【java源码】解读HashTable类背后的实现细节
HashTable这个类实现了哈希表从key映射到value的数据结构形式。任何非null的对象都可以作为key或者value。
要在hashtable中存储和检索对象,作为key的对象必须实现hashCode、equals方法。
一般来说,默认的加载因子(0.75)提供了一种对于空间、时间消耗比较好的权衡策略。太高的值(指加载因子loadFactor)虽然减少了空间开销但是增加了检索时间,这反应在对hashtable的很多操作中,比如get、put方法。
初始容量的控制也是在空间消耗和rehash操作耗时(该操作耗时较大)二者之间的权衡。 如果初始容量大于哈希表的当前最大的条目数除以加载因子,则不会发生rehash。但是,将初始容量设置过高会浪费空间。
如果有大量的数据需要放进hashtable,则选择设置较大的初始容量比它自动rehash更优。
在Java平台v1.2中,这个类被重新安装以实现Map接口,使它成为Java集合框架的成员。与新的集合实现不同,Hashtable是同步的。如果不需要线程安全的实现,建议使用HashMap代替Hashtable。如果想要一个线程安全的高并发实现,那么建议使用java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap取代了Hashtable。
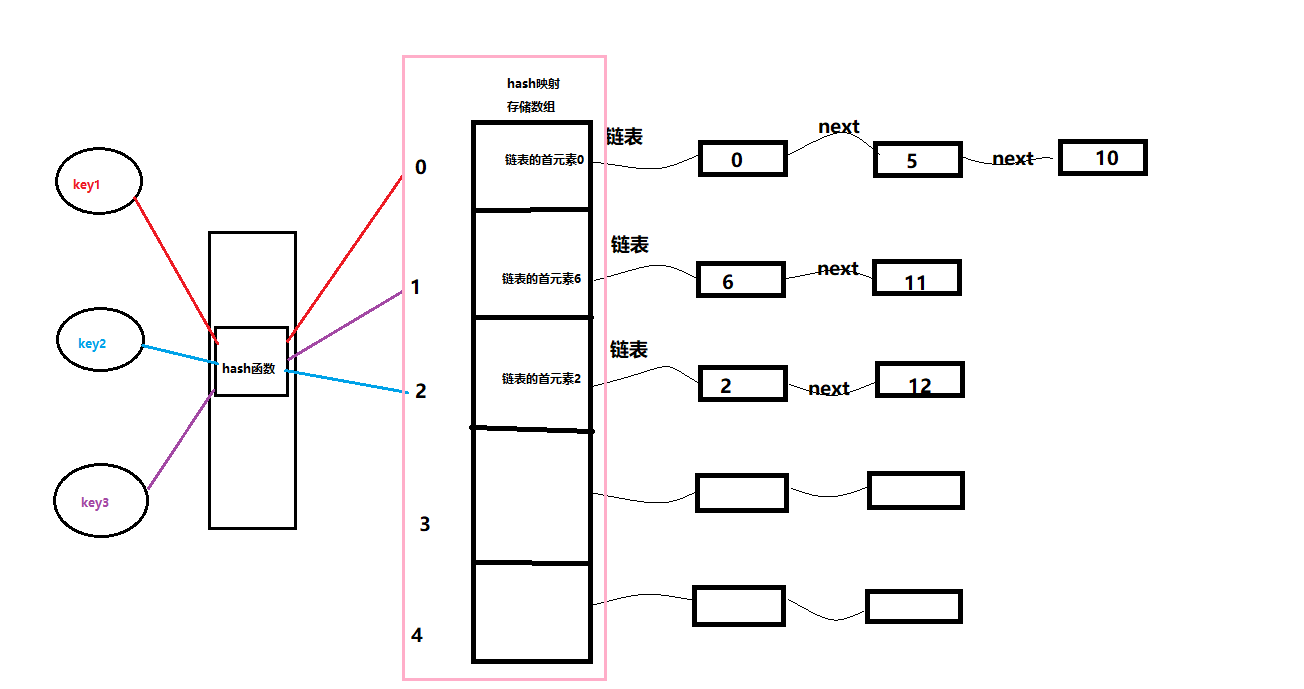
重要理解:Java中的HashTable数据存储结构
- HashTable 是以数组和单向链表结合的存储形式;
- 存储元素时,key通过hash映射函数得到在HashTable存储数组中的位置;
- 该位置存放的是hash值一致的单向链表的首元素;
- 新的元素存储到该位置指向的列表中;
- 数组存储哈希后的key,哈希值相同,则使用链表解决哈希碰撞,放到链表中。
结构示意图如下:
HashTable 的属性
private transient Entry<?,?>[] table; // table 是存储数据的数组。
private transient int count; // 在哈希表中已经存储的数据个数
private int threshold; // 哈希表将会在存储数据个数达到这个值时进行rehash,该值 = (int)容量 * 加载因子。
private float loadFactor; // 加载因子,默认为 0.75。
private transient int modCount = 0; // 哈希表发生结构性改变的次数(如新增、删除操作),这个字段用于在创建迭代器时发生快速失败(fail-fast)发生ConcurrentModificationException。
HashTable 构造器
HashTable 提供了常见的4个构造器,常见的有三个:
指定初始容量、加载因子的构造器
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);
if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity];
threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
}
指定初始容量的构造器
指定初始容量的构造器,其默认加载因子为0.75
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0.75f);
}
空构造器
空构造器,内部使用了默认初始容量为11,加载因子为0.75.
