Spring AOP 由浅入深
(分析基于Spring的版本:version = 4.1.6.RELEASE)
SpringAOP 和 AspectJ 的关系:
它们是两种不同的编程风格, SpringAOP 使用 xml 配置的形式配置 aop。而 AspectJ 使用 AspectJ 的注解来配置 aop
aspect、JoinPoint、Pointcut、Weaving、Advice
JoinPoint: 连接点。表示目标对象中的方法
Pointcut: 切点。表示连接点的集合
Weaving: 织入。把代理逻辑加入到目标对象上的过程叫织入
Advice: 通知。包括 “around”, “before” and “after 等
this、target
this: 产生的代理对象
target: 被代理的原始对象
JoinPoint、ProceedingJoinPoint
JoinPoint 接口可以拿到连接点的相关信息,比如:方法签名、方法参数、this、target
ProceedingJoinPoint 继承自 JoinPoint,它是用来支持环绕(around)通知的,多暴露了一个 proceed() 方法,用来执行目标对象的方法。
Spring AOP工厂: org.springframework.aop.framework.DefaultAopProxyFactory
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface()) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
从代码可以看出:
1. 如果AdvisedSupport中没有进行自定义设置,Spring去创建代理的时候,会默认使用JDK动态代理。
2. 如果AdvisedSupport中进行了设置,那么就去判断被代理的类是不是接口,如果是接口的话就使用JDK动态代理,否则才使用Cglib的代理。
(2020.1.17 更新)
从源码看, proxyTargetClass=true 时,如果 targetClass 是接口 or targetClass 是一个代理类型,也有可能走 jdk 动态代理。但是绝大多数情况是不会的。
首先,在源码中找到 targetClass 赋值的地方,可以发现 targetClass 是 bean 的实例的 class,所以通常是一个实体类,不是接口。至于 targetClass 什么时候会是代理类,还不太清楚。
那既然 targetClass 是 bean 的实例的 class 的话,它并不是一个接口,那么当 proxyTargetClass=false 的时候, jdk 怎么来产生代理呢?
答案是,spring 会找到 targetClass 对应的接口来生成代理,如果这个类没有接口的话,会将 proxyTargetClass 设置成 true,从而使用 cglib 来生成代理
Spring 基于JDK动态代理的AOP实现解析:
我们知道,使用JDK的动态代理,主要是实现 java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler#invoke(Object obj, Method method, Object[] aobj)方法。
Spring相关的源码如下:JdkDynamicAopProxy.class
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation invocation;
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false; TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Class<?> targetClass = null;
Object target = null; try {
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
}
if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
} Object retVal; if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
} // May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
target = targetSource.getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
} // Get the interception chain for this method.
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); // Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
retVal = invocation.proceed();
} // Massage return value if necessary.
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
从上面可以看出,spring 会先拿到一个 MethodInterceptor 的 chain 。
如果chain为空的话,就直接反射调用原方法;否则,就会根据这个 chain 来生成一个 MethodInvocation ,然后去执行 invocation.proceed() 。
invocation.proceed() 方法的实现,是递归调用 chain 中的 MethodInterceptor。
也就是说,我们所有的AOP拦截,都是通过一连串的 MethodInterceptor 来实现的。
而这个 MethodInterceptor 的 chain 是通过 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); 来生成的。
也就是基于 AdvisedSupport 来生成的。
Spring 对 AdvisedSupport 的注释是:Base class for AOP proxy configuration managers. 也就是说,AdvisedSupport 是产生AOP代理的配置管理者。
AdvisedSupport 中保存了一个List<Advisor> advisors 的集合。
满足条件的Advisor(即:能对此method进行拦截的Advisor),最终会被转换成 MethodInterceptor ,从而添加到chain中。
Spring 基于Cglib的AOP实现解析:
我们知道,使用Cglib实现AOP时,最主要的是要设置Callback来对Method进行拦截,即:void net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer.setCallback(Callback callback) 。
spring生成Callback的源码如下:CglibAopProxy.class
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {
// Parameters used for optimisation choices...
boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();
boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();
boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls).
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
..............
}
从上面的代码可以看出,spring在生成 Callback 时,也是基于 AdvisedSupport 来的(同JDK动态代理生成 MethodInterceptor 的chain一样)。
CglibAopProxy$DynamicAdvisedInterceptor.class
private static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
private final AdvisedSupport advised;
public DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(AdvisedSupport advised) {
this.advised = advised;
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Class<?> targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we
// "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, args);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null) {
releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
...............
