CF #296 (Div. 1) A. Glass Carving 线段树
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Leonid wants to become a glass carver (the person who creates beautiful artworks by cutting the glass). He already has a rectangular wmm × h mm sheet of glass, a diamond glass cutter and lots of enthusiasm. What he lacks is understanding of what to carve and how.
In order not to waste time, he decided to practice the technique of carving. To do this, he makes vertical and horizontal cuts through the entire sheet. This process results in making smaller rectangular fragments of glass. Leonid does not move the newly made glass fragments. In particular, a cut divides each fragment of glass that it goes through into smaller fragments.
After each cut Leonid tries to determine what area the largest of the currently available glass fragments has. Since there appear more and more fragments, this question takes him more and more time and distracts him from the fascinating process.
Leonid offers to divide the labor — he will cut glass, and you will calculate the area of the maximum fragment after each cut. Do you agree?
The first line contains three integers w, h, n (2 ≤ w, h ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000).
Next n lines contain the descriptions of the cuts. Each description has the form H y or V x. In the first case Leonid makes the horizontal cut at the distance y millimeters (1 ≤ y ≤ h - 1) from the lower edge of the original sheet of glass. In the second case Leonid makes a vertical cut at distance x (1 ≤ x ≤ w - 1) millimeters from the left edge of the original sheet of glass. It is guaranteed that Leonid won't make two identical cuts.
After each cut print on a single line the area of the maximum available glass fragment in mm2.
4 3 4
H 2
V 2
V 3
V 1
8
4
4
2
7 6 5
H 4
V 3
V 5
H 2
V 1
28
16
12
6
4
Picture for the first sample test:
 Picture for the second sample test:
Picture for the second sample test: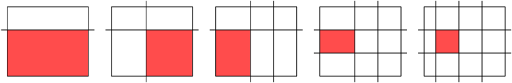
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
using namespace std; #define N 200005
#define ll root<<1
#define rr root<<1|1
#define mid1 (a[root].l+a[root].r)/2
#define mid2 (b[root].l+b[root].r)/2 int w, h, n;
struct node{
int l, r;
int lx, rx;
int maxh;
}a[N*], b[N*]; void build1(int l,int r,int root){
a[root].l=l;
a[root].r=r;
if(l==r){
if(l==) a[root].lx=a[root].rx=;
else if(l==w) a[root].lx=a[root].rx=w;
else a[root].lx=a[root].rx=-;
a[root].maxh=;
return;
}
build1(l,mid1,ll);
build1(mid1+,r,rr);
a[root].lx=a[ll].lx;
a[root].rx=a[rr].rx;
a[root].maxh=a[root].r-a[root].l;
} void build2(int l,int r,int root){
b[root].l=l;
b[root].r=r;
if(l==r){
if(l==) b[root].lx=b[root].rx=;
else if(l==h) b[root].lx=b[root].rx=h;
else b[root].lx=b[root].rx=-;
b[root].maxh=;
return;
}
build2(l,mid2,ll);
build2(mid2+,r,rr);
b[root].lx=b[ll].lx;
b[root].rx=b[rr].rx;
b[root].maxh=b[root].r-b[root].l;
} void update1(int p,int root){
if(a[root].l==p&&a[root].r==p){
a[root].lx=a[root].rx=p;return;
}
if(p<=a[ll].r) update1(p,ll);
else update1(p,rr);
int ln, rn;
if(a[ll].lx!=-) a[root].lx=a[ll].lx;
else if(a[ll].rx!=-) a[root].lx=a[ll].rx;
else if(a[rr].lx!=-) a[root].lx=a[rr].lx;
else if(a[rr].rx!=-) a[root].lx=a[rr].rx;
else a[root].lx=-; if(a[rr].rx!=-) a[root].rx=a[rr].rx;
else if(a[rr].lx!=-) a[root].rx=a[rr].lx;
else if(a[ll].rx!=-) a[root].rx=a[ll].rx;
else if(a[ll].lx!=-) a[root].rx=a[ll].lx;
else a[root].rx=-; if(a[ll].rx!=-) ln=a[ll].r-a[ll].rx;
else ln=a[ll].r-a[ll].l;
if(a[rr].lx!=-) rn=a[rr].lx-a[rr].l;
else rn=a[rr].r-a[rr].l; a[root].maxh=max(max(a[ll].maxh,a[rr].maxh),ln+rn+);
} void update2(int p,int root){
if(b[root].l==p&&b[root].r==p){
b[root].lx=b[root].rx=p;return;
}
if(p<=b[ll].r) update2(p,ll);
else update2(p,rr);
int ln, rn;
if(b[ll].lx!=-) b[root].lx=b[ll].lx;
else if(b[ll].rx!=-) b[root].lx=b[ll].rx;
else if(b[rr].lx!=-) b[root].lx=b[rr].lx;
else if(b[rr].rx!=-) b[root].lx=b[rr].rx;
else b[root].lx=-; if(b[rr].rx!=-) b[root].rx=b[rr].rx;
else if(b[rr].lx!=-) b[root].rx=b[rr].lx;
else if(b[ll].rx!=-) b[root].rx=b[ll].rx;
else if(b[ll].lx!=-) b[root].rx=b[ll].lx;
else b[root].rx=-;
if(b[ll].rx!=-) ln=b[ll].r-b[ll].rx;
else ln=b[ll].r-b[ll].l;
if(b[rr].lx!=-) rn=b[rr].lx-b[rr].l;
else rn=b[rr].r-b[rr].l;
b[root].maxh=max(max(b[ll].maxh,b[rr].maxh),ln+rn+);
} main()
{
int i, j, k;
while(scanf("%d %d %d",&w,&h,&n)==){
char s[];
build1(,w,);
build2(,h,);
// printf("%d %d\n",a[1].maxh,b[1].maxh);
while(n--){
scanf("%s%d",s,&k);
if(s[]=='H'){
update2(k,);
}
else{
update1(k,);
}
// printf("%d %d\n",a[1].maxh,b[1].maxh);
printf("%I64d\n",(__int64)a[].maxh*(__int64)b[].maxh);
}
}
}
CF #296 (Div. 1) A. Glass Carving 线段树的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #296 (Div. 1) A. Glass Carving Set的妙用
