Android RecyclerView使用详解(三)
在上一篇(RecyclerView使用详解(二))文章中介绍了RecyclerView的多Item布局实现,接下来要来讲讲RecyclerView的Cursor实现,相较于之前的实现,Cursor有更多的使用场景,也更加的常用,特别是配合LoaderManager和CursorLoader进行数据的缓存及加载显示,基于此我们来重点看看RecyclerView的CursorAdapter具体要怎么实现。
##一、CursorAdapter实现(配合LoaderManager和CursorLoader)
如果之前你用过ListView实现过此功能(CursorAdapter),那么你一定对下面这两个方法并不陌生
[代码]java代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@Overridepublic View newView(Context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent) { return null;}@Overridepublic void bindView(View view, Context context, Cursor cursor) {} |
其中newView方法是用来创建Item布局的,bindView 方法是用来绑定当前View数据的,就相当于之前的getView方法拆成了两个方法实现。
如果你用RecyclerView,你会发现CursorAdapter这个类没有了,既然没有了,那我们就自己仿照着ListView的CursorAdapter类来实现,具体的代码没什么大的出入,无非就是注册两个观察者去监听数据库数据的变化,但是有两个地方需要注意一下,一个就是hasStableIds() 这个方法RecyclerView.Adapter中不能复写父类的方法,需要在初始化的时候调用setHasStableIds(true); 来完成相同功能,第二个就是notifyDataSetInvalidated() 这个方法没有,统一修改成notifyDataSetChanged() 方法即可。
[代码]java代码:
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
|
void init(Context context, Cursor c, int flags) { boolean cursorPresent = c != null; mCursor = c; mDataValid = cursorPresent; mContext = context; mRowIDColumn = cursorPresent ? c.getColumnIndexOrThrow("_id") : -1; if ((flags & FLAG_REGISTER_CONTENT_OBSERVER) == FLAG_REGISTER_CONTENT_OBSERVER) { mChangeObserver = new ChangeObserver(); mDataSetObserver = new MyDataSetObserver(); } else { mChangeObserver = null; mDataSetObserver = null; } if (cursorPresent) { if (mChangeObserver != null) c.registerContentObserver(mChangeObserver); if (mDataSetObserver != null) c.registerDataSetObserver(mDataSetObserver); } setHasStableIds(true);//这个地方要注意一下,需要将表关联ID设置为true } //************// public Cursor swapCursor(Cursor newCursor) { if (newCursor == mCursor) { return null; } Cursor oldCursor = mCursor; if (oldCursor != null) { if (mChangeObserver != null) oldCursor.unregisterContentObserver(mChangeObserver); if (mDataSetObserver != null) oldCursor.unregisterDataSetObserver(mDataSetObserver); } mCursor = newCursor; if (newCursor != null) { if (mChangeObserver != null) newCursor.registerContentObserver(mChangeObserver); if (mDataSetObserver != null) newCursor.registerDataSetObserver(mDataSetObserver); mRowIDColumn = newCursor.getColumnIndexOrThrow("_id"); mDataValid = true; // notify the observers about the new cursor notifyDataSetChanged(); } else { mRowIDColumn = -1; mDataValid = false; // notify the observers about the lack of a data set //There is no notifyDataSetInvalidated() method in RecyclerView.Adapter notifyDataSetChanged();//注意此处 } return oldCursor; } //************// private class MyDataSetObserver extends DataSetObserver { @Override public void onChanged() { mDataValid = true; notifyDataSetChanged(); } @Override public void onInvalidated() { mDataValid = false; //There is no notifyDataSetInvalidated() method in RecyclerView.Adapter notifyDataSetChanged();//注意此处 } } |
怎么样,是不是很简单,没错,就是这么简单,这里是完整的BaseAbstractRecycleCursorAdapter代码,用法和ListView的CursorAdapter用法一致,具体的可以看看我的Recyclerview LoaderManager Provider
##二、Item的动画实现 RecyclerView本身就已经实现了ITEM的动画,只需要调用以下几个函数来增删Item即可出现默认动画。
[代码]java代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
notifyItemChanged(int)notifyItemInserted(int)notifyItemRemoved(int)notifyItemRangeChanged(int, int)notifyItemRangeInserted(int, int)notifyItemRangeRemoved(int, int) |
