ReentrantLock之Condition源码解读
1.背景
阅读该源码的前提是,已经阅读了reentrantLock的源码!
2.await源码解读
condition代码理解的核心,其实就是理解到:
线程节点如何从sync双向链表队列到指定的条件队列中,
然后又如何从条件队列中到sync双向链表队列的
一定要先把下面的2个图理解到,再去看源码和断点调试就很容易理解了
核心逻辑图:
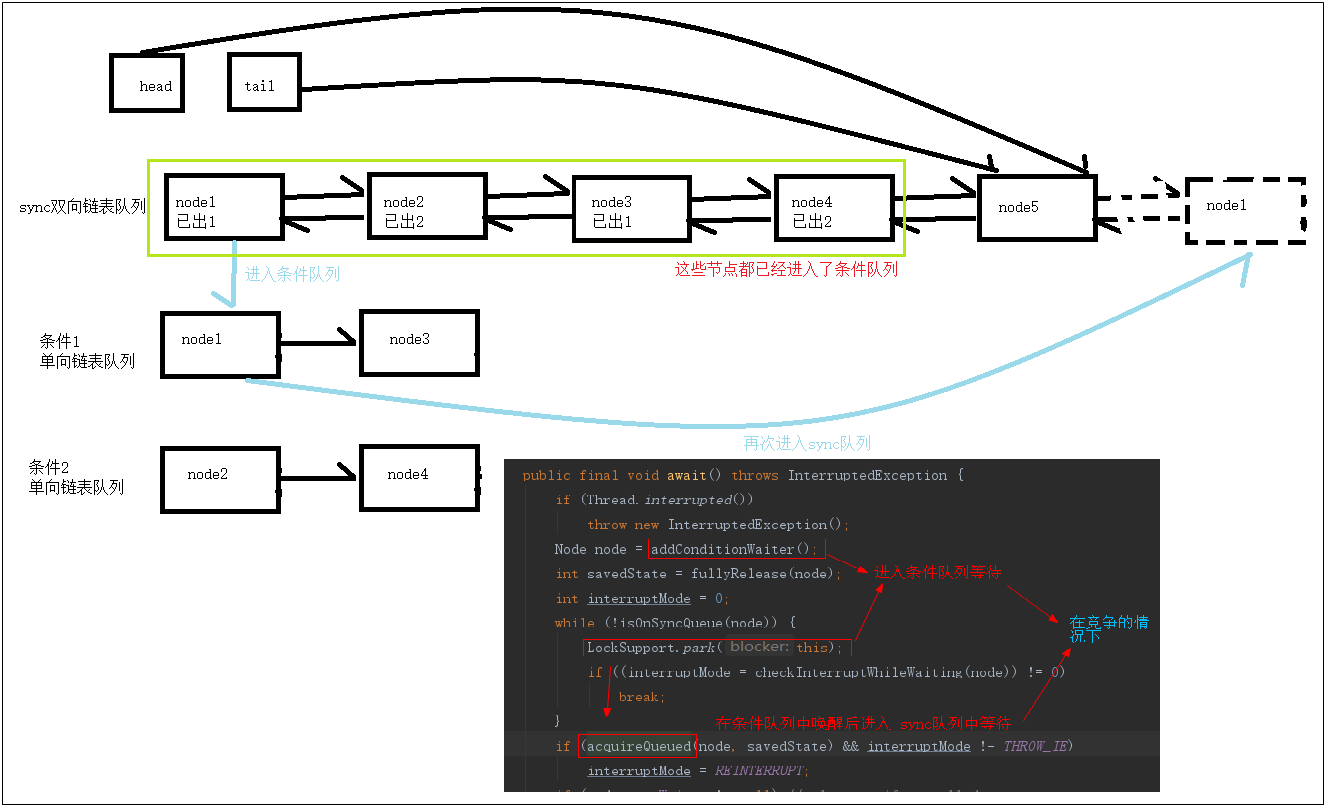
核心代码逻辑图:
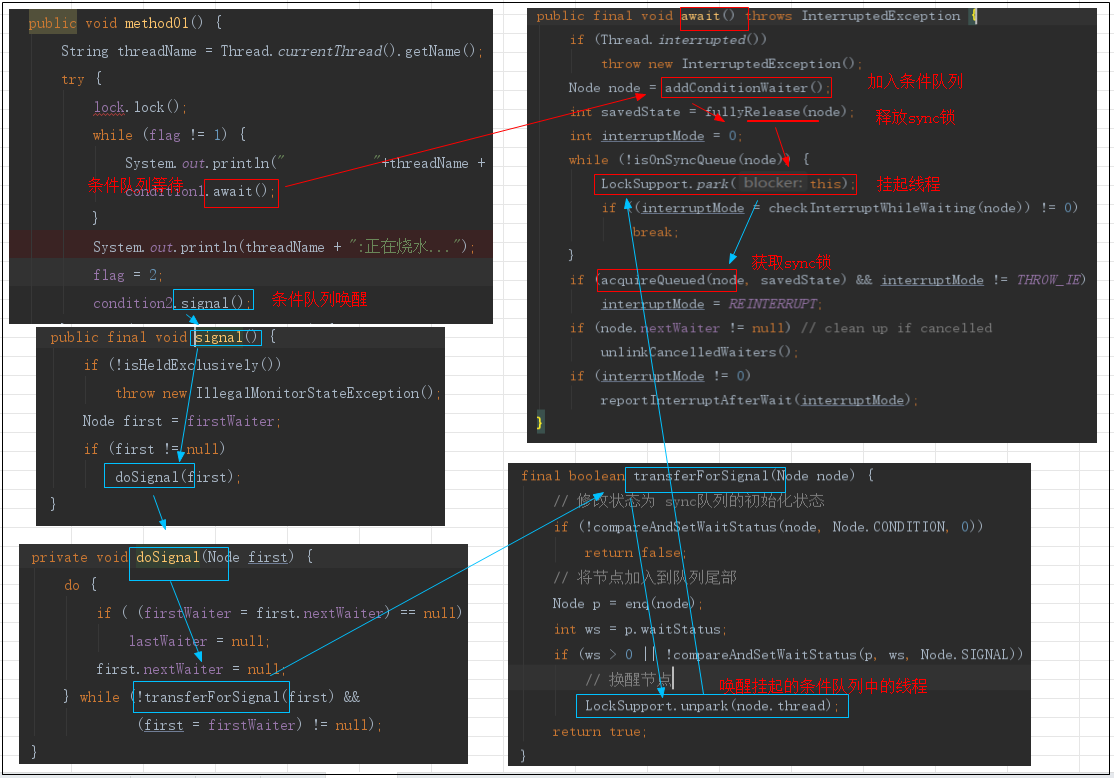
2.1.await方法详解
代码解读:
/**
* 进入条件等待
*/
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
// 是否有中断标记
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 将线程加入到条件等待队列
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
/* fullyRelease(node) 释放锁并唤醒后继节点
这里要结合ReentrantLock来理解,执行到这里说明是获取到了锁的,
这里就是要释放ReentrantLock锁,然后进入到条件队列中等待*/
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
// interruptMode =0表示没有中断, interruptMode =1表示退出时重新中断 ,interruptMode=-1表示退出时抛异常
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
// 在条件队列中等待
LockSupport.park(this);
// checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)返回0,表示没有中断
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
// acquireQueued(node, savedState) 从sync队列中重新获取锁,并处理中断标记
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
// node结点不是最后一个结点,清除条件队列中无效的节点
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
// 重新处理中断,具体中断方式取决于 interruptMode 的值,
// interruptMode =1表示退出时重新中断 ,interruptMode=-1表示退出时抛异常int interruptMode = 0;
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
2.2.addConditionWaiter方法详解
代码解读:
/**
* 添加新的节点到条件队列
* 这里的条件队列是 单链表,不是双链表
* CONDITION = -2 表示是条件队列
*/
private Node addConditionWaiter() {
Node t = lastWaiter;
// t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION ?? 这个条件的作用
