theano中的concolutional_mlp.py学习
(1) evaluate _lenet5中的导入数据部分
# 导入数据集,该函数定义在logistic_sgd中,返回的是一个list
datasets = load_data(dataset) # 从list中提取三个元素,每个元素都是一个tuple(每个tuple含有2个元素,分别为images数据和label数据)
train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0] #训练集
valid_set_x, valid_set_y = datasets[1] #校验集
test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2] #测试集 # 训练集、校验集、测试集分别含有的样本个数
n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0]
n_valid_batches = valid_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0]
n_test_batches = test_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0]
# 训练集、校验集、测试集中包含的minibatch个数(每个iter,只给一个minibatch,而不是整个数据集)
n_train_batches /= batch_size
n_valid_batches /= batch_size
n_test_batches /= batch_size

(2)evaluate _lenet5中的building model部分
# 首先,定义一些building model用到的符号变量
index = T.lscalar() # 用于指定具体哪个minibatch的指标 # start-snippet-1
x = T.matrix('x') # 存储图像的像素数据
y = T.ivector('y') # 存储每幅图像对应的label # 开始build model
print '... building the model' # 将输入的数据(batch_size, 28 * 28)reshape为4D tensor(batch_size是每个mini-batch包含的image个数)
layer0_input = x.reshape((batch_size, 1, 28, 28)) # 构造第一个卷积层
# (1)卷积核大小为5*5、个数为nkerns[0]、striding =1,padding=0
# 输出的feature map大小为:(28-5+1 , 28-5+1) = (24, 24)
# (2)含有max-pooling,pooling的大小为2*2、striding =1,padding=0
# 输出的map大小为:(24/2, 24/2) = (12, 12)
# (3)综上,第一个卷积层输出的feature map为一个4D tensor,形状为:(batch_size, nkerns[0], 12, 12)
layer0 = LeNetConvPoolLayer(
rng,
input=layer0_input,
image_shape=(batch_size, 1, 28, 28),
filter_shape=(nkerns[0], 1, 5, 5),
poolsize=(2, 2)
) # 构造第二个卷积层,卷积核大小为5*5
# (1)卷积核大小为5*5、个数为nkerns[0]、striding =1,padding=0
# 输出的feature map大小为:(12-5+1, 12-5+1) = (8, 8)
# (2)含有max-pooling,pooling的大小为2*2、striding =1,padding=0
# 输出的map大小为:(8/2, 8/2) = (4, 4)
# (3)综上,第二个卷积层输出的feature map为一个4D tensor,形状为:(batch_size, nkerns[1], 4, 4)
layer1 = LeNetConvPoolLayer(
rng,
input=layer0.output,
image_shape=(batch_size, nkerns[0], 12, 12),
filter_shape=(nkerns[1], nkerns[0], 5, 5),
poolsize=(2, 2)
) # 将第二个卷积层的输出map(形状为(batch_size, nkerns[1], 4, 4))转化为一个matrix的形式
