初探PApplet窗口打开方式(Processing程序)
使用Processing快6年了,是时候回过头来看看它的"main"方法了,也就是它从哪出生的?~~~
源码学习
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// MAIN
/**
* main() method for running this class from the command line.
* <p>
* Usage: PApplet [options] <class name> [sketch args]
* <ul>
* <li>The [options] are one or several of the parameters seen below.
* <li>The class name is required. If you're running outside the PDE and
* your class is in a package, this should include the full name. That means
* that if the class is called Sketchy and the package is com.sketchycompany
* then com.sketchycompany.Sketchy should be used as the class name.
* <li>The [sketch args] are any command line parameters you want to send to
* the sketch itself. These will be passed into the args[] array in PApplet.
* <p>
* The simplest way to turn and sketch into an application is to
* add the following code to your program:
* <PRE>static public void main(String args[]) {
* PApplet.main("YourSketchName");
* }</PRE>
* That will properly launch your code from a double-clickable .jar
* or from the command line.
* <PRE>
* Parameters useful for launching or also used by the PDE:
*
* --location=x,y Upper-lefthand corner of where the applet
* should appear on screen. If not used,
* the default is to center on the main screen.
*
* --present Presentation mode: blanks the entire screen and
* shows the sketch by itself. If the sketch is
* smaller than the screen, the background around it
* will use the --window-color setting.
*
* --hide-stop Use to hide the stop button in situations where
* you don't want to allow users to exit. also
* see the FAQ on information for capturing the ESC
* key when running in presentation mode.
*
* --stop-color=#xxxxxx Color of the 'stop' text used to quit an
* sketch when it's in present mode.
*
* --window-color=#xxxxxx Background color of the window. The color used
* around the sketch when it's smaller than the
* minimum window size for the OS, and the matte
* color when using 'present' mode.
*
* --sketch-path Location of where to save files from functions
* like saveStrings() or saveFrame(). defaults to
* the folder that the java application was
* launched from, which means if this isn't set by
* the pde, everything goes into the same folder
* as processing.exe.
*
* --display=n Set what display should be used by this sketch.
* Displays are numbered starting from 1. This will
* be overridden by fullScreen() calls that specify
* a display. Omitting this option will cause the
* default display to be used.
*
* Parameters used by Processing when running via the PDE
*
* --external set when the applet is being used by the PDE
*
* --editor-location=x,y position of the upper-lefthand corner of the
* editor window, for placement of applet window
*
* All parameters *after* the sketch class name are passed to the sketch
* itself and available from its 'args' array while the sketch is running.
*
* @see PApplet#args
* </PRE>
*/
static public void main(final String[] args) {
runSketch(args, null);
}
/**
* Convenience method so that PApplet.main(YourSketch.class)
* launches a sketch, rather than having to call getName() on it.
*/
static public void main(final Class<?> mainClass, String... args) {
main(mainClass.getName(), args);
}
/**
* Convenience method so that PApplet.main("YourSketch") launches a sketch,
* rather than having to wrap it into a single element String array.
* @param mainClass name of the class to load (with package if any)
*/
static public void main(final String mainClass) {
main(mainClass, null);
}
/**
* Convenience method so that PApplet.main("YourSketch", args) launches a
* sketch, rather than having to wrap it into a String array, and appending
* the 'args' array when not null.
* @param mainClass name of the class to load (with package if any)
* @param sketchArgs command line arguments to pass to the sketch's 'args'
* array. Note that this is <i>not</i> the same as the args passed
* to (and understood by) PApplet such as --display.
