IO (四)
1 深度遍历文件夹
- 示例:
package java20;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FilenameFilter;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 2017/10/14
* 说明:
*/
public class FileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File dir = new File("D:\\code");
listAll(dir);
}
/**
* 深度遍历文件夹
* @param dir
*/
private static void listAll(File dir) {
System.out.println("文件夹:"+dir.getAbsolutePath());
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
for(File file : files){
if(file.isDirectory()){
listAll(file);
}else{
System.out.println("文件:"+file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
}
2 Properties
2.1 Properties的特点
- 该集合中的键和值都是字符串类型的。
- 集合中的数据可以保存在流中,或者从流中获取。
2.2 构造方法
- 创建一个没有默认值的空属性列表
public Properties()
2.3 常用方法
- 设置属性值
public Object setProperty(String key,String value)
- 根据指定的键获取值
public String getProperty(String key)
- 返回属性列表的所有键的枚举
public Enumeration<?> propertyNames()
- 返回此属性列表中的键的set集合
public Set<String> stringPropertyNames()
- 示例:
package java20;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 2017/10/15
* 说明:
*/
public class PropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.setProperty("zhangsan","20");
pros.setProperty("lisi","26");
pros.setProperty("wangwu","27");
//第一种方式获取所有的键值
Enumeration<?> enumeration = pros.propertyNames();
while(enumeration.hasMoreElements()){
String name = (String) enumeration.nextElement();
String value = pros.getProperty(name);
System.out.println(name+":"+value);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------");
//第二种方式获取所有的键值
Set<String> names = pros.stringPropertyNames();
for(String name:names){
String value = pros.getProperty(name);
System.out.println(name+":"+value);
}
}
}

- 将属性列表写入输出流
public void store(OutputStream out,String comments) throws IOException
- 将属性列表写入输出流
public void store(Writer writer,String comments) throws IOException
- 示例:
package java20;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 2017/10/15
* 说明:
*/
public class PropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.setProperty("zhangsan","20");
pros.setProperty("lisi","26");
pros.setProperty("wangwu","27");
FileWriter fs = new FileWriter("pros.properties");
pros.store(fs,"properties文件");
fs.close();
}
}
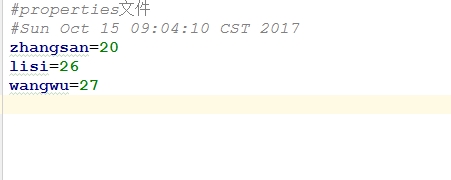
- 从输入流中读取属性列表
public void load(InputStream inStream) throws IOException
- 从输入流中读取属性列表
public void load(Reader reader) throws IOException
- 示例:
package java20;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 2017/10/15
* 说明:
*/
public class PropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties pros = new Properties();
FileReader fr = new FileReader("pros.properties");
pros.load(fr);
Set<String> names = pros.stringPropertyNames();
for(String name:names){
String value = pros.getProperty(name);
System.out.println(name+":"+value);
}
}
}

- 修改属性文件中的值
package java20;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 2017/10/15
* 说明:
*/
public class PropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties pros = new Properties();
FileReader fr = new FileReader("pros.properties");
pros.load(fr);
pros.setProperty("zhangsan","60");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("pros.properties");
pros.store(fw,"修改属性文件");
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
}
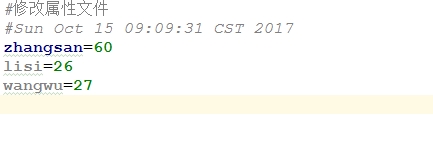
- 示例:获取一个应用程序运行的次数,如果超过5次,给出使用次数并体术请注册的信息,并不要运行程序。
package java20;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 2017/10/15
