Classification and Representation
Classification
To attempt classification, one method is to use linear regression and map all predictions greater than 0.5 as a 1 and all less than 0.5 as a 0. However, this method doesn't work well because classification is not actually a linear function.
The classification problem is just like the regression problem, except that the values we now want to predict take on only a small number of discrete values. For now, we will focus on the binary classification problem in which y can take on only two values, 0 and 1. (Most of what we say here will also generalize to the multiple-class case.) For instance, if we are trying to build a spam classifier for email, then 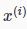 may be some features of a piece of email, and y may be 1 if it is a piece of spam mail, and 0 otherwise. Hence, y∈{0,1}. 0 is also called the negative class, and 1 the positive class, and they are sometimes also denoted by the symbols “-” and “+.” Given x(i), the corresponding
may be some features of a piece of email, and y may be 1 if it is a piece of spam mail, and 0 otherwise. Hence, y∈{0,1}. 0 is also called the negative class, and 1 the positive class, and they are sometimes also denoted by the symbols “-” and “+.” Given x(i), the corresponding  is also called the label for the training example.
is also called the label for the training example.
Hypothesis Representation
We could approach the classification problem ignoring the fact that y is discrete-valued, and use our old linear regression algorithm to try to predict y given x. However, it is easy to construct examples where this method performs very poorly. Intuitively, it also doesn’t make sense for hθ(x) to take values larger than 1 or smaller than 0 when we know that y ∈ {0, 1}. To fix this, let’s change the form for our hypotheses hθ(x) to satisfy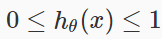 . This is accomplished by plugging
. This is accomplished by plugging  into the Logistic Function.
into the Logistic Function.
Our new form uses the "Sigmoid Function," also called the "Logistic Function":

The following image shows us what the sigmoid function looks like:

The function g(z), shown here, maps any real number to the (0, 1) interval, making it useful for transforming an arbitrary-valued function into a function better suited for classification.
hθ(x) will give us the probability that our output is 1. For example, hθ(x)=0.7 gives us a probability of 70% that our output is 1. Our probability that our prediction is 0 is just the complement of our probability that it is 1 (e.g. if probability that it is 1 is 70%, then the probability that it is 0 is 30%).
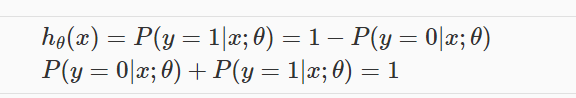
Decision Boundary
In order to get our discrete 0 or 1 classification, we can translate the output of the hypothesis function as follows:

The way our logistic function g behaves is that when its input is greater than or equal to zero, its output is greater than or equal to 0.5:

Remember.

So if our input to g is  , then that means:
, then that means:

From these statements we can now say:

The decision boundary is the line that separates the area where y = 0 and where y = 1. It is created by our hypothesis function.
Example:


Multiclass Classification: One-vs-all
Now we will approach the classification of data when we have more than two categories. Instead of y = {0,1} we will expand our definition so that y = {0,1...n}.
Since y = {0,1...n}, we divide our problem into n+1 (+1 because the index starts at 0) binary classification problems; in each one, we predict the probability that 'y' is a member of one of our classes.

The following image shows how one could classify 3 classes:We are basically choosing one class and then lumping all the others into a single second class. We do this repeatedly, applying binary logistic regression to each case, and then use the hypothesis that returned the highest value as our prediction.

