疑问:Spring中构造器、init-method、@PostConstruct、afterPropertiesSet孰先孰后,自动注入发生时间
一、前言
spring的一大优点就是扩展性很强,比如,在spring bean 的生命周期中,给我们预留了很多参与bean 的生命周期的方法。
大致梳理一下,有以下几种:
- 通过实现 InitializingBean/DisposableBean 接口来定制初始化之后/销毁之前的操作方法;
- 通过 <bean> 元素的 init-method/destroy-method属性指定初始化之后 /销毁之前调用的操作方法;
- 在指定方法上加上@PostConstruct 或@PreDestroy注解来制定该方法是在初始化之后还是销毁之前调用;
- 自定义 org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor ,来让 spring 回调我们的方法来参与 bean的生命周期。
但有个问题是,如果同时使用上面四种方式,会是什么结果? 谁先,谁后呢?
二、验证
1、新建工程
我这边建立了测试工程,源码在文末:

xml中定义如下:
<bean class="com.ckl.springbeanlifecycle.DemoController" init-method="init" destroy-method="cleanUp"></bean>
重点是我们的DemoController,该类作为一个 bean,在xml中已经定义了,我们为该类,实现了各种接口,以及各种生命周期的相关注解:
package com.ckl.springbeanlifecycle; import com.ckl.springbeanlifecycle.service.IDemoService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; /**
* desc:
*
* @author : caokunliang
* creat_date: 2019/7/20 0020
* creat_time: 18:45
**/
public class DemoController implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean { @Autowired
private IDemoService iDemoService; public DemoController() {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("constructor ");
System.out.println( "属性:" + iDemoService);
System.out.println();
} @Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("implements DisposableBean interface");
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (iDemoService != null));
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + iDemoService);
System.out.println();
} @Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet interface");
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (iDemoService != null));
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + iDemoService);
System.out.println();
} @PostConstruct
public void postConstruct(){
System.out.println();
System.out.println("@PostConstrut....");
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (iDemoService != null));
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + iDemoService);
System.out.println();
} @PreDestroy
public void preDestroy(){
System.out.println();
System.out.println("@PreDestroy.....");
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + iDemoService);
System.out.println();
} public void init(){
System.out.println();
System.out.println("init-method by xml 配置文件");
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (iDemoService != null));
System.out.println();
}
public void cleanUp(){
System.out.println();
System.out.println("destroy-method by xml 配置文件");
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + iDemoService);
System.out.println();
}
}
因为我们还需要验证 org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor,所以我们自定义了一个 org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor:
package com.ckl.springbeanlifecycle; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.lang.reflect.Field; /**
* desc:
*
* @author : caokunliang
* creat_date: 2019/7/20 0020
* creat_time: 18:52
**/
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof DemoController){
System.out.println();
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor:" + "postProcessBeforeInitialization");
Field field = null;
try {
field = bean.getClass().getDeclaredField("iDemoService");
field.setAccessible(true);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Object o = field.get(bean);
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (o != null));
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + o);
System.out.println();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return bean;
} @Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof DemoController){
System.out.println();
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor:" + "postProcessAfterInitialization");
Field field = null;
try {
field = bean.getClass().getDeclaredField("iDemoService");
field.setAccessible(true);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Object o = field.get(bean);
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (o != null));
