GPU CPU运算时间测试
GPU CPU运算时间测试
本文主要探讨GPU,CPU在做一些复杂运算的时间测试
实验任务
1.向量加法
两个相同维度的向量a,b做加法,分别测试GPU并行时间(包含数据拷贝时间),CPU串行时间。
2.双边滤波
简要介绍:
双边滤波(Bilateral filter)是一种非线性的滤波方法,是结合图像的空间邻近度和像素值相似度的一种折衷处理,同时考虑空域信息和灰度相似性,达到保边去噪的目的。具有简单、非迭代、局部的特点。
双边滤波在计算上是昂贵的,并且具有使优化复杂化的非线性分量。当在中央处理单元(CPU)上顺序运行时,这会花费很多时间,并且双边滤波算法的快速逼近范围很广,使得其算法优化极其困难。
任务描述:
测试\(sigmaColor = 15.0, sigmaSpace = 15.0\),高斯核直径\(d\)变化时, 在大小为 \(800 \times 1068\)图片上的效率。
样例图片:

实验环境
- Ubuntu 18.04
- Intel(R) Xeon(R) Silver 4210 CPU @ 2.20GHz
- RTX3090
ps:之前在本地电脑测过向量加法,现在突然放假回家,因此两个任务统一环境,重新测一遍。
实验结果
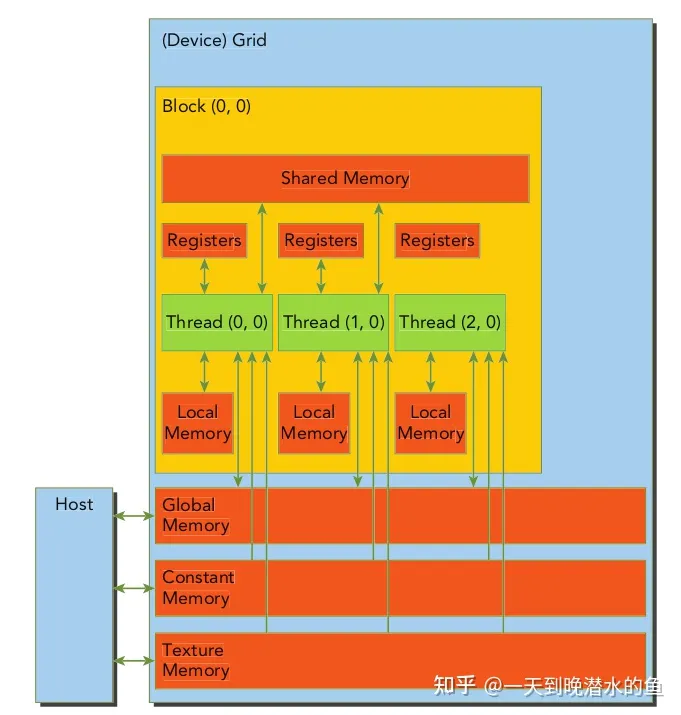
典型的 CUDA 程序的执行流程如下:

因此对于cuda程序的计时可以分为三部分:数据从内存拷贝到显存,执行计算,计算结果从显存拷贝回内存。
对于CPU的计时只有执行计算。
1.向量加法
| 向量a,b的维度 | 262144\((512 \times 512)\) | 1048576\((1024 \times 1024)\) | 4194304\((2048 \times 2048)\) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实验结果截图 | 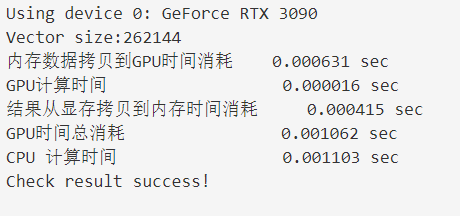 |
 |
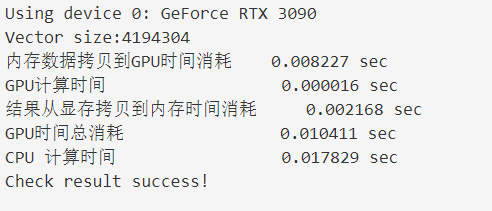 |
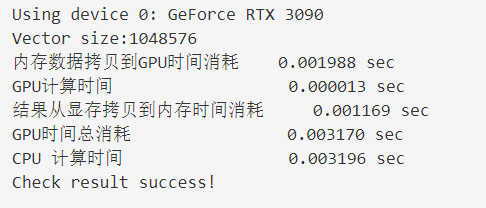
| 内存数据拷贝到GPU时间消耗 | 0.000631 sec | 0.001988 sec | 0.008227sec |
| GPU计算时间 | 0.000016 sec | 0.000013 sec | 0.000016 sec |
| 结果从显存拷贝到内存时间消耗 | 0.000415sec | 0.001169 sec | 0.002168 sec |
| 显存计算总时间(上述相加) | 0.001062sec | 0.003170 sec | 0.010411 sec |
| CPU 计算时间 | 0.001103 sec | 0.003196 sec | 0.017829 sec |
分析:
- 对比GPU和CPU的计算时间,随着数据维度增大,GPU并行计算时间没有明显的增大,CPU计算时间逐渐增大。
- 随着数据维度增大,数据在内存到显存双向拷贝时间逐渐增大。
- 在简单的向量相加任务上,GPU并没有突出的优势
2.双边滤波
| d = 2 | d = 4 | d = 8 | d = 64 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验截图 | 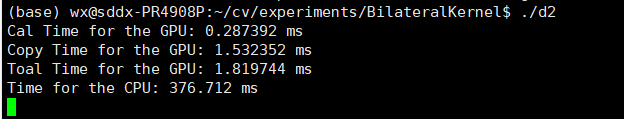 |
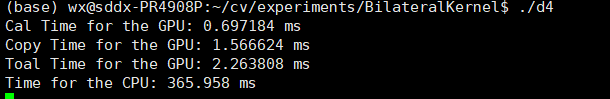 |
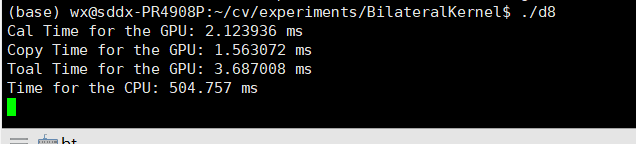 |
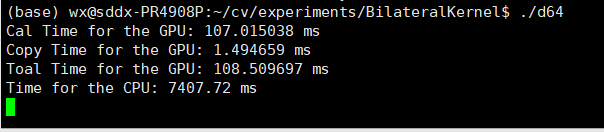 |
| 数据拷贝总时间 | 1.532352 ms | 1.566624 ms | 1.563072 ms | 1.494659 ms |
| GPU计算时间 | 0.287392 ms | 0.697184 ms | 2.123936 ms | 107.015038 ms |
| GPU总时间 | 1.819744 ms | 2.263808 ms | 3.687008 ms | 108.509697 ms |
| CPU计算时间 | 376.712 ms | 365.958 ms | 504.757 ms | 7407.72 ms |
可以发现GPU还是很猛的。
放一下d=8的结果,实现了类似于磨皮的效果:
| 原图 | CPU | GPU |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
实验代码
1.向量加法
sum.cu
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "freshman.h" // CPU 加法
void sumArrays(float *a, float *b, float *res, const int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i += 1)
{
res[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
} // GPU 加法
__global__ void sumArraysGPU(float *a, float *b, float *res, int N)
{
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < N)
res[i] = a[i] + b[i];
} int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// set up device
initDevice(0); int nElem = 512*512;
//int nElem = 1024*1024;
//int nElem = 2048*2048; printf("Vector size:%d\n", nElem); // 内存数据申请空间
int nByte = sizeof(float) * nElem;
float *a_h = (float *)malloc(nByte);
