Python中的__name__和__main__含义详解
1背景
在写Python代码和看Python代码时,我们常常可以看到这样的代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
def main(): ......if __name == "__main__": main(); |
其中的函数名main,也可以是其他任意的,你所设置的名字。
这里,就出现了,我们此处所要解释的
__name__和__main__
__name__和__main的含义
其实,对于Python中的这类问题,根据我之前的:
【整理】如何学习Python + 如何有效利用Python有关的网络资源 + 如何利用Python自带手册(Python Manual)
中的介绍,最好的学习的方法,其实就是去看官网文档:
__name__的含义
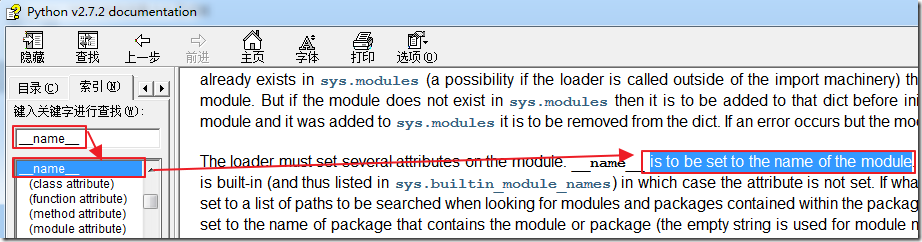
另外还有几处的解释:
Modules…
Predefined (writable) attributes: __name__ is the module’s name;
… Classes…
Special attributes: __name__ is the class name;
从这几处的解释,我们很容易理解其基本的意思:
__name__,
如果是放在Modules模块中,就表示是模块的名字;
如果是放在Classs类中,就表示类的名字;
__main__的含义
同理,先去官网文档中看对应的解释:
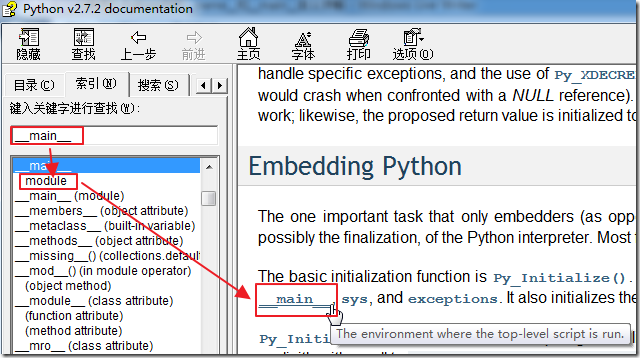
对应的其他几处的解释是:
4.1. Naming and binding
…
The namespace for a module is automatically created the first time a module is imported. The main module for a script is always called __main__.
8.1. Complete Python programs
While a language specification need not prescribe how the language interpreter is invoked, it is useful to have a notion of a complete Python program. A complete Python program is executed in a minimally initialized environment: all built-in and standard modules are available, but none have been initialized, except for sys (various system services), __builtin__ (built-in functions, exceptions and None) and __main__. The latter is used to provide the local and global namespace for execution of the complete program.
….
The interpreter may also be invoked in interactive mode; in this case, it does not read and execute a complete program but reads and executes one statement (possibly compound) at a time. The initial environment is identical to that of a complete program; each statement is executed in the namespace of __main__.
void Py_Initialize()
Initialize the Python interpreter. In an application embedding Python, this should be called before using any other Python/C API functions; with the exception of Py_SetProgramName(), PyEval_InitThreads(), PyEval_ReleaseLock(), and PyEval_AcquireLock(). This initializes the table of loaded modules (sys.modules), and creates the fundamental modules __builtin__, __main__ and sys.
说实话,对于__main__,上述的解释,并不是那么容易看的懂。
其实要看懂上面的解释,我们首先要知道的一些前提是:
python代码,是可以直接一行行写出来,然后去运行,是可以的。但是这只是针对我们的小程序来说的。
更多的Python代码,是写成更加通用的,可以被调用的,可以重复利用的,模块的形式;
所以都是写在对应的函数里面的。
而作为模块,就是上面的解释中的:
The namespace for a module is automatically created the first time a module is imported. The main module for a script is always called __main__.
模块第一次被导出(import)后,系统会自动为其创建一个域名空间(namespace);
(模块,都是有自己的名字的)此处的脚本的主模块的名字,始终都叫做__main__。
用代码来演示__name__和__main__的含义和用法
示例1
文字解释,还是很容易糊涂的,下面就来借用一个这里:
What is ‘if __name__ == “__main__”‘ for?