A. Glass Carving time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard in ...
- Codeforces Round #296 (Div. 2) C. Glass Carving [ set+multiset ]
传送门 C. Glass Carving time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- CF 552(div 3) E Two Teams 线段树,模拟链表
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/1154/problem/E 题意:两个人轮流取最大值与旁边k个数,问最后这所有的数分别被谁给取走了 分析:看这道题一点思路都没有 ...
- [Codeforces Round #296 div2 D] Clique Problem 【线段树+DP】
题目链接:CF - R296 - d2 - D 题目大意 一个特殊的图,一些数轴上的点,每个点有一个坐标 X,有一个权值 W,两点 (i, j) 之间有边当且仅当 |Xi - Xj| >= Wi ...
- CF 666E Forensic Examination 【SAM 倍增 线段树合并】
CF 666E Forensic Examination 题意: 给出一个串\(s\)和\(n\)个串\(t_i\),\(q\)次询问,每次询问串\(s\)的子串\(s[p_l:p_r]\)在串\(t ...
- Codeforces Round #222 (Div. 1) D. Developing Game 线段树有效区间合并
D. Developing Game Pavel is going to make a game of his dream. However, he knows that he can't mak ...
- Codeforces Round #275 Div.1 B Interesting Array --线段树
题意: 构造一个序列,满足m个形如:[l,r,c] 的条件. [l,r,c]表示[l,r]中的元素按位与(&)的和为c. 解法: 线段树维护,sum[rt]表示要满足到现在为止的条件时该子树的 ...
- CF 197 DIV2 Xenia and Bit Operations 线段树
线段树!!1A 代码如下: #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #define lson i<<1 #define rson i ...
- Codeforces Round #244 (Div. 2) B. Prison Transfer 线段树rmq
B. Prison Transfer Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/problemset/pro ...
随机推荐
- sqlalchemy中文乱码问题解决方案
本文参考http://firefish.blog.51cto.com/298258/112794/的解决方案 问题: 本文在Ubuntu上利用scrapy抓取数据写入mysql数据库时,用到sqlal ...
- Button的enabled和clickabled的区别
Button的enabled和clickabled的区别 setEnable设置用户是否可以点击此按钮,setClickable设置程序在某个条件下自动点击此按钮
- python学习之深入
一.迭代器和生成器 1.迭代器 迭代器是访问集合元素的一种方式.迭代器对象从集合的第一个元素开始访问,直到所有的元素被访问完结束.迭代器只能往前不会后退,不过这也没什么,因为人们很少在迭代途中往后退. ...
- reverseajax(comet) socket 杂记
http://blog.it985.com/7797.html http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/web/library/wa-reverseajax1/index. ...
- Linux文件搜索命令
文件搜索命令:locate locate 文件名 在后台数据库中按文件名搜索,搜索速度很快(比find命令要快得多) locate命令所搜索的后台数据库的位置:/var/bin/mlocate 支持模 ...
- ABAP开发顾问必备:SAP ABAP开发技术总结
声明:原创作品,转载时请注明文章来自SAP师太技术博客( 博/客/园www.cnblogs.com):www.cnblogs.com/jiangzhengjun,并以超链接形式标明文章原始出处,否则将 ...
- 基于ubuntu 14搭建nginx+php+mysql环境
基于最新的Ubuntu 14.04(2014年9月)搭建nginx.php.mysql环境, 以下全部命令行操作: 1 由于需要大量的权限操作,方便起见临时提升权限,使用root账号 sudo su ...
- Linux SHELL,环境变量
SHELL: 在计算机科学中,Shell俗称壳(用来区别于核),是指"提供使用者使用界面"的软件(命令解析器).它类似于DOS下的command和后来的cmd.exe.它接收用户命 ...
- 软件工程线上课程(C语言实践篇)学习心得总结
林牧 + 原创作品转载请注明出处 + <软件工程(C编码实践篇)>MOOC课程http://mooc.study.163.com/course/USTC-1000002006 软件工程的理 ...
- HTML5 十大新特性(四)——Canvas绘图
H5引入了canvas标签,默认是一个300*150的inline-block.canvas的宽高只能用它自身的width和height属性来指定,而不能使用css样式中的width.height. ...