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);
}
HashTable 的哈希函数
HashTable 的哈希函数 是将key的hashCode跟最大整数进行按位与,最后对哈希表的存储数组的长度进行取模,以便得到 该 key 在 存储数组中的索引值index。
- 获取key的hashCode值
- key的hashCode值 与 最大整数值进行按位后 对 存储数组的长度 进行取模,得到该key在存储数组中的安放位置index。
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
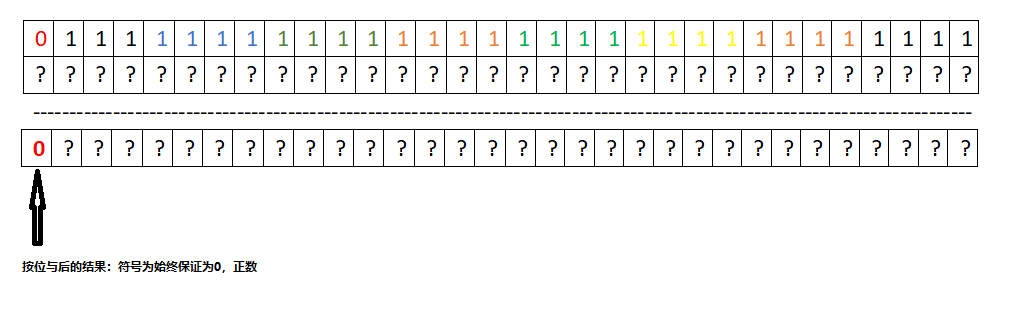
hash & 0x7FFFFFFF 使用该值(Integer的最大值进行按位与) 是为了取得绝对值,按位与高位为0,则保证符号位为正。
0x7FFFFFFF 的二进制编码如下,高位为0:
哈希桶内部存储数据结构类 Entry<K,V>
HashTable 内部存储数组中的链表对象:数据使用一个静态内部类对象存储,Entry<K,V>,该实体类包含四个属性:
- final int hash; // 哈希值 key.hashCode()
- final K key; // 键
- V value; // 值
- Entry<K,V> next; //指向存储数组的该位置的单向链表中的下一个元素
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
//......