# 该矩阵的形状为:(batch_size, nkerns[1] * 4 * 4),每一行为一个图形对应的feature map
layer2_input = layer1.output.flatten(2) # 第一个全链接层
# (1)输入的大小固定,即第二个卷积层的输出
# (2)输出大小自己选的,这里选定为500
# (3)sigmoid函数为tan函数
layer2 = HiddenLayer(
rng,
input=layer2_input,
n_in=nkerns[1] * 4 * 4,
n_out=500,
activation=T.tanh
) # 输出层,即逻辑回归层
layer3 = LogisticRegression(input=layer2.output, n_in=500, n_out=10) # 代价函数的计算
cost = layer3.negative_log_likelihood(y) # 测试model,输入为具体要测试的test集中的某个mini-batch
# 输出为训练得到的model在该mini-batch上的error
test_model = theano.function(
[index],
layer3.errors(y),
givens={
x: test_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: test_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
) # 校验model,输入为具体要测试的校验集中的某个mini-batch
# 输出为训练得到的model在该mini-batch上的error
validate_model = theano.function(
[index],
layer3.errors(y),
givens={
x: valid_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: valid_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
) # 创建一个list,该list存放的是该CNN网络的所有待利用梯度下降法优化的参数
params = layer3.params + layer2.params + layer1.params + layer0.params # 创建一个list,该list存放的是代价函数对该CNN网络的所有待利用梯度下降法优化的参数的梯度
grads = T.grad(cost, params) # 为train模型创建更新规则,即创建一个list,自动更新params、grads中每一组值
updates = [
(param_i, param_i - learning_rate * grad_i)
for param_i, grad_i in zip(params, grads)
] # 训练model,输入为具体要训练集中的某个mini-batch
# 输出为训练得到的model在该mini-batch上的error
train_model = theano.function(
[index],
cost,
updates=updates,
givens={
x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: train_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
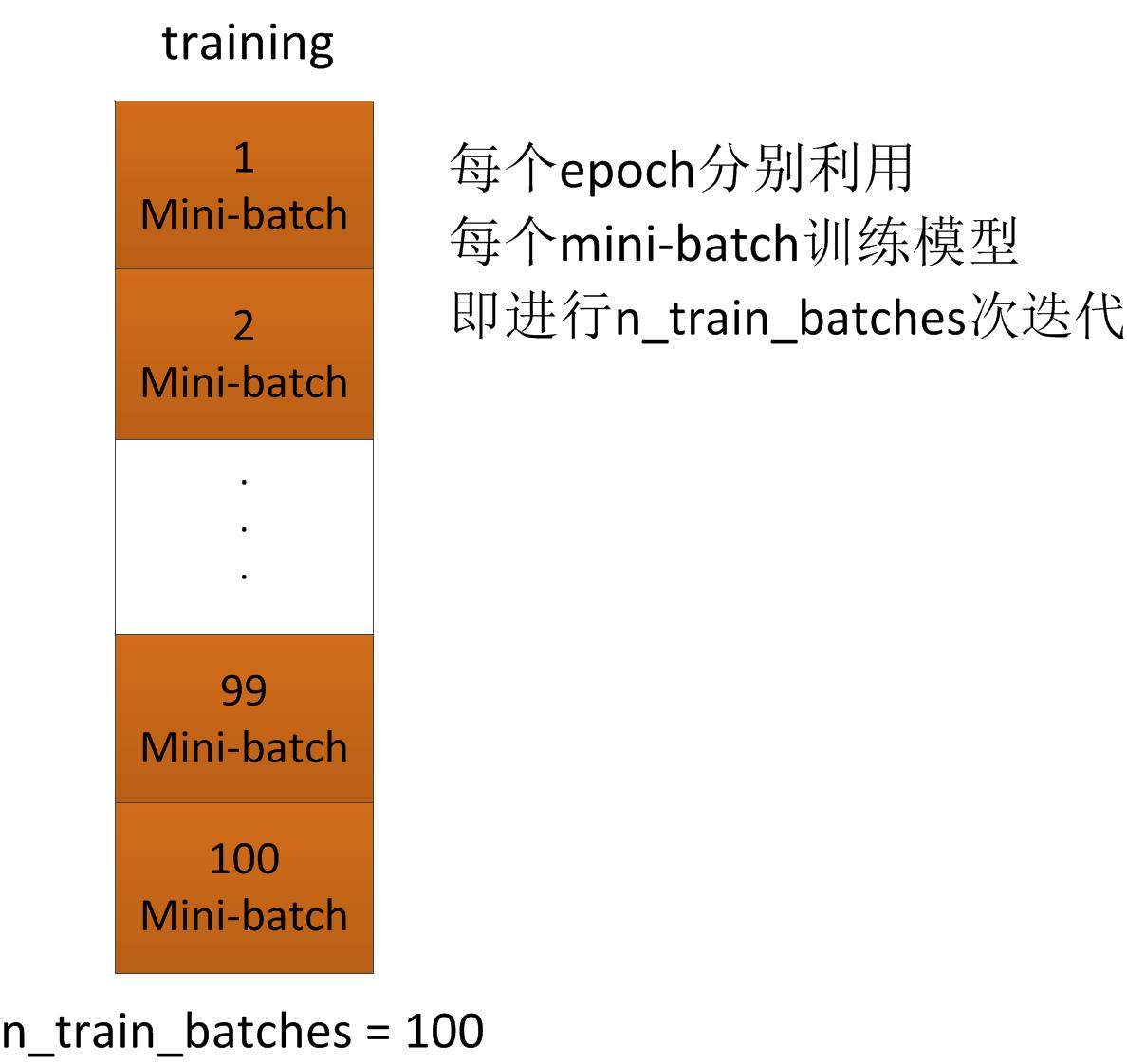
(3)Lenet-5中的training model部分
# 开始训练模型
print '... training' # 定义一些进行early-stopping的相关参数
# look as this many examples regardless
patience = 10000
# wait this much longer when a new best is found
patience_increase = 2
# a relative improvement of this much is considered significant
improvement_threshold = 0.995
# go through this many minibatche before checking the network on the validation set; in this case we check every epoch
validation_frequency = min(n_train_batches, patience / 2) # 训练过程中需要的其他参数
best_validation_loss = numpy.inf
best_iter = 0
test_score = 0.
