2.2 Rust 数据类型
2.2 数据类型
let guess: u32 = "42".parse().expect("Not a number!");
Rust has four primary scalar types: integers, floating-point numbers, Booleans, and characters.
整数类型
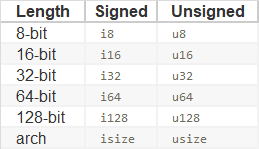
u32,this type declaration indicates that the value it’s associated with should be an unsigned integer (signed integer types start with i, instead of u) that takes up bits of space. Additionally, the isize and usize types depend on the kind of computer your program is running on: bits if you’re on a -bit architecture and bits if you’re on a -bit architecture.
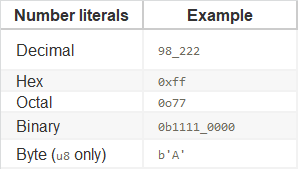
Note that all number literals except the byte literal allow a type suffix, such as 57u8, and _ as a visual separator, such as 1_000.
整数溢出
Let’s say that you have a u8, which can hold values between zero and . What happens if you try to change it to ? This is called “integer overflow,” and Rust has some interesting rules around this behavior. When compiling in debug mode, Rust checks for this kind of issue and will cause your program to panic, which is the term Rust uses when a program exits with an error. In release builds, Rust does not check for overflow, and instead will do something called “two’s complement wrapping.” In short, becomes , becomes , etc. Relying on overflow is considered an error, even if this behavior happens. If you want this behavior explicitly, the standard library has a type, Wrapping, that provides it explicitly.
浮点类型
Rust’s floating-point types are f32 and f64, which are 32 bits and 64 bits in size, respectively. The default type is f64 because on modern CPUs it’s roughly the same speed as f32 but is capable of more precision.
fn main() {
let x = 64.0 ; //f64
let y: f32 = 32.0; //f32
println!("64:{},32:{}",x,y);
}
The f32 type is a single-precision float, and f64 has double precision.
数字运算
fn main() {
// addition
let _sum = 5 + 10;
// subtraction
let _difference = 95.5 - 4.3;
// multiplication
let _product = 4 * 30;
// division
let _quotient = 56.7 / 32.2; //1.7608695652173911 小数点后16位
let _ff32 = 7f32 / 3f32; //2.3333333 7位小数
// remainder
let _remainder = 13 % 5; //3
println!{"32位除法:{}",_ff32}
println!{"默认64位除法:{}",_quotient};
println!{"求余:{}",_remainder};
}
整数与浮点数不可以混合运算,比如 let _cc = 10 * 3.0; 会报以下错误
^ no implementation for `{integer} * {float}`
error: Could not compile `datatype`.
布尔类型
fn main() {
let _t = true;
let _f: bool = false; // with explicit type annotation
}
字符类型
fn main() {
let _a = 'z';
let _b = 'ℤ';
let _c = 'Z';
}
Rust’s char type represents a Unicode Scalar Value, which means it can represent a lot more than just ASCII. Accented letters; Chinese, Japanese, and Korean characters; emoji; and zero-width spaces are all valid char values in Rust. Unicode Scalar Values range from U+ to U+D7FF and U+E000 to U+10FFFF inclusive. However, a “character” isn’t really a concept in Unicode, so your human intuition for what a “character” is may not match up with what a char is in Rust.
复合类型
Compound types can group multiple values into one type. Rust has two primitive compound types: tuples and arrays.
元组存放数据的数据类型可以不同,数组则必须是相同类型。
元组
A tuple is a general way of grouping together some number of other values with a variety of types into one compound type. Tuples have a fixed length: once declared, they cannot grow or shrink in size.
Each position in the tuple has a type, and the types of the different values in the tuple don’t have to be the same.
fn main() {
let _tup: (i32, f64, u8) = (500, 6.4, 1);
let _aa = (1,2.3,"wa ka ka ");
let (_x,_y,_z) = _aa;
println!("The value of z is:{}",_z)
}
This program first creates a tuple and binds it to the variable tup. It then uses a pattern with let to take tup and turn it into three separate variables, x, y, and z. This is called destructuring, because it breaks the single tuple into three parts. In addition to destructuring through pattern matching, we can access a tuple element directly by using a period (.) followed by the index of the value we want to access.
fn main() {
let _x: (i32, f64, u8) = (500, 6.4, 1);
let _five_hundred = _x.0;
let _six_point_four =_x.1;
let _one = _x.2;
println!("第三个元素:{}",_one);
}
数组类型
Unlike a tuple, every element of an array must have the same type. Arrays in Rust are different from arrays in some other languages because arrays in Rust have a fixed length, like tuples.
fn main() {
let _a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
}
Arrays are useful when you want your data allocated on the stack rather than the heap or when you want to ensure you always have a fixed number of elements. An array isn’t as flexible as the vector type, though. A vector is a similar collection type provided by the standard library that is allowed to grow or shrink in size. If you’re unsure whether to use an array or a vector, you should probably use a vector.
It’s very unlikely that such a program will need to add or remove months, so you can use an array because you know it will always contain 12 items
fn main() {
let _a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let _months = ["January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July",
"August", "September", "October", "November", "December"];
}
Arrays have an interesting type; it looks like this: [type; number]. For example:
fn main() {
let _b: [i32; 5] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
}
访问数组元素
fn main() {
let _b: [i32; 5] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let _c1 = _b[0];
let _c2 = _b[1];
}
数组越界
fn main() {
let a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let index = 10;
let element = a[index];
println!("The value of element is: {}", element);
}
编译阶段不会报错,在运行时会报错
[root@itoracle src]# cargo build
Compiling datatype v0.1.0 (/usr/local/automng/src/rust/test/datatype)
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 1.39s
[root@itoracle src]# cargo run
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.01s
Running `/usr/local/automng/src/rust/test/datatype/target/debug/datatype`
thread 'main' panicked at 'index out of bounds: the len is 5 but the index is 10', src/main.rs:5:19
note: Run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` for a backtrace.
