Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) A B C 暴力 二分 dp(字符串的反转)
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vasiliy lives at point (a, b) of the coordinate plane. He is hurrying up to work so he wants to get out of his house as soon as possible. New app suggested n available Beru-taxi nearby. The i-th taxi is located at point (xi, yi) and moves with a speed vi.
Consider that each of n drivers will move directly to Vasiliy and with a maximum possible speed. Compute the minimum time when Vasiliy will get in any of Beru-taxi cars.
The first line of the input contains two integers a and b ( - 100 ≤ a, b ≤ 100) — coordinates of Vasiliy's home.
The second line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000) — the number of available Beru-taxi cars nearby.
The i-th of the following n lines contains three integers xi, yi and vi ( - 100 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 100, 1 ≤ vi ≤ 100) — the coordinates of the i-th car and its speed.
It's allowed that several cars are located at the same point. Also, cars may be located at exactly the same point where Vasiliy lives.
Print a single real value — the minimum time Vasiliy needs to get in any of the Beru-taxi cars. You answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 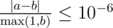 .
.
0 0
2
2 0 1
0 2 2
1.00000000000000000000
1 3
3
3 3 2
-2 3 6
-2 7 10
0.50000000000000000000
In the first sample, first taxi will get to Vasiliy in time 2, and second will do this in time 1, therefore 1 is the answer.
题意:起始点为(a,b) 给n辆出租车的位置以及速度 问你最短的时间出租车到达(a,b)
题解:暴力 注意精度
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
double a,b;
int n;
struct node
{
double x,y,v;
}N[];
double ans=;
int main()
{
ans=;
scanf("%lf %lf",&a,&b);
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%lf %lf %lf",&N[i].x,&N[i].y,&N[i].v);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
double exm=0.0;
exm=sqrt((a-N[i].x)*(a-N[i].x)+(b-N[i].y)*(b-N[i].y))/N[i].v;
if((ans-exm)>0.000001)
ans=exm;
}
printf("%.15f\n",ans);
return ;
}
In the second sample, cars 2 and 3 will arrive simultaneously.
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vasiliy likes to rest after a hard work, so you may often meet him in some bar nearby. As all programmers do, he loves the famous drink "Beecola", which can be bought in n different shops in the city. It's known that the price of one bottle in the shop i is equal to xi coins.
Vasiliy plans to buy his favorite drink for q consecutive days. He knows, that on the i-th day he will be able to spent mi coins. Now, for each of the days he want to know in how many different shops he can buy a bottle of "Beecola".
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of shops in the city that sell Vasiliy's favourite drink.
The second line contains n integers xi (1 ≤ xi ≤ 100 000) — prices of the bottles of the drink in the i-th shop.
The third line contains a single integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 100 000) — the number of days Vasiliy plans to buy the drink.
Then follow q lines each containing one integer mi (1 ≤ mi ≤ 109) — the number of coins Vasiliy can spent on the i-th day.
Print q integers. The i-th of them should be equal to the number of shops where Vasiliy will be able to buy a bottle of the drink on the i-th day.
5
3 10 8 6 11
4
1
10
3
11
0
4
1
5
On the first day, Vasiliy won't be able to buy a drink in any of the shops.
On the second day, Vasiliy can buy a drink in the shops 1, 2, 3 and 4.
On the third day, Vasiliy can buy a drink only in the shop number 1.
Finally, on the last day Vasiliy can buy a drink in any shop.
题意:给你n个值 q组查询m 输出这n个值中小于等于m的数量
题解:排序之后 二分
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n;
int a[];
int q,m;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sort(a,a+n);
scanf("%d",&q);
for(int i=;i<=q;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&m);
int pos=;
pos=upper_bound(a,a+n,m)-a;
printf("%d\n",pos);
}
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vasiliy is fond of solving different tasks. Today he found one he wasn't able to solve himself, so he asks you to help.
Vasiliy is given n strings consisting of lowercase English letters. He wants them to be sorted in lexicographical order (as in the dictionary), but he is not allowed to swap any of them. The only operation he is allowed to do is to reverse any of them (first character becomes last, second becomes one before last and so on).
To reverse the i-th string Vasiliy has to spent ci units of energy. He is interested in the minimum amount of energy he has to spent in order to have strings sorted in lexicographical order.
String A is lexicographically smaller than string B if it is shorter than B (|A| < |B|) and is its prefix, or if none of them is a prefix of the other and at the first position where they differ character in A is smaller than the character in B.
For the purpose of this problem, two equal strings nearby do not break the condition of sequence being sorted lexicographically.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of strings.
The second line contains n integers ci (0 ≤ ci ≤ 109), the i-th of them is equal to the amount of energy Vasiliy has to spent in order to reverse the i-th string.
Then follow n lines, each containing a string consisting of lowercase English letters. The total length of these strings doesn't exceed 100 000.
If it is impossible to reverse some of the strings such that they will be located in lexicographical order, print - 1. Otherwise, print the minimum total amount of energy Vasiliy has to spent.
2
1 2
ba
ac
1
3
1 3 1
aa
ba
ac
1
2
5 5
bbb
aaa
-1
2
3 3
aaa
aa
-1
In the second sample one has to reverse string 2 or string 3. To amount of energy required to reverse the string 3 is smaller.
In the third sample, both strings do not change after reverse and they go in the wrong order, so the answer is - 1.