if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {
// 去掉取消节点
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
// 将取消的节点,去掉后,尾节点可能会变
t = lastWaiter;
}
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION);
if (t == null)
// 第一次进入条件队列
firstWaiter = node;
else
// 将当前节点放在尾节点之后
t.nextWaiter = node;
// 设置新的尾节点
lastWaiter = node;
// 返回当前节点
return node;
}
2.3.fullyRelease方法详解
代码解读:
/**
* 释放锁,并唤醒后继节点
*
* @param node
* @return
*/
final int fullyRelease(Node node) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
// 获取当前资源状态
int savedState = getState();
// release(savedState) 释放锁并唤醒后继节点
if (release(savedState)) {
failed = false;
return savedState;
} else {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
} finally {
// 释放锁失败节点取消
if (failed)
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
}
}
2.4.isOnSyncQueue方法详解
代码解读:
/**
* 判定节点是否在sync队列中
*
* @param node
* @return
*/
final boolean isOnSyncQueue(Node node) {
// 如果节点标记位是CONDITION = -2的状态 或者 没有前继节点,说明节点不在队列中
if (node.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION || node.prev == null)
return false;
// 如果下一个节点不为空说明节点在队列里面
if (node.next != null) // If has successor, it must be on queue
return true;
// 遍历sync队列,查看节点是否在队列里面
return findNodeFromTail(node);
}
2.5.findNodeFromTail方法详解
代码解读:
/**
* 遍历节点,查看传入的节点是否在队列里面,在里面返回true
*
* @param node
* @return
*/
private boolean findNodeFromTail(Node node) {
Node t = tail;
for (; ; ) {
if (t == node)
return true;
if (t == null)
return false;
// 从后往前遍历,还记得之前我们在讲ReentrantLock的源码时说过为什么要从后往前遍历么?