* 说明:
*/
public class PropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//将所需要的配置文件封装成File对象
File config = new File("count.properties");
if(!config.exists()){
config.createNewFile();
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(config);
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(fis);
//从集合中通过键获取次数
String times = pros.getProperty("times");
int count = 0;
if(times != null){
count = Integer.parseInt(times);
if(count >= 5){
System.out.println("使用次数已到,请注册");
return;
}
}
count ++;
//将改变的后的次数重新存储到集合中
pros.setProperty("times",String.valueOf(count));
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(config);
pros.store(fos,"");
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
3 打印流
3.1 PrintStream
3.1.1 PrintStream简介
- PrintStream为其它输出流添加了功能,使得它们能够方便的打印各种数据值的表现形式。它还提供了其它两项功能。与其它输出流不同,PrintStream永远不会抛出IOException。
- 异常情况仅设置可通过checkError方法测试的内部标志。
- 为了自动刷新,可以创建一个PrintStream,这意味着可在写入byte数组之后调用flush方法,可调用其中一个println方法,或写入一个换行符或字节('\n')。
3.1.2 构造方法
- 创建一个具有指定文件且不带自动刷新的打印流
public PrintStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException
- 创建具有指定文件名称和字符集且不带自动刷新的打印流
public PrintStream(File file,String csn) throws FileNotFoundException UnsupportedEncodingException
- 创建打印流
public PrintStream(OutputStream out)
- 创建打印流
public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush)
- 创建打印流
public PrintStream(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush,String encoding) throws UnsupportedEncodingException
- 创建具有指定文件名且不带自定刷新的打印流
public PrintStream(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException
- 创建指定文件名称和字符集且不带自动刷新的打印流
public PrintStream(String fileName,String csn) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException
3.1.3 方法
- 将指定字符添加到此输出流
public PrintStream append(char c)
- 将指定字符序列添加到此输出流
public PrintStream append(CharSequence csq)
- 将指定字符序列的子序列添加到此输出流
public PrintStream append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end)
- 刷新流并检查其错误状态
public boolean checkError()
- 清除此流的内部标志
protected void clearError()
- 关闭流
public void close()
- 刷新该流的缓冲
public void flush()
- 使用指定格式字符串和参数将格式化字符串写入到此输出流中
public PrintStream format(Locale l,String format, Object... args)
- 使用指定格式字符串和参数将格式化字符串写入到此输出流中
public PrintStream format(String format, Object... args)
- 打印boolean值
public void print(boolean b)
- 打印字符
public void print(char c)
- 打印字符数组
public void print(char[] s)
- 打印double精度浮点数
public void print(double d)
- 打印float精度浮点数
public void print(double d)
- 打印整数
public void print(int i)
- 打印long整数
public void print(long l)
- 打印对象
public void print(Object obj)
- 打印字符串
public void print(String s)
- 使用指定格式字符串和参数将格式化的字符串写入此wirter的便捷方法
public PrintWriter printf(Locale l,String format,Object... args)
- 使用指定格式字符串和参数将格式的字符串写入此writer的便捷方法
public PrintWriter printf(String format,Object... args)
- 通过写入分隔符字符串终止当前行
public void println()
- 打印boolean值,然后终止该行
public void println(boolean x)
- 打印字符,然后终止该行
public void println(char x)
- 打印字符数组,然后终止该行
public void println(char[] x)
- 打印double精度浮点数,然后终止该行
public void println(double x)
- 打印float精度浮点数,然后终止该行
public void println(float x)
- 打印int整数,然后终止该行
public void println(int x)
- 打印long类型整数,然后终止该行
public void println(long x)
- 打印Object,然后终止该行
public void println(Object x)
- 打印String,然后终止该行
public void println(String x)
- 指示已发生错误
protected void setError()
- 写入字符数组
public void write(char[] buf)
- 写入字符数组的某一部分
public void write(char[] buf, int off,int len)