怎么样,是不是很轻松,如果你不满足系统默认动画,那么你可以自定义实现RecyclerView.ItemAnimator的接口方法,实现代码可以参考DefaultItemAnimator.当然,如果你不想自己实现,那么也没关系,这里有人已经写了开源库,你可以去看看recyclerview-animators,这里给出默认动画实现方式代码AnimFragment
##三、嵌套RecycleView
一般是不推荐使用嵌套RecycleView的,和ListView是类似的,遇到这种需要嵌套的View一般都是想别的办法来规避,比如动态AddView,或者通过RecycleView的MultipleItemAdapter来实现,通过设置不同的ItemType布局不同的View,但是有时候会闲麻烦,想直接就用嵌套的方式来做,那么和ListView实现方式不同的是,ListView的实现一般都是继承ListView然后复写onMeasure方法,如下所示:
[代码]java代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@Overrideprotected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { int expandSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(Integer.MAX_VALUE >> 2, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST); super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, expandSpec);} |
但是RecycleView的实现方式不再是继承RecycleView来做,而是通过修改LayoutManager的方式,即通过继承LinearLayoutManager GridLayoutManager StaggeredGridLayoutManager来修改子控件的测量,下面给出主要代码:
[代码]java代码:
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
|
private int[] mMeasuredDimension = new int[2]; @Override public void onMeasure(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state, int widthSpec, int heightSpec) { final int widthMode = View.MeasureSpec.getMode(widthSpec); final int heightMode = View.MeasureSpec.getMode(heightSpec); final int widthSize = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(widthSpec); final int heightSize = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(heightSpec); Log.i(TAG, "onMeasure called. \nwidthMode " + widthMode + " \nheightMode " + heightSpec + " \nwidthSize " + widthSize + " \nheightSize " + heightSize + " \ngetItemCount() " + getItemCount()); int width = 0; int height = 0; for (int i = 0; i < getItemCount(); i++) { measureScrapChild(recycler, i, View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(i, View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED), View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(i, View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED), mMeasuredDimension); if (getOrientation() == HORIZONTAL) { width = width + mMeasuredDimension[0]; if (i == 0) { height = mMeasuredDimension[1]; } } else { height = height + mMeasuredDimension[1]; if (i == 0) { width = mMeasuredDimension[0]; } } } switch (widthMode) { case View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: width = widthSize; case View.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: case View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: } switch (heightMode) { case View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: height = heightSize; case View.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: case View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: } setMeasuredDimension(width, height); } private void measureScrapChild(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, int position, int widthSpec, int heightSpec, int[] measuredDimension) { try { View view = recycler.getViewForPosition(0);//fix 动态添加时报IndexOutOfBoundsException if (view != null) { RecyclerView.LayoutParams p = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams(); int childWidthSpec = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(widthSpec, getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(), p.width); int childHeightSpec = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(heightSpec, getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom(), p.height); view.measure(childWidthSpec, childHeightSpec); measuredDimension[0] = view.getMeasuredWidth() + p.leftMargin + p.rightMargin; measuredDimension[1] = view.getMeasuredHeight() + p.bottomMargin + p.topMargin; recycler.recycleView(view); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { } } |
