一文教你快速修改ubuntu终端显示的主机名和用户名
为了让终端的显示更加简洁,清爽,改掉显示的用户名和主机名,改成你喜欢的名字。
创作不易,如果本文帮到了您;
如果本文帮到了您,请帮忙点个赞 ;
如果本文帮到了您,请帮忙点个赞 ;
如果本文帮到了您,请帮忙点个赞 ;
1 前言
为了让终端的显示更加简洁,清爽,在此记录一下。心急的读者可以直接跳到第四节。
快捷键 alt+ctrl+t 打开终端,首先它是这样的,如下图所示;
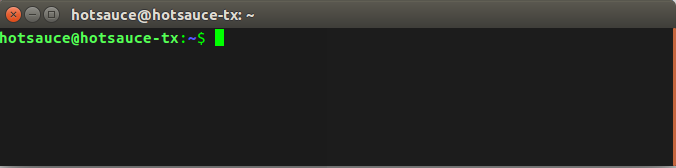
大概格式是这样子的:
用户名@主机名
hotsauce@hotsauce-tx
现在如何这些花里胡哨的字符串消失呢?
2 开始动手
首先,在系统启动bash终端的时候,会为用户读取一个文件名为.bashrc的文件,这个文件保存了用户一些个性化的设置,包括终端颜色,显示的用户名之类的东西;
现在打开.bashrc文件,具体如下:
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files (in the package bash-doc)
# for examples
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
case $- in
*i*) ;;
*) return;;
esac
# don't put duplicate lines or lines starting with space in the history.
# See bash(1) for more options
HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
# append to the history file, don't overwrite it
shopt -s histappend
# for setting history length see HISTSIZE and HISTFILESIZE in bash(1)
HISTSIZE=1000
HISTFILESIZE=2000
# check the window size after each command and, if necessary,
# update the values of LINES and COLUMNS.
shopt -s checkwinsize
# If set, the pattern "**" used in a pathname expansion context will
# match all files and zero or more directories and subdirectories.
#shopt -s globstar
# make less more friendly for non-text input files, see lesspipe(1)
[ -x /usr/bin/lesspipe ] && eval "$(SHELL=/bin/sh lesspipe)"
# set variable identifying the chroot you work in (used in the prompt below)
if [ -z "${debian_chroot:-}" ] && [ -r /etc/debian_chroot ]; then
debian_chroot=$(cat /etc/debian_chroot)
fi
# set a fancy prompt (non-c阿里通olor, unless we know we "want" color)
case "$TERM" in
xterm-color|*-256color) color_prompt=yes;;
esac
# uncomment for a colored prompt, if the terminal has the capability; turned
# off by default to not distract the user: the focus in a terminal window
# should be on the output of commands, not on the prompt
#force_color_prompt=yes
if [ -n "$force_color_prompt" ]; then
if [ -x /usr/bin/tput ] && tput setaf 1 >&/dev/null; then
# We have color support; assume it's compliant with Ecma-48
# (ISO/IEC-6429). (Lack of such support is extremely rare, and such
# a case would tend to support setf rather than setaf.)
color_prompt=yes
else
color_prompt=
fi
fi
if [ "$color_prompt" = yes ]; then
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$ '
else
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ '
fi
unset color_prompt force_color_prompt
# If this is an xterm set the title to user@host:dir
case "$TERM" in
xterm*|rxvt*)
PS1="\[\e]0;${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h: \w\a\]$PS1"
;;
*)
;;
esac
# enable color support of ls and also add handy aliases
if [ -x /usr/bin/dircolors ]; then
test -r ~/.dircolors && eval "$(dircolors -b ~/.dircolors)" || eval "$(dircolors -b)"
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
#alias dir='dir --color=auto'
#alias vdir='vdir --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
fi
# colored GCC warnings and errors
#export GCC_COLORS='error=01;31:warning=01;35:note=01;36:caret=01;32:locus=01:quote=01'
# some more ls aliases
alias ll='ls -alF'
alias la='ls -A'
alias l='ls -CF'
# Add an "alert" alias for long running commands. Use like so:
# sleep 10; alert
alias alert='notify-send --urgency=low -i "$([ $? = 0 ] && echo terminal || echo error)" "$(history|tail -n1|sed -e '\''s/^\s*[0-9]\+\s*//;s/[;&|]\s*alert$//'\'')"'
