The Java serialization algorithm revealed---reference
Serialization is the process of saving an object's state to a sequence of bytes; deserialization is the process of rebuilding those bytes into a live object. The Java Serialization API provides a standard mechanism for developers to handle object serialization. In this tip, you will see how to serialize an object, and why serialization is sometimes necessary. You'll learn about the serialization algorithm used in Java, and see an example that illustrates the serialized format of an object. By the time you're done, you should have a solid knowledge of how the serialization algorithm works and what entities are serialized as part of the object at a low level.
Why is serialization required?
In today's world, a typical enterprise application will have multiple components and will be distributed across various systems and networks. In Java, everything is represented as objects; if two Java components want to communicate with each other, there needs be a mechanism to exchange data. One way to achieve this is to define your own protocol and transfer an object. This means that the receiving end must know the protocol used by the sender to re-create the object, which would make it very difficult to talk to third-party components. Hence, there needs to be a generic and efficient protocol to transfer the object between components. Serialization is defined for this purpose, and Java components use this protocol to transfer objects.
Figure 1 shows a high-level view of client/server communication, where an object is transferred from the client to the server through serialization.
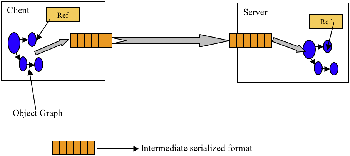
Figure 1. A high-level view of serialization in action
How to serialize an object
In order to serialize an object, you need to ensure that the class of the object implements thejava.io.Serializable interface, as shown in Listing 1.
Listing 1. Implementing Serializable
import java.io.Serializable;
classTestSerialimplementsSerializable{
publicbyte version =100;
publicbyte count =0;
}
In Listing 1, the only thing you had to do differently from creating a normal class is implement the java.io.Serializable interface. The Serializable interface is a marker interface; it declares no methods at all. It tells the serialization mechanism that the class can be serialized.
Now that you have made the class eligible for serialization, the next step is to actually serialize the object. That is done by calling the writeObject() method of thejava.io.ObjectOutputStream class, as shown in Listing 2.
Listing 2. Calling writeObject()
publicstaticvoid main(String args[])throwsIOException{
FileOutputStream fos =newFileOutputStream("temp.out");
ObjectOutputStream oos =newObjectOutputStream(fos);
TestSerial ts =newTestSerial();
oos.writeObject(ts);
oos.flush();
oos.close();}
Listing 2 stores the state of the TestSerial object in a file called temp.out.oos.writeObject(ts); actually kicks off the serialization algorithm, which in turn writes the object to temp.out.
To re-create the object from the persistent file, you would employ the code in Listing 3.
Listing 3. Recreating a serialized object
publicstaticvoid main(String args[])throwsIOException{
FileInputStream fis =newFileInputStream("temp.out");
ObjectInputStream oin =newObjectInputStream(fis);
TestSerial ts =(TestSerial) oin.readObject();
System.out.println("version="+ts.version);}
In Listing 3, the object's restoration occurs with theoin.readObject() method call. This method call reads in the raw bytes that we previously persisted and creates a live object that is an exact replica of the original object graph. Because readObject() can read any serializable object, a cast to the correct type is required.
Executing this code will print version=100 on the standard output.
The serialized format of an object
What does the serialized version of the object look like? Remember, the sample code in the previous section saved the serialized version of the TestSerial object into the file temp.out. Listing 4 shows the contents of temp.out, displayed in hexadecimal. (You need a hexadecimal editor to see the output in hexadecimal format.)
Listing 4. Hexadecimal form of TestSerial
AC ED 0A 6C
A0 0C FE B1 DD F9
6F 6E 6F 6E
If you look again at the actual TestSerial object, you'll see that it has only two byte members, as shown in Listing 5.
Listing 5. TestSerial's byte members
publicbyte version =100;
publicbyte count =0;
The size of a byte variable is one byte, and hence the total size of the object (without the header) is two bytes. But if you look at the size of the serialized object in Listing 4, you'll see 51 bytes. Surprise! Where did the extra bytes come from, and what is their significance? They are introduced by the serialization algorithm, and are required in order to to re-create the object. In the next section, you'll explore this algorithm in detail.
