201771010141 周强 面向对象程序设计(Java)第12周作业
实验十二 图形程序设计
实验时间 2018-11-14
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握Java GUI中框架创建及属性设置中常用类的API;
(2) 掌握Java GUI中2D图形绘制常用类的API;
(3) 了解Java GUI中2D图形中字体与颜色的设置方法;
(4) 了解Java GUI中2D图像的载入方法。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第10章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 运行下列程序,观察程序运行结果。
|
import javax.swing.*; public class SimpleFrameTest { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame frame = new JFrame(); frame.setBounds(0, 0,300, 200); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); } } |
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材407页程序10-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;与上面程序对比,思考异同;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.33 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SimpleFrameTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
SimpleFrame frame = new SimpleFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} class SimpleFrame extends JFrame
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = ;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = ; public SimpleFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
}
}
l 掌握空框架创建方法;
l 了解主线程与事件分派线程概念;
l 掌握GUI顶层窗口创建技术。
测试程序2:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材412页程序10-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握确定框架常用属性的设置方法。
package sizedFrame;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-16
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SizedFrameTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new SizedFrame();
frame.setTitle("SizedFrame");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
class SizedFrame extends JFrame
{
public SizedFrame()
{
// get screen dimensions
Toolkit kit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Dimension screenSize = kit.getScreenSize();
int screenHeight = screenSize.height;
int screenWidth = screenSize.width;
// set frame width, height and let platform pick screen location
setSize(screenWidth / 2, screenHeight / 2);
setLocationByPlatform(true);
// set frame icon
Image img = new ImageIcon("icon.gif").getImage();
setIconImage(img);
}
}
测试程序3:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材418页程序10-3,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握在框架中添加组件;
l 掌握自定义组件的用法。
package notHelloWorld;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
/**
* @version 1.33 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class NotHelloWorld
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new NotHelloWorldFrame();
frame.setTitle("NotHelloWorld");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
/**
* A frame that contains a message panel
*/
class NotHelloWorldFrame extends JFrame
{
public NotHelloWorldFrame()
{
add(new NotHelloWorldComponent());
pack();
}
}
/**
* A component that displays a message.
*/
class NotHelloWorldComponent extends JComponent
{
public static final int MESSAGE_X = 75;
public static final int MESSAGE_Y = 100;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
g.drawString("Not a Hello, World program", MESSAGE_X, MESSAGE_Y);
}
public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}

测试程序4:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材424 -425页程序10-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握2D图形的绘制方法。
package draw;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.33 2007-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class DrawTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new DrawFrame();
frame.setTitle("DrawTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
/**
* A frame that contains a panel with drawings
*/
class DrawFrame extends JFrame
{
public DrawFrame()
{
add(new DrawComponent());
pack();
}
}
/**
* A component that displays rectangles and ellipses.
*/
class DrawComponent extends JComponent
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 400;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400;
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
// draw a rectangle
double leftX = 100;
double topY = 100;
double width = 200;
double height = 150;
Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D.Double(leftX, topY, width, height);
g2.draw(rect);
// draw the enclosed ellipse
Ellipse2D ellipse = new Ellipse2D.Double();
ellipse.setFrame(rect);
g2.draw(ellipse);
// draw a diagonal line
g2.draw(new Line2D.Double(leftX, topY, leftX + width, topY + height));
// draw a circle with the same center
double centerX = rect.getCenterX();
double centerY = rect.getCenterY();
double radius = 150;
Ellipse2D circle = new Ellipse2D.Double();
circle.setFrameFromCenter(centerX, centerY, centerX + radius, centerY + radius);
g2.draw(circle);
}
public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}

测试程序5:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材432页-433程序10-5,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解2D图形中字体的设置的方法;
package font;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.font.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class FontTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new FontFrame();
frame.setTitle("FontTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
/**
* A frame with a text message component
*/
class FontFrame extends JFrame
{
public FontFrame()
{
add(new FontComponent());
pack();
}
}
/**
* A component that shows a centered message in a box.