t = t.prev;
}
}
2.6.checkInterruptWhileWaiting方法详解
代码解读:
/**
* // 该模式意味着在退出等待时重新中断
* private static final int REINTERRUPT = 1;
* // 该模式意味着在退出等待时抛出InterruptedException
* private static final int THROW_IE = -1;
*
* @param node
* @return
*/
private int checkInterruptWhileWaiting(Node node) {
// 当前线程没有被中断直接返回0
// 当前线程已经被中断了的话
return Thread.interrupted() ?
// 取消时重新入队列成功,标记为退出时抛出异常
// 取消时重新入队列失败,标记位退出时重新中断
(transferAfterCancelledWait(node) ? THROW_IE : REINTERRUPT) :
0;
}
2.7.transferAfterCancelledWait方法详解
代码解读:
/**
* 条件等待队列中的节点如果已经被取消,将节点添加到sync队列的尾部
*
* @param node
* @return 节点添加到尾部成功返回true, 否则返回false
*/
final boolean transferAfterCancelledWait(Node node) {
// 初始化节点
if (compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0)) {
// 将节点添加到尾部
enq(node);
// 添加到队列成功返回true
return true;
}
// 判断节点是否在Sync队列里面
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node))
// 不在队列里面则等待,直到线程执行完成
Thread.yield();
// 添加失败,返回false
return false;
}
2.8.unlinkCancelledWaiters方法详解
代码解读:
/**
* 作用:删除单项向链表中已经取消的节点,即状态不等于2的节点
* 这是典型单向链表删除节点的逻辑,如果对这个段代码不是很理解,
* 可以查看之前的数据结果部分
*/
private void unlinkCancelledWaiters() {
Node t = firstWaiter;
Node trail = null;
while (t != null) {
Node next = t.nextWaiter;
if (t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {
// 断开连接,帮助GC回收
t.nextWaiter = null;
if (trail == null)
// 重新定义头结点
firstWaiter = next;
else
trail.nextWaiter = next;
if (next == null)
// 最后的有效尾节点
lastWaiter = trail;
} else {
trail = t;
}
// 指针后移
t = next;
}
}
2.9.reportInterruptAfterWait方法详解
代码解读:
/**
* 中断的具体处理方式
* interruptMode =1表示退出时重新中断 ,interruptMode=-1表示退出时抛异常
*
* @param interruptMode
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
private void reportInterruptAfterWait(int interruptMode)
throws InterruptedException {
if (interruptMode == THROW_IE)
// 抛出异常的处理方式
throw new InterruptedException();
else if (interruptMode == REINTERRUPT)
// 自我中断的处理方式
selfInterrupt();
}
2.10.selfInterrupt方法详解
代码解读:
/**
* 当前线程执行中断处理
*/
static void selfInterrupt() {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
3.signal源码解读
3.1.signal源码解读
代码:
/**
* 唤醒条件队列中的节点
*/
public final void signal() {
// 检查当前线程是否是拥有锁的线程
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
// 执行唤醒方法
doSignal(first);
}
3.2.isHeldExclusively源码解读
代码:
/**
* 判定当前线程是否是拥有锁的线程
* @return
*/
protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();
}
3.3.doSignal源码解读
代码:
/**
* 执行唤醒条件队列中的节点
* @param first
*/
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
// 这个if的判定就是检查条件队列中是否还有节点,如果没有了,就将lastWaiter设置为null
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)
lastWaiter = null;
// 第一个节点出队列后,断开引用
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (!transferForSignal(first) && (first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
3.4.transferForSignal源码解读
/**
* 唤醒条件队列中的节点--> 到 sync对列中去
* @param node
* @return
*/
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
// 修改状态为 sync队列的初始化状态
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
// 将节点加入到队列尾部
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
// 换醒节点
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
return true;
}
4.测试
不论你是否理解了源码,都建议大家多使用断点调试查看
节点是如何进入队列,
如何出队列,
如何挂起线程,
如何唤醒线程的.....
