差分进化算法 DE-Differential Evolution
差分进化算法 (Differential Evolution)
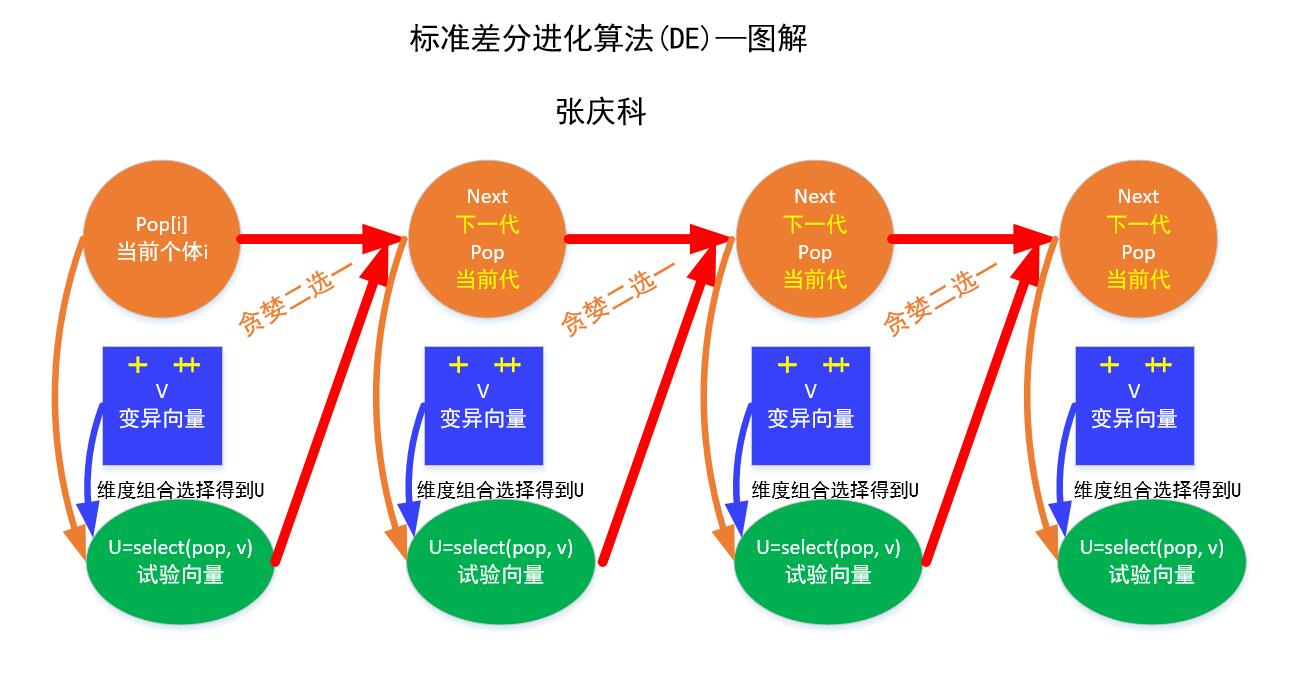

//********************************************************/
// DE/rand/1/bin --差分进化算法-(基本类型)
//********************************************************/ #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <float.h> /* Function definitions */ double func(double *);
int usage(char *); /* Random number generator defined by URAND should return
double-precision floating-point values uniformly distributed
over the interval [0.0, 1.0) */ #define URAND ((double)rand()/((double)RAND_MAX + 1.0)) /* Definition for random number generator initialization */ #define INITRAND srand(time(0)) /* Usage for the program */ int usage(char *str)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [-h] [-u] [-s] [-N NP (20*D)] ", str);
fprintf(stderr, "[-G Gmax (1000)]\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\t[-C crossover constant, CR (0.9)]\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\t[-F mutation scaling factor, F (0.9)]\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\t[-o <outputfile>]\n\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\t-s does not initialize random number generator\n");
exit(-);
} int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
register int i, j, k, r1, r2, r3, jrand, numofFE = ;
extern int D;
extern double Xl[], Xu[]; int NP = * D, Gmax = , c, index = -, s = ; double **popul, **next, **ptr, *iptr, *U, CR = 0.9, F = 0.9, min_value = DBL_MAX, totaltime = 0.0; char *ofile = NULL; FILE *fid;
clock_t starttime, endtime; /* Parse command line arguments given by user */ for (i = ; i < argc; i++)
{
if (argv[i][] != '-')
usage(argv[]); c = argv[i][]; switch (c)
{
case 'N':
if (++i >= argc)
usage(argv[]); NP = atoi(argv[i]);
break;
case 'G':
if (++i >= argc)
usage(argv[]); Gmax = atoi(argv[i]);
break;
case 'C':
if (++i >= argc)
usage(argv[]); CR = atof(argv[i]);
break;
case 'F':
if (++i >= argc)
usage(argv[]); F = atof(argv[i]);
break;
case 'o':
if (++i >= argc)
usage(argv[]); ofile = argv[i];
break;
case 's': /* Flag for using same seeds for */
s = ; /* different runs */
break;
case 'h':
case 'u':
default:
usage(argv[]);
}
} if (s) INITRAND; /* Printing out information about optimization process for the user */ printf("Program parameters: ");
printf("NP = %d, Gmax = %d, CR = %.2f, F = %.2f\n",
NP, Gmax, CR, F); printf("Dimension of the problem: %d\n", D); /* Starting timer */ starttime = clock(); /* Allocating memory for current and next populations, intializing
current population with uniformly distributed random values and
calculating value for the objective function */ // NP:种群大小, Gmax:迭代次数, CR:交叉概率, F:扰动向量的缩放因子 //当前种群
popul = (double **)malloc(NP*sizeof(double *));
if (popul == NULL) perror("malloc"); //下代种群