*/
static public void main(final String mainClass, final String[] sketchArgs) {
String[] args = new String[] { mainClass };
if (sketchArgs != null) {
args = concat(args, sketchArgs);
}
runSketch(args, null);
}
还有一个超长,也是最重要的runSketch()我这就不贴了。。。
可以看到,主要有两种方法运行PApplet对象,即JFrame窗口。如下:
PApplet.main()
下面是默认的pde输出程序自动生成的.java文件中的main方法:
static public void main(String[] passedArgs) {
String[] appletArgs = new String[] { "test4run" };
if (passedArgs != null) {
PApplet.main(concat(appletArgs, passedArgs));
} else {
PApplet.main(appletArgs);
}
}
一般只需调用PApplet.main()即可,参数为一个字符串数组,如果只填一个也可,填类名,必须一致,不然会报错!如果标准填法,如下:
String[] appletArgs = new String[] { "--present", "--window-color=#FFFFFF", "--stop-color=#cccccc", "Appname" };
这些字符串都是作为参数传给runSketch(),把相应的开关打开配置参数,简单看一下:
/*
* --location=x,y 窗口的悬浮位置,相对于桌面窗口坐标系,默认是居中
*
* --present 展示模式,全屏,有个底色,即window-color,只要size尺寸小于屏幕大小未填充区域则显示底色
*
* --hide-stop 展示模式中是否隐藏stop按钮,当然即使隐藏ESC仍旧有效
*
* --stop-color=#xxxxxx stop按钮颜色,主要是防止和底色相近难以辨别
*
* --window-color=#xxxxxx 底色
*
* --sketch-path 项目目录,针对保存帧等写操作的路径参数
*
* --display=n 显示的窗口索引,这和实际的显示设备和系统标定的显示标号相挂钩
*
* --external 扩展的一些方法判断依据(一般作为一个布尔值使用)[待研究]
*
* --editor-location=x,y 编辑器窗口位置,方便定义应用窗口位置[待研究]
*/
PApplet.runSketch()
这一种方法比较灵活,入口函数启动如下(kotlin):
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var app = ShowApp()
PApplet.runSketch(arrayOf("show"),app)
}
注意需要new一个PApplet对象,然后作为第二参数传入,第一参数类型为String[]。当然也可以在此拓展,我们可以任意创建窗口,实现多窗口开发或展示(kotlin):
var bsapp = BoardShowApp()
var bsapp2 = BoardShowApp()
PApplet.runSketch(arrayOf("BoardShow1"),bsapp)
PApplet.runSketch(arrayOf("BoardShow2"),bsapp2)
如果读者细心学习Processing官方示例,有个多窗口应用的范例(MultipleWindows):
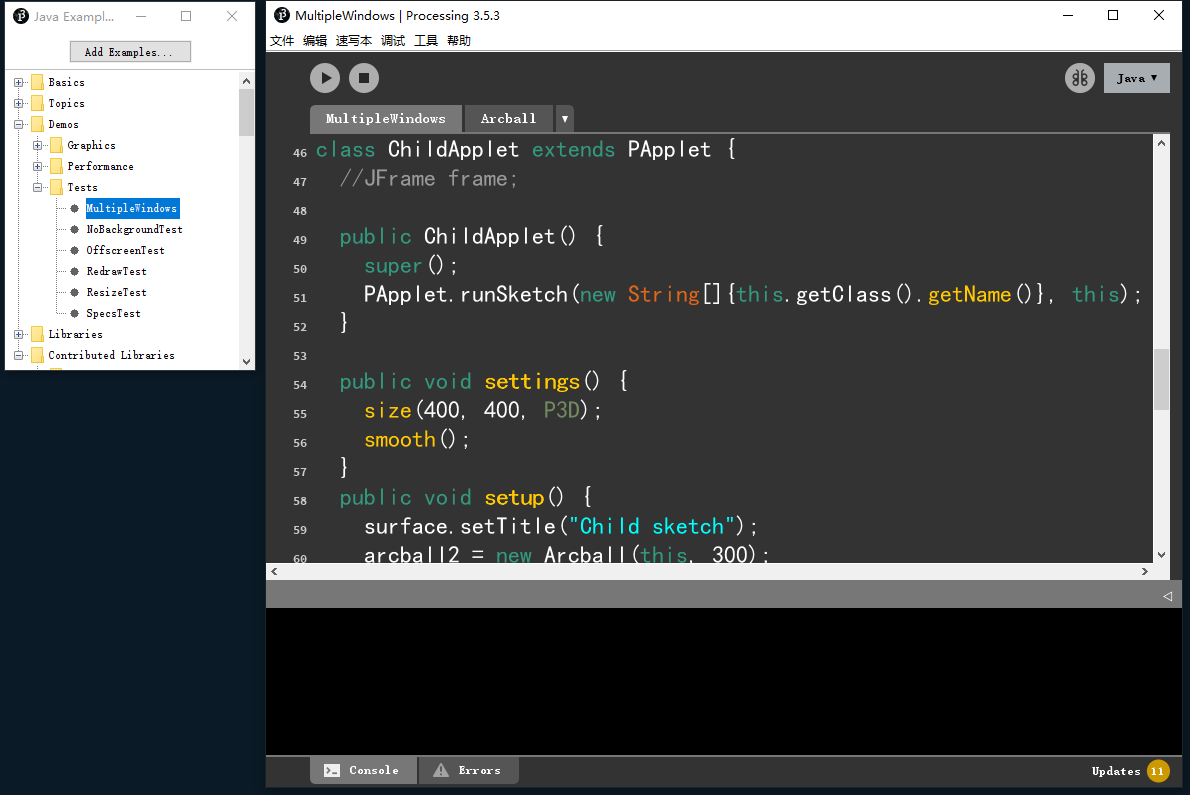
你会发现它就创建了一个PApplet类ChildApplet,作为子窗口,然后在构造器中使用了上述开启窗口的方法----PApplet.runSketch()。
笔者发现不再构造器中运行runSketch是无效的,因此如果在运行时想要打开第二个或多个窗口,必须在子类构造时执行这个方法。至于子窗口的种种参数那么跟surface对象有关了,我们往后再聊。
