profile.
- robot_cmd_vel:Alternatively, we can also compare the output velocity commands to end robot velocity commands to ensure we don't create very big jumps in the velocity profile. See robot_feedback parameter description below for more details.
发布的话题
- smooth_cmd_vel:Smoothed output velocity commands respecting velocity and acceleration limits. 限制幅度后的速度
launch文件
standalone.launch文件先运行一个名为nodelet_manager的nodelet manager节点,然后加载velocity_smoother.launch文件:
<!--
Example standalone launcher for the velocity smoother
-->
<launch>
<arg name="node_name" value="velocity_smoother"/>
<arg name="nodelet_manager_name" value="nodelet_manager"/>
<arg name="config_file" value="$(find yocs_velocity_smoother)/param/standalone.yaml"/>
<arg name="raw_cmd_vel_topic" value="raw_cmd_vel"/>
<arg name="smooth_cmd_vel_topic" value="smooth_cmd_vel"/>
<arg name="robot_cmd_vel_topic" value="robot_cmd_vel"/>
<arg name="odom_topic" value="odom"/> <!-- nodelet manager -->
<node pkg="nodelet" type="nodelet" name="$(arg nodelet_manager_name)" args="manager"/> <!-- velocity smoother -->
<include file="$(find yocs_velocity_smoother)/launch/velocity_smoother.launch">
<arg name="node_name" value="$(arg node_name)"/>
<arg name="nodelet_manager_name" value="$(arg nodelet_manager_name)"/>
<arg name="config_file" value="$(arg config_file)"/>
<arg name="raw_cmd_vel_topic" value="$(arg raw_cmd_vel_topic)"/>
<arg name="smooth_cmd_vel_topic" value="$(arg smooth_cmd_vel_topic)"/>
<arg name="robot_cmd_vel_topic" value="$(arg robot_cmd_vel_topic)"/>
<arg name="odom_topic" value="$(arg odom_topic)"/>
</include>
</launch>
在standalone.launch中使用nodelet_manager加载yocs_velocity_smoother/VelocitySmootherNodelet.
<!--
YOCS velocity smoother launcher
--> <launch>
<arg name="node_name" default="velocity_smoother"/>
<arg name="nodelet_manager_name" default="nodelet_manager"/>
<arg name="config_file" default="$(find yocs_velocity_smoother)/param/standalone.yaml"/>
<arg name="raw_cmd_vel_topic" default="raw_cmd_vel"/>
<arg name="smooth_cmd_vel_topic" default="smooth_cmd_vel"/>
<arg name="robot_cmd_vel_topic" default="robot_cmd_vel"/>
<arg name="odom_topic" default="odom"/> <node pkg="nodelet" type="nodelet" name="$(arg node_name)"
args="load yocs_velocity_smoother/VelocitySmootherNodelet $(arg nodelet_manager_name)"> <!-- parameters -->
<rosparam file="$(arg config_file)" command="load"/> <!-- velocity commands I/O -->
<remap from="$(arg node_name)/raw_cmd_vel" to="$(arg raw_cmd_vel_topic)"/>
<remap from="$(arg node_name)/smooth_cmd_vel" to="$(arg smooth_cmd_vel_topic)"/> <!-- Robot velocity feedbacks -->
<remap from="$(arg node_name)/robot_cmd_vel" to="$(arg robot_cmd_vel_topic)"/>
<remap from="$(arg node_name)/odometry" to="$(arg odom_topic)"/>
</node>
</launch>
standalone.yaml文件用于配置速度平滑参数:
