Python——collections模块、time模块、random模块、os模块、sys模块
1. collections模块
(1)namedtuple
# (1)点的坐标
from collections import namedtuple
Point = namedtuple('point',['x','y']) # 前两行可以用下面两行代替
# import collections
# Point = collections.namedtuple('point',['x','y'])
p = Point(1,2)
print(p.x) #
print(p.y) #
print(p) #point(x=1, y=2)
扑克牌的花色和数字
from collections import namedtuple
Card = namedtuple('card',['suits','number'])
c1 = Card('红桃',2)
print(c1.suits) #红桃
print(c1.number) #
print(c1) #card(suits='红桃', number=2)
(2)queue 队列——FIFO 先进先出
import queue q = queue.Queue()
q.put(10)
q.put(5)
q.put(8)
print(q.qsize()) #
print(q) #<queue.Queue object at 0x00000144985010B8>
print(q.get()) #
print(q.get()) #
print(q.get()) #
print(q.get()) #阻塞:取完值之后继续取,不会报错
(3)deque——双端队列
from collections import deque
dq = deque([5,6])
dq.appendleft('a') #从前面放数据 ['a',5,6]
dq.append('b') #从后面放数据 ['a',5,6,'b']
dq.insert(0,3) # [3,'a',5,6,'b']
print(dq) #deque([3, 'a', 5, 6, 'b'])
print(dq.popleft()) #从前面取数据:3
print(dq.popleft()) #从前面取数据:a
print(dq.pop()) #从后面取数据:b
print(dq.pop()) #从后面取数据:6
print(dq) #deque([5])
(4)OrderedDict 有序字典
字典取值快,但是存储时比列表占内存多
from collections import OrderedDict
od = dict([('a',1),('b',2),('c',3)])
print(od) #有序:{'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
print(od['a']) #
for k in od:
print(k) # a b c
(5)defaultdict——默认字典
key不存在时,返回一个默认值
举例:将大于66的数放在k1,小于66的数放在k2
from collections import defaultdict
values = [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,100]
my_dict = defaultdict(list) #默认list
for value in values:
if value>66:
my_dict['k1'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k2'].append(value)
print(my_dict['k1']) #[77, 88, 99, 100]
print(my_dict['k2']) #[11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66]
defaultdict的用法
from collections import defaultdict
d = defaultdict(list)
print(d['k']) #[] from collections import defaultdict
d1 = defaultdict(dict)
print(d1['k']) #{} from collections import defaultdict
dd = defaultdict(lambda:'默认值')
dd['key1'] = 'abc'
print(dd['key1']) #key1存在,返回:abc
print(dd['key2']) #key2不存在,返回:默认值(可以随意设置)
(6)Counter——跟踪值出现的次数
from collections import Counter
c = Counter('abacadfdcbcdf')
print(c) #Counter({'a': 3, 'c': 3, 'd': 3, 'b': 2, 'f': 2})
2. time模块
(1)时间戳时间(timestamp)——float时间:给计算机看的
(2)格式化时间(Format String)——字符串:给人看的
#格式化时间:时间字符串strftime
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %a %H:%M:%S' )) # 2018-10-08 Mon 15:04:01 Year month day week Hour Minute Seconds
print(time.strftime('%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S' )) # 2018/10/08 15:05:23 Year month day Hour Minute Seconds
print(time.strftime('%m-%d %H:%M:%S' )) # 10-08 15:04:01 month day Hour Minute Seconds
print(time.strftime('%H:%M:%S' )) # 15:04:01 Hour Minute Seconds
print(time.strftime('%H:%M' )) # 15:04 Hour Minute
(3)结构化时间(struct_time)——元祖:计算用的
#结构化时间 #localtime
struct_time = time.localtime()