[代码]java代码:
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
private int[] mMeasuredDimension = new int[2]; @Override public void onMeasure(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state, int widthSpec, int heightSpec) { final int widthMode = View.MeasureSpec.getMode(widthSpec); final int heightMode = View.MeasureSpec.getMode(heightSpec); final int widthSize = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(widthSpec); final int heightSize = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(heightSpec); int width = 0; int height = 0; int count = getItemCount(); int span = getSpanCount(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { measureScrapChild(recycler, i, View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(i, View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED), View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(i, View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED), mMeasuredDimension); if (getOrientation() == HORIZONTAL) { if (i % span == 0) { width = width + mMeasuredDimension[0]; } if (i == 0) { height = mMeasuredDimension[1]; } } else { if (i % span == 0) { height = height + mMeasuredDimension[1]; } if (i == 0) { width = mMeasuredDimension[0]; } } } switch (widthMode) { case View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: width = widthSize; case View.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: case View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: } switch (heightMode) { case View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: height = heightSize; case View.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: case View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: } setMeasuredDimension(width, height); } private void measureScrapChild(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, int position, int widthSpec, int heightSpec, int[] measuredDimension) { if (position < getItemCount()) { try { View view = recycler.getViewForPosition(0);//fix 动态添加时报IndexOutOfBoundsException if (view != null) { RecyclerView.LayoutParams p = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams(); int childWidthSpec = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(widthSpec, getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(), p.width); int childHeightSpec = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(heightSpec, getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom(), p.height); view.measure(childWidthSpec, childHeightSpec); measuredDimension[0] = view.getMeasuredWidth() + p.leftMargin + p.rightMargin; measuredDimension[1] = view.getMeasuredHeight() + p.bottomMargin + p.topMargin; recycler.recycleView(view); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
##四、效果图如下:
Item默认动画效果
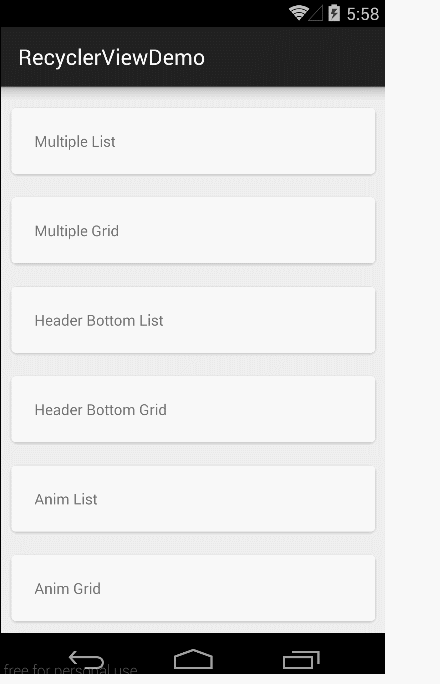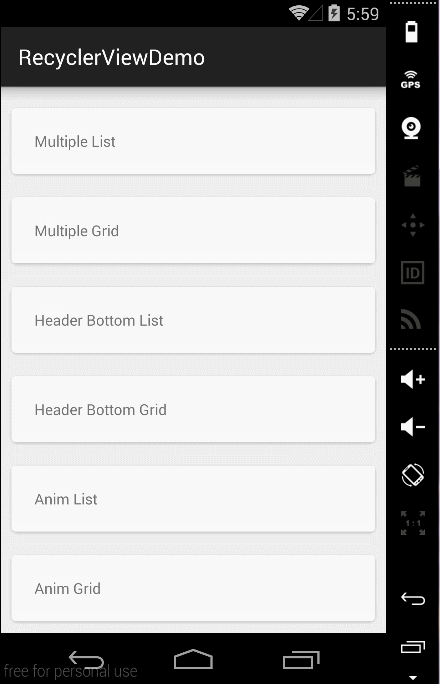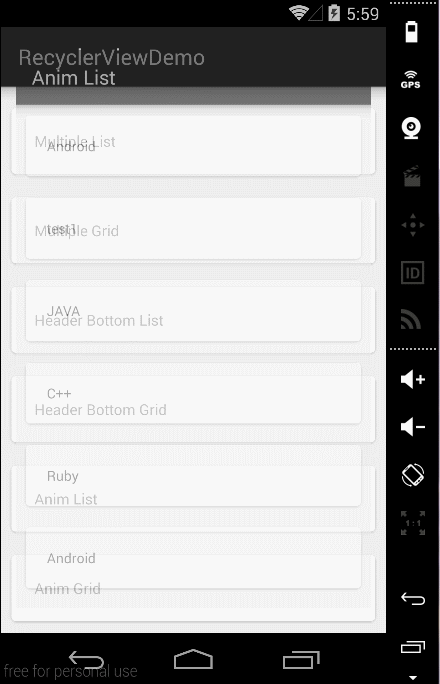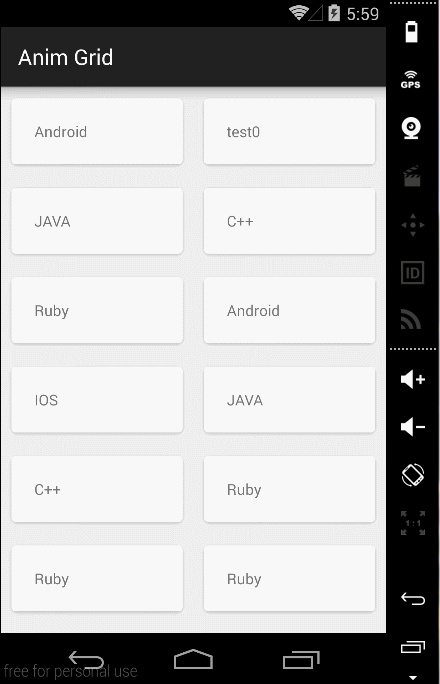
嵌套ScrollView效果
最后给出代码下载地址–>Demo Code
Android RecyclerView使用详解(三)的更多相关文章
- Android Studio 插件开发详解三:翻译插件实战
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/article/details/78113868 本文出自[赵彦军的博客] 一:概述 如果不了解插件开发基础的同学可以 ...