float *b_h = (float *)malloc(nByte);
float *res_h = (float *)malloc(nByte);
float *res_from_gpu_h = (float *)malloc(nByte);
memset(res_h, 0, nByte);
memset(res_from_gpu_h, 0, nByte); // 内存数据随机初始化
initialData(a_h, nElem);
initialData(b_h, nElem); // 显存申请空间
float *a_d, *b_d, *res_d;
CHECK(cudaMalloc((float **)&a_d, nByte));
CHECK(cudaMalloc((float **)&b_d, nByte));
CHECK(cudaMalloc((float **)&res_d, nByte)); // 内存到显存数据拷贝
clock_t start, end;
start = clock();
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(a_d, a_h, nByte, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(b_d, b_h, nByte, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
end = clock(); double copytime = (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("内存数据拷贝到GPU时间消耗\t %f sec\n", copytime); dim3 block(512);
dim3 grid((nElem - 1) / block.x + 1); // GPU 加法
double iStart, iElaps;
iStart = cpuSecond();
sumArraysGPU<<<grid, block>>>(a_d, b_d, res_d, nElem);
iElaps = cpuSecond() - iStart; double GPU_Cla = iElaps;
printf("GPU计算时间 \t\t\t\t %f sec\n", GPU_Cla); //显存到内存数据拷贝
start = clock();
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(res_from_gpu_h, res_d, nByte, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));
end = clock();
double copytime2 = (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("结果从显存拷贝到内存时间消耗\t %f sec\n", copytime2); printf("GPU时间总消耗\t\t\t\t %f sec\n", copytime2 + GPU_Cla + copytime); // CPU 加法
start = clock();
sumArrays(a_h,b_h,res_h,nElem);
end = clock();
printf("CPU 计算时间\t\t\t\t %f sec\n", (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC); checkResult(res_h, res_from_gpu_h, nElem);
cudaFree(a_d);
cudaFree(b_d);
cudaFree(res_d); free(a_h);
free(b_h);
free(res_h);
free(res_from_gpu_h); return 0;
}
freshman.h
#ifndef FRESHMAN_H
#define FRESHMAN_H
#define CHECK(call)\
{\
const cudaError_t error=call;\
if(error!=cudaSuccess)\
{\
printf("ERROR: %s:%d,",__FILE__,__LINE__);\
printf("code:%d,reason:%s\n",error,cudaGetErrorString(error));\
exit(1);\
}\
} #include <time.h>
#ifdef _WIN32
# include <windows.h>
#else
# include <sys/time.h>
#endif
#ifdef _WIN32
int gettimeofday(struct timeval *tp, void *tzp)
{
time_t clock;
struct tm tm;
SYSTEMTIME wtm;
GetLocalTime(&wtm);
tm.tm_year = wtm.wYear - 1900;
tm.tm_mon = wtm.wMonth - 1;
tm.tm_mday = wtm.wDay;
tm.tm_hour = wtm.wHour;
tm.tm_min = wtm.wMinute;
tm.tm_sec = wtm.wSecond;
tm. tm_isdst = -1;
clock = mktime(&tm);
tp->tv_sec = clock;
tp->tv_usec = wtm.wMilliseconds * 1000;
return (0);
}
#endif
double cpuSecond()
{
struct timeval tp;
gettimeofday(&tp,NULL);
return((double)tp.tv_sec+(double)tp.tv_usec*1e-6); }
void initialData(float* ip,int size)
{
time_t t;
srand((unsigned )time(&t));
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
ip[i]=(float)(rand()&0xffff)/1000.0f;
}
}
