Spring Cache缓存技术的介绍
缓存用于提升系统的性能,特别适用于一些对资源需求比较高的操作。本文介绍如何基于spring boot cache技术,使用caffeine作为具体的缓存实现,对操作的结果进行缓存。
demo场景
本demo将创建一个web应用,提供两个Rest接口。一个接口用于接受查询请求,并有条件的缓存查询结果。另一个接口用于获取所有缓存的数据,用于监控缓存的内部状态。
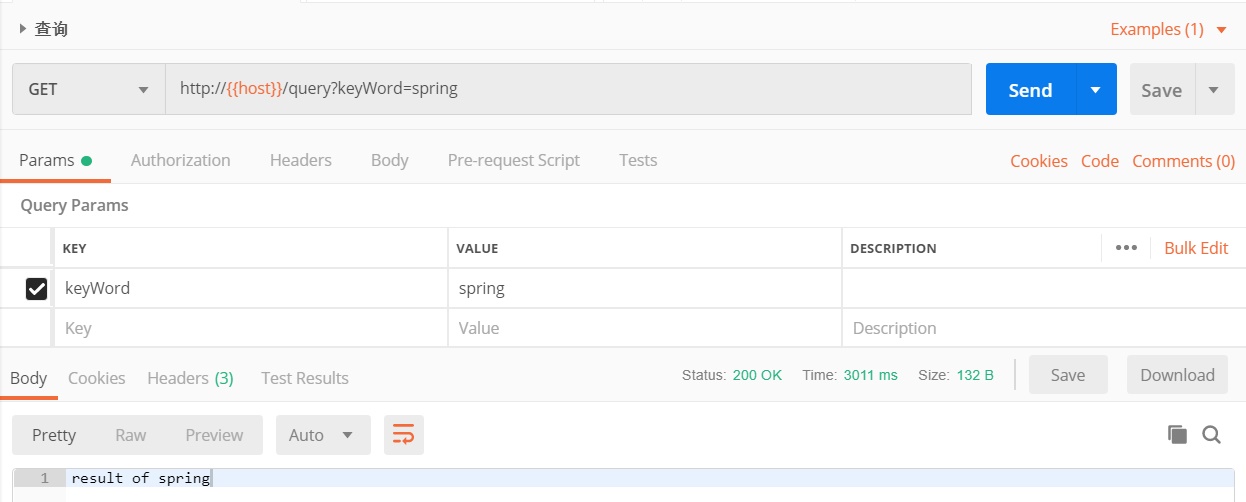
可以看到这次查询耗时3秒左右。
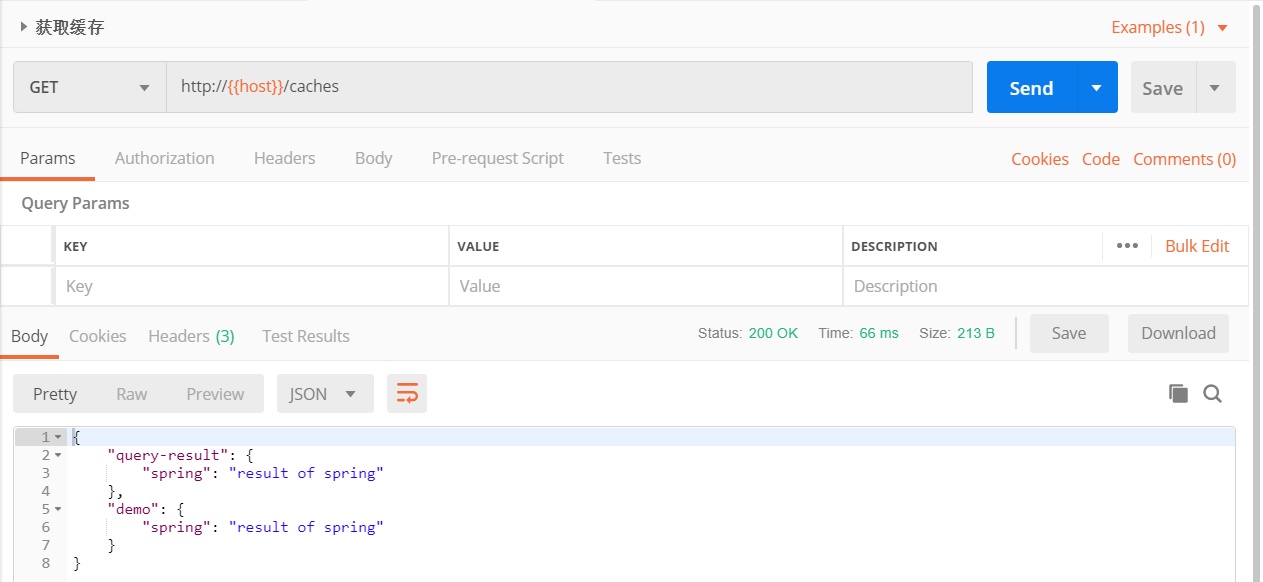
可以看到我们的查询结果已被缓存。这里将一次查询的结果缓存了两份,具体技术细节后面介绍。
接下来介绍具体demo的实现过程。
demo实现
本demo已经上传到github,读者可以在github上获取源码。
本demo使用Maven作为项目构建工具。按照作者的日常编程习惯,首先创建了一个root module,用于统一管理依赖。具体的功能在子module caffeine-cache中。
本demo的代码结构如下:
demo-spring-cache/
|- pom.xml
L caffeine-cache/
|- pom.xml
L src/
L main/
|- java/
| L heyikan
| |- Application.yml
| |- QueryController.java
| L QueryService.java
L resources/
L application.yml
创建root module
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.heyikan.demo</groupId>
<artifactId>demo-spring-cache</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<modules>
<module>caffeine-cache</module>
</modules>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<maven.compiler.source>${java.version}</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>${java.version}</maven.compiler.target>
<spring-boot.version>2.1.3.RELEASE</spring-boot.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>
root module的主要作用是统一管理依赖。当项目中有多个module的时候,作者一般会构建一个root module,然后其他的moudule都继承自这个module,形成一个两级module的继承结构。
网上大部分的demo,一般是直接创建目标module,且继承自
spring-boot-starter-parent。spring-boot-starter-parent管理了大部分常用的依赖,使用这些依赖我们不用再费心考虑版本的问题。但是maven是单继承结构,继承了
spring-boot-starter-parent就无法继承自己项目当中的parent module(root module)。在一个多module的项目当中,module之间的相互依赖就不是spring-boot-starter-parent能预先管理的了。所以在实际项目当中,我们一般不会直接继承
spring-boot-starter-parent。而是通过在root module中importspring-boot-dependencies,来享受spring-boot为我们管理依赖的便利,同时在root module管理额外的依赖。具体的技术细节需要读者参考Maven的知识。作者只是阐述下这么做的原因,实际上跟demo本身的功能没有多大关系。