测试代码


package com.my.aqs.condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class ConditionTest {
// 功能标记位
private int flag = 1;
// 创建非公平锁
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(false);
// 条件锁1-烧水
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
// 条件锁2-泡茶
private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
// 条件锁3-喝茶
private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition(); /**
* 功能:烧水
*/
public void method01() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
try {
lock.lock();
while (flag != 1) {
System.out.println(" "+threadName + ",需要,挂起当前线程,进入条件等待队列,因为当前不是烧水标记1,而是:" + flag);
condition1.await();
}
System.out.println(threadName + ":正在烧水...");
// System.out.println(threadName + ":烧水完成,唤醒泡茶线程");
flag = 2;
condition2.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} /**
* 功能:泡茶
*/
public void method02() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
try {
lock.lock();
while (flag != 2) {
System.out.println(" "+threadName + ",需要,挂起当前线程,进入条件等待队列,因为当前不是泡茶标记2,而是:" + flag);
condition2.await();
}
System.out.println(threadName + ":正在泡茶...");
// System.out.println(threadName + ":泡茶完成,唤醒喝茶线程");
flag = 3;
condition3.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} /**
* 功能:喝茶
*/
public void method03() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
try {
lock.lock();
while (flag != 3) {
System.out.println(" "+threadName + ",需要,挂起当前线程,进入条件等待队列,因为当前不是喝茶标记3,而是:" + flag);
condition3.await();
}
System.out.println(threadName + ":正在喝茶...");
// System.out.println(threadName + ":喝茶完成,唤醒烧水线程");
flag = 1;
condition1.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} /**
* 睡眠时间是为了让线程按照这个顺序进入队列等待 喝茶->泡茶->烧水
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConditionTest conditionTest = new ConditionTest();
for (int i = 1; i <= 2; i++) {
// 烧水
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5*1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
conditionTest.method01();
}, "烧水-线程 " + i).start();
// 泡茶
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5*100L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
conditionTest.method02();
}, "泡茶-线程 " + i).start();
// 喝茶
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(100L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
conditionTest.method03();
}, "喝茶-线程 " + i).start();
}
}
}
断点调试图:

测试结果:
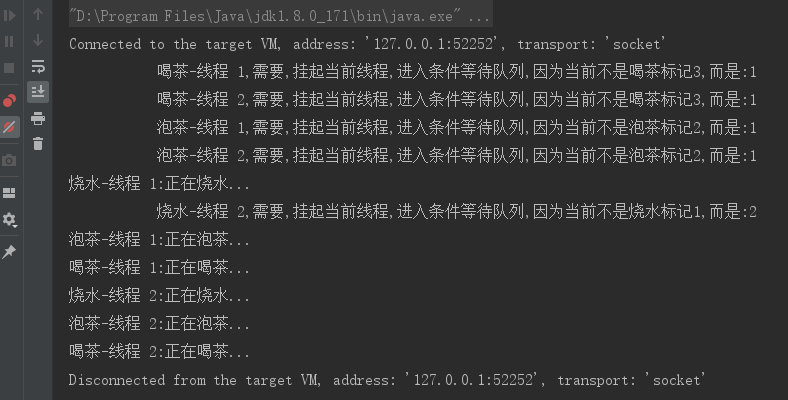
完美
ReentrantLock之Condition源码解读的更多相关文章
- ReentrantLock和condition源码浅析(二)
转载请注明出处... 接着上一篇的ReentrantLock和condition源码浅析(一),这篇围绕着condition 一.condition的介绍 在这里为了作对比,引入Object类的两个方 ...