System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + o);
System.out.println();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return bean;
}
}
2、运行
初始化时的顺序如下:
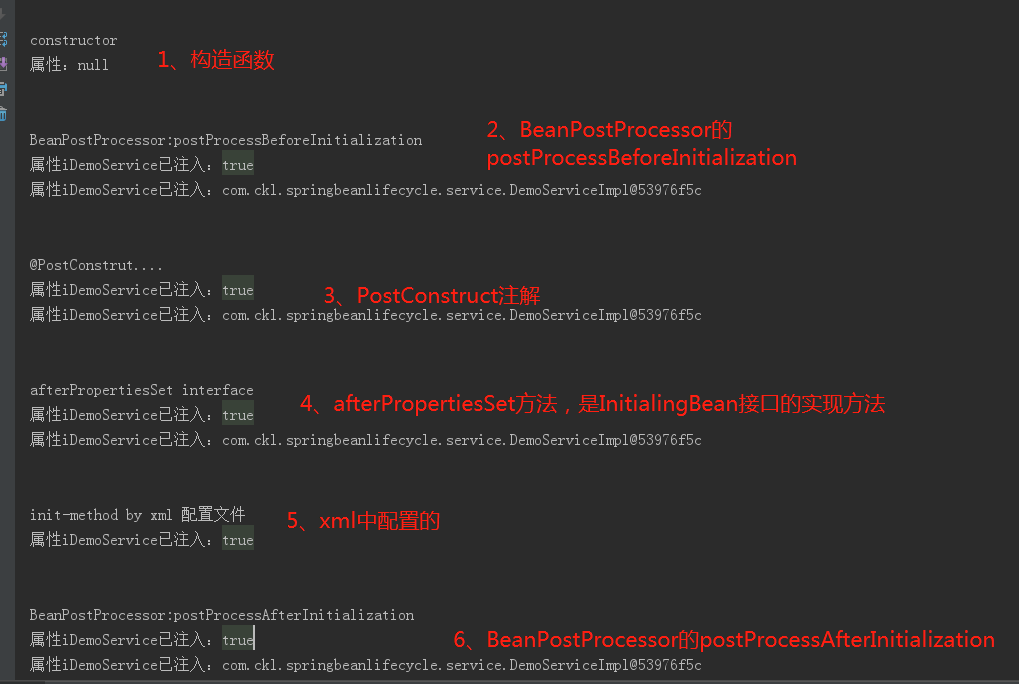
关闭容器时,执行顺序为:

3、扩展
可能部分朋友,还有这样的需求,即,在程序启动完成后,做点事情,比如,预热缓存之类的,那么,你可以这样:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /**
* desc:
*
* @author : caokunliang
* creat_date: 2018/11/20 0020
* creat_time: 14:50
**/
@Service
public class InitRunner implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> { @Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent contextRefreshedEvent) {
//root application context
if (contextRefreshedEvent.getApplicationContext().getParent() == null) {
/**
* 这里既是 root 容器初始化完毕后,会进入该分支,
*/
todo。。。 }else {
/**
* 如果是spring mvc的话, dispatchServlet对应的 applicationContext 会进入这个分支
*/ ApplicationContext applicationContext = contextRefreshedEvent.getApplicationContext();
todo。。。
} }
}
上面是针对启动时做的事情,关闭时,如果想做点事情,可以这样:
package com.ceiec.webservice.init; import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEvent;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /**
* desc:
*
* @author : caokunliang
* creat_date: 2018/11/20 0020
* creat_time: 14:50
**/
@Service
public class CloseRunner implements ApplicationListener<ContextClosedEvent> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CloseRunner.class); @Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextClosedEvent contextClosedEvent) {
logger.info("clean resources when close applicationContext");
if(contextClosedEvent.getApplicationContext().getParent() == null){ } }
}
4、spring boot 的扩展
针对spring boot,也可以注册我们的 listener来参与生命周期。
实现 org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener 即可,并将自定义的 listener 配置到 meta-inf 下的 spring.factories 文件。
举例如下:
package com.ceiec.router.config; import com.ceiec.router.config.servletconfig.MyServletContext;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.MutablePropertySources;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource; import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import java.util.Map; /**
* desc:
*
* @author : caokunliang
* creat_date: 2019/5/24 0024
* creat_time: 20:07
**/
@Data
@Slf4j
public class MyListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener { public MyListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
super();
} @Override
public void starting() { } @Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : propertySources) {
Object value = propertySource.getProperty("spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain"); if (value != null) {
MapPropertySource source = (MapPropertySource) propertySource;
Map<String, Object> map = source.getSource();
map.remove("spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain"); log.info("spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain: after: {}",propertySource.getProperty("spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain"));
}
}
} @Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
log.info("contextPrepared");
ServletContext servletContext = new MyServletContext();
ServletWebServerApplicationContext applicationContext = (ServletWebServerApplicationContext) context;
applicationContext.setServletContext(servletContext);
} @Override
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
//Not used.
} @Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { } @Override
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { } @Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) { } }

源码在交友网站: https://github.com/cctvckl/spring-bean-lifecycle
疑问:Spring中构造器、init-method、@PostConstruct、afterPropertiesSet孰先孰后,自动注入发生时间的更多相关文章
- Spring中构造器、init-method、@PostConstruct、afterPropertiesSet孰先孰后,自动注入发生时间以及单例多例的区别、SSH线程安全问题
首先明白,spring的IOC功能需要是利用反射原理,反射获取类的无参构造方法创建对象,如果一个类没有无参的构造方法spring是不会创建对象的.在这里需要提醒一下,如果我们在class中没有显示的声 ...
- 疑问:Spring 中构造器、init-method、@PostConstruct、afterPropertiesSet 孰先孰后,自动注入发生时间
一.前言 spring的一大优点就是扩展性很强,比如,在spring bean 的生命周期中,给我们预留了很多参与bean 的生命周期的方法.大致梳理一下,有以下几种: 通过实现 Initializi ...