*/
class FontComponent extends JComponent
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
String message = "Happy every day!";
Font f = new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, 36);
g2.setFont(f);
// measure the size of the message
FontRenderContext context = g2.getFontRenderContext();
Rectangle2D bounds = f.getStringBounds(message, context);
// set (x,y) = top left corner of text
double x = (getWidth() - bounds.getWidth()) / 2;
double y = (getHeight() - bounds.getHeight()) / 2;
// add ascent to y to reach the baseline
double ascent = -bounds.getY();
double baseY = y + ascent;
// draw the message
g2.drawString(message, (int) x, (int) baseY);
g2.setPaint(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
// draw the baseline
g2.draw(new Line2D.Double(x, baseY, x + bounds.getWidth(), baseY));
// draw the enclosing rectangle
Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D.Double(x, y, bounds.getWidth(), bounds.getHeight());
g2.draw(rect);
}
public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}

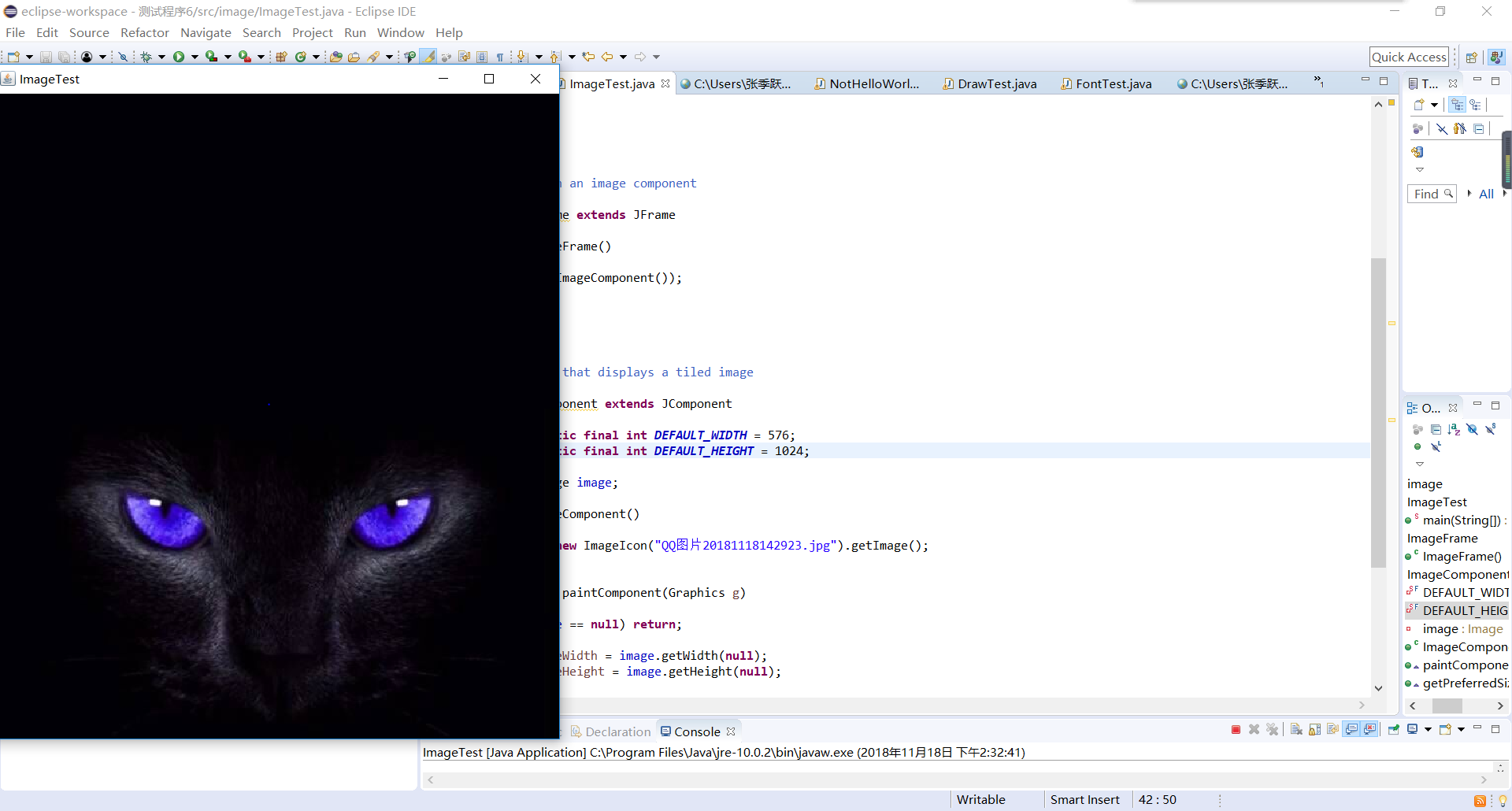
测试程序6:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材436页-437程序10-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解2D图形图像的显示方法。
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ImageTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new ImageFrame();
frame.setTitle("ImageTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
/**
* A frame with an image component
*/
class ImageFrame extends JFrame
{
public ImageFrame()
{
add(new ImageComponent());
pack();
}
}
/**
* A component that displays a tiled image
*/
class ImageComponent extends JComponent
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 576;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 1024;
private Image image;
public ImageComponent()
{
image = new ImageIcon("QQ图片20181118142923.jpg").getImage();
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