void initialData_int(int* ip, int size)
{
time_t t;
srand((unsigned)time(&t));
for (int i = 0; i<size; i++)
{
ip[i] = int(rand()&0xff);
}
}
void printMatrix(float * C,const int nx,const int ny)
{
float *ic=C;
printf("Matrix<%d,%d>:",ny,nx);
for(int i=0;i<ny;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<nx;j++)
{
printf("%6f ",C[j]);
}
ic+=nx;
printf("\n");
}
} void initDevice(int devNum)
{
int dev = devNum;
cudaDeviceProp deviceProp;
CHECK(cudaGetDeviceProperties(&deviceProp,dev));
printf("Using device %d: %s\n",dev,deviceProp.name);
CHECK(cudaSetDevice(dev)); }
void checkResult(float * hostRef,float * gpuRef,const int N)
{
double epsilon=1.0E-8;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
if(abs(hostRef[i]-gpuRef[i])>epsilon)
{
printf("Results don\'t match!\n");
printf("%f(hostRef[%d] )!= %f(gpuRef[%d])\n",hostRef[i],i,gpuRef[i],i);
return;
}
}
printf("Check result success!\n");
}
#endif//FRESHMAN_H
2. \(双边滤波^{[1]}\)
kernel.cu
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <cuda.h>
#include <device_functions.h>
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846 using namespace std;
using namespace cv; //一维高斯kernel数组
__constant__ float cGaussian[64];
//声明纹理参照系,以全局变量形式出现
texture<unsigned char, 2, cudaReadModeElementType> inTexture; //计算一维高斯距离权重,二维高斯权重可由一维高斯权重做积得到
void updateGaussian(int r, double sd)
{
float fGaussian[64];
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * r + 1; i++)
{
float x = i - r;
fGaussian[i] = 1 / (sqrt(2 * M_PI) * sd) * expf(-(x * x) / (2 * sd * sd));
}
cudaMemcpyToSymbol(cGaussian, fGaussian, sizeof(float) * (2 * r + 1));
} // 一维高斯函数,计算像素差异权重
__device__ inline double gaussian(float x, double sigma)
{
return 1 / (sqrt(2 * M_PI) * sigma) * __expf(-(powf(x, 2)) / (2 * powf(sigma, 2)));
} __global__ void gpuCalculation(unsigned char* input, unsigned char* output, int width ,int height, int r,double sigmaColor)
{
int txIndex = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int tyIndex = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y; if ((txIndex < width) && (tyIndex < height))
{
double iFiltered = 0;
double k = 0;
//纹理拾取,得到要计算的中心像素点
unsigned char centrePx = tex2D(inTexture, txIndex, tyIndex);
//进行卷积运算
for (int dy = -r; dy <= r; dy++) {
for (int dx = -r; dx <= r; dx++) {
//得到kernel区域内另一像素点
unsigned char currPx = tex2D(inTexture, txIndex + dx, tyIndex + dy);
// Weight = 1D Gaussian(x_axis) * 1D Gaussian(y_axis) * Gaussian(Color difference)
double w = (cGaussian[dy + r] * cGaussian[dx + r]) * gaussian(centrePx - currPx, sigmaColor);
iFiltered += w * currPx;
k += w;
}
}
output[tyIndex * width + txIndex] = iFiltered / k;
}
} void MyBilateralFilter(const Mat& input, Mat& output, int r, double sigmaColor, double sigmaSpace)
{
//GPU计时事件
cudaEvent_t start, stop, cal_start, cal_stop;
