Spring框架学习之第9节
- aop编程
aop(aspect oriented programming)面向切面(方面)编程,是所有对象或者是一类对象编程,核心是(在不增加代码的基础上,还增加新功能)
汇编(伪机器指令 mov jump)面向机器
C语言(面向过程)->系统软件(操作系统,数据库,语言本身,杀毒软件,防火墙,驱动)大部分都是用C语言软件写
语句1;
语句2;
…
C++
Java语言(面向对象->类-对象)
class Dog{
属性;->变量
行为->函数
}
面向切面 spring(->aop)面向很多对象编程
aop特别提醒:aop编程,实际上在开发框架本身用的很多,在实际项目开发中用的并不是很多,但是将来会越来越多,这是个编程的趋势
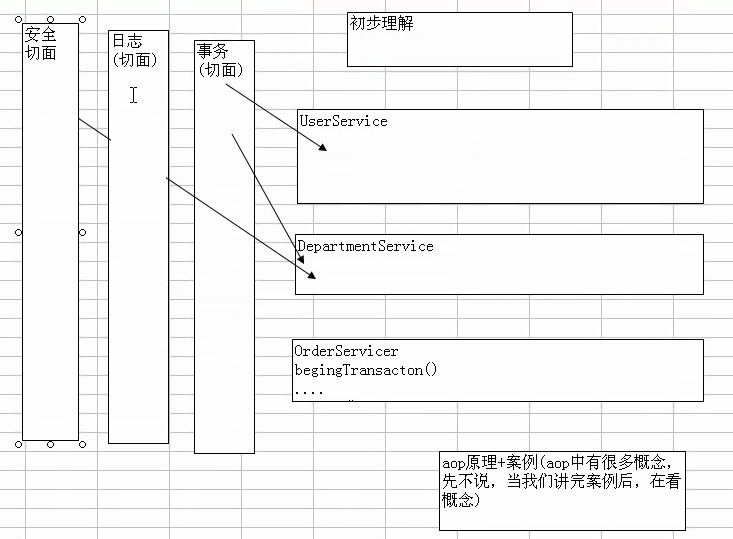
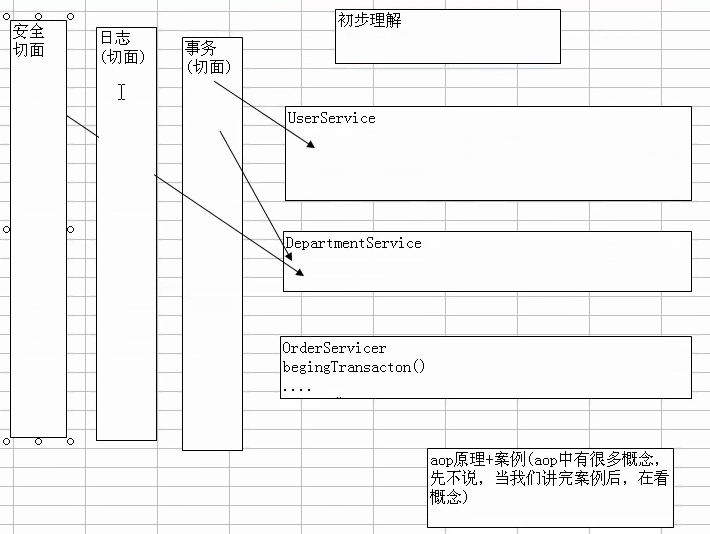
- aop原理+案例
aop原理+案例(aop中有很多概念,先不说,当我们讲完案例后,再看概念)
需求:在调用Test1Service sayHello()前完成日志记录功能,
在调用Test2Service sayHello()前也要完成日志
编程说明
beans.xml
- 被代理的对象
- 前置通知
- 代理对象
<!!!细节!!!>
步骤如下:
1、 定义接口
2、 编写对象(被代理对象=目标对象)
3、 编写通知(前置通知在目标方法调用前调用)
4、 在我们的beans.xml中配置
4.1、先配置被代理对象=目标对象
4.2、配置通知
4.3、配置代理对象是proxyFactoryBean对象实例
4.3.1、<!—代理接口集--à
4.3.2、织入通知
4.3.3、配置被代理对象
真正的织入发生时动态的,真正的织入发生应该是一个过程,当你在调用被代理对象方法的时候织入发生。
切入了定义了通知应该在哪些连接点上,定义了前置通知可以在sayHello之前被调用,连接点就会变成切入点,就好像连接点是一个静态的概念而切入点是一个动态的概念。
后面还有后置通知,环绕通知,异常通知,引入通知
上机练习:你把老师写的代码看看写一遍
需求:
在调用完Test1Service的sayHello()后,完成资源的关闭
提问?说spring的aop中,当你通过代理对象去实现aop的时候,获取的ProxyFactoryBean是什么类型?