next = (double **)malloc(NP*sizeof(double *));
if (next == NULL) perror("malloc"); //当前种群popul[NP][D+1]
for (i = ; i < NP; i++)
{
//个体维度空间分配
popul[i] = (double *)malloc((D + )*sizeof(double));
if (popul[i] == NULL) perror("malloc"); //初始化维度值
for (j = ; j < D; j++)
popul[i][j] = Xl[j] + (Xu[j] - Xl[j])*URAND; //最后的元素内存放该个体的适应度值
popul[i][D] = func(popul[i]); numofFE++;//统计评估次数 //下一代个体空间分配
next[i] = (double *)malloc((D + )*sizeof(double));
if (next[i] == NULL) perror("malloc");
} /* 为实验向量分配空间--Allocating memory for a trial vector U */ U = (double *)malloc((D + )*sizeof(double));
if (U == NULL) perror("malloc"); /* The main loop of the algorithm */ for (k = ; k < Gmax; k++)
{ for (i = ; i < NP; i++) /* Going through whole population */
{ /* Selecting random indeces r1, r2, and r3 to individuls of
the population such that i != r1 != r2 != r3 */ //1.选择三个互不相同的随机个体r1,r2,r3
do
{
r1 = (int)(NP*URAND);
} while (r1 == i); do
{
r2 = (int)(NP*URAND);
} while (r2 == i || r2 == r1);
do
{
r3 = (int)(NP*URAND);
} while (r3 == i || r3 == r1 || r3 == r2); jrand = (int)(D*URAND); /* Mutation and crossover */
//2. 执行变异和交叉操作
for (j = ; j < D; j++)
{
//执行二项式交叉
if (URAND < CR || j == jrand)
{
//试验向量部分来自变异后的向量
U[j] = popul[r3][j] + F*(popul[r1][j] - popul[r2][j]);
}
else
//试验向量部分来自个体i
U[j] = popul[i][j];
}
//3. 计算新生成向量的适应度值
U[D] = func(U); numofFE++; /* Comparing the trial vector 'U' and the old individual
'next[i]' and selecting better one to continue in the
next population.注意:空间的交替变换和使用 */ //贪婪策略从试验向量U和当前个体i中选择一个好的放入到下一代个体中
if (U[D] <= popul[i][D])//新向量好
{ //试验向量U牛逼, next指向当前的试验向量U,u指向next, 方法:指针交换
iptr = U;
U = next[i];
next[i] = iptr;
}
else//原始向量牛逼, next指向个体i, 方法: 直接拷贝
{
for (j = ; j <= D; j++)
next[i][j] = popul[i][j];
} } /* End of the going through whole population */ /* Pointers of old and new populations are swapped */
//指针交换,各指针指向的空间发生变化
ptr = popul;
popul = next;
next = ptr; } /* End of the main loop */ /* Stopping timer */ endtime = clock();
totaltime = (double)(endtime - starttime); /* If user has defined output file, the whole final population is
saved to the file */ if (ofile != NULL)
{
if ((fid = (FILE *)fopen(ofile, "a")) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error in opening file %s\n\n", ofile);
usage(argv[]);
} for (i = ; i < NP; i++)
{
for (j = ; j <= D; j++)
fprintf(fid, "%.15e ", popul[i][j]);
fprintf(fid, "\n");
}
fclose(fid);
} /* Finding best individual */ for (i = ; i < NP; i++)
{
if (popul[i][D] < min_value)
{
min_value = popul[i][D];
index = i;
}
} /* Printing out information about optimization process for the user */ printf("Execution time: %.3f s\n", totaltime / (double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("Number of objective function evaluations: %d\n", numofFE); printf("Solution:\nValues of variables: ");