float time_copy, total_time;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&stop); cudaEventCreate(&cal_start);
cudaEventCreate(&cal_stop); cudaEventRecord(start, 0); //计算图片大小
int gray_size = input.step * input.rows; //在device上开辟2维数据空间保存输入输出数据
unsigned char* d_input = NULL;
unsigned char* d_output; updateGaussian(r, sigmaSpace); //分配device内存
cudaMalloc<unsigned char>(&d_output, gray_size); //纹理绑定
size_t pitch;
cudaMallocPitch(&d_input, &pitch, sizeof(unsigned char) * input.step, input.rows);
cudaChannelFormatDesc desc = cudaCreateChannelDesc<unsigned char>();
cudaMemcpy2D(d_input, pitch, input.ptr(), sizeof(unsigned char) * input.step, sizeof(unsigned char) * input.step, input.rows, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
//将纹理参照系绑定到一个CUDA数组
cudaBindTexture2D(0, inTexture, d_input, desc, input.step, input.rows, pitch); dim3 block(16, 16);
dim3 grid((input.cols + block.x - 1) / block.x, (input.rows + block.y - 1) / block.y); cudaEventRecord(cal_start, 0);
gpuCalculation <<< grid, block >>> (d_input, d_output, input.cols, input.rows, r, sigmaColor);
cudaEventRecord(cal_stop, 0);
cudaEventSynchronize(cal_stop); cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_copy, cal_start, cal_stop);
printf("Cal Time for the GPU: %f ms\n", time_copy); //将device上的运算结果拷贝到host上
cudaMemcpy(output.ptr(), d_output, gray_size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaEventRecord(stop, 0);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop); //释放device和host上分配的内存
cudaFree(d_input);
cudaFree(d_output); // Calculate and print kernel run time
cudaEventElapsedTime(&total_time, start, stop);
printf("Copy Time for the GPU: %f ms\n", total_time - time_copy);
printf("Toal Time for the GPU: %f ms\n", total_time); }
main.cpp
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
using namespace cv; void MyBilateralFilter(const Mat& input, Mat& output, int r, double sI, double sS); int main() { //高斯核直径
int d = 64;
double sigmaColor = 15.0, sigmaSpace = 15.0;
//将原始图像转化为灰度图像再打开
Mat srcImg = imread("1.jpg", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
//分配host内存
Mat dstImg(srcImg.rows, srcImg.cols, CV_8UC1);
Mat dstImgCV; //在GPU上运行测速
MyBilateralFilter(srcImg, dstImg, d/2, sigmaColor, sigmaSpace); //使用OpenCV bilateral filter在cpu上测速
clock_t start_s = clock();
bilateralFilter(srcImg, dstImgCV, d, sigmaColor, sigmaSpace);
clock_t stop_s = clock();
cout << "Time for the CPU: " << (stop_s - start_s) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC) * 1000 << " ms" << endl;
//展示图片
imshow("原图", srcImg);
imwrite("space2.jpg", srcImg);
imshow("GPU加速双边滤波", dstImg);
imwrite("space2.jpg", dstImg);
imshow("CPU双边滤波", dstImgCV);
imwrite("space2.jpg", dstImgCV);
cv::waitKey();
}
进一步的讨论(双边滤波)
gird,block的划分对速度的影响?