创建目标module
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>demo-spring-cache</artifactId>
<groupId>com.heyikan.demo</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>caffeine-cache</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
这个module主要引入了三个依赖:
- spring-boot-starter-web
打包了web项目的常规依赖 - spring-boot-starter-cache
打包了依赖功能的常规依赖 - caffeine
具体的依赖实现
spring cache提供了一层抽象和使用接口,底层可以切换不同的cache实现,caffeine就是其中之一,且性能表现较优。
spring cache还可以与redis集成,提供分布式缓存的能力。
创建Application
package heyikan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
熟悉spring-boot项目的读者应该对此比较熟悉,spring-boot项目需要创建一个Application来启动整个应用。
@EnableCaching注解用于启用缓存,没有这个注解,我们后面的缓存功能将不会生效。
创建Controller
package heyikan;
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@RestController
public class QueryController {
@Autowired
private QueryService queryService;
@GetMapping("/query")
public ResponseEntity<?> query(String keyWord) {
String result = queryService.query(keyWord);
return ResponseEntity.ok(result);
}
@Autowired
@SuppressWarnings("all")
private CacheManager cacheManager;
@GetMapping("/caches")
public ResponseEntity<?> getCache() {
Map<String, ConcurrentMap> cacheMap = cacheManager.getCacheNames().stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Function.identity(), name -> {
Cache cache = (Cache) cacheManager.getCache(name).getNativeCache();
return cache.asMap();
}));
return ResponseEntity.ok(cacheMap);
}
}
QueryController提供了两个Rest接口,query用于模拟耗时的查询请求,getCache用于获取当前的缓存内容。
QueryController中引入了QueryService依赖,它是提供查询和缓存功能的核心组件。
QueryController中引入了CacheManager依赖,它持有所有的缓存,并提供了遍历的API。
创建缓存组件
package heyikan;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = {"query-result", "demo"})
public class QueryService {
private static Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(QueryService.class);