# Example configuration:
# - velocity limits are around a 10% above the physical limits
# - acceleration limits are just low enough to avoid jerking # Mandatory parameters
speed_lim_v: 0.8 # Linear velocity limit
speed_lim_w: 5.4 # Angular velocity limit accel_lim_v: 0.3 # Linear acceleration limit
accel_lim_w: 3.5 # Angular acceleration limit # Optional parameters
frequency: 20.0 # Output messages rate. The velocity smoother keeps it regardless incoming messages rate, interpolating whenever necessary
decel_factor: 1.0 # Deceleration/acceleration ratio. Useful to make deceleration more aggressive # Robot velocity feedback type:
# 0 - none
# 1 - odometry
# 2 - end robot commands
robot_feedback: 2
速度限制测试
yocs_velocity_smoothe包的源文件中有一个测试程序,可以测试速度限制的效果。测试launch文件test_translational_smoothing.launch如下:
<!--Tests the velocity smoother with varied translational inputs.-->
<launch> <!-- Launch a nodelet manager node -->
<node pkg="nodelet" type="nodelet" name="nodelet_manager" args="manager"/> <!-- Launch a nodelet of type pkg/Type on manager manager -->
<node pkg="nodelet" type="nodelet" name="velocity_smoother" args="load yocs_velocity_smoother/VelocitySmootherNodelet nodelet_manager" output="screen">
<rosparam file="$(find yocs_velocity_smoother)/param/standalone.yaml" command="load"/>
<!-- Subscribed Topics -->
<remap from="velocity_smoother/odometry" to="odom"/>
<remap from="velocity_smoother/robot_cmd_vel" to="cmd_vel/output"/>
<remap from="velocity_smoother/raw_cmd_vel" to="cmd_vel/input"/>
<!-- Published Topics -->
<remap from="velocity_smoother/smooth_cmd_vel" to="cmd_vel/output"/>
</node> <!-- Launch test node -->
<node pkg="yocs_velocity_smoother" type="test_translational_input.py" name="test_translational_input" output="screen">
<remap from="test_translational_input/cmd_vel" to="cmd_vel/input"/>
<remap from="test_translational_input/odom" to="odom"/>
<!--<param name="velocity_maximum" value="0.50"/> -->
<param name="ramp_increment" value="0.01"/>
<param name="ramp_decrement" value="0.01"/>
</node>
</launch>
test_translational_input.py程序中根据加速度参数(ramp_increment、ramp_decrement)周期性的调整X方向的移动速度,并将cmd_vel和odom信息发布出去。注意在launch文件中又分别将test_translational_input/cmd_vel和test_translational_input/odom重映射为cmd_vel/input与odom.
#!/usr/bin/env python
import roslib
roslib.load_manifest('yocs_velocity_smoother')
import rospy import os
import sys
import time
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
from nav_msgs.msg import Odometry
'''
Varied translational input for a velocity smoother test.
''' STATE_RAMP_UP = 0
STATE_RAMP_LEVEL = 1
STATE_RAMP_DOWN = 2
STATE_ZERO = 3
STATE_UP = 4
STATE_DOWN = 5
STATE_UP_AGAIN = 6
STATE_NOTHING = 7 def main():
rospy.init_node("test_velocity_smoother_input")
cmd_vel_publisher = rospy.Publisher("~cmd_vel", Twist)
odom_publisher = rospy.Publisher("~odom", Odometry)
param = {}