for (i = ; i < D; i++)
printf("%.15f ", popul[index][i]); printf("\nObjective function value: ");
printf("%.15f\n", popul[index][D]); /* Freeing dynamically allocated memory */ for (i = ; i < NP; i++)
{
free(popul[i]);
free(next[i]);
}
free(popul);
free(next);
free(U); return();
}
经典文献:
[1] Storn, R., "Designing Nonstandard Filters with Differential Evolution, IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, january 2005, pp. 103 - 106.
[2] Storn, R., "Sytem Design by Constraint Adaptation and Differential Evolution", IEEE Trans. on Evolutionary Computation, 1999, Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 22 - 34.
[3] Storn, R. and Price, K., "Differential Evolution - a Simple and Efficient Heuristic for Global Optimization over Continuous Spaces", Journal of Global Optimization, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1997, Vol. 11, pp. 341 - 359.
[4] Gitsels, M. and Storn, R., Internet-Videotelephonie nach dem H.323-Standard, ITG-Fachbericht 144, 7. Dortmunder Fernsehseminar, pp. 87 - 92.
[5] Storn, R., "Echo Cancellation Techniques for Multimedia Applications - A Survey", Technical Report TR-96-046, ICSI, November 1996, ftp.icsi.berkeley.edu.
[6] Storn, R., "System Design by Constraint Adaptation and Differential Evolution", Technical Report TR-96-039, ICSI, November 1996, ftp.icsi.berkeley.edu.
[7] Price, K. and Storn, R., "Differential Evolution: Numerical Optimization Made Easy", Dr. Dobb's Journal, April 97, pp. 18 - 24.
[8] Storn, R., "On the Usage of Differential Evolution for Function Optimization"NAFIPS 1996, Berkeley, pp. 519 - 523.
[9] Storn, R. and Price, K., "Minimizing the real functions of the ICEC'96 contest by Differential Evolution"IEEE Conference on Evolutionary Computation, Nagoya, 1996, pp. 842 - 844.
[10] Storn, R., "Efficient Input Reordering for the DCT Based on a Real-Valued Decimation in Time FFT"(IEEE Signal Processing Letters, Vol. 3, No. 8, August 1996, pp. 242 - 244), Technical Report TR-95-061, ICSI, September 1995, ftp.icsi.berkeley.edu.
[11] Storn, R., "Differential Evolution Design of an IIR-Filter with Requirements for Magnitude and Group Delay"IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation ICEC 96, pp. 268 - 273, Technical Report TR-95-026, ICSI, May 1995, ftp.icsi.berkeley.edu.
[12] Storn, R., "Modeling and Optimization of PET-Redundancy Assignment for MPEG Sequences", Technical Report TR-95-018, ICSI, May 1995, ftp.icsi.berkeley.edu.
[13] Storn, R. and Price, K., "Differential Evolution - a Simple and Efficient Adaptive Scheme for Global Optimization over Continuous Spaces", Technical Report TR-95-012, ICSI, March 1995, ftp.icsi.berkeley.edu. Anyone who is interested in trying Differential Evolution (DE) might access the source code.