要回答这个问题需要一些先验知识,所以最近去学习了一些GPU的组织架构,熟悉了一下相关概念。
由于 SM 的基本执行单元是包含 32 个线程的线程束,所以 block 大小一般要设置为 32 的倍数。
因此在d=8、32的时候,分别设置了以下五种情况:
d = 8 d = 32 
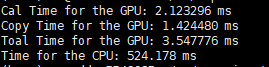
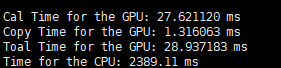

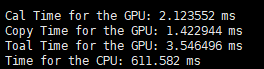
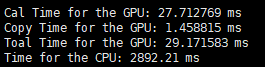

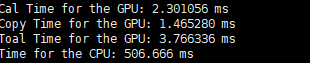
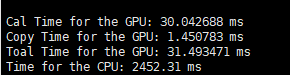

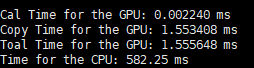
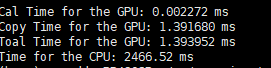

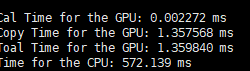

只关注第一行,Cal time for GPU就行。
就这个任务总体来看,对RTX3090来说,对于一张分辨率确定的图片,在
dim3 block(64,64)上发生了改变。我查了一下3090的SM数量是82。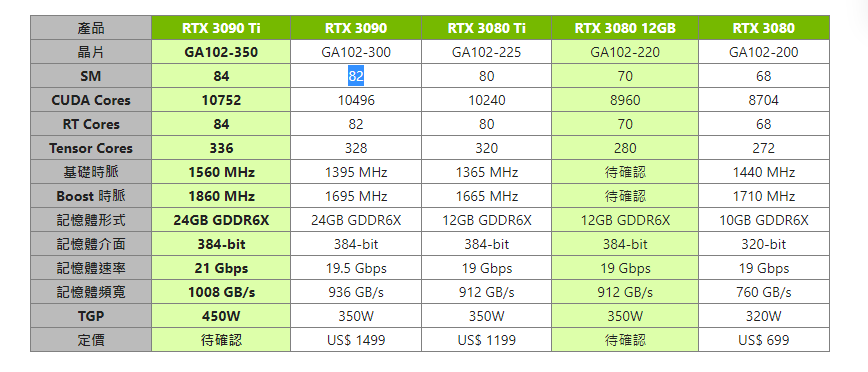
想了一下,还没法回答这个问题,需要以后继续深入探讨。
关于使用纹理内存的问题
我看互联网上的描述,差不多就是纹理内存有一些特性(比如可以归一化等等),访问二维矩阵的邻域会获得加速

但是这个访问邻域应该更多地体现在差值上:
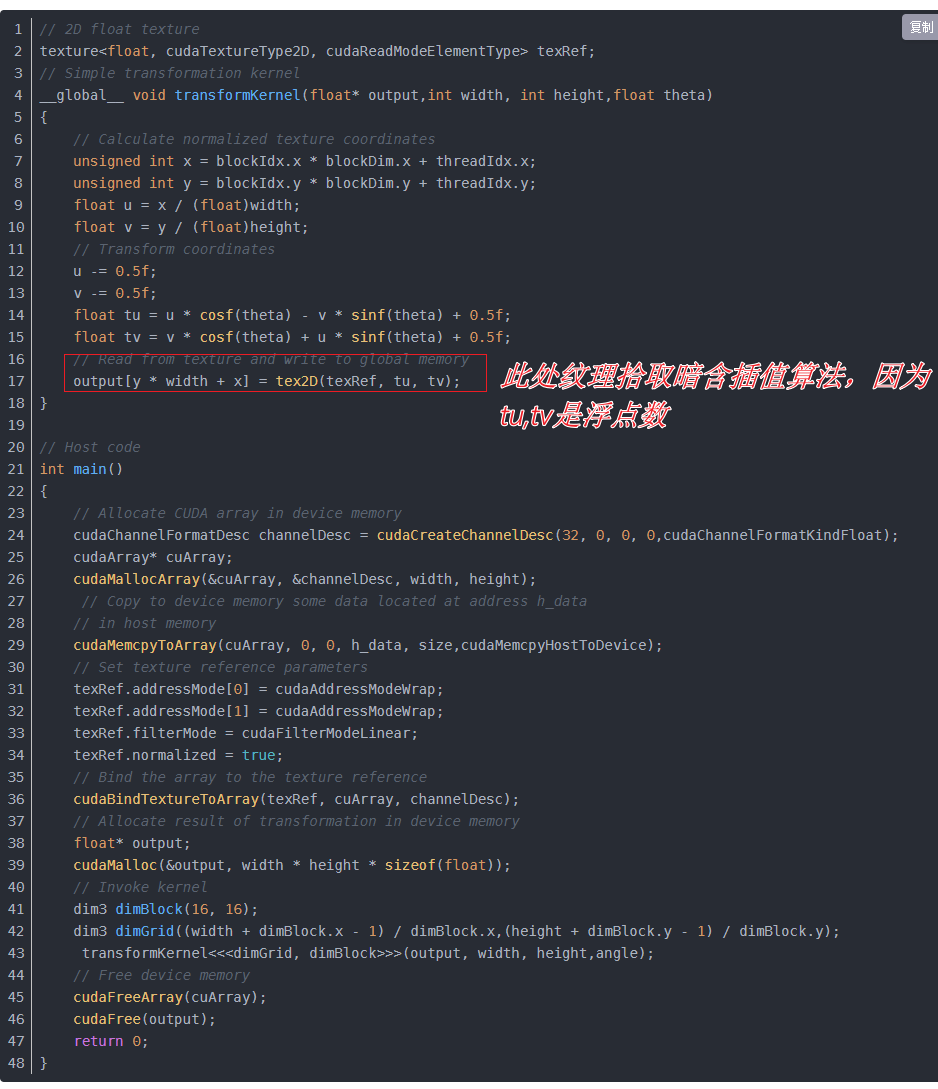
我又回头看了一下作者的代码:
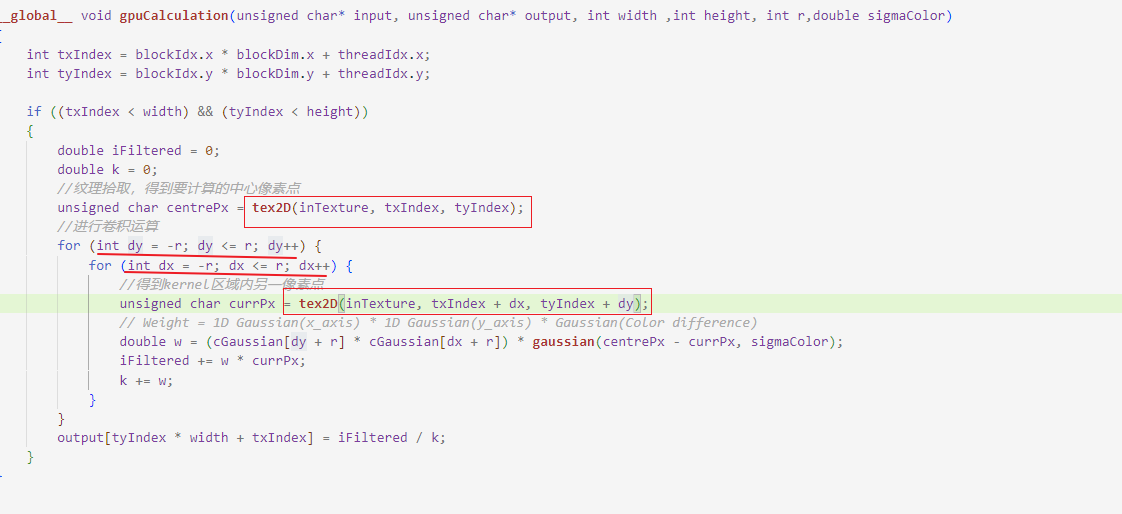
都是整型,其实也就是没有插值(因为都精确的落在了某个像素上),所以修改为直接从input读取数据,两种效果应该差不多,果不其然:
| texture memory | global memory | |
|---|---|---|
| d = 8 |  |
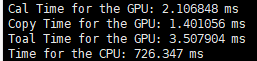 |
| d = 32 |  |
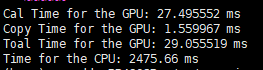 |
相关代码:
kernel_global_input.cu
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <cuda.h>
#include <device_functions.h>
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//一维高斯kernel数组
__constant__ float cGaussian[64];
//声明纹理参照系,以全局变量形式出现
texture<unsigned char, 2, cudaReadModeElementType> inTexture;
//计算一维高斯距离权重,二维高斯权重可由一维高斯权重做积得到
void updateGaussian(int r, double sd)
{
float fGaussian[64];
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * r + 1; i++)
{
float x = i - r;
fGaussian[i] = 1 / (sqrt(2 * M_PI) * sd) * expf(-(x * x) / (2 * sd * sd));
}