}
不难看出,最终JDK动态代理 与 Cglib代理 对AOP的实现都是基于 AdvisedSupport 的 MethodInterceptor 链。
参考:
http://www.jianshu.com/p/0734ec855183
http://www.cnblogs.com/digdeep/p/4528353.html
http://my.oschina.net/robinyao/blog/649518
http://lgbolgger.iteye.com/blog/2180251
http://www.cnblogs.com/chanedi/p/4552555.html (原码说明)
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable {
Spring 异步@Async也是基于Spring AOP来做的:
在bean创建完成后,会调用 AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) 来生成一个代理bean
2018.07.23 add:
编程式使用aop https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26525215/article/details/52422395/
2019.01.11 add:
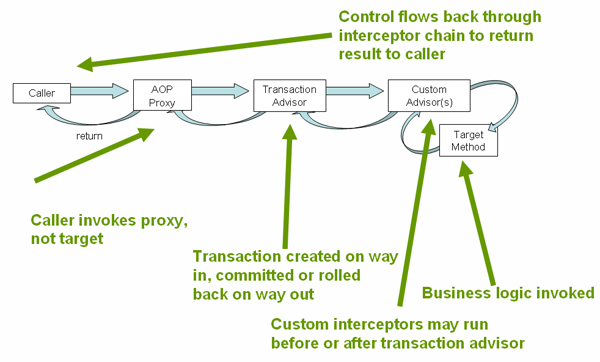
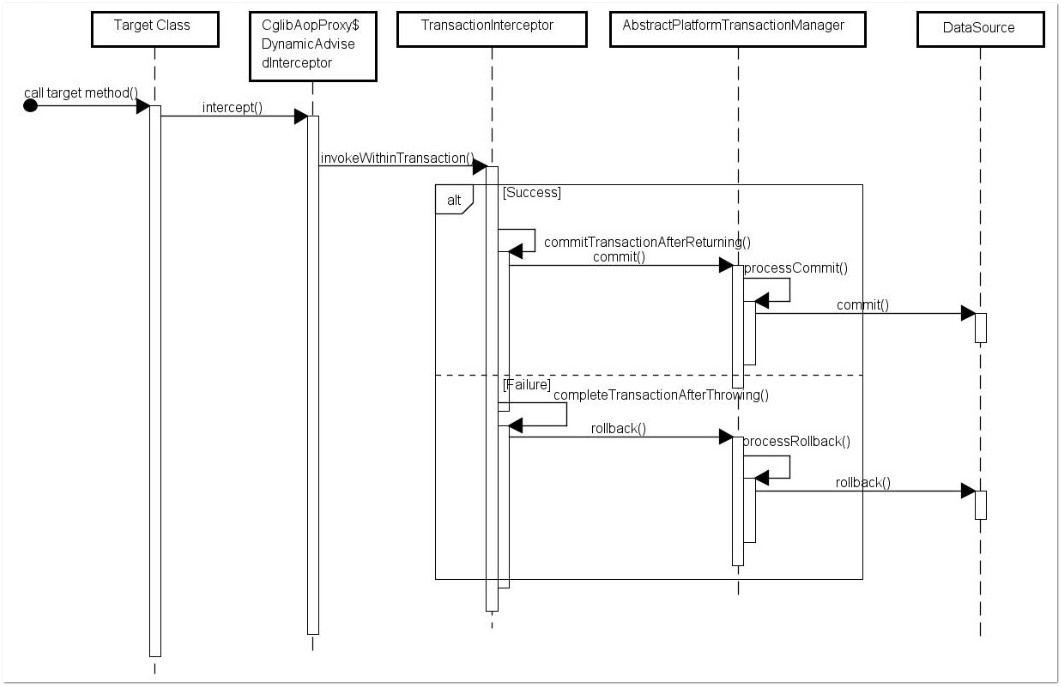
spring @Transactional 的原理解析:
TransactionAspectSupport#completeTransactionAfterThrowing 对 @Transactional 事务的处理,默认回滚 RuntimeException
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-master-spring-transactional-use/index.html
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/data-access.html#tx-decl-explained
https://doanduyhai.wordpress.com/2011/11/20/spring-transactional-explained/
Spring AOP 由浅入深的更多相关文章
- Spring AOP 系列总括
Spring有两大核心,IOC和AOP.IOC在Java Web项目中无时无刻不在使用,然而AOP用的比较少,尤其是对一些初级程序员,在架构师搭好的框架上开发应用代码,AOP几乎是透明的.然而,项目中 ...