param['velocity_maximum'] = rospy.get_param("~velocity_maximum", 0.50)
param['ramp_increment'] = rospy.get_param("~ramp_increment", 0.02)
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : ramp increment [%f]",param['ramp_increment'])
param['ramp_decrement'] = rospy.get_param("~ramp_decrement", 0.02)
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : ramp decrement [%f]",param['ramp_decrement'])
cmd_vel = Twist()
cmd_vel.linear.x = 0
cmd_vel.linear.y = 0
cmd_vel.linear.z = 0
cmd_vel.angular.x = 0
cmd_vel.angular.y = 0
cmd_vel.angular.z = 0
odom = Odometry()
odom.header.frame_id = "base_link"
odom.pose.pose.position.x = 0.0
odom.pose.pose.position.y = 0.0
odom.pose.pose.position.z = 0.0
odom.pose.pose.orientation.x = 0.0
odom.pose.pose.orientation.y = 0.0
odom.pose.pose.orientation.z = 0.0
odom.pose.pose.orientation.w = 1.0 odom.pose.covariance[0] = 0.1
odom.pose.covariance[7] = 0.1
odom.pose.covariance[35] = 0.2
odom.pose.covariance[14] = 10.0
odom.pose.covariance[21] = 10.0
odom.pose.covariance[28] = 10.0 odom.twist.twist.linear.x = 0.0
odom.twist.twist.linear.y = 0.0
odom.twist.twist.linear.z = 0.0
odom.twist.twist.angular.x = 0.0
odom.twist.twist.angular.y = 0.0
odom.twist.twist.angular.z = 0.0
state = STATE_RAMP_UP
count = 0
count_max = 100
publish = True
#period = 0.01
timer = rospy.Rate(100) # 10hz
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : STATE_RAMP_UP")
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
if state == STATE_RAMP_UP:
cmd_vel.linear.x = cmd_vel.linear.x + param['ramp_increment']
if cmd_vel.linear.x >= param['velocity_maximum']:
state = STATE_RAMP_LEVEL
count = 0
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : STATE_RAMP_UP -> STATE_RAMP_LEVEL")
elif state == STATE_RAMP_LEVEL:
if count > count_max: # 0.5s
state = STATE_RAMP_DOWN
count = 0
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : STATE_RAMP_LEVEL -> STATE_RAMP_DOWN")
else:
count = count + 1
elif state == STATE_RAMP_DOWN:
cmd_vel.linear.x = cmd_vel.linear.x - param['ramp_decrement']
if cmd_vel.linear.x <= 0.0:
cmd_vel.linear.x = 0.0
state = STATE_ZERO
count = 0
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : STATE_RAMP_DOWN -> STATE_ZERO")
elif state == STATE_ZERO:
if count > count_max: # 0.5s
state = STATE_UP
cmd_vel.linear.x = param['velocity_maximum']
count = 0
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : STATE_ZERO -> STATE_UP")
else:
count = count + 1
elif state == STATE_UP:
if count > count_max: # 0.5s
state = STATE_DOWN
cmd_vel.linear.x = 0.0
count = 0
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : STATE_UP -> STATE_DOWN")
else:
count = count + 1
elif state == STATE_DOWN:
if count > count_max: # 0.5s
#state = STATE_UP_AGAIN
#cmd_vel.linear.x = param['velocity_maximum']
#rospy.loginfo("Test Input : STATE_DOWN -> STATE_UP_AGAIN")
state = STATE_RAMP_UP
cmd_vel.linear.x = 0.0