In the fourth sample, both strings consists of characters 'a' only, but in the sorted order string "aa" should go before string "aaa", thus the answer is - 1.
题意:给你n个字符串 对于每个字符串进行反转操作会有一个权值 为了使得这n个字符串的字典升序
输出的最小的权值和 ,如果不存在则输出-1
题解:dp[i][1]表示第i个字符串反转的最优解
dp[i][0]表示第i个字符串不反转的最优解
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n;
ll w[];
string c[],s[];
ll dp[][];
ll ans;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%I64d",&w[i]);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
cin>>c[i];
s[i]=c[i];
reverse(s[i].begin(),s[i].end());
}
memset(dp,,sizeof(dp));
dp[][]=;
dp[][]=w[];
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
dp[i][]=1e18;
dp[i][]=1e18;
if(c[i]>=c[i-]) {
dp[i][]=dp[i-][];
}
if(c[i]>=s[i-]){
dp[i][]=min(dp[i][],dp[i-][]);
}
if(s[i]>=c[i-]){
dp[i][]=dp[i-][]+w[i];
}
if(s[i]>=s[i-]){
dp[i][]=min(dp[i][],dp[i-][]+w[i]);
}
}
ans=min(dp[n][],dp[n][]);
if(ans==1e18)
cout<<"-1"<<endl;
else
cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) A B C 暴力 二分 dp(字符串的反转)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #345 (Div. 2) D. Image Preview 暴力 二分
D. Image Preview 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/651/problem/D Description Vasya's telephone ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) D. Vasiliy's Multiset (0/1-Trie树)
Vasiliy's Multiset 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/D Description Author has gone out ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) C. Hard problem(DP)
Hard problem 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/C Description Vasiliy is fond of solvin ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) B. Interesting drink (模拟)
Interesting drink 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/B Description Vasiliy likes to res ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) A. Beru-taxi (水题)
Beru-taxi 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/A Description Vasiliy lives at point (a, b ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) D. Vasiliy's Multiset
题目链接:Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) D. Vasiliy's Multiset 题意: 给你一些操作,往一个集合插入和删除一些数,然后?x让你找出与x异或后的最大值 ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) C. Hard problem
题目链接:Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) C. Hard problem 题意: 给你一些字符串,字符串可以倒置,如果要倒置,就会消耗vi的能量,问你花最少的能量将这些字 ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) (A,B,C,D,E)
Codeforces Round 367 Div. 2 点击打开链接 A. Beru-taxi (1s, 256MB) 题目大意:在平面上 \(n\) 个点 \((x_i,y_i)\) 上有出租车,每 ...
- Codeforces Round #365 (Div. 2) C - Chris and Road 二分找切点
// Codeforces Round #365 (Div. 2) // C - Chris and Road 二分找切点 // 题意:给你一个凸边行,凸边行有个初始的速度往左走,人有最大速度,可以停 ...
随机推荐
- document.cookie的使用
设置cookie每个cookie都是一个名/值对,可以把下面这样一个字符串赋值给document.cookie:document.cookie="userId=828";如果要一次 ...
- cocopods的使用方法
虽然网上关于CocoaPods安装教程多不胜数,但是我在安装的过程中还是出现了很多错误,所以大家可以照下来步骤装一下,我相信会很好用. 前言 在iOS项目中使用第三方类库可以说是非常常见的事,但是要正 ...
- 2.精通前端系列技术之JavaScript模块化开发 seajs(一)
在使用seajs模块化开发之前,直接在页面引用js会容易出现冲突及依赖相关的问题,具体问题如下 问题1:多人开发脚本的时候容易产生冲突(比如全局参数冲突,方法名冲突),可以使用命名空间降低冲突,不能完 ...
- Rhel6-haproxy+keepalived配置文档
系统环境: rhel6 x86_64 iptables and selinux disabled 主机: 192.168.122.119:haproxy,keepalived server19.exa ...
- iOS 高效添加圆角效果实战讲解
圆角(RounderCorner)是一种很常见的视图效果,相比于直角,它更加柔和优美,易于接受.但很多人并不清楚如何设置圆角的正确方式和原理.设置圆角会带来一定的性能损耗,如何提高性能是另一个需要重点 ...
- android listview getviewtypecount和getItemViewType
package newdemo.jeno.listviewdemo; import android.app.Activity;import android.os.Bundle;import andro ...
- 黑马程序员——C语言基础 scanf函数 基本运算 三目运算符
Java培训.Android培训.iOS培训..Net培训.期待与您交流! (一下内容是对黑马苹果入学视频的个人知识点总结) (一)scanf函数 1> 简单介绍一下scanf函数 这是在 ...
- C++指针详解
指针的概念 指针是一个特殊的变量,它里面存储的数值被解释成为内存里的一个地址.要搞清一个指针需要搞清指针的四方面的内容:指针的类型,指针所指向的类型,指针的值或者叫指针所指向的内存区,还有指针本身所占 ...
- JS内置对象
字符串对象 <script> //字符串对象 var str = "Hello worldlsgjlsjg"; document.write('string.lengt ...
- POJ题目分类(按初级\中级\高级等分类,有助于大家根据个人情况学习)
本文来自:http://www.cppblog.com/snowshine09/archive/2011/08/02/152272.spx 多版本的POJ分类 流传最广的一种分类: 初期: 一.基本算 ...
