spring框架学习笔记7:事务管理及案例
Spring提供了一套管理项目中的事务的机制
以前写过一篇简单的介绍事务的随笔:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuyiqing/p/8430214.html
还有一篇Hibernate的事务管理:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuyiqing/p/8449167.html
可以做个对比
Spring管理事务特有的属性:
事务传播行为:事务传播行为(propagation behavior)指的就是当一个事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,这个事务方法应该如何进行。
例如:methodA事务方法调用methodB事务方法时,methodB是继续在调用者methodA的事务中运行呢,还是为自己开启一个新事务运行,这就是由methodB的事务传播行为决定的。
1、PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就创建一个新事务,如果当前存在事务,就加入该事务,该设置是最常用的设置。
2、PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前存在事务,就加入该事务,如果当前不存在事务,就以非事务执行。‘
3、PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:支持当前事务,如果当前存在事务,就加入该事务,如果当前不存在事务,就抛出异常。
4、PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:创建新事务,无论当前存不存在事务,都创建新事务。
5、PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。
6、PROPAGATION_NEVER:以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
7、PROPAGATION_NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED类似的操作
接下来演示事务案例:简单模拟转账
需要的包:
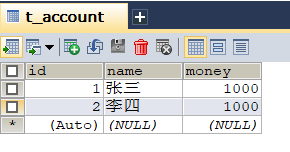
新建一张表,放入数据:
package dao;
public interface AccountDao {
//加钱
void increaseMoney(Integer id,Double money);
//减钱
void decreaseMoney(Integer id,Double money);
}
package dao;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements AccountDao {
@Override
public void increaseMoney(Integer id, Double money) {
getJdbcTemplate().update("update t_account set money = money+? where id = ? ", money,id);
}
@Override
public void decreaseMoney(Integer id, Double money) {
getJdbcTemplate().update("update t_account set money = money-? where id = ? ", money,id);
}
}
package service;
public interface AccountService {
//转账方法
void transfer(Integer from,Integer to,Double money);
}
package service;
import dao.AccountDao;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao ad;
@Override
public void transfer(final Integer from, final Integer to, final Double money) {
// 减钱
ad.decreaseMoney(from, money);
// 加钱
ad.increaseMoney(to, money);
}
public void setAd(AccountDao ad) {
this.ad = ad;
}
}
package tx; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import service.AccountService; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Resource(name="accountService")
private AccountService as; @Test
public void fun1(){ as.transfer(1, 2, 100d); }
}
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd "> <!-- 指定spring读取db.properties配置 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" /> <!-- 事务核心管理器,封装了所有事务操作. 依赖于连接池 -->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager" >
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 以方法为单位,指定方法应用什么事务属性
isolation:隔离级别
propagation:传播行为
read-only:是否只读
其他方法的配置没有用到,但它们通常是统一配置
-->
<tx:method name="save*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="persist*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="modify*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="delete*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="remove*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="get*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="find*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice> <!-- 配置织入 -->
<aop:config >
<!-- 配置切点表达式 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="txPc"/>
<!-- 配置切面 : 通知+切点
advice-ref:通知的名称
pointcut-ref:切点的名称
-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPc" />
</aop:config> <!-- 1.将连接池 -->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" >
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" ></property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" ></property>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" ></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" ></property>
</bean> <!-- 2.Dao-->
<bean name="accountDao" class="dao.AccountDaoImpl" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property>
</bean>
<!-- 3.Service-->
<bean name="accountService" class="service.AccountServiceImpl" >
<property name="ad" ref="accountDao" ></property>
</bean> </beans>
db.properties
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///mybase
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=xuyiqing
运行Demo后结果:
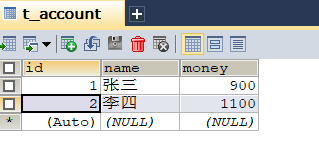
转账成功!
补充:
可以采用注解方式代替XML配置文件:
配置文件只要一行即可:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd "> <!-- 指定spring读取db.properties配置 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" /> <!-- 事务核心管理器,封装了所有事务操作. 依赖于连接池 -->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property>
</bean>
<!-- 事务模板对象 -->
<bean name="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate" >
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" ></property>
</bean> <!-- 开启使用注解管理aop事务 -->
<tx:annotation-driven/> <!-- 1.将连接池 -->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" >
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" ></property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" ></property>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" ></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" ></property>
</bean> <!-- 2.Dao-->
<bean name="accountDao" class="dao.AccountDaoImpl" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property>
</bean>
<!-- 3.Service-->
<bean name="accountService" class="service.AccountServiceImpl" >
<property name="ad" ref="accountDao" ></property>
</bean> </beans>
package service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import dao.AccountDao; @Transactional(isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, readOnly = true)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private AccountDao ad; @Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, readOnly = false)
public void transfer(final Integer from, final Integer to, final Double money) {
// 减钱
ad.decreaseMoney(from, money);
// 加钱
ad.increaseMoney(to, money);
} public void setAd(AccountDao ad) {
this.ad = ad;
} }
测试后同样成功!