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : STATE_DOWN -> STATE_RAMP_UP")
count = 0
else:
count = count + 1
elif state == STATE_UP_AGAIN:
if count > count_max: # 0.5s
state = STATE_NOTHING
count = 0
publish = False
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : STATE_UP_AGAIN -> STATE_NOTHING")
else:
count = count + 1
elif state == STATE_NOTHING:
if count > count_max: # 0.5s
state = STATE_RAMP_UP
cmd_vel.linear.x = 0.0
count = 0
publish = True
rospy.loginfo("Test Input : STATE_NOTHING -> STATE_RAMP_UP")
else:
count = count + 1
if publish:
odom.twist.twist.linear.x = cmd_vel.linear.x
cmd_vel_publisher.publish(cmd_vel)
else:
# How to fake it when it's not publishing a cmd velocity? Up to the velocity controller there
odom.twist.twist.linear.x = cmd_vel.linear.x
odom.header.stamp = rospy.Time().now()
odom_publisher.publish(odom)
timer.sleep() if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
输入下面的命令运行测试程序:
roslaunch yocs_velocity_smoother test_translational_smoothing.launch
可以使用rqt_plot工具绘制速度变化曲线,在终端中输入下面的命令进行绘制:
rqt_plot /cmd_vel/output/linear/x
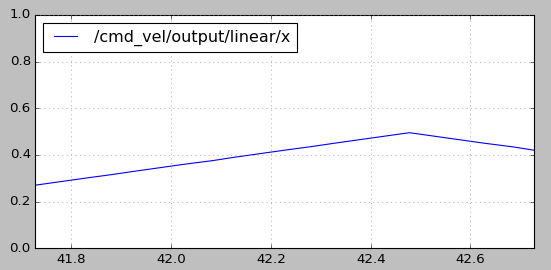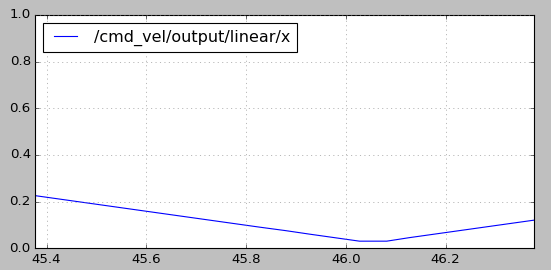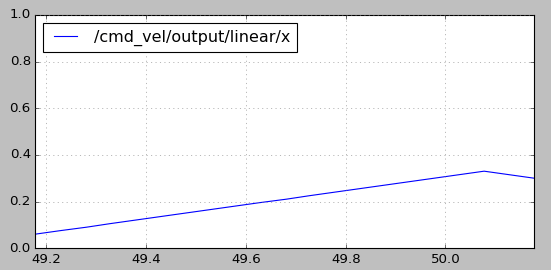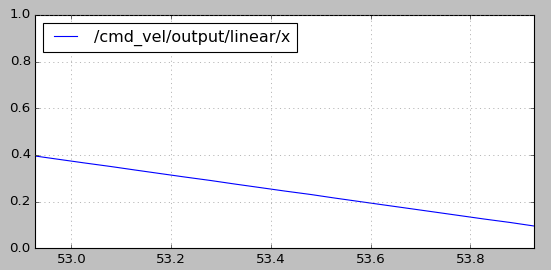
可以将默认配置文件中的速度上限(speed_lim_v)从0.8改为0.4,再次运行测试程序。从速度曲线图中可以看出,最大速度已经被限制在0.4m/s

velocity_smoother还可以防止速度指令的跳变引起机器人的抖动。比如使用cmd_vel_mux进行速度切换时,前一个控制速度为2m/s,某一时刻切换到另一个速度假设为15m/s,如果不做处理瞬时加速度会很大。如下图所示,使用velocity_smoother对加速度进行限制,在速度指令跳变时能够使其不超出限制:
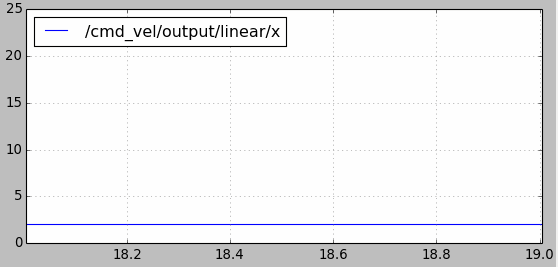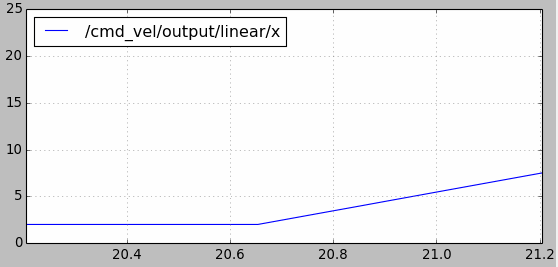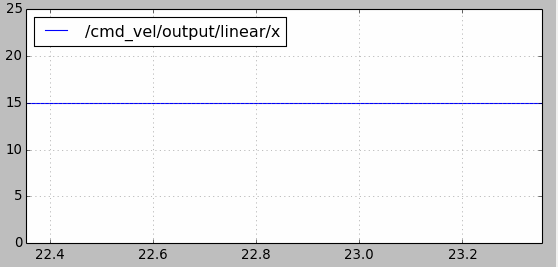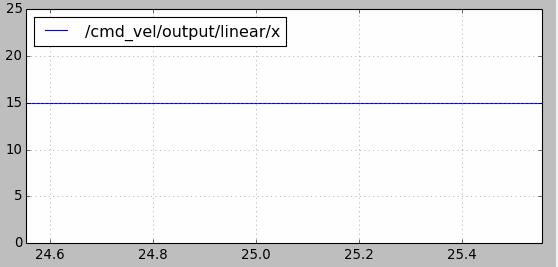
另外要注意yocs_velocity_smoother包中使用了动态参数配置的功能(参考ROS的参数应用以及动态调整),在yocs_velocity_smoother/cfg文件夹下的params.cfg文件如下。注意standalone.yaml配置文件中的速度和加速度参数不要超过cfg文件中动态参数的最大值。
#!/usr/bin/env python
PACKAGE = "yocs_velocity_smoother"
from dynamic_reconfigure.parameter_generator_catkin import *
gen = ParameterGenerator()
gen.add("speed_lim_v", double_t, 0, "Maximum linear velocity", 1.0, 0.0, 100.0)
gen.add("speed_lim_w", double_t, 0, "Maximum angular velocity", 5.0, 0.0, 100.0)
gen.add("accel_lim_v", double_t, 0, "Maximum linear acceleration", 0.5, 0.0, 100.0)
gen.add("accel_lim_w", double_t, 0, "Maximum angular acceleration", 2.5, 0.0, 100.0)
gen.add("decel_factor", double_t, 0, "Deceleration to acceleration ratio", 1.0, 0.0, 10.0)
# Second arg is node name it will run in (doc purposes only), third is generated filename prefix
exit(gen.generate(PACKAGE, "velocity_smoother_configure", "params"))
params.cfg其实是一个基于python的模块,首先创建一个ParameterGenerator对象,然后调用其add()函数将参数添加到参数列表中。add()的参数含义分别是:参数名,参数类型,级别,描述,缺省值,最小值,最大值。
参考:
使用yocs_velocity_smoother对机器人速度进行限制的更多相关文章
- ROS探索总结(十九)——如何配置机器人的导航功能
1.概述 ROS的二维导航功能包,简单来说,就是根据输入的里程计等传感器的信息流和机器人的全局位置,通过导航算法,计算得出安全可靠的机器人速度控制指令.但是,如何在特定的机器人上实现导航功能包的功能, ...