start_time = timeit.default_timer() epoch = 0
done_looping = False while (epoch < n_epochs) and (not done_looping): #epoch次数增加1,每轮epoch,利用所有组mini-batch进行一次模型训练
# 每轮epoch,整体的迭代次数iter增加n_train_batches次
epoch = epoch + 1 # 对于整个训练集中的第minibatch_index 个mini-batch
# minibatch_index=0,1,...,n_train_batches-1
for minibatch_index in xrange(n_train_batches): # 总的iter次数(每一轮epoch,iter个数都增加n_train_batches)
# 即每一个iter,只利用一个mini-batch进行训练
# 而每一个epoch,利用了所有的mini-batch进行训练
iter = (epoch - 1) * n_train_batches + minibatch_index # 整体的迭代次数可以被100整除时,显示一次迭代次数
if iter % 100 == 0:
print 'training @ iter = ', iter # 利用第minibatch_index个mini-batch训练model,得到model的代价函数
cost_ij = train_model(minibatch_index) # 如果整体的迭代次数满足需要进行校验的条件,则对该次iter对应的model进行校验
if (iter + 1) % validation_frequency == 0: # 计算该model在校验集上的loss函数值
validation_losses = [validate_model(i) for i
in xrange(n_valid_batches)]
this_validation_loss = numpy.mean(validation_losses)
print('epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, validation error %f %%' %
(epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches,
this_validation_loss * 100.)) # 如果该model在校验集的loss值小于之前的值
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss: # 增加patience的值,目的是为了进行更多次的iter
# 也就是说,如果在测试集上的性能不如之前好,证明模型开始恶化,那么,不再进行那么多次的training了
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss * \
improvement_threshold:
patience = max(patience, iter * patience_increase) # save best validation score and iteration number
best_validation_loss = this_validation_loss
best_iter = iter # 利用测试集测试该模型
test_losses = [
test_model(i)
for i in xrange(n_test_batches)
]
# 计算测试集的loss值
test_score = numpy.mean(test_losses)
print((' epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, test error of '
'best model %f %%') %
(epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches,
test_score * 100.)) if patience <= iter:
done_looping = True
break # 整个训练过程结束,记录training时间
end_time = timeit.default_timer()
print('Optimization complete.')
print('Best validation score of %f %% obtained at iteration %i, '
'with test performance %f %%' %
(best_validation_loss * 100., best_iter + 1, test_score * 100.))
print >> sys.stderr, ('The code for file ' +
os.path.split(__file__)[1] +
' ran for %.2fm' % ((end_time - start_time) / 60.))
(4)真个convolutional_mlp的原始代码
"""This tutorial introduces the LeNet5 neural network architecture
using Theano. LeNet5 is a convolutional neural network, good for
classifying images. This tutorial shows how to build the architecture,
and comes with all the hyper-parameters you need to reproduce the
paper's MNIST results. This implementation simplifies the model in the following ways: - LeNetConvPool doesn't implement location-specific gain and bias parameters
- LeNetConvPool doesn't implement pooling by average, it implements pooling
by max.
- Digit classification is implemented with a logistic regression rather than
an RBF network
- LeNet5 was not fully-connected convolutions at second layer References:
- Y. LeCun, L. Bottou, Y. Bengio and P. Haffner:
Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document
Recognition, Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(11):2278-2324, November 1998.