cudaMemcpyToSymbol(cGaussian, fGaussian, sizeof(float) * (2 * r + 1));
}
// 一维高斯函数,计算像素差异权重
__device__ inline double gaussian(float x, double sigma)
{
return 1 / (sqrt(2 * M_PI) * sigma) * __expf(-(powf(x, 2)) / (2 * powf(sigma, 2)));
}
__global__ void gpuCalculation(unsigned char* input, unsigned char* output, int width ,int height, int r,double sigmaColor)
{
int txIndex = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int tyIndex = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
if ((txIndex < width) && (tyIndex < height))
{
double iFiltered = 0;
double k = 0;
unsigned char centrePx = input[tyIndex * width + txIndex];
//进行卷积运算
for (int dy = -r; dy <= r; dy++) {
for (int dx = -r; dx <= r; dx++) {
if(txIndex+dx >= 0 && tyIndex+dy >=0 && txIndex+dx <= width && tyIndex+dy <= height)
{
//得到kernel区域内另一像素点
unsigned char currPx = input[(tyIndex+dy) * width + txIndex+dx];
// Weight = 1D Gaussian(x_axis) * 1D Gaussian(y_axis) * Gaussian(Color difference)
double w = (cGaussian[dy + r] * cGaussian[dx + r]) * gaussian(centrePx - currPx, sigmaColor);
iFiltered += w * currPx;
k += w;
}
}
}
output[tyIndex * width + txIndex] = iFiltered / k;
}
}
void MyBilateralFilter(const Mat& input, Mat& output, int r, double sigmaColor, double sigmaSpace)
{
//GPU计时事件
cudaEvent_t start, stop, cal_start, cal_stop;
float time_copy, total_time;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&stop);
cudaEventCreate(&cal_start);
cudaEventCreate(&cal_stop);
cudaEventRecord(start, 0);
//计算图片大小
int gray_size = input.step * input.rows;
//在device上开辟2维数据空间保存输入输出数据
unsigned char* d_input;
unsigned char* d_output;
updateGaussian(r, sigmaSpace);
//分配device内存
cudaMalloc<unsigned char>(&d_input, gray_size);