- ROS中测试机器人里程计信息
在移动机器人建图和导航过程中,提供相对准确的里程计信息非常关键,是后续很多工作的基础,因此需要对其进行测试保证没有严重的错误或偏差.实际中最可能发生错误的地方在于机器人运动学公式有误,或者正负号不对, ...
- ROS探索总结(十九)——怎样配置机器人的导航功能
1.概述 ROS的二维导航功能包.简单来说.就是依据输入的里程计等传感器的信息流和机器人的全局位置,通过导航算法,计算得出安全可靠的机器人速度控制指令. 可是,怎样在特定的机器人上实现导航功能包的功能 ...
- 基于 Mathematica 的机器人仿真环境(机械臂篇)[转]
完美的教程,没有之一,收藏学习. 目的 本文手把手教你在 Mathematica 软件中搭建机器人的仿真环境,具体包括以下内容(所使用的版本是 Mathematica 11.1,更早的版本可能缺少某些 ...
- RPA简介
开篇: 公司正在全面推广RPA,正好借此机会学习一下,发现国内对RPA的了解较少,萌生了在博客园开博,同时锻炼一下自己的输出能力,纯笔记,如有不足之处,请指正,共勉. 阅读目录: 1. 什么是RPA ...
- [转]RPA简介
本文转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/wendyzheng/articles/9211530.html 开篇: 公司正在全面推广RPA,正好借此机会学习一下,发现国内对RPA的了解 ...
- 全向轮运动学与V-rep中全向移动机器人仿真
Wheeled mobile robots may be classified in two major categories, omnidirectional and nonholonomic. O ...
- Track and Follow an Object----4
原创博文:转载请标明出处(周学伟):http://www.cnblogs.com/zxouxuewei/tag/ ntroduction: 在本示例中,我们将探索包含Kinect摄像头的自主行为. 这 ...
- ROS导航包的介绍
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/handsome_for_kill/article/details/53130707#t3 ROS导航包的应用 利用ROS Navigation ...
随机推荐
- 《剑指offer》-判断对称二叉树
题目描述 请实现一个函数,用来判断一颗二叉树是不是对称的.注意,如果一个二叉树同此二叉树的镜像是同样的,定义其为对称的. 思路上还是广度优先搜索(BFS)来做的.BFS是依托于STL的queue作为容 ...
- DDD领域模型之分配权限(十三)
权限分配和权限查找. 在DDD.Domain工程中新建:BAS_PermissionAssign类 public partial class BAS_PermissionAssgin:Aggreate ...
- SPFILEOPENBANKDB.ORA 手动编辑产生问题
因为最近启动后发现经常内存高占用,一个ORACLE实例占用超过7G内存,两个就15G,卡的让人坐立不安.于是百度了一下,使用下面的命令将sga_max_size从7G修改为200M show para ...
- Mac上c语言连接mysql遇到的问题
参照<Beginning Linux Programming>上的例程写了一个连接mysql的c语言小程序connect1.c.但是按照书上的编译命令无法编译.然后经过查阅资料解决了问题. ...
- 启用mysql的sql日志
在mysql命令行或者客户端管理工具中执行:SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "general_log%"; 结果: general_log OFFgeneral_log_f ...
- A+B Problem(再升级)
洛谷P1832 A+B Problem(再升级) ·给定一个正整数n,求将其分解成若干个素数之和的方案总数. 先说我的垃圾思路,根本没有验证它的正确性就xjb写的,过了垃圾样例,还水了20分,笑哭.. ...
- Spring框架学习06——AOP底层实现原理
在Java中有多种动态代理技术,如JDK.CGLIB.Javassist.ASM,其中最常用的动态代理技术是JDK和CGLIB. 1.JDK的动态代理 JDK动态代理是java.lang.reflec ...
- SSID 已经一个路由器设多个SSID
SSID(Service Set Identifier) SSID,AP唯一的ID码,许多人认为可以将SSID写成ESSID,其实不然,SSID是个笼统的概念,包含了ESSID和BSSID,用来区 ...
- 在webpack中使用postcss之插件cssnext
学习了precss插件包在webpack中的用法后,下面介绍postcss的另一个重要插件cssnext,步骤没有precss用法详细,主要介绍css4的语法,cssnext目前支持了部分新特性,你可 ...
- Struts2 架构图
Struts2架构图 请求首先通过Filter chain,Filter主要包括ActionContextCleanUp,它主要清理当前线程的ActionContext和Dispatcher:Filt ...