if (image == null) return;
int imageWidth = image.getWidth(null);
int imageHeight = image.getHeight(null);
// draw the image in the upper-left corner
g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, null);
// tile the image across the component
for (int i = 0; i * imageWidth <= getWidth(); i++)
for (int j = 0; j * imageHeight <= getHeight(); j++)
if (i + j > 0)
g.copyArea(0, 0, imageWidth, imageHeight, i * imageWidth, j * imageHeight);
}
public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}
201771010141 周强 面向对象程序设计(Java)第12周作业的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 面向对象程序设计--Java语言第二周编程题:有秒计时的数字时钟
有秒计时的数字时钟 题目内容: 这一周的编程题是需要你在课程所给的时钟程序的基础上修改而成.但是我们并不直接给你时钟程序的代码,请根据视频自己输入时钟程序的Display和Clock类的代码,然后来做 ...
随机推荐
- linux所有命令不能用显示-bash: ls: command not found
所有的命令都显示找不到了,原因是修改了/etc/profile造成的 解决方法 1.修正属性文件中的错误 /usr/bin/vi /etc/profile 2.生效属性文件 source /etc/p ...
- js前端性能优化之函数节流和函数防抖
前言:针对一些会频繁触发的事件如scroll.resize,如果正常绑定事件处理函数的话,有可能在很短的时间内多次连续触发事件,十分影响性能 节流: 节流:使得一定时间内只触发一次函数. 它和防抖动最 ...
- Ajax、Flash优缺点
Ajax的优势:1.可搜索性 2.开放性 3.费用 4.易用性 5.易于开发.可搜索性 普通的文本网页会更有利于SEO.文本内容是搜索引擎容易检索的,而繁琐的swf字节码却是搜索引擎不愿触及的.虽然G ...
- 深入理解CADisplayLink和NSTimer
一.什么是CADisplayLink 简单地说,它就是一个定时器,每隔几毫秒刷新一次屏幕. CADisplayLink是一个能让我们以和屏幕刷新率相同的频率将内容画到屏幕上的定时器.我们在应用中创建一 ...
- Xshell配置使用linux的图形界面
1.配置Xshell如下图 2.在命令行中执行"gnome-panel". 3.或者使用xstart,配置如下图:
- 从码农到技术总监分享Leader经验
从一个毕业的IT小伙或者一个码农成长为一个管理者,有很多需要转变的思想,那么当你遇到了瓶颈,或许我的经验能帮到你,感谢. 系统的掌握了.NET,JAVA技术,能够熟练的使用springcloud + ...
- Win10系列:C#应用控件进阶9
RectangleGeometry 在使用RectangleGeometry控件绘制矩形时,矩形的位置和尺寸由Rect属性定义,该属性指定矩形的相对位置.高度和宽度.Rect有四个参数,前两个参数表示 ...
- Html+css学习笔记一 创建一个网页
第一个网页 新建一个记事本,把名字改成first.html <html> <head> <title>MyFristHtml</title> </ ...
- 用with打开文件
rep_word = 'The piece is gone, left the puzzle undone' # \ 换行,跟shell一样 with open('nothing', 'r', enc ...
- seo相关知识
网络营销菜鸟SEO入门必杀技(转载:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_5ef0fe8b0100n9cw.html) 搜索引擎优化(Search Engine Optimiz ...