- 写入单个字符
public void write(int c)
- 写入字符串
public void write(String s)
- 写入字符串的某一部分
public void write(String s,int off,int len)
3.1.4 示例:
- 示例:
package java20;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
/**
* 2017/10/15
* 说明:
*/
public class PrintStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("aaa.txt"),true);
ps.print(1);
ps.print('a');
ps.println("你好啊");
ps.println("你好啊");
ps.flush();
ps.close();
}
}
3.2 PrintWriter
3.2.1 PrintWriter简介
- 向文本输出流打印对象的格式化表示形式,此类实现了在PrintStream的所有print方法,它不包含用于写入原始字节的方法,对于这些字节,程序应该使用未编码的字节流进行写入。
- 如果启用了自动刷新,则只有调用println、printf或format的其中一个方法时才可能完成此操作,而不是每当正好输出换行符的时候才完成。这些方法使用平台自有的行分隔符概念,而不是换行符。
- 此类中的方法不会抛出IO异常,尽管其某些构造方法可能会抛出异常。
3.2.2 构造方法
- 使用指定文件创建不具有自动刷新的PrintWriter
public PrintWriter(File file) throws FileNotFoundException
- 创建具有指定文件和字符集且不带有自动刷新的PrintWriter
public PrintWriter(File file,String csn) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException
- 根据现有的OutputStream创建不带有自动刷新的PrintWriter
public PrintWriter(OutputStream out)
- 根据现有的OutputStream创建PrintWriter
public PrintWriter(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush)
- 创建具有指定文件名且不带有自动刷新的PrintWriter
public PrintWriter(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException
- 创建具有制定文件名称和字符集且不带有自动刷新的PrintWriter
public PrintWriter(String fileName,String csn) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException
- 创建不带有自动刷新的PrintWriter
public PrintWriter(Writer out)
- 创建带自动刷新的PrintWriter
public PrintWriter(Writer out, boolean autoFlush)
3.2.3 方法
- 将指定字符添加到此writer
public PrintWriter append(char c)
- 将指定的字符序列添加到此writer
public PrintWriter append(CharSequence csq)
- 将指定字符序列的子序列添加到此writer
public PrintWriter append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end)
- 如果流没有关闭,则刷新流且检查其错误状态
public boolean checkError()
- 清除此流的错误状态
protected void clearError()
- 关闭该流并释放与之关联的所有系统资源
public void close()
- 刷新该流的缓冲
public void flush()
- 使用指定格式的字符串和参数将一个格式化字符串写入此writer中
public PrintWriter format(Locale l,String format,Object... args)
- 使用指定格式的字符串和参数将一个格式化字符串写入此writer中
public PrintWriter format(String format,Object... args)
- 打印boolean值
public void print(boolean b)
- 打印字符
public void print(char c)
- 打印字符数组
public void print(char[] s)
- 打印double类型的值
public void print(double d)
- 打印float类型的值
public void print(float f)
- 打印int类型的值
public void print(int i)
- 打印long类型的值
public void print(long l)
- 打印对象
public void print(Object obj)
- 打印字符串
public void print(String s)
- 使用指定格式字符串和参数将格式化的字符串写入此writer的便捷方法
public PrintWriter printf(Locale l,String format, Object... args)
- 使用指定格式字符串和参数将格式化的字符串写入此writer的便捷方法
public PrintWriter printf(String format,Object... args)
- 通过写入行分隔符字符串终止当前行
public void println()
- 打印boolean类型的值,然后终止该行
public void println(boolean x)
- 打印字符,然后终止该行
public void println(char x)
- 打印字符数组,然后终止该行
public void println(char[] x)
- 打印double类型的值,然后终止改行
public void println(double x)
- 打印浮点数,然后终止该行
public void println(float x)
- 打印整数,然后终止该行
public void println(int x)
- 打印long类型整数,然后终止该行
public void println(long x)
- 打印Object类型的值,然后终止该行
public void println(Object x)
- 打印String类型的值,然后终止该行
public void println(String x)
- 指示已发生错误
protected void setError()
- 写入字符数组
public void write(char[] buf)
- 写入字符数组的一部分
public void write(char[] buf,int off, int len)
- 写入单个字符
public void write(int c)
- 写入字符串
public void write(String s)
- 写入字符串的某一部分
public void write(String s, int off, int len)
4 SequenceInputStream 序列流
4.1 SequenceInputStream简介