print(struct_time) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=8, tm_hour=15, tm_min=7, tm_sec=53, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=281, tm_isdst=0)
print(struct_time.tm_year) # #gmtime
struct_time1 = time.gmtime()
print(struct_time1) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=8, tm_hour=15, tm_min=7, tm_sec=53, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=281, tm_isdst=0)
print(struct_time1.tm_year) #
(4)三者的相互转换
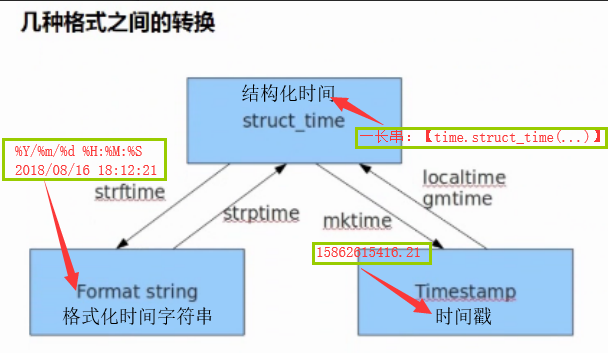
(5)相互转换代码
t = time.time()
print(t) #1538982828.2859974
print(time.localtime(t)) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=8, tm_hour=15, tm_min=13, tm_sec=3, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=281, tm_isdst=0)
print(time.gmtime(t)) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=8, tm_hour=7, tm_min=13, tm_sec=3, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=281, tm_isdst=0)
print(time.localtime(1500000000)) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2017, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=14, tm_hour=10, tm_min=40, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=195, tm_isdst=0) print(time.mktime(time.localtime())) #1538982958.0 t = time.strptime('2000-12.31','%Y-%m.%d')
print(t) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2000, tm_mon=12, tm_mday=31, tm_hour=0, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=6, tm_yday=366, tm_isdst=-1)
print(time.strftime('%m/%d/%y %H:%M:%S',time.localtime(3000000000))) #01/24/65 13:20:00 print(time.asctime()) # Mon Oct 8 15:21:02 2018
print(time.asctime(time.localtime())) # Mon Oct 8 15:21:02 2018
print(time.asctime(time.localtime(2000000000))) # Wed May 18 11:33:20 2033
print(time.ctime()) # Mon Oct 8 15:21:02 2018
print(time.ctime(2000000000)) # Wed May 18 11:33:20 2033
3. random模块
(1)随机小数
import random print(random.random()) # (0,1)之间的任意一个小数
print(random.uniform(1,3)) # (1,3)之间的任意一个小数
(2)随机整数
import random print(random.randint(1,5)) # [1,5]之间的任意一个整数
print(random.randrange(1,5)) # [1,4]之间的任意一个整数
print(random.randrange(1,10,2)) # [1,9]之间的任意一个整数奇数
(3)选择一个返回
import random print(random.choice([1,'',[4,5]])) # 随机选择一个返回:列表任意一个元素
(4)选择多个返回
import random print(random.sample([1,'',[4,5],5,4,9],3)) # 随机选择多个返回:返回个数是函数的第二个参数
(5)打乱列表序列
import random item = [1,3,5,7,9]
print(item) # [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
random.shuffle(item)
print(item) # [5, 9, 3, 7, 1]
(6)验证码的生成
详见:笔试面试题 https://www.cnblogs.com/xc-718/p/9632731.html
4. sys模块
import sys sys.exit() # 退出程序:exit(1) 错误退出,exit(0) 正常退出
print(sys.platform) # win32【不准】
# 获取Python解释程序的版本信息
print(sys.version) # 3.6.3 (v3.6.3:2c5fed8, Oct 3 2017, 18:11:49) [MSC v.1900 64 bit (AMD64)] # 返回模块的搜索路径
print(sys.path) # 所有路径
print(sys.path.clear()) # 清空之后,import sys 会报错
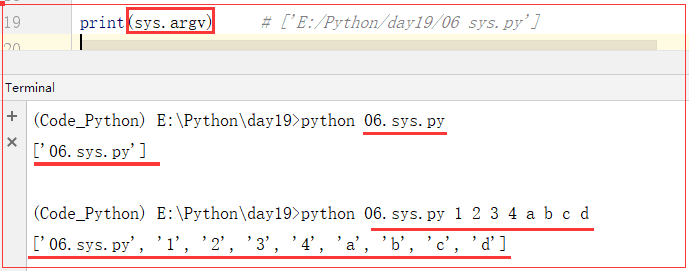
sys.argv
import sys print(sys.argv) # ['E:/Python/day19/06 sys.py'] ret = sys.argv
name = ret[1]