http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/publis/pdf/lecun-98.pdf """
import os
import sys
import timeit import numpy import theano
import theano.tensor as T
from theano.tensor.signal import downsample
from theano.tensor.nnet import conv from logistic_sgd import LogisticRegression, load_data
from mlp import HiddenLayer class LeNetConvPoolLayer(object):
"""Pool Layer of a convolutional network """ def __init__(self, rng, input, filter_shape, image_shape, poolsize=(2, 2)):
"""
Allocate a LeNetConvPoolLayer with shared variable internal parameters. :type rng: numpy.random.RandomState
:param rng: a random number generator used to initialize weights :type input: theano.tensor.dtensor4
:param input: symbolic image tensor, of shape image_shape :type filter_shape: tuple or list of length 4
:param filter_shape: (number of filters, num input feature maps,
filter height, filter width) :type image_shape: tuple or list of length 4
:param image_shape: (batch size, num input feature maps,
image height, image width) :type poolsize: tuple or list of length 2
:param poolsize: the downsampling (pooling) factor (#rows, #cols)
""" assert image_shape[1] == filter_shape[1]
self.input = input # there are "num input feature maps * filter height * filter width"
# inputs to each hidden unit
fan_in = numpy.prod(filter_shape[1:])
# each unit in the lower layer receives a gradient from:
# "num output feature maps * filter height * filter width" /
# pooling size
fan_out = (filter_shape[0] * numpy.prod(filter_shape[2:]) /
numpy.prod(poolsize))
# initialize weights with random weights
W_bound = numpy.sqrt(6. / (fan_in + fan_out))
self.W = theano.shared(
numpy.asarray(
rng.uniform(low=-W_bound, high=W_bound, size=filter_shape),
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
borrow=True
) # the bias is a 1D tensor -- one bias per output feature map
b_values = numpy.zeros((filter_shape[0],), dtype=theano.config.floatX)
self.b = theano.shared(value=b_values, borrow=True) # convolve input feature maps with filters
conv_out = conv.conv2d(
input=input,
filters=self.W,
filter_shape=filter_shape,
image_shape=image_shape
) # downsample each feature map individually, using maxpooling
pooled_out = downsample.max_pool_2d(
input=conv_out,
ds=poolsize,
ignore_border=True
) # add the bias term. Since the bias is a vector (1D array), we first
# reshape it to a tensor of shape (1, n_filters, 1, 1). Each bias will
# thus be broadcasted across mini-batches and feature map
# width & height
self.output = T.tanh(pooled_out + self.b.dimshuffle('x', 0, 'x', 'x')) # store parameters of this layer
self.params = [self.W, self.b] # keep track of model input
self.input = input def evaluate_lenet5(learning_rate=0.1, n_epochs=200,
dataset='mnist.pkl.gz',
nkerns=[20, 50], batch_size=500):
""" Demonstrates lenet on MNIST dataset :type learning_rate: float
:param learning_rate: learning rate used (factor for the stochastic
gradient) :type n_epochs: int
:param n_epochs: maximal number of epochs to run the optimizer :type dataset: string
:param dataset: path to the dataset used for training /testing (MNIST here) :type nkerns: list of ints
:param nkerns: number of kernels on each layer
""" rng = numpy.random.RandomState(23455) datasets = load_data(dataset) train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0]
valid_set_x, valid_set_y = datasets[1]
test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2] # compute number of minibatches for training, validation and testing
n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0]
n_valid_batches = valid_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0]
n_test_batches = test_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0]
n_train_batches /= batch_size
n_valid_batches /= batch_size
n_test_batches /= batch_size # allocate symbolic variables for the data
index = T.lscalar() # index to a [mini]batch # start-snippet-1
x = T.matrix('x') # the data is presented as rasterized images
y = T.ivector('y') # the labels are presented as 1D vector of
# [int] labels ######################
# BUILD ACTUAL MODEL #
######################
print '... building the model' # Reshape matrix of rasterized images of shape (batch_size, 28 * 28)
# to a 4D tensor, compatible with our LeNetConvPoolLayer
# (28, 28) is the size of MNIST images.
layer0_input = x.reshape((batch_size, 1, 28, 28)) # Construct the first convolutional pooling layer:
# filtering reduces the image size to (28-5+1 , 28-5+1) = (24, 24)
# maxpooling reduces this further to (24/2, 24/2) = (12, 12)
# 4D output tensor is thus of shape (batch_size, nkerns[0], 12, 12)
layer0 = LeNetConvPoolLayer(
rng,
input=layer0_input,
image_shape=(batch_size, 1, 28, 28),
filter_shape=(nkerns[0], 1, 5, 5),
poolsize=(2, 2)
) # Construct the second convolutional pooling layer
# filtering reduces the image size to (12-5+1, 12-5+1) = (8, 8)
# maxpooling reduces this further to (8/2, 8/2) = (4, 4)
# 4D output tensor is thus of shape (batch_size, nkerns[1], 4, 4)
layer1 = LeNetConvPoolLayer(
rng,
input=layer0.output,
image_shape=(batch_size, nkerns[0], 12, 12),
filter_shape=(nkerns[1], nkerns[0], 5, 5),
poolsize=(2, 2)