- SequenceInputStream表示其他输入流的逻辑串联,它从输入流的有序集合开始,并从第一个输入流开始读取,直到达文件末尾,接着从第二个输入流读取,依次类推,直到达到包含的最后一个输入流的文件末尾处为止。
4.2 构造方法
- 通过参数来初始化新建SequenceInputStream,该参数必须是生成运行时类型为InputStream对象的Enumeration类型参数
public SequenceInputStream(Enumeration<? extends InputStream> e)
- 通过参数来初始化新建SequenceInputStream(将按顺序读取这两个参数,先读取s1,然后读取s2),以提供此SequenceInputStream读取的字节
public SequenceInputStream(InputStream s1, InputStream s2)
4.3 方法
- 关闭此输入流病释放与此流相关联的所有系统资源
public void close() throws IOException
- 从此输入流中读取下一个数据字节
public int read() throws IOException
- 将最多len个数据字节从此输入流读入byte数组
public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException
4.4 示例
- 示例:
package java20;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Vector;
/**
* 2017/10/15
* 说明:
*/
public class SequenceInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Vector<InputStream> vector = new Vector<>();
vector.add(new FileInputStream("test1.txt"));
vector.add(new FileInputStream("test2.txt"));
vector.add(new FileInputStream("test3.txt"));
SequenceInputStream si = new SequenceInputStream(vector.elements());
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = si.read(buffer)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
}
}
- 示例:
package java20;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 2017/10/15
* 说明:
*/
public class SequenceInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
List<InputStream> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new FileInputStream("test1.txt"));
list.add(new FileInputStream("test2.txt"));
list.add(new FileInputStream("test3.txt"));
Iterator<InputStream> iterator = list.iterator();
Enumeration<InputStream> enumerations = new Enumeration<InputStream>() {
@Override
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return iterator.hasNext();
}
@Override
public InputStream nextElement() {
return iterator.next();
}
};
SequenceInputStream si = new SequenceInputStream(enumerations);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = si.read(buffer)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
}
}
- 示例:
package java20;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 2017/10/15
* 说明:
*/
public class SequenceInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
List<InputStream> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new FileInputStream("test1.txt"));
list.add(new FileInputStream("test2.txt"));
list.add(new FileInputStream("test3.txt"));
Enumeration<InputStream> enumerations = Collections.enumeration(list);
SequenceInputStream si = new SequenceInputStream(enumerations);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = si.read(buffer)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
}
}
IO (四)的更多相关文章
- Java IO(四)
对象序列化 对象序列化又叫对象的持久化,对象的串行化(或反串行化) 当使用Serializable接口实现序列化操作时,如果一个对象中的某个属性不希望被序列化,则可以使用transient关键字进行声 ...
- java IO(四):键盘录入
*/ .hljs { display: block; overflow-x: auto; padding: 0.5em; color: #333; background: #f8f8f8; } .hl ...
- Java之IO(四)DataInputStream和DataOutputStream
转载请注明源出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lighten/p/6986155.html 1.前言 DataInputStream和DataOutputStream分别继承了Fil ...
- 系统学习 Java IO (四)----文件的读写和随机访问 FileInputStream/FileOutputStream & RandomAccessFile
目录:系统学习 Java IO---- 目录,概览 文件输入流 FileInputStream 这是一个简单的FileInputStream示例: InputStream input = new Fi ...
- linux系统编程之文件与io(四)
今天继续学习文件与io,主要是学习文件共享及文件.复制文件描述符,有点抽象,主要是概念上的理解,但是很重要,下面一一来分解: 文件共享: 回顾一下,在linux系统调用中,是通过文件描述符来访问文件的 ...
