CodeForces 438D 线段树 剪枝
4 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
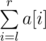 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
- Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space: a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 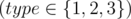 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond the operation 1.
- If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 2.
- If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 5 4 3 3 5 1 2 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 3
8 5
10 10 6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5 1 3 9 2 7 10 9 2 5 10 8 1 4 7 3 3 7 2 7 9 9 1 2 4 1 6 6 1 5 9 3 1 10
49 15 23 1 9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
注意:剪枝:若x<mod,x=x;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<map> #define N 100010
#define M 15
//#define mod 1000000007
//#define mod2 100000000
#define ll long long
#define maxi(a,b) (a)>(b)? (a) : (b)
#define mini(a,b) (a)<(b)? (a) : (b) using namespace std; int n,q;
int x[N];
int type;
int a,b,c; struct node
{
ll sum;
int ma;
}tree[*N];
/*
void update(int l,int r,int i)
{
if(!tree[i].mark) return;
int mid=(l+r)/2;
tree[2*i].sum+=tree[i].mark*(ll)(mid-l+1);
tree[2*i+1].sum+=tree[i].mark*(ll)(r-mid);
tree[2*i].mark+=tree[i].mark;
tree[2*i+1].mark+=tree[i].mark;
tree[i].mark=0; }*/ ll query(int tl,int tr,int l,int r,int i)
{
if(tl>r || tr<l)
return ;
if(tl<=l && r<=tr)
return tree[i].sum;
// update(l,r,i);
int mid=(l+r)/; return query(tl,tr,l,mid,*i)+query(tl,tr,mid+,r,*i+);
}
/*
void addd(int tl,int tr,int l,int r,int i,int val)
{
if(tl>r || tr<l)
return;
if(tl<=l && tr>=r){
tree[i].sum+=val*(ll)(r-l+1);
tree[i].mark+=val;
return;
}
update(l,r,i);
int mid=(l+r)/2;
addd(tl,tr,l,mid,2*i,val);
addd(tl,tr,mid+1,r,2*i+1,val);
tree[i].sum=tree[2*i].sum+tree[2*i+1].sum;
}*/ void modefiyMod(int tl,int tr, int l, int r,int i,int mod)
{
if(tree[i].ma<mod) return;
if(l==r){
tree[i].sum=tree[i].ma=tree[i].sum%mod;
return;
}
else{
int mid=(l+r)/;
if(tr<=mid){
modefiyMod(tl,tr,l,mid,i*,mod);
}
else if(tl>mid){
modefiyMod(tl,tr,mid+,r,i*+,mod);
}
else{
modefiyMod(tl,tr,l,mid,i*,mod);
modefiyMod(tl,tr,mid+,r,i*+,mod);
}
tree[i].sum=tree[*i].sum+tree[*i+].sum;
tree[i].ma=max(tree[*i].ma,tree[*i+].ma);
}
} void setVal(int i, int l, int r,int x,int v)
{
if(l==r){
tree[i].sum=tree[i].ma=v;
return;
}
else{
int mid=(l+r)/;
if(x<=mid){
setVal(i*,l,mid,x,v);
}
else{
setVal(i*+,mid+,r,x,v);
}
tree[i].sum=tree[*i].sum+tree[*i+].sum;
tree[i].ma=max(tree[*i].ma,tree[*i+].ma);
}
} void build_tree(int l,int r,int i)
{
if(l==r){
tree[i].sum=x[l];
tree[i].ma=x[l];
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)/;
build_tree(l,mid,*i);
build_tree(mid+,r,*i+);
tree[i].sum=tree[*i].sum+tree[*i+].sum;
tree[i].ma=max(tree[*i].ma,tree[*i+].ma);
} int main()
{
int i;
//freopen("data.in","r",stdin);
//scanf("%d",&T);
//for(int cnt=1;cnt<=T;cnt++)
//while(T--)
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&q)!=EOF)
{
for(i=;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&x[i]);
memset(tree,,sizeof(tree));
build_tree(,n,);
while(q--){
scanf("%d",&type);
if(type==){
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
ll ans=query(a,b,,n,);
printf("%I64d\n",ans); }
else if(type==){
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
modefiyMod(a, b, , n, , c);
}
else{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
setVal(, , n, a, b);
}
}
} return ;
}
CodeForces 438D 线段树 剪枝的更多相关文章
- Bash and a Tough Math Puzzle CodeForces 914D 线段树+gcd数论
Bash and a Tough Math Puzzle CodeForces 914D 线段树+gcd数论 题意 给你一段数,然后小明去猜某一区间内的gcd,这里不一定是准确值,如果在这个区间内改变 ...