) # the HiddenLayer being fully-connected, it operates on 2D matrices of
# shape (batch_size, num_pixels) (i.e matrix of rasterized images).
# This will generate a matrix of shape (batch_size, nkerns[1] * 4 * 4),
# or (500, 50 * 4 * 4) = (500, 800) with the default values.
layer2_input = layer1.output.flatten(2) # construct a fully-connected sigmoidal layer
layer2 = HiddenLayer(
rng,
input=layer2_input,
n_in=nkerns[1] * 4 * 4,
n_out=500,
activation=T.tanh
) # classify the values of the fully-connected sigmoidal layer
layer3 = LogisticRegression(input=layer2.output, n_in=500, n_out=10) # the cost we minimize during training is the NLL of the model
cost = layer3.negative_log_likelihood(y) # create a function to compute the mistakes that are made by the model
test_model = theano.function(
[index],
layer3.errors(y),
givens={
x: test_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: test_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
) validate_model = theano.function(
[index],
layer3.errors(y),
givens={
x: valid_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: valid_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
) # create a list of all model parameters to be fit by gradient descent
params = layer3.params + layer2.params + layer1.params + layer0.params # create a list of gradients for all model parameters
grads = T.grad(cost, params) # train_model is a function that updates the model parameters by
# SGD Since this model has many parameters, it would be tedious to
# manually create an update rule for each model parameter. We thus
# create the updates list by automatically looping over all
# (params[i], grads[i]) pairs.
updates = [
(param_i, param_i - learning_rate * grad_i)
for param_i, grad_i in zip(params, grads)
] train_model = theano.function(
[index],
cost,
updates=updates,
givens={
x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: train_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
# end-snippet-1 ###############
# TRAIN MODEL #
###############
print '... training'
# early-stopping parameters
patience = 10000 # look as this many examples regardless
patience_increase = 2 # wait this much longer when a new best is
# found
improvement_threshold = 0.995 # a relative improvement of this much is
# considered significant
validation_frequency = min(n_train_batches, patience / 2)
# go through this many
# minibatche before checking the network
# on the validation set; in this case we
# check every epoch best_validation_loss = numpy.inf
best_iter = 0
test_score = 0.
start_time = timeit.default_timer() epoch = 0
done_looping = False while (epoch < n_epochs) and (not done_looping):
epoch = epoch + 1
for minibatch_index in xrange(n_train_batches): iter = (epoch - 1) * n_train_batches + minibatch_index if iter % 100 == 0:
print 'training @ iter = ', iter
cost_ij = train_model(minibatch_index) if (iter + 1) % validation_frequency == 0: # compute zero-one loss on validation set
validation_losses = [validate_model(i) for i
in xrange(n_valid_batches)]
this_validation_loss = numpy.mean(validation_losses)
print('epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, validation error %f %%' %
(epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches,
this_validation_loss * 100.)) # if we got the best validation score until now
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss: #improve patience if loss improvement is good enough
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss * \
improvement_threshold:
patience = max(patience, iter * patience_increase) # save best validation score and iteration number
best_validation_loss = this_validation_loss
best_iter = iter # test it on the test set
test_losses = [
test_model(i)
for i in xrange(n_test_batches)
]
test_score = numpy.mean(test_losses)
print((' epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, test error of '
'best model %f %%') %
(epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches,
test_score * 100.)) if patience <= iter:
done_looping = True
break end_time = timeit.default_timer()
print('Optimization complete.')
print('Best validation score of %f %% obtained at iteration %i, '
'with test performance %f %%' %
(best_validation_loss * 100., best_iter + 1, test_score * 100.))
print >> sys.stderr, ('The code for file ' +
os.path.split(__file__)[1] +
' ran for %.2fm' % ((end_time - start_time) / 60.)) if __name__ == '__main__':
evaluate_lenet5() def experiment(state, channel):
evaluate_lenet5(state.learning_rate, dataset=state.dataset)
theano中的concolutional_mlp.py学习的更多相关文章
- theano中的logisticregression代码学习
1 class LogisticRegression (object): 2 def __int__(self,...): 3 4 #定义一些与逻辑回归相关的各种函数 5 6 def method1( ...
- 『德不孤』Pytest框架 — 14、Pytest中的conftest.py文件
目录 1.conftest.py文件介绍 2.conftest.py的注意事项 3.conftest.py的使用 4.不同位置conftest.py文件的优先级 5.conftest.py中Fixtu ...