}
put(K key, V value) 存储数据到哈希表
HashTable的put(key, value) 方法,可以将非空数据key-value 键值对放到哈希表中。
put 方法获取 key 的 hashCode值,再将其与Integer的最大值进行按位与(保证符号为正),得到哈希值,哈希值再对存储数组长度取模得到存储位置index。
然后遍历该链表,选择合适的位置放入该元素。
index 作为开始在存储数组中的索引值进行匹配,如果index处没有存储数据(即没有进入到for循环中),则直接在此位置上添加该key-value键值对(调用 addEntry(hash, key, value, index); 方法)。
如果在index中已经存储过数据了,又分两种情况:
- (1) 已经存在的数据的 hash 值 和当前要存储的数据的 hash 值相等, 且 key 也相等。 就表示是数据对象相等,则将旧的数据对象的value设置为此次需要存储的数据对象的value, 并返回旧的数据对象的value。
- (2) 如果不相等且找到链表末尾,则在链尾位置插入数据----进入 addEntry(hash, key, value, index); 方法。
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode(); //hash值
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; // 高位按位与操作:取得绝对值,按位与高位为0,则保证符号位为正
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; // 哈希函数后,得到指定的存储数组元素(是一个单项链表的首元素)
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
// 遍历链表
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
// hash 值相等,且 key值equals,则说明已经存在该ke,则替换旧值
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
// 链表为空, 则
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index)
该方法用于存储数据key-value对象。
首先会将 modCount 自增, 表示该哈希表会发生结构性改变。
如果哈希表数据个数 count 还没有达到 阈值 threshold,则直接添加该key-value到index此位置,同时count自增。
如果 count >= threshold 了,就 执行rehash操作(详见rehash方法描述),哈希表扩大,
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;//结构性改变
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
rehash()
rehash 操作是哈希表的重要且耗时的操作。
rehash 操作会扩大、重新组织哈希表,newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1: 新的容量 = 旧容量 * 2 + 1。
存储数组的最大长度设置为Integer的最大值 - 8。
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
如果新容量大于存储数组的最大容量:如果旧容量已经等于存储数组的最大容量,则不做任何动作直接返回; 否则,新容量 置为 存储数组的最大容量(已满)。
步骤:
创建一个新的存储数组,容量为新容量newCapacity。
modCount++,结构性变更。
使用新容量更新阈值 threshold。
双层for循环,使用新的容量取模重新计算在新的存储数组中的位置。
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table;
// 设置rehash后的新容量 START...
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1; // 新的容量 = 旧容量 * 2 + 1
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) { //如果新容量大于存储数组的最大容量
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
// 设置rehash后的新容量 END.
Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity];
modCount++;
// 使用新容量更新阈值
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap;
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
// 遍历旧的存储数组
for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
// 如果当前索引位置的链表存在元素,则处理
Entry<K,V> e = old; // 记录旧的元素
old = old.next; // 下一次内层for循环则处理当前元素的下一个元素
//旧的元素重新根据新容量计算hash
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];
//将旧数据放到新表中的新index位置上
newMap[index] = e;//放置旧元素
}
}
//for循环完成旧表数据堆放到新表中去, 就是一次rehash
}
get(Object key)
get(Object key) 方法根据指定的key获取其value。该方法通过key的hash值,再进行高位按位与,获取到索引index,然后遍历存储数组,直到找到 hash、key均相等的元素,返回其value。
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
contains(Object value)
contains(Object value) 判断哈希表的存储数组中是否包含指定的value。会遍历数组,去匹配value,找到一个就返回true。
public synchronized boolean contains(Object value) {
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if (e.value.equals(value)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
containsKey(Object key)
containsKey(Object key) 方法用于检查哈希表中是否包含指定的key。
public synchronized boolean containsKey(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
remove(Object key)
remove 操作移除指定的key。会改变 modCount 、count 的值。
public synchronized V remove(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(Entry<K,V> prev = null ; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count--;
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = null;
return oldValue;
}
}
return null;
}
clear()
clear() 方法会改变 modCount、count 的值。将存储数组中元素置为 null。
public synchronized void clear() {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
modCount++;
for (int index = tab.length; --index >= 0; )
tab[index] = null;
count = 0;
}
hashCode()
hashTable 的hashCode(0 方法也是有点意思的。
loadFactor = -loadFactor; 这行代码用于防止递归调用hashCode导致堆栈溢出。
public synchronized int hashCode() {
/*
* This code detects the recursion caused by computing the hash code
* of a self-referential hash table and prevents the stack overflow
* that would otherwise result. This allows certain 1.1-era
* applets with self-referential hash tables to work. This code
* abuses the loadFactor field to do double-duty as a hashCode
* in progress flag, so as not to worsen the space performance.
* A negative load factor indicates that hash code computation is
* in progress.
*/
int h = 0;
if (count == 0 || loadFactor < 0)
return h; // Returns zero
loadFactor = -loadFactor; // Mark hashCode computation in progress
Entry<?,?>[] tab = table;
for (Entry<?,?> entry : tab) {
while (entry != null) {
h += entry.hashCode();
entry = entry.next;
}
}
loadFactor = -loadFactor; // Mark hashCode computation complete
return h;
}
【java源码】解读HashTable类背后的实现细节的更多相关文章
- 源码解读—HashTable
在上一篇学习过HashMap(源码解读—HashMap)之后对hashTable也产生了兴趣,随即便把hashTable的源码看了一下.和hashMap类似,但是也有不同之处. public clas ...