答:返回的是一个代理对象,如果目标对象实现了接口,则spring使用jdk的动态代理技术完成,如果目标对象没有实现接口,则spring使用CGLIB动态代理技术完成.
提一个问题
Class A{
private String name;
public void setName(String name){
system.out.println(“name” + name);
}
}
beans.xml
<bean id=”a” class=”A”>
<property name=”name” value=”顺平” />
</bean>
理解:
A a = new A();
a.setName(“顺平”);
需求:
在进入sayhello()函数以后
sayHello(){
连接点
bi.xx
}
需求:
织入的通知会对所有的函数都有影响,通过引入通知来选择织入
我们只希望在调用sayHello()来进行前置通知或后置通知的处理,我不希望我们的sayBye参与
通过引入通知我们可以自定义切入点。
切入点允许使用正则表达式过滤
使用spring的静态切入点(续)
正则表达式切入点
RegexpMethodPointcut
|
符号 |
描述 |
示例 |
匹配 |
不匹配 |
|
. |
匹配任何单个字符 |
setFoo. |
setFooB |
setFoo setFooBar |
|
+ |
匹配前一个字符一次或多次 |
setFoo.+ |
setFooBar setFooB |
setFoo |
|
* |
匹配前一个字符0次或多次 |
setFoo.* |
setFoo setFooB, setFooBar |
|
|
\ |
匹配任何正则表达式符号 |
\.setFoo. |
bar.setFoo |
setFoo |




项目结构

beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"
> <!-- 配置被代理的对象 -->
<bean id="test1Service" class="com.litao.aop.Test1Service">
<property name="name" value="顺平" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置前置通知 proxyFactoryBean implements TestServiceInter,TestServiceInter2{
public void sayHello();
} 思考
interface Inter1{};
class A implements Inter1,Inter2{
}
Inter1 a=new A();
Inter2 b=(Inter2)a;
-->
<!-- 配置异常通知 -->
<bean id="myMethodBeforeAdvice" class="com.litao.aop.MyMethodBeforeAdvice" />
<!-- 配置后置通知 -->
<bean id="myAfterReturnningAdvice" class="com.litao.aop.MyAfterReturnningAdvice" />
<!-- 配置环绕通知 -->
<bean id="myMethodInterceptor" class="com.litao.aop.MyMethodInterceptor" />
<!-- 配置异常通知 -->
<bean id="myThrowsAdvice" class="com.litao.aop.MyThrowsAdvice" />
<!-- 定义前置通知的切入点 -->
<bean id="myMethodBeforeAdviceFilter" class="org.springframework.aop.support.NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice" ref="myMethodBeforeAdvice" />
<property name="mappedNames">
<list>
<value>sayHello</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置代理对象 -->
<bean id="proxyFactoryBean" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<!-- 代理接口集 -->
<property name="proxyInterfaces">
<list>
<value>com.litao.aop.TestServiceInter</value>
<value>com.litao.aop.TestServiceInter2</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 把通知织入到代理对象 -->
<property name="interceptorNames">
<!-- 相当于包MyMethodBeforeAdvice前置通知和代理对象关联,我们也
可以把通知看出拦截器,struts2核心拦截器 -->
<list>
<!-- 相当于使用自定义切入点来控制前置通知 -->
<value>myMethodBeforeAdviceFilter</value>
<!-- 织入后置通知 -->
<value>myAfterReturnningAdvice</value>
<!-- 织入环绕通知 -->
<value>myMethodInterceptor</value>
<!-- 织入异常通知 -->
<value>myThrowsAdvice</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 配置被代理对象,可以指定 -->
<property name="target" ref="test1Service"/>
</bean>
</beans>
App1.java
package com.litao.aop; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class App1 { /**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/litao/aop/beans.xml");
TestServiceInter ts = (TestServiceInter)ac.getBean("proxyFactoryBean");
System.out.println("ts 类型是什么"+ts);
ts.sayHello(); ((TestServiceInter2)ts).sayBye(); } }
MyAfterReturnningAdvice.java
package com.litao.aop;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
public class MyAfterReturnningAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice {
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method,
Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("关闭资源 ...");
}
}
MyMethodBeforeAdvice.java
package com.litao.aop;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
public class MyMethodBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
/**
* method:被调用的方法
* args:给method传递的参数
* target:目标对象
*/
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target)
throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("*********************************");
System.out.println("记录日志..."+method.getName());
}
}
MyMethodInterceptor.java
package com.litao.aop; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation; public class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor { @Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation arg0) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("调用方法前执行...");
Object obj = arg0.proceed();
System.out.println("调用方法后执行...");
return obj;
} }
MyThrowsAdvice.java
package com.litao.aop;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice;
public class MyThrowsAdvice implements ThrowsAdvice {
public void afterThrowing(Method m,Object[] os,Object target,Exception e){
System.out.println("出异常了" + e.getMessage());
}
}
Test1Service.java
package com.litao.aop;
public class Test1Service implements TestServiceInter,TestServiceInter2 {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void sayHello() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("hi " + name);
}
public void sayBye() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("bye " + name);
//int i = 9/0;
}
}
TestServiceInter.java
package com.litao.aop;
public interface TestServiceInter {
public void sayHello();
}
TestServiceInter2.java
package com.litao.aop;
public interface TestServiceInter2 {
public void sayBye();
}
Spring框架学习之第9节的更多相关文章
- Spring框架学习之第2节
传统的方法和使用spring的方法 使用spring,没有new对象,我们把创建对象的任务交给了spring的框架,通过配置用时get一下就行. 项目结构 applicationContext.xml ...