附件
下面是完整代码的参考:
import processing.core.*;
import processing.data.*;
import processing.event.*;
import processing.opengl.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test4run extends PApplet {
public void setup() {
}
public void draw() {
}
public void settings() {
size(400, 400);
}
static public void main(String[] passedArgs) {
String[] appletArgs = new String[] { "Test4run" };
if (passedArgs != null) {
PApplet.main(concat(appletArgs, passedArgs));
} else {
PApplet.main(appletArgs);
}
}
}
import processing.core.PApplet
class ChildApp : PApplet() {
override fun settings() {
size(400, 400)
smooth()
}
override fun setup() {
surface.setTitle("Child sketch")
}
override fun draw() {
background(0)
}
override fun mousePressed() {
}
override fun mouseDragged() {
}
//JFrame frame;
init {
runSketch(arrayOf(this.javaClass.name), this)
}
}
class ShowApp : PApplet(){
val childapp = ChildApp()
override fun settings() {
size(800,400)
}
override fun setup() {
}
override fun draw() {
background(20)
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var sapp = ShowApp()
var sapp2 = ShowApp()
PApplet.runSketch(arrayOf("Show1"),sapp)
PApplet.runSketch(arrayOf("Show2"),sapp2)
}
有哪里出现遗漏的或是错误的讲解,请指正,感谢您的阅读!
初探PApplet窗口打开方式(Processing程序)的更多相关文章
- Xcode 的正确打开方式——Debugging(转载)
Xcode 的正确打开方式——Debugging 程序员日常开发中有大量时间都会花费在 debug 上,从事 iOS 开发不可避免地需要使用 Xcode.这篇博客就主要介绍了 Xcode 中几种能 ...
- 添加/删除/修改Windows 7右键的“打开方式”
右键菜单添加/删除"打开方式" 此"打开方式"非系统的"打开方式",二者可以并存. 右键菜单添加"打开方式" 在HKEY ...
- 解决:win7右键打开方式添加应用程序无法设置和删除多余的打开方式
win7右键打开方式添加应用程序无法设置 点击“开始”—“运行”,输入“regedit”打开注册表,在“HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Applications\”中找到无法添加的程序 ( 比如“ ...
- windows右键打开方式里面添加新的应用程序
1.打开注册表编辑器.打开运行窗口,快捷键,开始+R.输入“regedit”,回车确定. 2.进入注册表编辑器的HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT文件夹下的*子文件夹下的shell文件夹. 3.右键s ...
