SPI协议背景知识简介与FTDI的FT4232H配成USB to SPI(MPSSE)使用实例
MPSSE Application Example:
http://ftdichip.cn/Support/SoftwareExamples/MPSSE.htm
MPSSE: AN_129 FTDI USB To JTAG TAP Example
MPSS: AN_114 FTDI USB to SPI Example
MPSSE: AN_113 FTDI USB to I2C Example
MPSS: AN_114 FTDI USB to SPI Example
Acronyms and Abbreviations
| Terms | Description |
|---|---|
| MPSSE | Multi Purpose Synchronous Serial Engine |
| I2C | Inter-Integrated Circuit |
| JTAG | Joint Test Action Group |
| SPI | Serial Peripheral Interface |
| SPI Master | A SPI device that initiates and manages serial communication to all devices connected to its SPI bus. |
| SPI Slave | A SPI device that responds to commands sent to it by the SPI master. |
| MISO | Master In, Slave Out |
| MOSI | Master Out, Slave In |
| Serial EEPROM | A programmable memory chip that uses a bitwise serial interface such as I2C or SPI. |
| USB | Universal Serial bus |
FTDI MPSSE(Multi-Protocol Synchronous Serial Engine)
Using the MPSSE can simplify the synchronous serial protocol (USB to SPI, I2C, JTAG, etc.) design. This application note illustrates how to use the MPSSE of the FT2232H to interface with the SPI bus. The FT232H and FT4232H can also be used with the example in this document, though pin-out and port selection will need to match the respective part.
Users can use the example schematic (refer to Figure 3) and software code (section 3) to begin their design.
Note that software code listing is provided as an illustration only and not supported by FTDI.
1 Introduction
The FT2232H and FT4232H are the FTDI's first USB 2.0 Hi-Speed(480Mbits/s) USB to UART/FIFO ICs.
They have the capability of being configured in a variety of serial interfaces using the internal MPSSE (Multi-Protocol Synchronous Serial Engine). The FT2232H device has two independent ports, both of which can be configured using MPSSE while only Channel A and B of FT4232H can be configured using MPSSE.
1.1 Overview & Scope
This application note gives details of how to interface and configure the FT2232H to read and write data from a host PC to a serial EEPROM over the serial SPI interface bus. This note includes:
- Overview of SPI communications interface.
- Hardware example of a USB to a serial EEPROM SPI interface using the FT2232H.
- Code example in C++ showing how to configure the FT2232H in SPI mode.
- Oscilloscope plots showing example SPI read and write cycles.
1.2 Overview of SPI Interface
The SPI (Serial to Peripheral Interface) is a master/slave synchronous serial bus that consists of 4 signals.
Both command signals and data are sent across the interface.
The SPI master initiates all data transactions.
There is no fixed bit length in SPI.
Full duplex data transfers can be made up to 30Mbits/sec with the FT2232H.
A generic SPI system consists of the following signals and is illustrated in Figure 1.:
- SCLK(Serial Clock) from master to slave.
- CS(Chip Select) from master.
- MOSI(Serial Data Out, also called Master Out Slave In) from master.
- MISO(Serial Data In, also called Master In Slave Out) from slave.
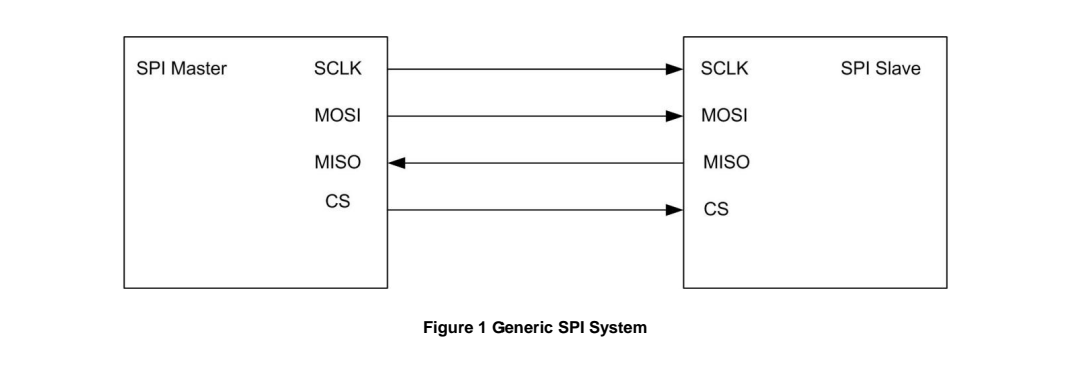
The FT2232H always acts as the SPI master. Multiple slave devices can be enabled by multiplexing the chip select line. As SPI data is shifted out of the master and in to a slave device, SPI data will also be shifted out from the slave and clocked in to the master.