- Spring 中IOC(控制反转)&& 通过SET方式为属性注入值 && Spring表达式
### 1. Spring IoC IoC:Inversion of control:控制反转:在传统开发模式下,对象的创建过程和管理过程都是由开发者通过Java程序来实现的,操作权在开发者的Java ...
- 谈谈Spring中的对象跟Bean,你知道Spring怎么创建对象的吗?
本系列文章: 读源码,我们可以从第一行读起 你知道Spring是怎么解析配置类的吗? 配置类为什么要添加@Configuration注解? 推荐阅读: Spring官网阅读 | 总结篇 Spring杂 ...
- 原创 | 我被面试官给虐懵了,竟然是因为我不懂Spring中的@Configuration
GitHub 3.7k Star 的Java工程师成神之路 ,不来了解一下吗? GitHub 3.7k Star 的Java工程师成神之路 ,真的不来了解一下吗? GitHub 3.7k Star 的 ...
- 我被面试官给虐懵了,竟然是因为我不懂Spring中的@Configuration
现在大部分的Spring项目都采用了基于注解的配置,采用了@Configuration 替换标签的做法.一行简单的注解就可以解决很多事情.但是,其实每一个注解背后都有很多值得学习和思考的内容.这些思考 ...
- Spring官网阅读(十)Spring中Bean的生命周期(下)
文章目录 生命周期概念补充 实例化 createBean流程分析 doCreateBean流程分析 第一步:factoryBeanInstanceCache什么时候不为空? 第二步:创建对象(crea ...
- Spring中的Autowired注解和Resource注解的区别
1.所属jar包不同,Autowired是Spring中的Resource是JSR-250规范定义的注解
- Spring中的ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
在观察线上系统的运行情况下,发现在错误日志中有这类错误信息,org.springframework.core.task.TaskRejectedException,于是便对ThreadPoolTa ...
随机推荐
- wamp修改空密码以及设置虚拟站点
近来重装了一下wamp,索性记录一下,wamp安装完后,我的常用配置.首先,肯定要修改默认的空密码:其次,便要配置虚拟站点,因为当项目多的时候,每个项目分配成一个站点,对于开发来说,很方便管理.其实网 ...
- PLSQL触发器
触发器权限 数据库创建用户时想要在本用户下使用触发器,需要给用户触发器的权限 使用DBA用户执行 GRANT CREATE TRIGGER TO user_name; 如果想在当前用户下创建其他用户 ...
- java流和文件 保存字节级数据(写)
重要的知识点: 流的概念: 从数据源到I/O类的输入流(in) 从I/O类到数据接收器的输出流(out) I/O包含子类较多的有四大家族:InputStream,OutputStream,Re ...
- bootstrap3 响应式布局栅格式布局
抓住重点 下面开始实现Bootstrap版本3的Demo 案例 首先去官方网站 http://www.bootcss.com/ 下载 点击 进入 点击 进入 下载 把 相关的js和css 拷贝到项目 ...
- [Hadoop] - TaskTracker源码分析
在Hadoop1.x版本中,MapReduce采用master/salve架构,TaskTracker就是这个架构中的slave部分.TaskTracker以服务组件的形式存在,负责任务的执行和任务状 ...
- sqlalchemy ORM模块使用介绍
前几天用到了flask框架,所以顺带介绍了flask-sqlalchemy扩展模块,去瞄一眼,由于有好多非web的python程序也用到了数据库,所以今天分享一下sqlalchemy的模块的使用方法. ...
- p1144一元三次方程求解
题目描述: 有形如:f(x)=ax^3+bx^2+cx+d=0这样的一元三次方程,给出该方程中各项的系数a,b,c,d,它们均为实数,并约定该方程一定存在着3个不同的实数解,解的范围在-100至100 ...
- HTTP和HTTPS协议
网络协议为计算机网络中进行数据交换而建立的规则.标准或约定的集合. URL:就是网址.http://www.hcios.com/archives/1547 URL就是资源的地址,位置.互联网上的每一个 ...
- IOS 中openGL使用(使用基准图快速制作滤镜)
Color Lookup Table 在影像处理领域中,当我们想要调整一个影像的色彩时,经常会用到 Color Lookup Table 的技术. 举个简单的例子,如果我们想要让影像中的每个像素的R值 ...
- java poi 从服务器下载模板写入数据再导出
最近写了一个,Excel 的 写入和导出. 需求是这样的. 在新建合同的时候,会有导出合同的数据, 导出的模板是固定的,,需要在模板里面写入合同的信息. first : 下载模板 ...