- 关于无法把程序(Adobe Fireworks CS5)添加到打开方式的解决办法
关于无法把程序(Adobe Fireworks CS5)添加到打开方式的解决办法 最近换了新版的Adobe Fireworks CS5,发现打开图片文件时在右键“打开方式”里仍然是以前的Firewor ...
- 删除 Mac OS X 中“打开方式”里重复或无用的程序列表
如果右键菜单的「打开方式」里出现了已不存在的应用程序或者重复的项目,打开终端,执行以下命令: /System/Library/Frameworks/CoreServices.framework/Ver ...
- python实现应用程序在右键菜单中添加打开方式
最近项目组开发的一个小工具想要在右键菜单中添加打开方式,以有道云笔记为例进行了需求拆解和代码编写 1.需求拆解: 如何实现手动添加右键菜单的打开方式: Step1:打开注册表编辑器,Win+R-> ...
- ubuntu 添加右键打开方式,无法添加程序打开方式
最近把工作环境迁移到ubuntu,装了WPS for Linux ,说实话确实是十分良心啊!运行效率奇高,绿色无广告,并且和windows版本无异,感觉就可以抛弃自带的libreoffice了. 但是 ...
- 【转载】win10解决设置默认打开方式不生效问题(双击每次都要选择默认打开程序)
win10解决设置默认打开方式不生效问题(双击每次都要选择默认打开程序) 以下文章 部分选自 https://blog.csdn.net/shan165310175/article/details/8 ...
- ppt标签打开文件 word标签打开文件 窗口打开文件 粘贴默认方式
ppt标签打开文件 word标签打开文件 word窗口打开文件 ppt粘贴默认方式 word粘贴默认方式 ppt粘贴默认方式 只保留文本 == 通过 视图 切换窗口. == 层叠 样式 如下. == ...
随机推荐
- PDFsharp 1.50
PDFsharp 1.50 Preview Information - PDFsharp & MigraDoc PDFShapr 1.50 修复与改进 支持 Object Streams - ...
- Netty有关
https://www.baeldung.com/tag/netty/ https://github.com/eugenp/tutorials https://stackoverflow.com/qu ...
- (已解决)Public Key Retrieval is not allowed异常
Public Key Retrieval is not allowed解决方法Public Key Retrieval is not allowed解决方法项目场景:问题描述:原因分析:解决方案:Pu ...
- Qt/C++编写手机版本视频播放器和Onvif工具(可云台和录像)
一.前言 用Qt+ffmpeg写播放器很多人有疑问,为何不用Qt自己的多媒体框架来写,最重要的原因是Qt自带的目前都依赖具体的本地解码器,如果解码器不支持,那就是歇菜的,最多支持个MP4格式,而且在手 ...
- Qt交叉编译整理的几点说明
关于交叉编译,对于初学者来说是个极难跨过去的砍(一旦跨过去了,以后遇到需要交叉编译的时候都是顺水推舟.信手拈来.),因为需要搭建交叉编译环境,好在现在厂家提供的板子基本上都是测试好的环境,尤其是提供的 ...
- 11.15javaweb学习
- [转]奇异值分解(SVD)方法求解最小二乘问题的原理
原文链接:奇异值分解(SVD)方法求解最小二乘问题的原理 翻译 搜索 复制
- 基于AT89C51的数字时钟课程设计
摘要:单片微型计算机简称单片机,又称为微控制器,是将CPU.RAM.ROM.定时/计数器.I/O接口电路集成到一块电路芯片上构成的微型计算机.本次设计的系统由单片机系统.数码管显示系统.键盘.蜂鸣器等 ...
- Windows安全加固(一)
目录: 1.在win ser2016中如何管理重命名administrator,禁用GUEST 2.禁用GUEST账户 3.系统不显示上次登录的账户名. 4.清理系统无效账户. 5.按用户类型分配账号 ...
- Bolt.new 30秒做了一个网站,还能自动部署,难道要吊打 Cursor?
大家好,我是汤师爷~ 这篇聊聊 Bolt.new 和 Cursor 的对比. Bolt.new 是一款基于 SaaS 的 AI 编码平台.它由 LLM 驱动的智能体作为底层,并结合 WebContai ...