Depending on which type of slave device is being
implemented, data can be shifted MSB first or LSB first.
Slave devices can have active low or active high chip select inputs.
This SPI device uses SPI Mode 0, with active low Chip Select.
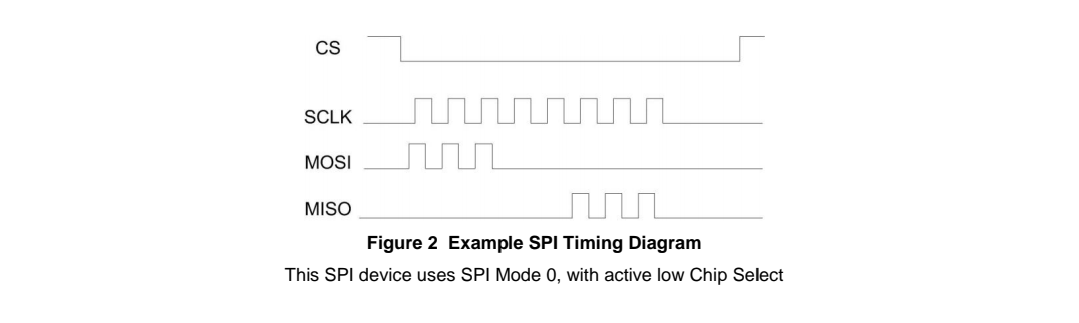
In addition, the SPI interface has 4 unique modes of clock phase(CPHA) and clock polarity (CPOL), known as Mode 0, Mode 1, Mode 2 and Mode 3. Table 1 summarizes these modes:
| Mode | CPOL | CPHA |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 |
Table 1 Clock Phase/Polarity Modes
For CPOL = 0, the base (inactive) level of SCLK is 0. In this mode:
- When CPHA = 0, data will be read in on the rising edge of SCLK, and data will be clocked out on the falling edge of SCLK.
- When CPHA = 1, data will be read in on the falling edge of SCLK, and data will be clocked out on the rising edge of SCLK.
For CPOL = 1, the base (inactive) level of SCLK is 1. In this mode:
- When CPHA = 0, data will be read in on the falling edge of SCLK, and data will be clocked out on the rising edge of SCLK.
- When CPHA = 1, data will be read in on the rising edge of SCLK, and data will be clocked out on the falling edge of SCLK.
It is worth noting that the SPI slave interface can be implemented in various ways. The FT2232H can be configured to handle these different implementations.
It is recommended that designers review the SPI Slave data sheet to determine the SPI mode implementation.
FTDI device can only support mode 0 and mode 2 due to the limitation of MPSSE engine.