- Android RecyclerView使用详解(二)
在上一篇(RecyclerView使用详解(一))文章中简单的介绍了RecyclerView的基本用法,接下来要来讲讲RecyclerView的更多用法,要实现不同的功能效果,大部分都还是在于Recy ...
- Android WebView 开发详解(三)
转载请注明出处 http://blog.csdn.net/typename/article/details/40302351 powered by miechal zhao 概览 Android ...
- Android RecyclerView使用详解(一)
一.前言 RecyclerView是谷歌V7包下新增的控件,用来替代ListView的使用,在RecyclerView标准化了ViewHolder类似于ListView中convertView用来做视 ...
- Android事件分发详解(三)——ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent()源码学习
package cc.aa; import android.os.Environment; import android.view.MotionEvent; import android.view.V ...
- Android清单文件详解(三)----应用程序的根节点<application>
<application>节点是AndroidManifest.xml文件中必须持有的一个节点,它包含在<manifest>节点下.通过<application>节 ...
- Android Studio 插件开发详解四:填坑
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/article/details/78265540 本文出自[赵彦军的博客] 在前面我介绍了插件开发的基本流程 [And ...
- Android Studio 插件开发详解二:工具类
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/article/details/78112856 本文出自[赵彦军的博客] 在插件开发过程中,我们按照开发一个正式的项 ...
- Android 高级UI设计笔记07:RecyclerView 的详解
1. 使用RecyclerView 在 Android 应用程序中列表是一个非常重要的控件,适用场合非常多,如新闻列表.应用列表.消息列表等等,但是从Android 一出生到现在并没有非常 ...
随机推荐
- Linux网络编程5——使用UDP协议实现群聊
引言 本文实现的功能类似于我之前所写的一篇博文(Linux之select系统调用_2),区别在于进程之间的通信方式有所不同.之前的文章中,我所使用的是管道,而本文我将会使用socket接口. 需求 客 ...
- POJ2402/UVA 12050 Palindrome Numbers 数学思维
A palindrome is a word, number, or phrase that reads the same forwards as backwards. For example,the ...
- hadoop 1 testcase运行方法
转入hadoop2.0后,逐渐忘记了之前做testcase运行的方法,记录一下: ant -Dtestcase=Test*** 如果只运行core包得testcase可以 an ...
- 客户端用httpurlconnection来进行http连接的
客户端用httpurlconnection来进行http连接的,并设置restful风格 请求响应流程 设置连接参数的方法 setAllowUserInteraction setDoInput set ...
- photoshop:找不到增效工具入口点
按Ctrl+k+9 ,到预设的增效工具栏设置为要存储的文件夹路径:
- PHPStorm IDE 快捷键(MAC)
⌘——Command ⌃ ——Control ⌥——Option/Alt ⇧——Shift ⇪——Caps Lock fn——功能键就是fn 编辑 Command+alt+T 用 (if..else, ...
- http://blog.csdn.net/lvyuanj/article/details/51235135
http://blog.csdn.net/lvyuanj/article/details/51235135
- SSIS ->> Error Handling
Event Handler Each task and container raises events as it runs, such as an OnError event, among seve ...
- Windows下搭建Android开发环境
1.下载eclipse google eclipse,到官网去下载最新版的,推荐java ee版本的,当然你要用android版本或者standard也无妨 2.下载android sdk,安装相关的 ...
- dojo 三 类和继承 dojo/_base/declare
这里要讲有关类的定义.继承和实现.官方教程:http://dojotoolkit.org/documentation/tutorials/1.7/declare/类的声明是通过declare 这个方法 ...
