codeforces 631C C. Report
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Each month Blake gets the report containing main economic indicators of the company "Blake Technologies". There are n commodities produced by the company. For each of them there is exactly one integer in the final report, that denotes corresponding revenue. Before the report gets to Blake, it passes through the hands of m managers. Each of them may reorder the elements in some order. Namely, the i-th manager either sorts first ri numbers in non-descending or non-ascending order and then passes the report to the manageri + 1, or directly to Blake (if this manager has number i = m).
Employees of the "Blake Technologies" are preparing the report right now. You know the initial sequence ai of length n and the description of each manager, that is value ri and his favourite order. You are asked to speed up the process and determine how the final report will look like.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 200 000) — the number of commodities in the report and the number of managers, respectively.
The second line contains n integers ai (|ai| ≤ 109) — the initial report before it gets to the first manager.
Then follow m lines with the descriptions of the operations managers are going to perform. The i-th of these lines contains two integersti and ri (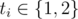 , 1 ≤ ri ≤ n), meaning that the i-th manager sorts the first ri numbers either in the non-descending (if ti = 1) or non-ascending (if ti = 2) order.
, 1 ≤ ri ≤ n), meaning that the i-th manager sorts the first ri numbers either in the non-descending (if ti = 1) or non-ascending (if ti = 2) order.
Print n integers — the final report, which will be passed to Blake by manager number m.
3 1
1 2 3
2 2
2 1 3
4 2
1 2 4 3
2 3
1 2
2 4 1 3
In the first sample, the initial report looked like: 1 2 3. After the first manager the first two numbers were transposed: 2 1 3. The report got to Blake in this form.
In the second sample the original report was like this: 1 2 4 3. After the first manager the report changed to: 4 2 1 3. After the second manager the report changed to: 2 4 1 3. This report was handed over to Blake.
题意:m次变换,把前ri个数要么升序要么降序排列,输出最后得顺序;
思路:单调栈找到有效的操作顺序,再在两个操作范围没重合的的那些数填上剩下的最大的那些数或最小的那些数,talk is cheap,show you the code,见代码;
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+4;
int a[N],b[N],c[N],temp[N],ans[N];
int n,m;
stack<int>Q;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)scanf("%d%d",&b[i],&c[i]);
Q.push(1);
for(int i=2;i<=m;i++)
{
if(c[i]<c[Q.top()])Q.push(i);
else if(c[i]==c[Q.top()]){Q.pop();Q.push(i);}
else
{
while(!Q.empty())
{
if(c[Q.top()]>c[i])break;
Q.pop();
}
Q.push(i);
}
}
int len=Q.size();
temp[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++)
{
temp[i]=Q.top();
Q.pop();
}
sort(a+1,a+c[temp[len]]+1);
int high=c[temp[len]],low=1,num=c[temp[len]];
for(int i=len;i>0;i--)
{
if(b[temp[i]]==1)
{
while(num>c[temp[i-1]])ans[num]=a[high],high--,num--;
}
else
{
while(num>c[temp[i-1]])ans[num]=a[low],low++,num--;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=c[temp[len]];i++)
{
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
}
for(int i=c[temp[len]]+1;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
} return 0;
}
codeforces 631C C. Report的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 631C. Report 模拟
C. Report time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard input out ...
- codeforces 631C. Report
题目链接 按题目给出的r, 维护一个递减的数列,然后在末尾补一个0. 比如样例给出的 4 21 2 4 32 31 2 递减的数列就是3 2 0, 操作的时候, 先变[3, 2), 然后变[2, 0) ...
- Report CodeForces - 631C (栈)
题目链接 题目大意:给定序列, 给定若干操作, 每次操作将$[1,r]$元素升序或降序排列, 求操作完序列 首先可以发现对最后结果有影响的序列$r$一定非增, 并且是升序降序交替的 可以用单调栈维护这 ...
- Codeforces 631C Report【其他】
题意: 给定序列,将前a个数进行逆序或正序排列,多次操作后,求最终得到的序列. 分析: 仔细分析可以想到j<i,且rj小于ri的操作是没有意义的,对于每个i把类似j的操作删去(这里可以用mult ...
- CodeForces - 631C (截取法)
C. Report time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input out ...
- CodeForces - 631C ——(思维题)
Each month Blake gets the report containing main economic indicators of the company "Blake Tech ...
- Codeforces 631C
题意:给定n和m. 给定一个长度为n的序列,m次操作. 接下来m次操作,每行第一个数若为1,则增序排列,若为2则降序排列,第二个数是排列的范围,即从第一个数排序到第某个数. 思路: 首先,对于其中范围 ...
- CodeForces 631C Print Check
排序+构造+预处理 #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<algorithm ...
- Codeforces Round #344 (Div. 2) C. Report 其他
C. Report 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/631/problem/C Description Each month Blake gets th ...
随机推荐
- Android Studio 2.0 稳定版新特性介绍
Android Studio 2.0 最终迎来了稳定版本号,喜大普奔. 以下这篇文章是2.0新特性的一些简介. 假设想看具体内容请看这里<Android Studio有用指南> 文章转自这 ...
- html5小趣味知识点系列(一)contentEditable
在这里纠正一下某些书籍说 这个修改后的文字内容是无法保存的 的错误必须发送到服务器进行保存才可以(因为我可以保存到内容)看代码吧 也许我理解的不对 <!DOCTYPE html> < ...
- onCreate中获得控件的大小
@Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setC ...
- Nodejs通过thrift访问Java服务
上一篇文章中实现了用Java作为thrift客户端和服务端.接下来我们用nodejs作为客户端访问一下.Nodejs的安装可以查看http://www.cnblogs.com/xucheng/p/39 ...
- 简单记事本&Java
目标: 学习java的IO流和文件的打开保存 内容: 使用javaSwing包里面的一些东西,比如按钮.菜单来进行布局 代码: package myNotePad; import java.awt.F ...
- 逻辑英语 第四季 Speaking and Listening
1. 发音的变革 背字典:牛津双解/朗文英汉 a. 如何一分钟变伦敦腔 发音有两种:伦敦腔/其他 生理分析: ① 后置发音:瞬间华丽变声第一步 东方人靠嘴巴发音: 西方人用胸腔发音[有共鸣] 方法1: ...
- python多进程-----multiprocessing包
multiprocessing并非是python的一个模块,而是python中多进程管理的一个包,在学习的时候可以与threading这个模块作类比,正如我们在上一篇转载的文章中所提,python的多 ...
- 【BZOJ2006】[NOI2010]超级钢琴 ST表+堆
[BZOJ2006][NOI2010]超级钢琴 Description 小Z是一个小有名气的钢琴家,最近C博士送给了小Z一架超级钢琴,小Z希望能够用这架钢琴创作出世界上最美妙的音乐. 这架超级钢琴可以 ...
- Computer Transformation(简单数学题+大数)
H - Computer Transformation Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d &am ...
- SVM vs. Softmax
http://cs231n.github.io/linear-classify/