pwd = ret[2]
if name == 'xc' and pwd == '':
print('登陆成功')
else:
print('错误的用户名或密码')
sys.exit()
print('你可以使用本系统了')
5.os模块
(1)os.getcwd()
import os print(os.getcwd()) #获取当前工作目录: E:\Python\day19
os.chdir(r'E:\Python') #改变当前脚本的工作目录,一般不会用到
print(os.getcwd()) #获取当前工作目录: E:\Python
os.chdir(r'E:\Python\day19') #改变回原本的工作目录
print(os.getcwd()) #获取当前工作目录: E:\Python\day19
import sys print(sys.argv) # ['E:/Python/day19/06 sys.py'] ret = sys.argv
name = ret[1]
pwd = ret[2]
if name == 'xc' and pwd == '':
print('登陆成功')
else:
print('错误的用户名或密码')
sys.exit()
print('你可以使用本系统了')
(2)文件和目录操作
import os print(os.getcwd()) #E:\Python\day19
os.chdir('..') #改变目录到当前目录的父目录
print(os.getcwd()) #E:\Python print(os.curdir) # . 当前目录
print(os.pardir) # .. 当前目录的父目录,也就是上一层目录 os.makedirs('dir1/dir2') #创建多层目录
os.removedirs('dir1/dir2') #递归删除,一直删到上层目录不为空为止
os.mkdir('dir1') #创建单级目录
os.rmdir('dir1') #删除单极空目录,不为空不删除 print(os.listdir(r'E:\Python\day19')) #列出指定目录下所有的文件和子目录,包含隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印 os.rename('06.sys.py','06 sys.py') # 重命名文件
os.remove('E:/Python/day19/07 delete') # 删除一个文件 print(os.stat('E:/Python/day19/06 作业.py')) # 获取文件/目录信息
(3)代码跨平台
import os # python 代码跨平台
print(os.sep)
# 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符
# windows \ E:\Python\day19
# linux / E:/Python/day19
print(os.pathsep)
# 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串
# windows ; E:\Python\day19;E:\Python\day19;E:\Python\day19
# linux : E:\Python\day19:E:\Python\day19:E:\Python\day19
print(os.name)
# 输出字符串指示当前平台
# windows nt
# linux posix
(4)与路经有关
import os # 与路径有关的
print(os.path) #绝对路径 <module 'ntpath' from 'D:\\download\\Python\\lib\\ntpath.py'>
# 返回path规范化的绝对路径
print(os.path.abspath(os.getcwd())) #E:\Python\day19 print(os.getcwd()) # 获取当前路径 E:\Python\day19
# 用split将路径分割成:(目录,文件名)
print(os.path.split(os.getcwd())) #('E:\\Python', 'day19') # 返回path的目录
print(os.path.split(os.getcwd())) #('E:\\Python', 'day19')
print(os.path.dirname(os.getcwd())) # E:\Python
print(os.path.basename(os.getcwd())) # day19 print(os.path.exists()) # path存在,返回True;不存在,返回False
print(os.path.isabs()) # path是绝对路径,返回True
print(os.path.isfile()) # path是一个存在的文件,返回True
print(os.path.isdir()) # path 是一个存在的目录,返回True
print(os.path.join('c:','user','local')) # c:user\local 多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数被忽略
print(os.path.getatime()) # 返回path所指向的文件/目录的最后访问时间
print(os.path.getmtime()) # 返回path所指向的文件/目录的最后修改时间 # 返回path的大小
print(os.path.getsize(os.getcwd())) # 4096【文件夹最大这么大】
print(os.path.getsize(os.path.join(os.getcwd(),'03 time.py'))) # 2546【文件大小】
(5)其他
import os
os.system('dir') # 运行shell命令,直接显示,无返回值不能直接操作
print(os.popen('dir').read()) # 运行shell命令,获取执行结果,有返回值
# 获取系统的环境变量
print(os.environ)
Python——collections模块、time模块、random模块、os模块、sys模块的更多相关文章
- collections,time,random,os, sys 模块的使用
主要内容:1. 模块的简单认识2. collections模块3. time时间模块4. random模块5. os模块6. sys模块 一. 模块的简单认识什么是模块. 模块就是我们把装有特定功能的 ...