- ReentrantLock和condition源码浅析(一)
转载请注明出处..... 一.介绍 大家都知道,在java中如果要对一段代码做线程安全操作,都用到了锁,当然锁的实现很多,用的比较多的是sysnchronize和reentrantLock,前者是ja ...
- AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码解读--续篇之Condition
1. 背景 在之前的AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码解读中,介绍了AQS的基本概念.互斥锁.共享锁.AQS对同步队列状态流转管理.线程阻塞与唤醒等内容.其中并不涉及Condit ...
- AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码解读
1. 背景 AQS(java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)是Doug Lea大师创作的用来构建锁或者其他同步组件(信号量.事件等) ...
- CyclicBarrier源码解读
1. 简介 JUC中的CyclicBarrier提供了一种多线程间的同步机制,可以让多个线程在barrier等待其它线程到达barrier.正如其名CyclicBarrier含义就是可以循环使用的屏障 ...
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor源码解读
1. 背景 在之前的博文--ThreadPoolExecutor源码解读已经对ThreadPoolExecutor的实现原理与源码进行了分析.ScheduledExecutorService也是我们在 ...
- JDK容器类List,Set,Queue源码解读
List,Set,Queue都是继承Collection接口的单列集合接口.List常用的实现主要有ArrayList,LinkedList,List中的数据是有序可重复的.Set常用的实现主要是Ha ...
- AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 源码解读(转载)
转载文章,拜读了一下原文感觉很不错,转载一下,侵删 链接地址:http://objcoding.com/2019/05/05/aqs-exclusive-lock/ Java并发之AQS源码分析(一) ...
- SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageDownloaderOperation
第七篇 前言 本篇文章主要讲解下载操作的相关知识,SDWebImageDownloaderOperation的主要任务是把一张图片从服务器下载到内存中.下载数据并不难,如何对下载这一系列的任务进行设计 ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(三)之 AFURLRequestSerialization
这篇就讲到了跟请求相关的类了 关于AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读 的文章篇幅都会很长,因为不仅仅要把代码进行详细的的解释,还会大概讲解和代码相关的知识点. 上半篇: URI编码的知识 关于 ...
随机推荐
- IDEA环境编译Spring源码
一.下载源码 1.官网下载 官网地址 如下图 2.github git下载 github地址 如下图 3.gitee git下载(国内推荐使用) gitee地址 如图 查看对应的gradle版本 在下 ...
- FreeRTOS简单内核实现2 双向链表
FreeRTOS Kernel V10.3.1 FreeRTOS 的 list.c / list.h 文件中有 3 个数据结构.2 个初始化函数.2 个插入函数.1 个移除函数和一些宏函数,链表是 F ...
- 『手写Mybatis』实现映射器的注册和使用
前言 如何面对复杂系统的设计? 我们可以把 Spring.MyBatis.Dubbo 这样的大型框架或者一些公司内部的较核心的项目,都可以称为复杂的系统. 这样的工程也不在是初学编程手里的玩具项目,没 ...
- 解决Linux下无法编译带有中文的JAVA程序问题
只要在编译的时候加上-encoding gbk即可 例如: javac -encoding gbk Myclass.java
- 移动web开发入门
一,视口 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, user-scal ...
- C语言:不定长结构体的实现方式
需求 有时候,我们会遇到一些情况:数据前部分相同,但是后部分长度不固定:数据格式相似,只是尾缀的长度不同,例如某些数据包,需要不定长度. 为了能够同时使用上不同长度的数据.可以用以下的方式实现. 方案 ...
- Ubuntu 22.04单机部署K3s
安装docker 从docker官网获取最新的一键安装脚本,安装docker运行环境 curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh sudo s ...
- TI AM64x开发板规格书(双核ARM Cortex-A53 + 单/四核Cortex-R5F + 单核Cortex-M4F,主频1GHz)
1 评估板简介 创龙科技TL64x-EVM是一款基于TI Sitara系列AM64x双核ARM Cortex-A53 + 单/四核Cortex-R5F + 单核Cortex-M4F多核处理器设计的高性 ...
- Codeforces Global Round 26 A~C2
惹啊啊啊啊,这场做得我发昏,最近总感觉不在状态,但还是再在冲击1600-1800的题目. A. Strange Splitting ---------------------------------题 ...
- SpringBoot集成Knife4j
Knife4j简介 Knife4j 官网地址:https://doc.xiaominfo.com/ knife4j 是为Java MVC框架集成Swagger生成Api文档的增强解决方案. Knife ...