# Alias definitions.
# You may want to put all your additions into a separate file like
# ~/.bash_aliases, instead of adding them here directly.
# See /usr/share/doc/bash-doc/examples in the bash-doc package.
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
# enable programmable completion features (you don't need to enable
# this, if it's already enabled in /etc/bash.bashrc and /etc/profile
# sources /etc/bash.bashrc).
if ! shopt -oq posix; then
if [ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ]; then
. /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
elif [ -f /etc/bash_completion ]; then
. /etc/bash_completion
fi
fi
3 PS1变量
这里暂时不分析这个脚本了,因为我们要快速解决问题;
直接搜索PS1找到关键代码如下:
if [ "$color_prompt" = yes ]; then
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$ '
else
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ '
fi
unset color_prompt force_color_prompt
# If this is an xterm set the title to user@host:dir
case "$TERM" in
xterm*|rxvt*)
PS1="\[\e]0;${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h: \w\a\]$PS1"
;;
*)
;;
esac
解释一下,这里的
PS1是一个全局变量,用于显示用户主机名称工作目录,所以只要修改这个变量即可;
再打开一个终端,输入以下指令;
echo $PS1
具体输出如下所示;
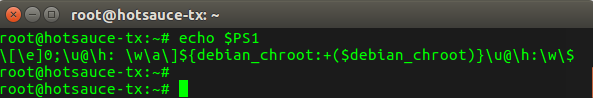
这样我们大概知道具体是脚本里哪句代码生效了,下面是这些参数的作用,可以看一下,如下表所示;
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| \d | 代表日期,格式为weekday month date,例如:“Mon Aug 1” |
| \H | 完整的主机名称 |
| \h | 仅取主机的第一个名字,如上例,则为fc4,.linux则被省略 |
| \t | 显示时间为24小时格式,如:HH:MM:SS |
| \T | 显示时间为12小时格式 |
| \A | 显示时间为24小时格式:HH:MM |
| \u | 当前用户的账号名称 |
| \v | BASH的版本信息 |
| \w | 完整的工作目录名称。家目录会以 ~代替 |
| \W | 利用basename取得工作目录名称,所以只会列出最后一个目录 |
| # | 下达的第几个命令 |
| $ | 提示字符,如果是root时,提示符为:# ,普通用户则为:$ |
4 解决办法
4.1 主机名和用户名消失
打开文件;
sudo vi ~/.bashrc
如果单纯只是消失的话,在.bashrc的最后一行加上
PS1='\[\e]0;#: \w\a\]${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]#\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$'
直接删除\u和\h,另外我不喜欢@,所以这里加了一个#。
输入以下指令让修改生效;
sudo source ~/.bashrc
再次启动终端;

4.2 修改显示的主机名和用户名
那如果我们没有那么残忍,只是希望修改显示的主机名和用户名,又该怎么做呢?
OK!!!
sudo vi /etc/hostname
这里将hostname改成unclemac,并且需要重启一下电脑;
然后打开.bashrc,在文件最后添加下面这行代码;
PS1='\[\e]0;\h@\h: \w\a\]${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\h@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$'
这里已经将\u全都替换为\h,所以最终会显示新的主机名@主机名的格式;
打开终端,发现,生效了;

笔者能力和水平有限,文中难免有错误和纰漏之处,请大佬们不吝赐教;
创作不易,如果本文帮到了您;
如果本文帮到了您,请帮忙点个赞 ;
如果本文帮到了您,请帮忙点个赞 ;
如果本文帮到了您,请帮忙点个赞 ;
一文教你快速修改ubuntu终端显示的主机名和用户名的更多相关文章
- Ubuntu修改终端显示的主机名、用户名、目录不同颜色
打开终端输入:echo $PS1 输入:gedit ~/.bashrc #定位到如下代码: if [ "$color_prompt" = yes ]; then PS1='${de ...
- 修改ubuntu终端显示目录和计算机名称(转)
注意:使用方法:# PS1='自定义内容' 注意两边的单引号 示例: PS1='(\u@\H \d \t)\$' ------------------------------------------- ...