@Cacheable(unless = "#result.length() > 20")
public String query(String keyWord) {
LOG.info("do query by keyWord: {}", keyWord);
String queryResult = doQuery(keyWord);
return queryResult;
}
private String doQuery(String keyWord) {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
String result = "result of " + keyWord;
return result;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
}
我们使用@CacheConfig配置缓存,如代码所示,数据将会同时缓存到"query-result"和"demo"中。
query方法是查询的入口,@Cacheable注解用于表示query方法的返回结果将被放到缓存中,默认以方法的参数作为key。
@Cacheable注解的unless属性补充了缓存的条件,按照代码所示,当query的返回结果其长度大于20的时候,就不会进行缓存。
doQuery方法代表实际的查询操作,模拟耗时的查询过程。
创建配置
application.yml文件内容如下:
spring:
cache:
caffeine:
spec: maximumSize=500, expireAfterAccess=30s
logging:
pattern:
console: "%-5level - %msg%n"
level:
- error
- heyikan=ALL
spring.cache.caffeine.spec配置了两个缓存指标:
- maximumSize
配置缓存的最大容量,当快要达到容量上限的时候,缓存管理器会根据一定的策略将部分缓存项移除。 - expireAfterAccess
配置缓存项的过期机制,如代码所示当缓存项被访问后30秒将会过期,从而被移除。
技术要点
缓存的结构
在上文获取缓存的接口中,我们得到的结果是:
{
"query-result": {
"spring": "result of spring"
},
"demo": {
"spring": "result of spring"
}
}
缓存的结构大概像Map<cacheName, Map<key, value>>,其中每一对key-value又称为一个缓存项。
上文中,我们缓存组件的query方法的返回结果,就是以参数为key,以结果为value,构建缓存项进行缓存的。
另外,我们配置的超时时间,也是以缓存项为粒度进行控制的。
包含缓存项的Map我们称为缓存实例,每一个实例有一个实例名(cacheName)。
cache结构相关的类图如下:
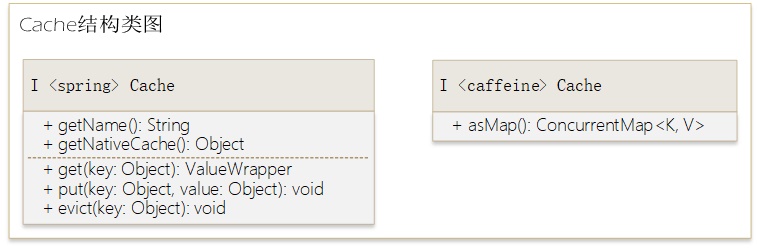
上图简单绘制了Spring中定义的Cache接口和caffeine中定义的Cache接口。
Spring的Cache定义了极其通用的方法,包括获取实例名、根据缓存项的key获取、更新和移除缓存项。
Spring并没有限定缓存所使用的具体存储结构,不管使用哪一种存储结构,在Spring的Cache中都以nativeCache进行表示,注意它是Object类型的。
caffeine的Cache接口,就是caffeine对nativeCache的又一层抽象,它提供了asMap方法可以对缓存项进行遍历。
使用缓存
在上文中,我们已经简单演示了如何使用缓存。除了获取缓存之外,我们几乎没有任何额外的代码,只是在合适的地方,添加了注解,就添加了缓存的功能。
所以在日常开发中,如果我们意识到某个操作可能会有很大开销,不妨把它移到一个独立的组件,实现之后根据具体情况考虑是否为它添加缓存。
注意:如果缓存的方法是组件内部调用的,可能没有缓存的效果。