[14] Storn, R., "A Debug/Trace Tool for C SW Projects", Dr. Dobb's Journal, February 1997, pp. 22 - 26.
[15] Storn, R., "Constrained Optimization", Dr. Dobb's Journal, May 1995, pp. 119 - 123.
[16] Christ, J., Storn, R. and Lueder, E., " New Shortlength DFTs for the Prime Factor Implementation on DSP Architectures", Frequenz, 1995, Band 49, Issue 1-2, pp. 8 - 10.
[17] Ballay, H. and Storn, R., "A Tool for Checking C Coding Conventions", C User's Journal, july 94, pp. 41 - 50..
[18] Storn, R., "A Hashing Function Based on Algebraic Coding", submitted for publication in the I.E.E. Proceedings~E, Computers and Digital Techniques.
[19] Storn, R., "A Radix-2 FFT-Pipeline Architecture With Reduced Noise to Signal Ratio", I.E.E. Proceedings~F, Radar and Signal Processing, 1994.
[20] Storn, R. , "Datensicherung mit Prüfsummen", ST-Computer, 1994.
[21] Storn, R., "Some Results in Fixed Point Error Analysis of the Bruun-FFT Algorithm, IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, Vol. 41, No. 7, July 93, pp. 2371 - 2375.
[22] Storn, R. , "Statistische Optimierung", ST-Computer, Issues 12/1992 and 1/1993.
[23] Storn, R. , "On the Bruun Algorithm and its Inverse", Frequenz, Vol. 3-4, 1992, pp. 110 -116.
[24] Storn, R. , "Logische Schaltungen und deren Vereinfachung nach Quine-McCluskey", ST-Computer, Issues 3, 4 and 5, 1990.
[25] Storn, R. , "A novel Radix-2 Pipeline Architecture for the Computation of the DFT", IEEE Proc. of the ISCAS 1988, pp. 1899 -1902.
[26] Storn, R. , "On the Reduction of Arithmetic Complexity in the Chirp-Transform", Proc. ECCTD, 1987, pp. 239 -244.
[27] Storn, R. , "Ein Primfaktor-Algorithmus für die diskrete Hartley-Transformation", 9. DFG-Kolloquium über digitale Signalverarbeitung, 1986, pp. 79 -82.
[28] Storn, R. , "Fast Algorithms for the Discrete Hartley Transform", AEÜ, Band 40, Heft 4, 1986, pp. 233 -240.
[29] Storn, R. , "Dreieck-Quadratur-Oszillator. Nur ein zeitbestimmendes Glied erforderlich", Elektronik, Issue 5, 1982, p. 74.
[30] Storn, R. , "Constant Current Adapter", Elektor, Issue 7/8, 1981.
[31] Storn, R. , "De Luxe Transistor Tester", Elektor, Issue 7/8, 1979. (The corresponding circuit was among the winners of the european circuit design contest "EUROTRONIK").
BOOKS
[1] Price K., Storn R., Lampinen J., Differential Evolution - A Practical Approach to Global Optimization, Springer, Berlin, 2005.
[2] Contributor for Babu, B.V., Onwubolu, G. (Editors), New Optimization Techniques in Engineering, Springer, Berlin, 2004.
[3] Contributor for Corne, D., Dorigo., M, and Glover., F. (Editors), New Ideas in Optimization, McGraw-Hill, 1999.
差分进化算法 DE-Differential Evolution的更多相关文章
- 标准差分进化算法matlab程序实现(转载)
标准差分进化算法matlab程序实现 自适应差分演化算法方面的Matlab和C++代码及论文 差分进化算法 DE-Differential Evolution matlab练习程序(差异演化DE) [ ...
- SBX(Simulated binary crossover)模拟二进制交叉算子和DE(differential evolution)差分进化算子
一起来学演化计算-SBX(Simulated binary crossover)模拟二进制交叉算子和DE(differential evolution)差分进化算子 觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习 ...
- 差分进化算法介绍及matlab实现
引言 差分进化算法是基于群体智能理论的优化算法,是通过群体内个体间的合作与竞争而产生的智能优化搜索算法,它保留了基于种群的全局搜索策略,采用实数编码.基于差分的简单变异操作和"一对一&quo ...