To summarize:

Classification and Representation的更多相关文章
- 浅谈Logistic回归及过拟合
判断学习速率是否合适?每步都下降即可.这篇先不整理吧... 这节学习的是逻辑回归(Logistic Regression),也算进入了比较正统的机器学习算法.啥叫正统呢?我概念里面机器学习算法一般是这 ...
- Stanford机器学习---第三讲. 逻辑回归和过拟合问题的解决 logistic Regression & Regularization
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7716281 本栏目(Machine learning)包括单参数的线性回归.多参数的线性回归 ...
- Machine Learning - 第3周(Logistic Regression、Regularization)
Logistic regression is a method for classifying data into discrete outcomes. For example, we might u ...
- 《Machine Learning》系列学习笔记之第三周
第三周 第一部分 Classification and Representation Classification 为了尝试分类,一种方法是使用线性回归,并将大于0.5的所有预测映射为1,所有小于0. ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记--week3(逻辑回归&正则化参数)
Logistic Regression 一.内容概要 Classification and Representation Classification Hypothesis Representatio ...
- ICLR 2014 International Conference on Learning Representations深度学习论文papers
ICLR 2014 International Conference on Learning Representations Apr 14 - 16, 2014, Banff, Canada Work ...
- Course Machine Learning Note
Machine Learning Note Introduction Introduction What is Machine Learning? Two definitions of Machine ...
- Survey of single-target visual tracking methods based on online learning 翻译
基于在线学习的单目标跟踪算法调研 摘要 视觉跟踪在计算机视觉和机器人学领域是一个流行和有挑战的话题.由于多种场景下出现的目标外貌和复杂环境变量的改变,先进的跟踪框架就有必要采用在线学习的原理.本论文简 ...
- 《Learning Structured Representation for Text Classification via Reinforcement Learning》论文翻译.md
摘要 表征学习是自然语言处理中的一个基本问题.本文研究了如何学习文本分类的结构化表示.与大多数既不使用结构又依赖于预先指定结构的现有表示模型不同,我们提出了一种强化学习(RL)方法,通过自动覆盖优化结 ...
随机推荐
- CMDB学习之三数据采集
判断系统因为是公用的方法,所有要写基类方法使用,首先在插件中创建一个基类 将插件文件继承基类 思路是创建基类使用handler.cmd ,命令去获取系统信息,然后进行判断,然后去执行 磁盘 ,cpu, ...
- 小米开源文件管理器MiCodeFileExplorer-源码研究(6)-媒体文件MediaFile和文件类型MimeUtils
接着之前的第4篇,本篇的2个类,仍然是工具类.MediaFile,媒体文件,定义了一大堆的常量,真正的有用的方法就几个.isAudioFileType.isVideoFileType之类的. Mime ...
- 【hdu 4289】Control
[Link]:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4289 [Description] 给出一个又n个点,m条边组成的无向图.给出两个点s,t.对于图中 ...
- crmjs区分窗口是否是高速编辑
有时候,我们须要区分打开的窗口是否是高速编辑页面,在上面做一些逻辑处理: 窗口上面附加的js代码: function loadFrom() { var formType = Xrm.Page. ...
- Codeforces #258 Div.2 E Devu and Flowers
大致题意: 从n个盒子里面取出s多花.每一个盒子里面的花都同样,而且每一个盒子里面花的多数为f[i],求取法总数. 解题思路: 我们知道假设n个盒子里面花的数量无限,那么取法总数为:C(s+n-1, ...
- worktools-不同分辨率下图片移植
1.下载需要移植的平台代码 1)查看手机需要的项目平台信息:adb shell getprop | gerp flavor ----->mt6732_m561_p2_kangjia_cc ...
- 【arc062e】Building Cubes with AtCoDeer
Description STL有n块瓷砖,编号从1到n,并且将这个编号写在瓷砖的正中央: 瓷砖的四个角上分别有四种颜色(可能相等可能不相等),并且用Ci,0,Ci,1,Ci,2,Ci,3分别表示左上. ...
- call、apply、bind 区别
1.为什么要用 call .apply? 为了 改变方法里面的属性而不去改变原来的方法 function fruits() {} fruits.prototype = { color: "r ...
- slice深拷贝数组
var a = [1, 2, 3, 4] var b = a.slice(0) b[0] = 2 // a = [1, 2, 3, 4] // b = [2, 2, 3, 4]
- cf1051F. The Shortest Statement(最短路/dfs树)
You are given a weighed undirected connected graph, consisting of nn vertices and mm edges. You shou ...