比如,上文中的QueryService的query方法,是由QueryController调用的,缓存生效了。如果该方法由QueryService自身的其他方法调用,缓存无效。
在上文的demo中,我们已经使用了一些基本的功能,还有一些常用的功能如下:
指定key构建规则
在上文中,我们使用默认的规则来构建缓存项的key,即以参数keyWord作为key。
在必要的情况下,我们可以指定key构建的规则,使用spring el表达式:
@Cacheable(cacheNames="books", key="#isbn")
public Book findBook(ISBN isbn, boolean checkWarehouse, boolean includeUsed)
@Cacheable(cacheNames="books", key="#isbn.rawNumber")
public Book findBook(ISBN isbn, boolean checkWarehouse, boolean includeUsed)
@Cacheable(cacheNames="books", key="T(someType).hash(#isbn)")
public Book findBook(ISBN isbn, boolean checkWarehouse, boolean includeUsed)
第一个实例,我们使用三个参数中的其中一个来构建key。
第二个实例,我们使用参数内部的field来构建key。
第三个实例,我们使用静态方法来生成key。
更多内容可以参考Custom Key Generation Declaration。
有选择的cache
上文demo中我们使用unless属性对方法返回的结果进行判断,当返回结果满足一定条件时才进行缓存。
另外,我们还可以使用condition属性对方法的参数进行判断:
@Cacheable(cacheNames="book", condition="#name.length() < 32")
public Book findBook(String name)
上述代码表示,只有当参数的长度小于32时,我们才会缓存。
更多内容可以参考Conditional Caching。
扩展阅读
- Spring官方demo
这里提供了使用默认缓存的demo,内容更加简单,适合对spring-boot不熟悉的读者。 - Spring官方文档
这里有对如何使用cache的详细介绍,比如如何主动更新缓存、移除缓存,都是本demo中没有的内容。 - Spring Boot Caffeine Caching Example Configuration
这里介绍了如何使用Caffeine缓存,本文的内容相当一部分参考了这篇文章。
Spring Cache缓存技术的介绍的更多相关文章
- Spring Cache缓存技术,Cacheable、CachePut、CacheEvict、Caching、CacheConfig注解的使用
前置知识: 在Spring Cache缓存中有两大组件CacheManager和Cache.在整个缓存中可以有多个CacheManager,他们负责管理他们里边的Cache.一个CacheManage ...
- 注释驱动的 Spring cache 缓存介绍
概述 Spring 3.1 引入了激动人心的基于注释(annotation)的缓存(cache)技术,它本质上不是一个具体的缓存实现方案(例如 EHCache 或者 OSCache),而是一个对缓存使 ...
- [转]注释驱动的 Spring cache 缓存介绍
原文:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-spring-cache/ 概述 Spring 3.1 引入了激动人心的基于注释(an ...
- 注释驱动的 Spring cache 缓存介绍--转载
概述 Spring 3.1 引入了激动人心的基于注释(annotation)的缓存(cache)技术,它本质上不是一个具体的缓存实现方案(例如 EHCache 或者 OSCache),而是一个对缓存使 ...