的代码来详细解释一下。
作为普通的代码,我们是可以这么写的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""【整理】Python中的__name__和__main__含义详解Version: 2012-11-17Author: CrifanContact: http://www.crifan.com/contact_me/"""def square(x): return x * xprint "test: square(42) ==",square(42); |
对应的,运行结果也是很正常的:
|
1
2
|
E:\Dev_Root\python\__name___and___main__>__name___and___main__.pytest: square(42) == 1764 |
但是呢,往往我们所见到的,和我们以后自己也会遇到的,自己写的,有条理的,可复用的做法,那肯定是
那对应的square等函数,专门放到一个文件中,然后被别人调用,此时,就是这样的:
对应的模块文件是mymath.py,里面有我们实现的函数square:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""【整理】Python中的__name__和__main__含义详解Version: 2012-11-17Author: CrifanContact: http://www.crifan.com/contact_me/"""def square(x): return x * xprint "test: square(42) ==",square(42); |
然后别的python文件__name___and___main__.py中,导入此mymath模块,然后使用其square函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""【整理】Python中的__name__和__main__含义详解Version: 2012-11-17Author: CrifanContact: http://www.crifan.com/contact_me/"""import mymath;print "In caller, test for mymath: square(12)=",mymath.square(12); |
然后运行结果是:
|
1
2
3
|
E:\Dev_Root\python\__name___and___main__>__name___and___main__.pytest: square(42) == 1764In caller, test for mymath: square(12)= 144 |
此处,我们看到了,也同时出现了,原本用于mymath.py中去测试square函数的打印结果:
test: square(42) == 1764
而这样的内容,很明显,是作为我模块的调用者,不希望看到的。也不关心的。
此时,我们所希望的是:
作为模块mymath.py本身,希望有自己的相关的调试的代码,用于调试自己模块函数,演示如何使用等等代码;
但是又不希望在被别的,本模块的调用者,所执行到,所看到;
此时,就可以用上述的__main__来实现了:
把mymath.py改为:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""【整理】Python中的__name__和__main__含义详解Version: 2012-11-17Author: CrifanContact: http://www.crifan.com/contact_me/"""def square(x): return x * xif __name__ == "__main__": print "test: square(42) ==",square(42); |
此时:
1. 作为mymath.py本身,自己运行时,可以运行到此处的代码,调试,验证自己的函数square执行的是否正确:
|
1
2
|
E:\Dev_Root\python\__name___and___main__>mymath.pytest: square(42) == 1764 |
2.同时,作为mymath.py的调用者__name___and___main__.py,在import mymath的时候,也不会看到对应的代码执行的结果了:
|
1
2
|
E:\Dev_Root\python\__name___and___main__>__name___and___main__.pyIn caller, test for mymath: square(12)= 144 |
其中的__main__,就是:
作为模块mymath.py本身:
- 作为脚本自己去运行的话,对应的模块名,就是上面所解释的,始终叫做__main__
- 关于这点,上述代码已经验证过了。因为mymath.py中的__name__,就是对应的,内置的变量,通过判断,的确是__main__,然后才会去执行到对应的模块的测试代码的。
- 如果被当做一个模块被别人调用的时候,对应的模块mymath.py的模块名,就是mymath;
- 关于这点,我们可以来验证一下,把__name___and___main__.py改为:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""【整理】Python中的__name__和__main__含义详解Version: 2012-11-17Author: CrifanContact: http://www.crifan.com/contact_me/"""import mymath;print "In caller, test for mymath: square(12)=",mymath.square(12);print "As module be imported, mymath module name=",mymath.__name__; |
- 再去运行,就可以看到输出的结果是mymath了:
|
1
2
3
|
E:\Dev_Root\python\__name___and___main__>__name___and___main__.pyIn caller, test for mymath: square(12)= 144As module be imported, mymath module name= mymath |
示例2
另外,这里:
A Byte of Python – A module’s __name__
也有个例子,相对更加简洁,需要的可以参考一下。
摘录其代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
#!/usr/bin/python# Filename: using_name.pyif __name__ == '__main__': print 'This program is being run by itself'else: print 'I am being imported from another module' |
【总结】
__name__:表示模块,类等的名字;
__main__:模块,xxx.py文件本身:
- 被直接执行时,对应的模块名就是__main__了
- 可以在
- if __name__ == “__main__”:
- 中添加你自己想要的,用于测试模块,演示模块用法等代码。
- 作为模块,被别的Python程序导入(import)时,模块名就是本身文件名xxx了。
【后记 2012-12-27】
后来又专门针对上述的
A Byte of Python – A module’s __name__
的代码去测试了一下实际效果。
其中,此处由于我中间包含了中文,所以必须添加对应的coding声明,否则,是会出现错误:
D:\tmp\tmp_dev_root\python\tutorial_summary\__name___and___main__>name_and_main.py
File “D:\tmp\tmp_dev_root\python\tutorial_summary\__name___and___main__\name_and_main.py”, line 6
SyntaxError: Non-ASCII character ‘\xe3’ in file
D:\tmp\tmp_dev_root\python\tutorial_summary\__name___and___main__\name_and_main.py
on line 7, but no encoding declared; see http://www.python.org/peps/p
ep-0263.html for details
添加了coding声明后,就正常了。
然后,最终的测试的代码是:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# Filename: name_and_main.py"""Function:【整理】Python中的__name__和__main__含义详解Author: Crifan LiVersion: 2012-12-27Contact: admin at crifan dot com"""if __name__ == '__main__': print 'This program is being run by itself' #This program is being run by itselfelse: print 'I am being imported from another module' |
和
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-#Filename: caller_demo.py"""Function:【整理】Python中的__name__和__main__含义详解Author: Crifan LiVersion: 2012-12-27Contact: admin at crifan dot com"""import name_and_main;print "Demo call name_and_main.py";# I am being imported from another module# demo call name_and_main.py |
最终,测试出来的效果是:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
D:\tmp\tmp_dev_root\python\tutorial_summary\__name___and___main__>caller_demo.pyI am being imported from another moduleDemo call name_and_main.pyD:\tmp\tmp_dev_root\python\tutorial_summary\__name___and___main__>name_and_main.pyThis program is being run by itself |
总的来说,的确是我们所要的效果的,即:
python文件本身自己运行时,显示的是:This program is being run by itself
Python文件被别人import导入时,显示的是:I am being imported from another module
Python中的__name__和__main__含义详解的更多相关文章
- 基于python中staticmethod和classmethod的区别(详解)
例子 ? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class A(object): def foo(self,x): print "executing foo ...