- Java IO(四--字符流基本使用
在上一节,介绍了字节流的基本使用,本节介绍一下字符流的使用 Reader: public abstract class Reader implements Readable, Closeable { ...
- java I/O框架 (四)文件流
文件读取 FileInputStream FileReader 文件写入 FileOutputStream FileWriter 随机文件读写 RandomAccessFile 一.文件读取 File ...
- {python之IO多路复用} IO模型介绍 阻塞IO(blocking IO) 非阻塞IO(non-blocking IO) 多路复用IO(IO multiplexing) 异步IO(Asynchronous I/O) IO模型比较分析 selectors模块
python之IO多路复用 阅读目录 一 IO模型介绍 二 阻塞IO(blocking IO) 三 非阻塞IO(non-blocking IO) 四 多路复用IO(IO multiplexing) 五 ...
- 并发编程(IO多路复用)
阅读目录 一 IO模型介绍 二 阻塞IO(blocking IO) 三 非阻塞IO(non-blocking IO) 四 多路复用IO(IO multiplexing) 五 异步IO(Asynchro ...
- Java之IO(零)总结
转载请注明原出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lighten/p/7274378.html 1.前言 本章是对之前所讲述的整个Java的IO包的一个总结,抽出个人认为比较重要的知识点 ...
随机推荐
- Watch time
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); ; i <= ; i++) { ; j <= ; j++) { ; k <= ; ...
- squashfs文件系统
一.Squashfs文件系统简介 squashfs是以linux 内核源码补丁的形式发布,附带mksquashfs工具,用于创建squash文件系统.squashfs可以将整个文件系统或者某个单一的目 ...
- 近期热门微信小程序demo源码下载汇总
近期微信小程序demo源码下载汇总,乃小程序学习分析必备素材!点击标题即可下载: 即速应用首发!原创!电商商场Demo 优质微信小程序推荐 -秀人美女图 图片下载.滑动翻页 微信小程序 - 新词 GE ...
- 开发 | 微信小程序API-wx.setScreenBrightness/wx.getScreenBrightness
前言 最近接触了微信小程序 API - wx.setScreenBrightness .wx.getScreenBrightness 接口,调用该接口可以调节并显示手机屏幕亮度数据.对于喜欢腾讯新闻. ...
- 循序渐进之Spring AOP(3) - 配置代理
上一篇介绍了几种Advice(增强),并通过代码演示了生成代理的方式,下面来看通过配置文件配置方式把Advice织入目标类. 注意,配置文件方式仍然不是spring AOP的最好方式,学习配置方式也是 ...
- COGS 2482. Franky的胡子【二分,高精度】
2482. Franky的胡子 ☆ 输入文件:beard.in 输出文件:beard.out 简单对比 时间限制:1 s 内存限制:128 MB [题目描述] Franky很苦恼他一直 ...
- BZOJ 1411&&Vijos 1544 : [ZJOI2009]硬币游戏【递推,快速幂】
1411: [ZJOI2009]硬币游戏 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSubmit: 897 Solved: 394[Submit][Status ...
- [bzoj1731] [Usaco2005 dec]Layout 排队布局
差分约束系统...因为题目要求的是1和n的最大距离所以这题就跑最长路.. 对于互相反感的牛(i与j互相反感,彼此距离至少为len,i<j),就有dis[j]-dis[i]>=len.就加一 ...
- c++(线性队列)
这里的线性结构实际上指的就是连续内存的意思,只不过使用“线性”这个词显得比较专业而已.前面一篇博客介绍了现象结构的处理方法,那么在这个基础之上我们是不是添加一些属性形成一种新的数据结构类型呢?答案是肯 ...
- 访问taotao-portal 中controller中返回taotaoresult 测试httppost方法 出现406错误
方案:1.检查jackson包是否存在 @controller @RequestMapping(value = "/httpclient/post",method=RequestM ...