- Java源码解读(一)——HashMap
HashMap作为常用的一种数据结构,阅读源码去了解其底层的实现是十分有必要的.在这里也分享自己阅读源码遇到的困难以及自己的思考. HashMap的源码介绍已经有许许多多的博客,这里只记录了一些我看源 ...
- java源码阅读Hashtable
1类签名与注释 public class Hashtable<K,V> extends Dictionary<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, C ...
- java源码解析——Stack类
在java中,Stack类继承了Vector类.Vector类和我们经常使用的ArrayList是类似的,底层也是使用了数组来实现,只不过Vector是线程安全的.因此可以知道Stack也是线程安全的 ...
- [Java源码解析] -- String类的compareTo(String otherString)方法的源码解析
String类下的compareTo(String otherString)方法的源码解析 一. 前言 近日研究了一下String类的一些方法, 通过查看源码, 对一些常用的方法也有了更透彻的认识, ...
- 【数据结构】9.java源码关于HashTable
1.hashtable的内部结构 基础存储数据的hash桶由Entry结构的数组存放而entry数据结构,有hash,key和value,还有一个指向下一个节点的引用next对象 这里就和hashma ...
- Java源码解读(一) 8种基本类型对应的封装类型
说起源码其实第一个要看的应该是我们的父类Object,这里就不对它进行描述了大家各自对其进行阅读即可. 一.八种基本类型 接下来介绍我们的八种基本类型(这个大家都知道吧):char.byte.shor ...
- 自己动手实现springboot运行时执行java源码(运行时编译、加载、注册bean、调用)
看来断点.单步调试还不够硬核,根本没多少人看,这次再来个硬核的.依然是由于apaas平台越来越流行了,如果apaas平台选择了java语言作为平台内的业务代码,那么不仅仅面临着IDE外的断点.单步调试 ...
- java.lang.system 类源码解读
通过每块代码进行源码解读,并发现源码使用的技术栈,扩展视野. registerNatives 方法解读 /* register the natives via the static initializ ...
随机推荐
- 什么是HTML?
html是很多人编程的入门领域.作为初学者,不管你是在哪里学的,学校,视频教程,网络教程等等……它们都会告诉你HTML即:超文本标记语言(Hyper Text Markup Language).但第一 ...
- tomcat启动慢
securerandom.source=file:/dev/./urandom 搜索 /""
- 在windows下使用jenkins部署docker容器
在windows下使用jenkins部署docker容器最近在学习jenkins,docker部署来实现集成部署,所以想在windows下面实现测试,但是发现在windows下docker支持不是很好 ...
- CVTE C/C++开发工程师笔试题(一)
问题描述: 字符串组装. 现在需要将一些数据格式不同的数据组装成一个char型字符串输出,数据来源包含一个char型的字符串,一个short型的16进制数据: 举例: 假若定义如下2个变量: 1.ch ...
- spring boot1.0 集成quartz 动态配置定时任务
转载自 https://www.imooc.com/article/36278 一.Quartz简介了解 Quartz Quartz 是一个完全由 Java 编写的开源作业调度框架,为在 Java 应 ...
- mysql保存乱码(C#)
解决办法只有一个就是在配置文件中强制指定编码格式:<add name="TSDBEntities" connectionString="metadata=res:/ ...
- JS 中常见数组API使用方法(join、concat、slice、splice、reverce)
刚接触前端不久,个人觉得学习程序还是需要经常总结的.下面是我的一些知识的归纳总结,如果哪里说得不对的还请各位大神指点! 1.to str (1)String(arr)将数组中的每个元素转为字符串并用逗 ...
- 微信小程序实战[01]
接触微信小程序也有一段时间了,以天气预报练一下手. 主要实现了以下功能: (1) 首页图标式菜单,便于以后扩展功能 (2)首页顶部滚动消息 (3)页面右上角三点菜单转发功能,便于小程序的传播 (4)天 ...
- 《笨方法学Python》加分题28
#!usr/bin/python # -*-coding:utf-8-*- True and True print ("True") False and True print (& ...
- 文件操作命令(del)
del 命令: // 描述: 删除一个或多个文件.同等于 erase 命令. 相比较 rd 命令来说,del 命令只能删除文件,不能删除文件夹. // 语法: del [/p] [/f] [/s] [ ...