3.2 FT2232H to 93LC56 Read/Write Timing on Scope
The following screenshots show examples of the Read and write waveforms on the SPI interface. These are provided to illustrate the operational details of the SPI write and read commands sent from the FT2232H to the 93LC56 EEPROM:
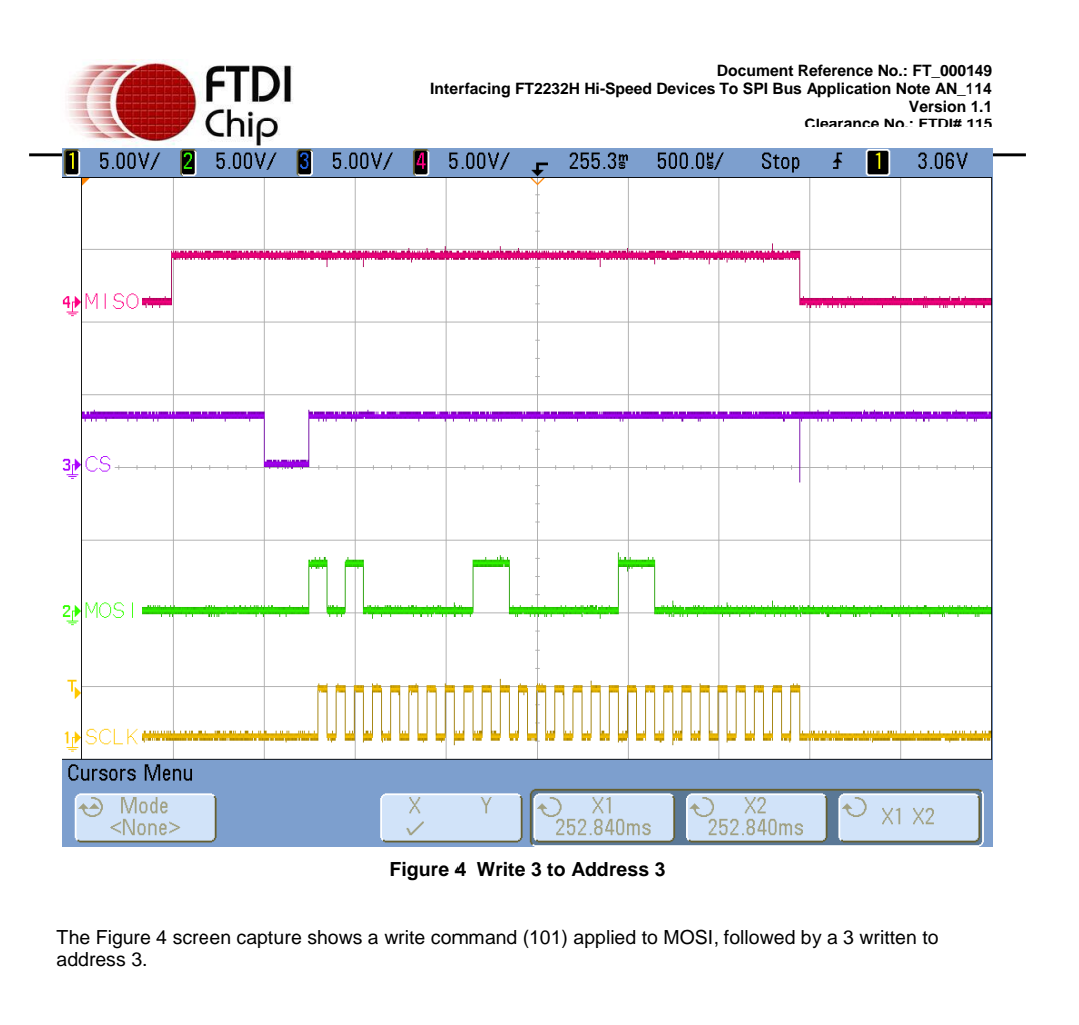
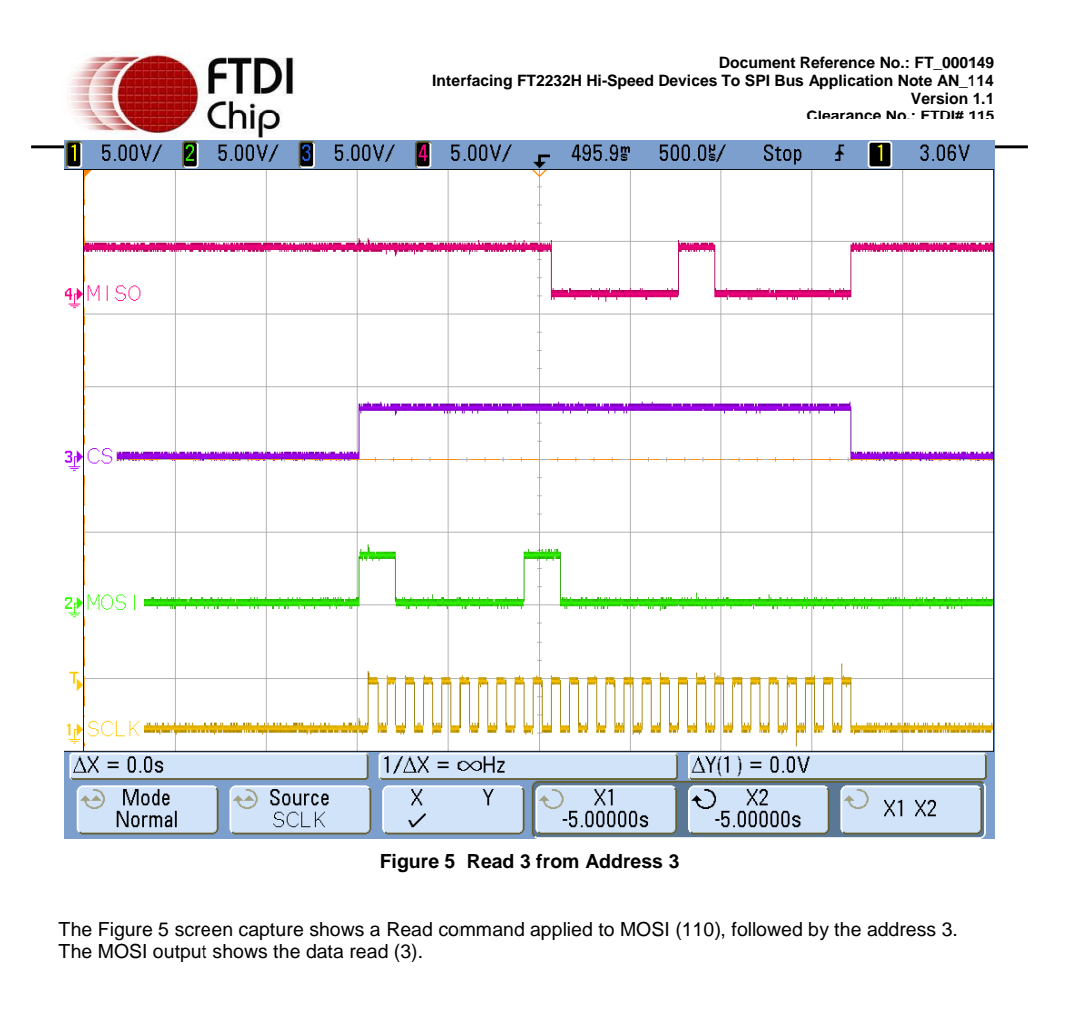
SPI协议背景知识简介与FTDI的FT4232H配成USB to SPI(MPSSE)使用实例的更多相关文章
- Http协议基本知识简介
HTTP协议是指超文本传输协议,位于应用层,HTTP规定数据格式,然后用tcp进行传输. 请求响应模式:简单理解为客户端对服务器发起请求,服务器响应客户端. 主要特点 无连接:无连接的含义是限制每次连 ...
- 『Python基础-1 』 编程语言Python的基础背景知识
#『Python基础-1 』 编程语言Python的基础背景知识 目录: 1.编程语言 1.1 什么是编程语言 1.2 编程语言的种类 1.3 常见的编程语言 1.4 编译型语言和解释型语言的对比 2 ...
- [SPI]SPI协议详解
转自:https://my.oschina.net/freeblues/blog/67400 1.SPI协议简介 1.1.SPI协议概括 SPI,是英语Serial Peripheral interf ...
- [SPI&I2C]I2C和SPI协议介绍
IIC vs SPI 现今,在低端数字通信应用领域,我们随处可见IIC (Inter-Integrated Circuit) 和 SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface)的身 ...
- Mozilla研究—深入理解mozilla所需的背景知识
mozilla是一个以浏览器为中心的软件平台,它在我们平台中占有重要地位.我们用它来实现WEB浏览器.WAP浏览器.邮件系统.电子书和帮助阅读器等应用程序.为此,我最近花了不少时间去阅读mozilla ...