- 差分进化算法-python实现
DEIndividual.py import numpy as np import ObjFunction class DEIndividual: ''' individual of differen ...
- 离散的差分进化Discrete DE
一般的差分算法的变异规则:Xmutation=Xr1+F(Xr2-Xr3),F为缩放因子, 离散差分进化DDE的变异规则:设每个解为K个元素的集合,则Xr2-Xr3:求出Xr2与Xr3有m个共同元素, ...
- 差分进化算法(DE)的C++面向对象方法实现
代码来源于网络,写得非常棒 /*DE_test *对相应的Matlab程序进行测试 */ #include <iostream> #include <cmath> #inclu ...
- Python遗传和进化算法框架(一)Geatpy快速入门
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33353186/article/details/82014986 Geatpy是一个高性能的Python遗传算法库以及开放式进化算法框架,由华南理工 ...
- Evolution of Image Classifiers,进化算法在神经网络结构搜索的首次尝试 | ICML 2017
论文提出使用进化算法来进行神经网络结构搜索,整体搜索逻辑十分简单,结合权重继承,搜索速度很快,从实验结果来看,搜索的网络准确率挺不错的.由于论文是个比较早期的想法,所以可以有很大的改进空间,后面的很大 ...
- CARS: 华为提出基于进化算法和权值共享的神经网络结构搜索,CIFAR-10上仅需单卡半天 | CVPR 2020
为了优化进化算法在神经网络结构搜索时候选网络训练过长的问题,参考ENAS和NSGA-III,论文提出连续进化结构搜索方法(continuous evolution architecture searc ...
随机推荐
- Mongodb 3.2 Manual阅读笔记:CH9 存储
9. 存储 9. 存储 9.1 存储引擎 9.1.1 WiredTiger存储引擎 9.1.1.1 文档级别并发 9.1.1.2 快照和检查点 9.1.1.3 Journaling 9.1.1.4 压 ...
- JS 字符串
var str = "aaddaabbcdddefg" console.log(str.charAt());//b 没有返回空不是null console.log(str.inde ...
- centos7的网络设置
必备知识:linux下对文件的编辑操作 首先给出的是vi的基础 后面会有详细的远程连接Centos的方法 vi的基本概念 基本上vi可分为三种操作状态,分别是命令模式(Command mode).插 ...
- (转)dubbo框架基本分析
原文地址: https://my.oschina.net/zhengweishan/blog/698591 Dubbo架构基本分析 1. dubbo简单介绍 1.1 dubbo是什么 dubbo是一个 ...
- 破解 Windows 下Markdown 编辑器 MarkdownPad 2
MarkdownPad 是 Windows 平台下一款优秀的 Markdown 编辑器,本文简单介绍 Markdown 以及使用一种方法破解 MarkdownPad 使其升级到专业版.该方法仅限于教育 ...
- index+match函数在压实度中对盒号盒质量随机不重复的最佳使用
首先按照升序排列好盒号和盒质量,使其一一对应, 盒号 盒重量 随机值rand() 随机值大小排列rank 1 2001 0.01 ...
- ajax的循环
一.业务需求 在开发中,当一个列表页面加载完成后,我需要根据列表每一项的id去服务器端获取对应的数据然后再把获取的数据赋给当前id对应的标签. 例如如下表格: 我有一系列的商品编号,我需要根据商品编号 ...
- PyVISA介绍
针对测量仪器进行编程比较痛苦,存在各种各样的协议以及通过不同接口和总线(GPIB.USB.RS232).使用任何一种语言去编程,你必须找到支持仪器和对应总线的合适的库. 为了解决这种问题,VISA应运 ...
- Codeforces Round #382(div 2)
A.= = B. 题意:给出n个数和n1和n2,从n个数中分别选出n1,n2个数来,得到n1个数和n2个数的平均值,求这两个平均值的最大和 分析:排个序从后面抽,注意先从末尾抽个数小的,再抽个数大的 ...
- mac mysql5.7重置root密码
先停止mysql服务 //停止表权限 cd /usr/local/mysql/bin/ ./mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables & 直接mysql 进入数据库 up ...
