A - Investment
A - Investment
John never knew he had a grand-uncle, until he received the notary’s letter. He learned that his late grand-uncle had gathered a lot of money, somewhere in South-America, and that John was the only inheritor.
John did not need that much money for the moment. But he realized that it would be a good idea to store this capital in a safe place, and have it grow until he decided to retire. The bank convinced him that a certain kind of bond was interesting for him.
This kind of bond has a fixed value, and gives a fixed amount of yearly interest, payed to the owner at the end of each year. The bond has no fixed term. Bonds are available in different sizes. The larger ones usually give a better interest. Soon John realized that the optimal set of bonds to buy was not trivial to figure out. Moreover, after a few years his capital would have grown, and the schedule had to be re-evaluated.
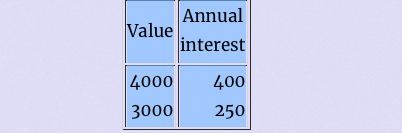
Assume the following bonds are available:
With a capital of e10 000 one could buy two bonds of $4 000, giving a yearly interest of $800. Buying two bonds of $3 000, and one of $4 000 is a better idea, as it gives a yearly interest of $900. After two years the capital has grown to $11 800, and it makes sense to sell a $3 000 one and buy a $4 000 one, so the annual interest grows to $1 050. This is where this story grows unlikely: the bank does not charge for buying and selling bonds. Next year the total sum is $12 850, which allows for three times $4 000, giving a yearly interest of $1 200.
Here is your problem: given an amount to begin with, a number of years, and a set of bonds with their values and interests, find out how big the amount may grow in the given period, using the best schedule for buying and selling bonds.
Input
The first line contains a single positive integer N which is the number of test cases. The test cases follow.
The first line of a test case contains two positive integers: the amount to start with (at most $1 000 000), and the number of years the capital may grow (at most 40).
The following line contains a single number: the number d (1 <= d <= 10) of available bonds.
The next d lines each contain the description of a bond. The description of a bond consists of two positive integers: the value of the bond, and the yearly interest for that bond. The value of a bond is always a multiple of $1 000. The interest of a bond is never more than 10% of its value.
Output
For each test case, output – on a separate line – the capital at the end of the period, after an optimal schedule of buying and selling.
Sample Input
1
10000 4
2
4000 400
3000 250
Sample Output
14050
思路如下
这一题是一个完全背包的模型,在做题的时候我们需要注意一些地方,我 手中的总钱数money在每一过一年是会增加的(因为股票的利润),所以我们的 前变为:money += f[money/1000](该年的利润);其次这一个题的数据范围非常大,而数组是不可能开这么大的,但是这一题又说了 股票的价格是以1000的倍数,手中的钱money也是1000倍数 ,所以我们可以同时 讲 每支股票的价格 与手中的金钱 同除以1000,这样我们开的数组就足放的下所有数据了
题解如下
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int pri;
int val;
};
Node node[100];
int main()
{
int q;
//cin>>q;
scanf("%d",&q);
while(q--)
{
int money,year,spci; //spci 为股票的种类
//cin>>money>>year>>spci;
scanf("%d%d%d",&money,&year,&spci);
for(int i = 1;i <= spci;i ++)
{
int temp;
//cin>>temp>>node[i].val;
scanf("%d%d",&temp,&node[i].val);
node[i].pri = temp/1000; //除以1000缩小范围
}
while(year--)
{
int f[100005] = {0}; //状态转移方程
for(int i = 1;i <= spci;i ++)
for(int mon = node[i].pri;mon <= money/1000;mon ++)
f[mon] = max(f[mon],f[mon - node[i].pri ] + node[i].val);
money += f[money/1000];
}
cout<<money<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
A - Investment的更多相关文章
- Case Studies: Retail and Investment Banks Use of Social Media
The past couple of months have seen an increased acknowledgement of the role social media has to pla ...
- [HDU 1963] Investment
Investment Time Limit:10000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu Descrip ...
- POJ2063 Investment 【全然背包】
Investment Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 30000K Total Submissions: 8019 Accepted: 2747 Descri ...
- POJ 2063 Investment (完全背包)
A - Investment Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:30000KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Subm ...
- POJ 2063 Investment 完全背包
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=2063 今天果然是卡题的一天.白天被hdu那道01背包的变形卡到现在还没想通就不说了,然后晚上又被这道有个不大也不小的坑的完全背包卡了好 ...
- [POJ 2063] Investment (动态规划)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=2063 题意:银行每年提供d种债券,每种债券需要付出p[i]块钱,然后一年的收入是v[i],到期后我们把本金+收入取出来作为下一年度本金 ...
- hdu 1963 Investment 多重背包
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1963 //多重背包 #include <cstdio> #include <cstr ...
- poj 2063 Investment
题意:给定一个初始资金capital,然后给定d种投资方案,每种投资方案中有投资额value[i](是1000的倍数)和利息interest[i],每年的投资就可以拿到全部利息,然后累加起来继续投资利 ...
- 【HDOJ】1963 Investment
完全背包. #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define max(a, b) (a>b) ? a:b ], an[]; ] ...
随机推荐
- mysql从5.5升级到5.7遇到的坑
在安装mysql5.7时很顺利安装完成,但在启动项目时报错: [Err] 1055 - Expression #1 of ORDER BY clause is not in GROUP BY clau ...
- 点云3d检测模型pointpillar
PointPillars 一个来自工业界的模型.https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.05784 3D目标检测通常做法 3d卷积 投影到前平面 在bird-view上操作 处理思路依然 ...
- es6的解构函数
话说,解构无处不在啊,鄙人自从用了vue写项目以来,总是遇到各路大神莫名其妙的写法,然并未出任何错,查之,然解构也,呜呼哀哉,进而习之. 解构(Destructuring):是将一个数据结构分解为更小 ...
- GPS授时器简介
GPS授时器简介 GPS是全球定位系统的简称.GPS定位卫星在全球范围内进行定位.导航的系统.GPS所具有的全天候.高精度和自动测量的特点,已经融入到国民经济建设.国防建设和社会发展的各个领域.而在授 ...
- 【面试经验分享】java面试中的那些潜规则
1.大纲 潜规则1:面试的本质不是考试,而是告诉面试官你会做什么 很多刚入行的小伙伴特别容易犯的一个错误,不清楚面试官到底想问什么,其实整个面试中面试官并没有想难道你的意思,只是想通过提问的方式来知道 ...
- asyncio在爬虫中的使用
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # 协程基础.py import asyncio import time async def request(url): print("正在请 ...
- 关于emgucv控制多摄像头问题
看到这篇文章你或许已经查阅很多资料,也可能你刚准备深入研究,但是关于调用多摄像头问题我要说明一点,关于多摄像头调用 取决于你电脑本身USB控制器数量,不是说你电脑上5个usb就可以同时控制5台摄像头, ...
- 使用Netty如何解决拆包粘包的问题
首先,我们通过一个DEMO来模拟TCP的拆包粘包的情况:客户端连续向服务端发送100个相同消息.服务端的代码如下: AtomicLong count = new AtomicLong(0); NioE ...
- SpringBoot2整合Redis多数据源
配置文件属性 spring: redis: database: 1 host: 192.168.50.144 port: 6379 password: timeout: 600 #Springboot ...
- 搭建Hadoop集群需要注意的问题:
搭建Hadoop集群需要注意的问题: 1.检查三台主机名是否正确 2.检查三台IP是否正确 3.检查 /etc/hosts 映射是否正确 4.检查 JDK和Hadoop 是否安装成功(看环境变量配置) ...