- Spring框架学习之第1节
spring快速入门 ① spring是什么? Struts是web框架(jsp/action/actionform) hibernate是orm框架(对象和关系映射框架),处于持久层 sprin ...
- Spring框架学习之第8节
<bean id=”foo” class=”…Foo”> <property name=”属性”> <!—第一方法引用--> <ref bean=”bean对 ...
- Spring框架学习之第3节
model层(业务层+dao层+持久层) spring开发提倡接口编程,配合di技术可以更好的达到层与层之间的解耦 举例: 现在我们体验一下spring的di配合接口编程,完成一个字母大小写转换的案例 ...
- Spring框架学习之第7节
配置Bean的细节 ☞尽量使用scope=”singleton”,不要使用prototype,因为这样对我们的性能影响较大 ②如何给集合类型注入值 Java中主要的map,set,list / 数组 ...
- Spring框架学习之第6节
bean的生命周期 为什么总是一个生命当做一个重点? Servlet –> servlet生命周期 Java对象生命周期 往往笔试,面试总喜欢问生命周期的问题? ① 实例化(当我们的程序加载 ...
- Spring框架学习之第5节
request session global-session 三个在web开发中才有意义 如果配置成prototype有点类似于request 如果配置成singleton有点类似于web开发中的gl ...
- Spring框架学习之第4节
从ApplicaionContext应用上下文容器中获取bean和从bean工厂容器中有什么区别: 具体案例如下 结论: 1.如果使用上下文ApplicationContext,则配置的bean如果是 ...
- Spring框架学习一
Spring框架学习,转自http://blog.csdn.net/lishuangzhe7047/article/details/20740209 Spring框架学习(一) 1.什么是Spring ...
随机推荐
- 高德地图JavaScript API开发研究
高德地图JavaScript API是一套用JavaScript 语言编写的应用程序接口,可以通过各种API接口向地图添加内容,创建功能丰富.交互性强的地图应用.高德地图JavaScript API ...
- CRC校验算法
typedef unsigned char UCHAR;typedef unsigned char BOOL; /* 计算cnt字节数据的crc,最后一个字节的低7比特必须是0,实际上求的是(cnt× ...
- C++中栈的出栈,入栈规则:A,B,C,D,E
考题: 栈底至栈顶一次存放元素 ABCD 在第五个元素E入栈之前 栈中元素可以出栈,则出栈序列可能是_____a d___________. a. ABCED b. DBCEA c. CD ...
- windows多线程编程(一)(转)
源出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/TenosDoIt/archive/2013/04/15/3022036.html CreateThread:Windows的API函数(SDK函 ...
- VBS基础篇 - 常用函数
Option Explicit '*********************************Date/Time函数******************************* 'CDate函 ...
- 团队开发之《极速蜗牛》NABC分析
一.简介 项目名称:极速蜗牛 特点:操作简单,视觉与听觉配合,让用户有最完美的体验. 二.NABC分析 N(need):在人们无时无刻离不开手机的今天,难免有无聊的时候,此刻一款操作简单又能令人们动脑 ...
- Leetcode#108 Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
原题地址 对于已排序数组,二分法递归构造BST 代码: TreeNode *buildBST(vector<int> &num, int i, int j) { if (i > ...
- aspx文件、aspx.cs文件、aspx.designer.cs文件之讲解
.aspx文件:(页面)书写页面代码.存储的是页面design代码.只是放各个控件的代码,处理代码一般放在.cs文件中. .aspx.cs文件:(代码隐藏页)书写类代码.存储的是程序代码.一般存放与数 ...
- PowerDesigner(六)-物理数据模型(PDM逆向工程)(转)
物理数据模型PDM 物理数据模型(Physical Data Model,PDM):在数据库的逻辑结构设计好之后,就需要完成其物理设计,PDM就是为实现这一目的而设计的. 物理数据模型是以常用的DBM ...
- Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2) C题
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/424/problem/C, 想来一个小时,就是做不出,都做出来了,悲剧! 分析:我们知道交换异或的顺序不影响答案! 然后就是求t ...