cudaMalloc<unsigned char>(&d_output, gray_size);
// global memory 图片数据拷贝
cudaMemcpy(d_input, input.ptr(), gray_size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
dim3 block(16, 16);
dim3 grid((input.cols + block.x - 1) / block.x, (input.rows + block.y - 1) / block.y);
cudaEventRecord(cal_start, 0);
gpuCalculation <<< grid, block >>> (d_input, d_output, input.cols, input.rows, r, sigmaColor);
cudaEventRecord(cal_stop, 0);
cudaEventSynchronize(cal_stop);
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_copy, cal_start, cal_stop);
printf("Cal Time for the GPU: %f ms\n", time_copy);
//将device上的运算结果拷贝到host上
cudaMemcpy(output.ptr(), d_output, gray_size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaEventRecord(stop, 0);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop);
//释放device和host上分配的内存
cudaFree(d_input);
cudaFree(d_output);
// Calculate and print kernel run time
cudaEventElapsedTime(&total_time, start, stop);
printf("Copy Time for the GPU: %f ms\n", total_time - time_copy);
printf("Toal Time for the GPU: %f ms\n", total_time);
}
引用
[1] https://github.com/xytroot/Bilateral-Filter
GPU CPU运算时间测试的更多相关文章
- 教你从头到尾利用DQN自动玩flappy bird(全程命令提示,GPU+CPU版)【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/52810219?locationNum=3&fps=1 目录(?)[-] 教你从头到尾利用D ...
- matlab 中使用 GPU 加速运算
为了提高大规模数据处理的能力,matlab 的 GPU 并行计算,本质上是在 cuda 的基础上开发的 wrapper,也就是说 matlab 目前只支持 NVIDIA 的显卡. 1. GPU 硬件支 ...
- GPU虚拟机创建时间深度优化
桔妹导读:GPU虚拟机实例创建速度慢是公有云面临的普遍问题,由于通常情况下创建虚拟机属于低频操作而未引起业界的重视,实际生产中还是存在对GPU实例创建时间有苛刻要求的业务场景.本文将介绍滴滴云在解决 ...
- 既然CPU同一时间只能执行一个线程,为什么存在并发问题
一点小疑惑终于解开啦 1.CPU的时间是按时间片分的,而不是一个时间点,并发问题是由于CPU线程切换导致的. 现在假设有一段代码 if(i == 1) { i++; //断点1 system.out. ...