类型转换
fn data02(){
println!("-------显式类型转换-------");
let a = ;
let b = a as f64;
let c = b * 2.0;
println!("c={}",c); //c=2
println!("-------------------------------------------------------");
}
2.2 Rust 数据类型的更多相关文章
- Rust 数据类型
Rust中的每个值都具有特定的数据类型. 基础类型: 整数,浮点数,布尔值和字符 i8,i16,i32,i64,i64,i128,isize, u8,u16,u32,u64,u64,u128,usiz ...
- rust数据类型
fn main() { //char支持4个字节,支持emoji let jp = "ゆ"; let emoji = "✨"; let ch = "囧 ...
- Rust学习笔记一 数据类型
写在前面 我也不是什么特别厉害的大牛,学历也很低,只是对一些新语言比较感兴趣,接触过的语言不算多也不算少,大部分也都浅尝辄止,所以理解上可能会有一些偏差. 自学了Java.Kotlin.Python. ...
- Rust <1>:数据类型、变量、可变性、常量、隐藏
rust 是强类型语言,所有变量.常量都必须有明确的数据类型:很多情况下,省略类型声明,编译器可自动推导,但不是所有情况下都会成功. rust 有整型.浮点型.布尔型.字符型.数组.元组.枚举.结构体 ...
- Rust之路(2)——数据类型 上篇
[未经书面同意,严禁转载] -- 2020-10-13 -- Rust是系统编程语言.什么意思呢?其主要领域是编写贴近操作系统的软件,文件操作.办公工具.网络系统,日常用的各种客户端.浏览器.记事本. ...
- Rust之路(3)——数据类型 下篇
[未经书面同意,严禁转载] -- 2020-10-14 -- 架构是道,数据是术.道可道,非常道:术不名,不成术!道无常形,术却可循规. 学习与分析数据类型,最基本的方法就是搞清楚其存储原理,变量和对 ...
- Rust基本数据类型
基本类型 Rust 每个值都有其确切的数据类型,总的来说可以分为两类:基本类型和复合类型. 基本类型意味着它们往往是一个最小化原子类型,无法解构为其它类型(一般意义上来说),由以下组成: 数值类型: ...
- Rust语言中的常量,变量,运算符,数据类型
简单练练, 夏天太热. const MAX_POINTS: u32 = 100_100; fn main() { let mut x = 5; let y = 5; let y = y + 1; le ...
- Rust语言的多线程编程
我写这篇短文的时候,正值Rust1.0发布不久,严格来说这是一门兼具C语言的执行效率和Java的开发效率的强大语言,它的所有权机制竟然让你无法写出线程不安全的代码,它是一门可以用来写操作系统的系统级语 ...
随机推荐
- mac 彻底卸载Paragon NTFS
之前安装了paragon NTFS,试用期过了就卸载了,但是每天还是会提示“试用期已到期”,看着很烦. 百度了一下,发现网上的版本可能比较老了,和我的情况不太一样,但道理应该是一样的. 彻底删除方法: ...
- UTF8转unicode说明
1.最新版iconv中的char *encTo = "UNICODE//IGNORE"; 是没有这个字符串的,它里面有UNICODELITTLE 和 UNICODEBIG 而且是没 ...
- 关于MySQL隐式转换
一.如果表定义的是varchar字段,传入的是数字,则会发生隐式转换. 1.表DDL 2.传int的sql 3.传字符串的sql 仔细看下表结构,rid的字段类型: 而用户传入的是int,这里会有一个 ...
- ZROI2018提高day5t1
传送门 分析 我们不难将条件转换为前缀和的形式,即 pre[i]>=pre[i-1]*2,pre[i]>0,pre[k]=n. 所以我们用dp[i][j]表示考虑到第i个数且pre[i]= ...
- web.xml中url-pattern匹配规则.RP
一.url-pattern的三种写法 精确匹配.以"/"开头,加上servlet名称. /ad 路径匹配.以"/"开头,加上通配符"*" ...
- mybatis spring maven
maven版本:3.3.9 解压即可使用 spring版本:4.3.9 通过maven进行管理下载 mybatis版本:3.4.4 通过maven进行管理下载 mysql版本:5.7 conne ...
- 国外物联网平台(2):微软Azure IoT
国外物联网平台(2)——微软Azure IoT 马智 平台定位 连接设备.其它 M2M 资产和人员,以便在业务和操作中更好地利用数据. 连接 IoT 设备 将所有设备连接到云,从这些设备接收大规模数据 ...
- 使用DDE传输数据至SQL Server
DDE即是Dynamic Data Exchange,相关可以搜索MSDN在线帮助. 想把SPC-Light的数据传送至SQL Server中.刚开始是尝试了<Transfer data to ...
- spring分布式事务学习笔记(2)
此文已由作者夏昀授权网易云社区发布. 欢迎访问网易云社区,了解更多网易技术产品运营经验. Model类如下:package com.xy.model 1 package com.xy.model; ...
- 不准使用xib自定义控制器view的大小
1.AppDelegate.m // // 文 件 名:AppDelegate.m // // 版权所有:Copyright © 2018年 leLight. All rights reserved. ...