- Mac终端中主机名与用户名的修改
Mac终端的主机名称+用户名全部显示出来的话会可能显得特别长,影响整体美观,可以切换至root用户后 修改.bashrc文件进行格式化. 1. 终端中切换root用户 su - root 2. 修改/ ...
- ubuntu下如何设置主机名
方法如下: 在终端输入 hostname 查看主机名主机名存放在/etc/hostname中 ,sudo gedit /etc/hostname 修改后保存/etc/hosts 还有一份 , sudo ...
- 阿里云修改CentOS Linux服务器的主机名
阿里云主机的默认主机名是为AY开头的随机名称,如何修改为易于区分的友好名称呢?请看下面的操作步骤: 1. vi /etc/hosts i键,修改主机名,esc键,:wq键保存退出 2. vi /etc ...
- 改变ubuntu终端显示语言(桌面系统是中文,终端提示是英文)
打开终端: $ vi .bashrc 最后添加 if [ "$TERM"="linux" ] ;then export LANGUAGE=en_US expor ...
- 设置ubuntu 终端显示路径长度
~/.bashrc 这个文件记录了用户终端配置. 打开~/.bashrc 这个文件 $: sudo vim ~/.bashrc 找到 将蓝色的w由小写改成大写,可以表示只显示当前目录名称.
- 修改oracle服务器所在linux主机名
1.修改/etc/hosts 2.修改 /etc/sysconfig/network 3.修改oracle的 listener.ora 4.修改 tnsnames.ora
- ubuntu如何修改terminal终端的主机名(修改/etc/hostname文件)
有时候安装完Ubuntu系统后,打开命令终端,终端显示的主机名格式比较难看,例如 我最近买的国内某云的VPS. xxx@VM-1560-ubuntu$ xxx@VM-1560-ubuntu$ 对于有洁 ...
随机推荐
- stand up meeting 12-14
今日更新: 项目的refactor部分均已经基本完成.答题界面和结果展示界面与code hunters team项目的merge部分也已经完成. 当然在这其中我们也遇到了一个小问题,在背单词模块中的词 ...
- SpringBoot系列(八)分分钟学会Springboot多种解决跨域方式
SpringBoot系列(八) 分分钟学会SpringBoot多种跨域解决方式 往期推荐 SpringBoot系列(一)idea新建Springboot项目 SpringBoot系列(二)入门知识 s ...
- mybatis配置的逻辑删除不好使了
在使用mybatisplus中,可使用逻辑删除.案例中,使用mybatisplus逆向生成model,使用delete_status为识别逻辑删除字段. springboot 中配置启动逻辑删除 my ...
- S7通信协议之你不知道的事儿
在电气学习的路上,西门子PLC应该是我的启蒙PLC,从早期的S7-300/400 PLC搭建Profibus-DP网络开始接触,到后来的S7-200Smart PLC,再到现在的S7-1200/150 ...
- PHP函数:array_chunk
array_chunk() - 将一个数组分割成多个. 说明: array_chunk ( array $array , int $size [, bool $preserve_keys = fa ...
- 【08NOIP提高组】笨小猴
笨 小 猴 来自08年NOIP提高组的第一题 1.题目描述 [题目描述] 笨小猴的词汇量很小,所以每次做英语选择题的时候都很头痛.经实验证明,用这种方法去选择选项的时候选对的几率非常大!这种方法的具体 ...
- prefetch 和 preload 及 webpack 的相关处理
使用预取和预加载是网站性能和用户体验提升的一个很好的途径,本文介绍了使用 prefetch 和 prefetch 进行预取和预加载的方法,并使用 webpack 进行实现 Link 的链接类型 < ...
- Python - 生成随机验证码的3种实现方式
生成6位随机验证码的3种实现方式如下: 1. 简单粗暴型:所有数字和字母都放入字符串: 2. 利用ascii编码的规律,遍历获取字符串和数字的字符串格式: 3. 引用string库. 方法1代码: i ...
- VideoView--简单获取进度条的方法
使用MediaController类就可以简单的把视频中的进度条加进去 实例: 现在布局哪里放一个VideoView,然后: videoView = (VideoView) findViewById( ...
- 总结php删除html标签和标签内的内容的方法
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/shaoguan/p/7336984.html 经常扒别人网站文章的坑们:我是指那种批量式采集的压根不看内容的:少不了都会用到删除html标签的函 ...