- Python3中的字符串函数学习总结
这篇文章主要介绍了Python3中的字符串函数学习总结,本文讲解了格式化类方法.查找 & 替换类方法.拆分 & 组合类方法等内容,需要的朋友可以参考下. Sequence Types ...
- theano中的scan用法
scan函数是theano中的循环函数,相当于for loop.在读别人的代码时第一次看到,有点迷糊,不知道输入.输出怎么定义,网上也很少有example,大多数都是相互转载同一篇.所以,还是要看官方 ...
- theano中的dimshuffle
theano中的dimshuffle函数用于对张量的维度进行操作,可以增加维度,也可以交换维度,删除维度. 注意的是只有shared才能调用dimshuffle() 'x'表示增加一维,从0d sca ...
- Android中的SQLite使用学习
Android中的SQLite使用学习 SQLite是非常流行的嵌入式关系型数据库,轻载, 速度快,而且是开源.在Android中,runtime提供SQLite,所以我们可以使用SQLite,而且是 ...
- Java中的回调函数学习
Java中的回调函数学习 博客分类: J2SE JavaJ# 一般来说分为以下几步: 声明回调函数的统一接口interface A,包含方法callback(); 在调用类caller内将该接口设置 ...
- JavaSE中Collection集合框架学习笔记(1)——具有索引的List
前言:因为最近要重新找工作,Collection(集合)是面试中出现频率非常高的基础考察点,所以好好恶补了一番. 复习过程中深感之前的学习不系统,而且不能再像刚毕业那样死背面试题,例如:String是 ...
- JavaSE中Collection集合框架学习笔记(2)——拒绝重复内容的Set和支持队列操作的Queue
前言:俗话说“金三银四铜五”,不知道我要在这段时间找工作会不会很艰难.不管了,工作三年之后就当给自己放个暑假. 面试当中Collection(集合)是基础重点.我在网上看了几篇讲Collection的 ...
随机推荐
- IOS开发之——使用Segue在StoryBoard之间切换
使用Segue能够在ViewController之间来回切换,以下就来说下切换方法: 1. 使用点击button进行切换 直接上图,在须要切换的View属性界面,点击Modal然后拉到前一个view界 ...
- MFC ListControl使用方法
在原来博客中有:MF CListControl 简单功能使用 推荐文章:MFC类CtrlList用法 今天又又一次来介绍点新东西:双击击listcontrol 做出响应.当然你能够做的还有非常多,比 ...
- fscanf函数
函数定义: int fscanf( FILE *stream, const char *format [, argument ]... ); 以下是csdn的样例: /* FSCANF.C: This ...
- GDB反向调试 + 指令记录+函数历史记录
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26941022-id-3199961.html b.c void fun(int a, int b){ int c; c=a+b; } v ...
- Android开发之使用广播监听网络状态变化
我们经常需要判断网络状态的变化,如有无网络,所以需要监听网络状态的变化,比如网络断开,网络连接给予友好提示.如何监听网络状态的变化呢,最近工作中需要用到这个,于是就用广播机制来实现了网络状态的监听. ...
- Java的浮点数
为了防止无良网站的爬虫抓取文章,特此标识,转载请注明文章出处.LaplaceDemon/ShiJiaqi. http://www.cnblogs.com/shijiaqi1066/p/5160771. ...
- 原生js日期时间插件鼠标点击文本框弹出日期时间表格选择日期时间
原文出处 (这是我从互联网上搜来的,感觉能满足各方面的需求.个人感觉挺不错的,所以后期修改了一下向大家推荐!) 效果图: html代码: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC " ...
- asp.net之动态页面和静态页面的区别
asp.net之动态页面和静态页面的区别 当我开始接触web开发的时候,首先学到的是html.css.js这一类网页语言,通过布局可以搭建出一个静态网站,效果也跟我们上网时经常看到的一些网站一样了.于 ...
- Windows I/O模型、同步/异步、阻塞/非阻塞
转载自:http://www.cppblog.com/tx7do/articles/5954.html 同步 所谓同步,就是在发出一个功能调用时,在没有得到结果之前,该调用就不返回.按照这个定义,其实 ...
- servlet(一)
百度百科是这样的: Servlet 是在服务器上运行的小程序.这个词是在 Java applet 的环境中创造的.虽然后者已很少被使用,但 Servlet 却发展的很好.是一般面试都会常考的知识. 维 ...