- 对权值线段树剪枝的误解--以HDU6703为例
引子 对hdu6703,首先将问题转化为"询问一个排列中大于等于k的值里,下标超过r的最小权值是多少" 我们采用官方题解中的做法:权值线段树+剪枝 对(a[i],i)建线段树,查询 ...
- Codeforces 444 C. DZY Loves Colors (线段树+剪枝)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/444/problem/C 给定一个长度为n的序列,初始时ai=i,vali=0(1≤i≤n).有两种操作: 将区间[L,R]的值 ...
- Codeforces Round #424 (Div. 2, rated, based on VK Cup Finals) Problem E (Codeforces 831E) - 线段树 - 树状数组
Vasily has a deck of cards consisting of n cards. There is an integer on each of the cards, this int ...
- HDOJ:6356-Glad You Came(线段树剪枝)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6356 解题心得: 现在深深的知道了算法复杂度的重要了,这个题算复杂度的时候还要把一些常数也算出来,不然 ...
- LibreOJ #6190. 序列查询(线段树+剪枝)
莫队貌似是过不了的,这题是我没见过的科技... 首先区间按右端点排序,然后一个扫描线,扫到某个区间右端点时候计算答案,线段树上节点的信息并不需要明确定义,我们只要求线段树做到当前扫到now时,查询[L ...
- HDU4391(线段树+剪枝)
Paint The Wall Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- Codeforces 938G 线段树分治 线性基 可撤销并查集
Codeforces 938G Shortest Path Queries 一张连通图,三种操作 1.给x和y之间加上边权为d的边,保证不会产生重边 2.删除x和y之间的边,保证此边之前存在 3.询问 ...
- codeforces 1136E 线段树
codeforces 1136E: 题意:给你一个长度为n的序列a和长度为n-1的序列k,序列a在任何时候都满足如下性质,a[i+1]>=ai+ki,如果更新后a[i+1]<ai+ki了, ...
随机推荐
- chrom浏览器-F12使用方法二
文摘摘自:https://blog.csdn.net/run65536/article/details/80568543 提示:右键点击图片选择在新窗口或新标签页中打开可查看大图. 一.Element ...
- softmax_loss.cu 和 softmax_loss.cpp源码
#include <algorithm> #include <cfloat> #include <vector> #include "caffe/laye ...
- rpn网络结构再分析
这是rpn网络train阶段的网络结构图 rpn_conv1之前的网络是特征提取层,也是和fast rcnn共享的层.rpn_conv1是一层1*1的卷积,这一层是单独为rpn网络多提取一层特征,这一 ...
- javascript中typeof、undefined 和 null
typeof 是运算符,注意不是函数,是运算符,其作用,是考察变量究竟是什么类型.或曰,是变量是否定义或是否初始化的照妖镜.返回值是字符串. undefined 表示一个对象没有被定义或者没有被初始化 ...
- javascript(九)事件冒泡 onmouseenter onmouseenter 默认事件 和 键盘事件
1 事件冒泡 子元素触发的事件,会往上(父元素)传递: 例子: <div id="box"> <p></p> </div> < ...
- NOIP 2018数据点
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/14jXQGPSac3b9_m5h5x2wGQ 提取码: 1cbk 好文别忘点赞!!!
- 【Java_基础】java类加载过程与双亲委派机制
1.类的加载.连接和初始化 当程序使用某个类时,如果该类还未被加载到内存中,则系统会通过加载.连接.初始化三个步骤来对类进行初始化.如果没有意外,jvm将会连续完成这三个步骤,有时也把这三个步骤统称为 ...
- laravel如何利用数据库的形式发送通知
具体实现需要分几步: 1.修改驱动为database; 2.创建database的queue表 3.创建任务sendMessage 4.创建发送逻辑dispatch 5.启动队列 接下来我们进行实操: ...
- 设置 TabBarItemt图片颜色
UIImage *discussSelectedImage = [UIImage imageNamed:@"discuss_selected"];//设置图片不渲染 discuss ...
- (转))iOS App上架AppStore 会遇到的坑
iOS App上架AppStore 会遇到的坑 前言:非原创 文章摘自:http://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/100000PM/20010725 相信大家一定非常「深恶痛疾」AppS ...