Spring框架的学习就到这里
spring框架学习笔记7:事务管理及案例的更多相关文章
- Spring框架学习笔记(1)
Spring 框架学习笔记(1) 一.简介 Rod Johnson(spring之父) Spring是分层的Java SE/EE应用 full-stack(服务端的全栈)轻量级(跟EJB比)开源框架, ...
- Spring框架学习笔记(5)——Spring Boot创建与使用
Spring Boot可以更为方便地搭建一个Web系统,之后服务器上部署也较为方便 创建Spring boot项目 1. 使用IDEA创建项目 2. 修改groupid和artifact 3. 一路n ...
- Spring框架学习笔记(8)——spring boot+mybatis plus+mysql项目环境搭建
之前写的那篇Spring框架学习笔记(5)--Spring Boot创建与使用,发现有多小细节没有提及,,正好现在又学习了mybatis plus这款框架,打算重新整理一遍,并将细节说清楚 1.通过I ...
- Spring框架学习笔记(10)——Spring中的事务管理
什么是事务 举例:A给B转500,两个动作,A的账户少500,B的账户多500 事务就是一系列的动作, 它们被当做一个单独的工作单元. 这些动作要么全部完成, 要么全部不起作用 一.注解添加事务管理方 ...
- 深入学习Spring框架(四)- 事务管理
1.什么是事务? 事务(Transaction)是一个操作序列.这些操作要么都做,要么都不做,是一个不可分割的工作单位,是数据库环境中的逻辑工作单位.事务是为了保证数据库的完整性.例如:A给B转账,需 ...
- 手写Spring框架学习笔记
以下是咕泡公开课的学习笔记 一.创建工程springdemo 二.在pom中配置servlet <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</ ...
- Spring框架学习笔记(3)——SpringMVC框架
SpringMVC框架是基于Spring框架,可以让我们更为方便的进行Web的开发,实现前后端分离 思路和原理 我们之前仿照SpringMVC定义了一个自定义MVC框架,两者的思路其实都是一样的. 建 ...
- Spring框架学习笔记(4)——SSM整合以及创建Maven自定义模版
Spring+Spring MVC+MyBatis+Maven SSM整合的核心还是Spring+MyBatis的整合,回顾一下MyBatis操作数据库流程,我们是使用一个SQLSessionFact ...
- spring框架学习笔记1:搭建测试
Spring框架介绍: Spring框架涵盖了web.service.dao三层,本身是一个存放对象的容器 形象来说:Spring是项目中对象管家 Spring框架的两大核心思想:控制反转(IOC). ...
随机推荐
- python的相对导入
最近断断续续学习flask,学到蓝本时候有点小问题卡住了,问题如下 导入包的时候py文件里使用了相对路径导入,但是这种导入方法不是很明白,就自己搜索加实验了终于有点眉目了 先定义一个包 adb包 这个 ...
- [C语言]进阶|图形库
---------------------------------------------------------------------- // main.c // Created by weich ...
- tensorflow读取本地MNIST数据集
tensorflow读取本地MNIST数据集 数据放入文件夹(不要解压gz): >>> import tensorflow as tf >>> from tenso ...
- 【Nodejs】Nodejsの環境構築
参考URL:http://www.runoob.com/nodejs/nodejs-install-setup.html Windowにインストールする方法を紹介します. ▲ダウンロードURL:htt ...
- FortiGate上架前准备
1.收集信息 1.网络拓扑信息(了解网络拓扑信息有助于网络方案的规划) 2.环境信息(了解部署位置.部署模式.最大吞吐.最大用户数有助于对设备性能的评估) 3.客户需求,对FortiGate部署的功能 ...
- 【转载】一个小时学会MySQL数据库
一个小时学会MySQL数据库 目录 一.数据库概要 1.1.发展历史 1.1.1.人工处理阶段 1.1.2.文件系统 1.1.3.数据库管理系统 1.2.常见数据库技术品牌.服务与架构 1.3.数 ...
- python问题:AttributeError: 'module' object has no attribute 'SSL_ST_INIT'(转)
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaijiahui/p/7344778.html AttributeError: 'module' object has no attribu ...
- 微信小程序之----获取设备信息
1. 获取系统信息 wx.getSystemInfo(OBJECT) wx.getSystemInfoSync() 同步获取系统信息 回调常用 ...
- Python中操作Redis
一 Rdis基本介绍 redis是一个key-value存储系统.它支持存储的value类型相对更多,包括string(字符串).list(链表).set(集合).zset(sorted set -- ...
- 正则RegExp的懒惰性和贪婪性; 分组捕获;
1.正则的懒惰性??? 每次在它的方法exec中捕获的时候,只捕获第一次匹配的内容,而不往下捕获,我们把这种情况称为正则的懒惰性 且每一次捕获的位置都是从索引0开始 正则的实例对象上有一个lastin ...