- python time、datetime、random、os、sys模块
一.模块1.定义模块:用来从逻辑上组织Python代码(变量,函数,类,逻辑:实现一个功能),本质就是.py结尾的python文件(文件名:test.py,对应的模块名:test)包:用来从逻辑上组织 ...
- python常用模块---collections、time、random、os、sys、序列号模块
collections模块 在内置数据类型(dict.list.set.tuple)的基础上,collections模块还提供了几个额外的数据类型:Counter.deque.defaultdict. ...
- Python进阶-XI 常用模块之一:collections、time、random、os、sys
简要介绍一下各种集合: 列表.元组.字典.集合(含frozenset).字符串.堆栈(如手枪弹夹:先进后出).队列(如马克沁机枪的弹夹:先进先出) 1.collections 1)queue 队列介绍 ...
- python之random 、os 、sys 模块
一.random模块 import random print(random.random())#(0,1)----float 大于0且小于1之间的小数 print(random.randint(1,3 ...
- Python (time、datetime、random、os、sys、shutil)模块的使用
######################################################### 模块time ################################### ...
- Python os与sys模块解析
os与sys模块的官方解释如下: os: This module provides a portable way of using operating system dependent functio ...
- Python中os与sys模块的区别
os与sys模块的官方解释如下: os: This module provides a portable way of using operating system dependent functio ...
- python os和sys模块使用
python os和sys模块使用 os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径 os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录:相 ...
- Python 的 os 与 sys 模块
os与sys模块的官方解释如下: os: This module provides a portable way of using operating system dependent functio ...
随机推荐
- MySql和Sql的单行注释和多行注释的区别
这里,请允许我把mysqlserver和sqlserver注释一起说明 1.单行注释 1)mysql中,可以用“-- ”和“ --”来注释 -- 方式1:单行注释 -- create database ...
- UVALive 5844 dfs暴力搜索
题目链接:UVAive 5844 Leet DES:大意是给出两个字符串.第一个字符串里的字符可以由1-k个字符代替.问这两个字符串是不是相等.因为1<=k<=3.而且第一个字符串长度小于 ...
- 前端:jQuery笔记
前端:jQuery笔记 此系列文章乃是学习jQuery的学习笔记. Asp.net MVC Comet推送 摘要: 一.简介 在Asp.net MVC实现的Comet推送的原理很简单. 服务器端:接收 ...
- MySQL 5.6比较重要的参数,以及5.5到5.6默认值有过变化的参数
新参数说明和设置,这里说下5.6比较重要的参数,以及5.5到5.6默认值有过变化的参数. MySQL Server参数: 1,optimizer_switch:优化器选项. Variable_name ...
- Python Django 之 MVT
一.Django的MVT模式 M: Model, 模型 与MVC中的M相同,负责对数据的处理 V: View, 视图 与MVC中的C类似,负责处理用户请求,调用M和T,响应请求 T: Template ...
- Oracle11g dump 部分参数解读
一.Oracle dump expdp CONTENT ALL ALL ,将导出对象定义及其所有数据 DATA_ONLY DATA_ONLY,只导出对象数据 METADATA_ONLY ...
- Maven入门-5.Maven的聚合和继承
1.Maven的聚合1.1 聚合的配置2.Maven的继承2.1 可被继承的POM元素2.2 POM中使用继承2.3 继承dependency 1.Maven的聚合 在Maven入门-4.Maven的 ...
- C++设计模式之解释器模式
2013年07月06日 19:43:00 阅读数:8853 概述: 未来机器智能化已然成为趋势,现在手机都能听懂英语和普通话,那我大中华几万种方言的被智能化也许也是趋势,我们的方言虽然和普通话相似,但 ...
- 想ACCESS数据库插入新的用户
public string AddUserN = ""; //定义用户名字符串 public string paswrd1 = ""; //密码1 public ...
- pygame经典sprite精灵类
import cStringIO, base64 import pygame from pygame.locals import * class Ball(pygame.sprite.Sprite): ...