- 数据库访问优化漏斗法则- 四、减少数据库服务器CPU运算
数据库访问优化漏斗法则这个优化法则归纳为5个层次:1.减少数据访问次数(减少磁盘访问)2.返回更少数据(减少网络传输或磁盘访问)3.减少交互次数(减少网络传输)4.减少服务器CPU开销(减少CPU及内 ...
- 用于.NET环境的时间测试(转)
用于.NET环境的时间测试 在.NET环境中,衡量运行完整算法所花费的时间长度,需要考虑很多 需要考虑很多种情况 ,如:程序运行所处的线程以及无用单位收集(GC垃圾回收). 在程序执行过程中无用单 ...
- 笔记-python-实用-程序运算时间计算
方法1 import datetime starttime = datetime.datetime.now() #long running endtime = datetime.datetime.no ...
- TensorFlow指定GPU/CPU进行训练和输出devices信息
TensorFlow指定GPU/CPU进行训练和输出devices信息 1.在tensorflow代码中指定GPU/CPU进行训练 with tf.device('/gpu:0'): .... wit ...
- Docker容器CPU限制选项测试
目录 Docker容器CPU限制选项测试 参考 实验环境 --cpu-shares选项 测试 结论 --cpus选项 测试 结论 --cpuset-cpus选项 测试 结论 Docker容器CPU限制 ...
- 2018最新win10 安装tensorflow1.4(GPU/CPU)+cuda8.0+cudnn8.0-v6 + keras 安装CUDA失败 导入tensorflow失败报错问题解决
原文作者:aircraft 原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/DOMLX/p/9747019.html 基本开发环境搭建 1. Microsoft Windows 版本 关于W ...
随机推荐
- 重温Go语法笔记 | 结构体
结构体 多个任意类型聚合成的复合类型 1.字段拥有自己的类型和值 2.字段名必须唯一 3.字段可以是结构体 结构体的定义是一种内存布局的描述 只有实例化才会真正分配内存,必须实例化之后才能使用结构体的 ...
- Phi小模型开发教程:用C#开发本地部署AI聊天工具,只需CPU,不需要GPU,3G内存就可以运行,不输GPT-3.5
大家好,我是编程乐趣. 行业诸多大佬一直在说:"2025年将是AI应用元年",虽然说大佬的说法不一定对,但AI趋势肯定没错的. 对于我们程序员来说,储备AI应用开发技能,不管对 ...
- ctfshow--web11session置空绕过
代码审计 点击查看代码 <?php function replaceSpecialChar($strParam){ $regex = "/(select|from|where|join ...
- 银杏叶也是yxy
今年下半年(9月后)第一个使我震撼而狂喜的书籍,金阁寺. 翻译是林少华.他翻译这个可比村上春树好多了 一切都像梦寐一般,一切都如此完美 完美的结构,完美的心理叙述,撕心裂肺的景色描写 战后无限的虚无与 ...
- Q:浏览器不能上网,但是可以ping通外网ip,dns配置也没问题(TCP/IP 无法建立传出连接)
问题症状 每隔一段时间,浏览器不能访问外网,重启电脑又正常,重置网卡无效 可以ping通外网ip地址,可以ping通外网域名 ping不通外网端口端口 查看日志 每次出现不能上网情况时都会有至少两条T ...
- Flink同步kafka到iceberg(cos存储)
一.flink到logger 1.source create table source_table ( id bigint comment '唯一编号' ,order_number bigint co ...
- 性能测试-Oceanus 测试FLink mysql到Iceberg性能
一.任务依赖信息 1.mysql测试库信息 地址:127.0.0.1.gomysql_bdg_test 库:bdg_test 表:order_info1 2.iceberg库 hive地址:thrif ...
- FLink16--计数窗口--CountWindiwApp
一.依赖 https://www.cnblogs.com/robots2/p/16048648.html 二.代码 概念:窗口来多少条计算一次,存在滚动和滑动两种情况 package net.xdcl ...
- 腾讯ima接入deepseek-r1,借用别人脑子用用成真了~
大家好,我是汤师爷! 最近,腾讯发布了一款ima产品,主打用AI来帮你搜索信息.管理知识库. 说实话,一开始用混元大模型,感觉不咋地,很鸡肋的. 不过最近腾讯把DeepSeek R1接进来了,一下子解 ...
- [BZOJ3811] 玛里苟斯 题解
不得不说这题的确挺苟的. 注:下述"引理"表示: 对于长度为 \(n\) 的数组 \(V\),其线性基为 \(B\),定义 \(c_v=\bigoplus\limits_{a\in ...