- Python中操作mysql的pymysql模块详解
Python中操作mysql的pymysql模块详解 前言 pymsql是Python中操作MySQL的模块,其使用方法和MySQLdb几乎相同.但目前pymysql支持python3.x而后者不支持 ...
- Python中__init__.py文件的作用详解
转自http://www.jb51.net/article/92863.htm Python中__init__.py文件的作用详解 http://www.jb51.net/article/86580. ...
- python中验证码连通域分割的方法详解
python中验证码连通域分割的方法详解 这篇文章主要给大家介绍了关于python中验证码连通域分割的相关资料,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家学习或者使用python具有一定的参考学习价值,需 ...
- Python中__init__和__new__的区别详解
__init__ 方法是什么? 使用Python写过面向对象的代码的同学,可能对 __init__ 方法已经非常熟悉了,__init__ 方法通常用在初始化一个类实例的时候.例如: # -*- cod ...
- Python中的zip()与*zip()函数详解
前言 实验环境: Python 3.6: 示例代码地址:下载示例: 本文中元素是指列表.元组.字典等集合类数据类型中的下一级项目(可能是单个元素或嵌套列表). zip(*iterables)函数详解 ...
- Python中防止sql注入的方法详解
SQL注入是比较常见的网络攻击方式之一,它不是利用操作系统的BUG来实现攻击,而是针对程序员编程时的疏忽,通过SQL语句,实现无帐号登录,甚至篡改数据库.下面这篇文章主要给大家介绍了关于Python中 ...
- (转)Python中操作mysql的pymysql模块详解
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wt11/p/6141225.html https://shockerli.net/post/python3-pymysql/----Python ...
- python中赋值、浅拷贝、深拷贝详解(转)
一.赋值 >>> a = [1, 2, 3]>>> b = a>>> print(id(a), id(b), sep='\n')139701469 ...
随机推荐
- docker 安装的centos7.4中无法识别文件中的中文
在容器内执行命令: 命令: yum -y install kde-l10n-Chinese && yum -y reinstall glibc-common 命令: localedef ...
- my.副本
梦幻西游手游 天蓬下凡 副本 第三关:天蓬终于决定要告白了,主怪大唐,护卫狮驼岭,帮凶是龙宫,打过这关也很简单. 第四关:康太尉找来了天兵,怪仍然是有法有攻,但是打起来也是不难. ZC: 姚太尉是物理 ...
- 转 Relinking Causes Many Warning on AIX
SYMPTOMS Relink returns many warnings Running make for target ioracle OPatch found the word "er ...
- js中的内置对象
在js里,一切皆为或者皆可以被用作对象.可通过new一个对象或者直接以字面量形式创建变量(如var i="aaa"),所有变量都有对象的性质.注意:通过字面量创建的对象在调用属性和 ...
- JqGrid查询数据为空时给表格添加提示信息
在JqGrid的loadComplete事件中添加下面的代码就可以实现上图的效果 loadComplete: function () { var rowNum = $("#purchaser ...
- CAD安装失败怎样卸载CAD 2013?错误提示某些产品无法安装
AUTODESK系列软件着实令人头疼,安装失败之后不能完全卸载!!!(比如maya,cad,3dsmax等).有时手动删除注册表重装之后还是会出现各种问题,每个版本的C++Runtime和.NET f ...
- attr()与setAttribute()的区别
先看红色标注的: 这里传过来的this是个元素节点,因此currentTr也得用获取节点的方式parentNode去获取,而不能写parent(),这是第一个需要注意的地方. 第二个问题,就是怎么给c ...
- Devexpress GridControl使用
//不显示内置的导航条. gc1.UseEmbeddedNavigator = false; //不显示分组的面板 gv1.Opti ...
- VMWare 9 安装 win8
http://tieba.baidu.com/p/1954912175 http://down.51cto.com/data/497803 win8专业版:NBCCB-JJJDX-PKBKJ-KQX8 ...
- Java的类成员变量、实例变量、类变量,成员方法、实例方法、类方法
总是被这些相似的概念搞晕,查阅了资料后做个小总结,以变量为例,方法辨析类似. 1.多胞胎名字汇总辨析 成员变量和成员方法是范围最大的定义,提到成员变量就可以理解成你所定义在一个类体中的各类变量的统称, ...