- Tomcat(一):背景知识和安装tomcat
Tomcat系列文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/f-ck-need-u/p/7576137.html 1. 基础背景知识 1.1 java和jdk概念 无论是何种程序,要能在计算机 ...
- jenkins X实践系列(1) —— 背景知识
本文介绍jenkins X(以下简称jx)相关的背景技术. jenkins X 简介 Jenkins X 是一个高度集成化的CI/CD平台,基于Jenkins和Kubernetes实现,旨在解决微服务 ...
- {Python之进程} 背景知识 什么是进程 进程调度 并发与并行 同步\异步\阻塞\非阻塞 进程的创建与结束 multiprocess模块 进程池和mutiprocess.Poll
Python之进程 进程 本节目录 一 背景知识 二 什么是进程 三 进程调度 四 并发与并行 五 同步\异步\阻塞\非阻塞 六 进程的创建与结束 七 multiprocess模块 八 进程池和mut ...
- http协议与url简介(转)
一 知识简介 HTTP:(Hypertext transfer protocol)超文本传输协议,是用于从万维网(WWW:World Wide Web)服务器传输超文本到本地浏览器的传送协议. URL ...
- 『Linux基础 - 2 』操作系统,Linux背景知识和Ubuntu操作系统安装
这篇笔记记录了以下几个知识点: 1.目前常见的操作系统及分类,虚拟机 2.Linux操作系统背景知识,Windows和Linux两个操作系统的对比 3.在虚拟机中安装Ubuntu系统的详细步骤 OS( ...
随机推荐
- Stream流式编程工具类,开发必备
把自己写的流式编程工具分享出来,不涉及公司业务,非常便捷,不用在业务层看到一条龙式的Stream代码了: 大家用的最多的应该是转list,转set,以及setVFromE: 觉得好用点个赞就行 imp ...
- sonarqube+gitlab+jenkins+maven集成搭建(二)
SonarQubeScanner 下载[root@localhost ~]# wget https://binaries.sonarsource.com/Distribution/sonar-scan ...
- EFCore与List的随机算法
IQurable<T>,数据库层面的随机,OrderBy(x => EF.Functions.Random()); _coreDbContext.org.OrderBy(x => ...
- .net6 Api添加跨域
参照:(7条消息) .net6使用最小api(8)- 开启跨域模式,通过扩展服务实现_hailang2ll的博客-CSDN博客 步骤: 一.在appsetting.json里添加配置文件 //配置文件 ...
- Java---switch...case中case可以匹配些什么
switch-case语句 case 标签可以是 : •类型为 char.byte.short 或 int 的常量表达式. •枚举常量. •从 Java SE 7 开始,case 标签还可以是字符串字 ...
- JS的哪些新特性,你都用过么?
@charset "UTF-8"; .markdown-body { line-height: 1.75; font-weight: 400; font-size: 15px; o ...
- SpringAI更新:废弃tools方法、正式支持DeepSeek!
AI 技术发展很快,同样 AI 配套的相关技术发展也很快.这不今天刚打开 Spring AI 的官网就发现它又又又又更新了,而这次更新距离上次更新 M7 版本才不过半个月的时间,那这次 Spring ...
- QuickSort之C#实现
/// <summary> /// 快速排序中的切分 /// lIndex已经是基准值,i记录基准值的大小值的边界,j记录目前遍历的边界: /// i值必须从lIndex+1开始,因为基准 ...
- Jupyter notebook添加Anaconda中的虚拟环境
1.创建虚拟环境 conda create -n your_virtual_env python=3.6 2.激活新创建的环境 activate your_virtual_env 3.安装nb_con ...
- B1037 在霍格沃茨找零钱
如果你是哈利·波特迷,你会知道魔法世界有它自己的货币系统 -- 就如海格告诉哈利的:"十七个银西可(Sickle)兑一个加隆(Galleon),二十九个纳特(Knut)兑一个西可,很容易.& ...