- 学习AOP之深入一点Spring Aop
上一篇<学习AOP之认识一下SpringAOP>中大体的了解了代理.动态代理及SpringAop的知识.因为写的篇幅长了点所以还是再写一篇吧.接下来开始深入一点Spring aop的一些实 ...
- 学习AOP之认识一下Spring AOP
心碎之事 要说知道AOP这个词倒是很久很久以前了,但是直到今天我也不敢说非常的理解它,其中的各种概念即抽象又太拗口. 在几次面试中都被问及AOP,但是真的没有答上来,或者都在面上,这给面试官的感觉就是 ...
- spring aop
什么是AOP AOP(Aspect-OrientedProgramming,面向方面编程),它利用一种称为“横切”的技术,剖解开封装的对象内部,并将那些影响了多个类的公共行为封装到一个可重用模块,并将 ...
- spring aop注解方式与xml方式配置
注解方式 applicationContext.xml 加入下面配置 <!--Spring Aop 启用自动代理注解 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy ...
- 基于Spring AOP的JDK动态代理和CGLIB代理
一.AOP的概念 在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术.AOP是OOP的 ...
- Spring AOP详解
一.前言 在以前的项目中,很少去关注spring aop的具体实现与理论,只是简单了解了一下什么是aop具体怎么用,看到了一篇博文写得还不错,就转载来学习一下,博文地址:http://www.cnbl ...
- Spring AOP实例——异常处理和记录程序执行时间
实例简介: 这个实例主要用于在一个系统的所有方法执行过程中出线异常时,把异常信息都记录下来,另外记录每个方法的执行时间. 用两个业务逻辑来说明上述功能,这两个业务逻辑首先使用Spring AOP的自动 ...
- 从零开始学 Java - Spring AOP 实现用户权限验证
每个项目都会有权限管理系统 无论你是一个简单的企业站,还是一个复杂到爆的平台级项目,都会涉及到用户登录.权限管理这些必不可少的业务逻辑.有人说,企业站需要什么权限管理阿?那行吧,你那可能叫静态页面,就 ...
随机推荐
- Android模拟器Genymotion如何访问本地服务器?
Genymotion能否访问到本地服务器,其实与Genymotion本身并无太大关系.Genymotion作为VirtualBox中的一个虚拟OS运行,所以它访问网络的方式与其他VirtualBox中 ...
- java.lang.ClassCastException: org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory cannot be cast to ch.qos.logback.classic.LoggerContext问题原因及解决方法
一.错误信息 java.lang.ClassCastException: org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory cannot be cast to ch.qos.logb ...
- python中try except执行顺序
python中try except finally的执行顺序 先执行try中语句 如果try中抛出异常, 执行异常中语句. 如果try 或 except 中没有return语句,执行完try 或者 e ...
- Tomcat的ISO-8859-1
Tomcat的默认编码时ISO8859-1,有些老工程,遗留项目很可能没改这块,这样写代码时如果传输中文,服务器收到的就可能是乱码. 昨天就被郁闷了1小时,左右都不通. 后来发现Android里的字符 ...
- Windows下的Eclipse启动出现:a java runtime environment(JRE) or java development kit(JDK) must be
打开eclipse的时候回遇到这种情况 解决方案: 进入eclipse.exe所在的目录,在eclipse.ini文件中加入以下两行: -vm <your path to jdk|jre> ...
- React(JSX语法)----动态UI
1.React honws how to bubble and capture events according to the spec,and events passed to your event ...
- <a>标签的用法。
1.创建电子邮件链接: <html> <head> <title>发给朱永成</title> </head> <body> &l ...
- DLL编程学习
原文出处:http://www.blogjava.net/wxb_nudt/archive/2007/09/11/144371.html DLL编写教程 半年不能上网,最近网络终于通了,终于可以更新博 ...
- Roslyn 学习笔记(二)
参考:https://github.com/dotnet/roslyn/wiki/Getting-Started-C%23-Syntax-Analysis 语法分析过程主要用到以下类或结构: Synt ...
- BZOJ1433 ZJOI2009 假期的宿舍 二分图匹配
1433: [ZJOI2009]假期的宿舍 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSubmit: 2375 Solved: 1005[Submit][Sta ...