- Spring cache 缓存
概述 Spring 3.1 引入了激动人心的基于注释(annotation)的缓存(cache)技术,它本质上不是一个具体的缓存实现方案(例如 EHCache 或者 OSCache),而是一个对缓存使 ...
- Ajax跨域问题及解决方案 asp.net core 系列之允许跨越访问(Enable Cross-Origin Requests:CORS) c#中的Cache缓存技术 C#中的Cookie C#串口扫描枪的简单实现 c#Socket服务器与客户端的开发(2)
Ajax跨域问题及解决方案 目录 复现Ajax跨域问题 Ajax跨域介绍 Ajax跨域解决方案 一. 在服务端添加响应头Access-Control-Allow-Origin 二. 使用JSONP ...
- Spring Cache缓存注解
目录 Spring Cache缓存注解 @Cacheable 键生成器 @CachePut @CacheEvict @Caching @CacheConfig Spring Cache缓存注解 本篇文 ...
- Spring Cache缓存框架
一.序言 Spring Cache是Spring体系下标准化缓存框架.Spring Cache有如下优势: 缓存品种多 支持缓存品种多,常见缓存Redis.EhCache.Caffeine均支持.它们 ...
- 【快学SpringBoot】快速上手好用方便的Spring Cache缓存框架
前言 缓存,在开发中是非常常用的.在高并发系统中,如果没有缓存,纯靠数据库来扛,那么数据库压力会非常大,搞不好还会出现宕机的情况.本篇文章,将会带大家学习Spring Cache缓存框架. 原创声明 ...
随机推荐
- oracle递归查询(查询条件ID下得所有子集)
一.CREATE TABLE TBL_TEST ( ID NUMBER, NAME VARCHAR2(100 BYTE), PID NUMBER ...
- c++并发编程之原子操作的实现原理
原子(atomic)本意是”不能被进一步分割的最小粒子”,而原子操作(atomic operation)意为”不可被中断的一个或一系列操作”. 处理器如何实现原子操作 (1) 使用总线锁保证原子性 如 ...
- lca 欧拉序+rmq(st) 欧拉序+rmq(线段树) 离线dfs 倍增
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P3379 1.欧拉序+rmq(st) /* 在这里,对于一个数,选择最左边的 选择任意一个都可以,[left_index, ...
- CF&&CC百套计划4 Codeforces Round #276 (Div. 1) A. Bits
http://codeforces.com/contest/484/problem/A 题意: 询问[a,b]中二进制位1最多且最小的数 贪心,假设开始每一位都是1 从高位i开始枚举, 如果当前数&g ...
- 流媒体技术学习笔记之(六)FFmpeg官方文档先进音频编码(AAC)
先进音频编码(AAC)的后继格式到MP3,和以MPEG-4部分3(ISO / IEC 14496-3)被定义.它通常用于MP4容器格式; 对于音乐,通常使用.m4a扩展名.第二最常见的用途是在MKV( ...
- Spring RedisTemplate操作-Set操作(5)
@Autowired @Resource(name="redisTemplate") private RedisTemplate<String, String> rt; ...
- [转载]Cross-Platform Development in Visual Studio
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn771552.aspx http://www.cnblogs.com/mengkzhaoyun/p/4152823. ...
- Metasploit输出重定向到文件
Metasploit是我们经常会使用到的神器,但是运行exploit/run无法保存输出信息,查看不是很方便. 现在可以使用spool来保存输出信息: Metasploit Framework Con ...
- nginx tomcat 自动部署python脚本【转】
#!/usr/bin/env python #--coding:utf8-- import sys,subprocess,os,datetime,paramiko,re local_path='/ho ...
- php的递归函数示例
递归函数太难理解了,写了一个示例放在这里方便没事的时候看一下. <?php /** *php递归函数示例 *(从1到100的累加和计算) * */ function summation($num ...