Java's serialization algorithm
By now, you should have a pretty good knowledge of how to serialize an object. But how does the process work under the hood? In general the serialization algorithm does the following:
- It writes out the metadata of the class associated with an instance.
- It recursively writes out the description of the superclass until it finds
java.lang.object. - Once it finishes writing the metadata information, it then starts with the actual data associated with the instance. But this time, it starts from the topmost superclass.
- It recursively writes the data associated with the instance, starting from the least superclass to the most-derived class.
I've written a different example object for this section that will cover all possible cases. The new sample object to be serialized is shown in Listing 6.
Listing 6. Sample serialized object
class parent implementsSerializable{
int parentVersion =10;
}
class contain implementsSerializable{
int containVersion =11;
}
public classSerialTestextends parent implementsSeriali zable{
int version =66;
contain con =new contain();
publicint getVersion(){
return version;}
public static void main(String args[])throwsIOException{
FileOutputStream fos =newFileOutputStream("temp.out");
ObjectOutputStream oos =newObjectOutputStream(fos);
SerialTest st =newSerialTest();
oos.writeObject(st);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
}
}
This example is a straightforward one. It serializes an object of type SerialTest, which is derived from parent and has a container object, contain. The serialized format of this object is shown in Listing 7.
Listing 7. Serialized form of sample object
AC ED 00057372000A53657269616C546573740552815A AC F6 02000249000776657273696F6E4C0003636F6E7400094C636F6E7461696E3B78720006706172656E740E DB D2 BD EE 637A02000149000D706172656E7456657273696F6E78700000000A0000004273720007636F6E7461696E FC BB E6 0E FB CB C7 02000149000E636F6E7461696E56657273696F6E78700000000B
Figure 2 offers a high-level look at the serialization algorithm for this scenario.
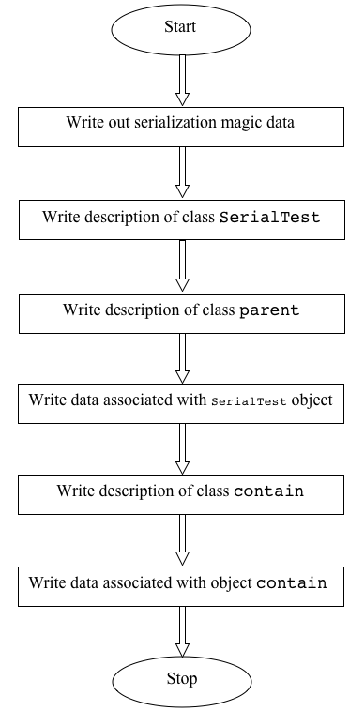
Figure 2. An outline of the serialization algorithm
Let's go through the serialized format of the object in detail and see what each byte represents. Begin with the serialization protocol information:
AC ED:STREAM_MAGIC. Specifies that this is a serialization protocol.00 05:STREAM_VERSION. The serialization version.0x73:TC_OBJECT. Specifies that this is a newObject.
The first step of the serialization algorithm is to write the description of the class associated with an instance. The example serializes an object of type SerialTest, so the algorithm starts by writing the description of theSerialTest class.
0x72:TC_CLASSDESC. Specifies that this is a new class.00 0A: Length of the class name.53 65 72 69 61 6c 54 65 73 74:SerialTest, the name of the class.05 52 81 5A AC 66 02 F6:SerialVersionUID, the serial version identifier of this class.0x02: Various flags. This particular flag says that the object supports serialization.00 02: Number of fields in this class.
Next, the algorithm writes the fieldint version = 66;.
0x49: Field type code. 49 represents "I", which stands forInt.00 07: Length of the field name.76 65 72 73 69 6F 6E:version, the name of the field.
And then the algorithm writes the next field, contain con = new contain();. This is an object, so it will write the canonical JVM signature of this field.
0x74:TC_STRING. Represents a new string.00 09: Length of the string.4C 63 6F 6E 74 61 69 6E 3B:Lcontain;, the canonical JVM signature.0x78:TC_ENDBLOCKDATA, the end of the optional block data for an object.
The next step of the algorithm is to write the description of the parent class, which is the immediate superclass of SerialTest.
0x72:TC_CLASSDESC. Specifies that this is a new class.00 06: Length of the class name.70 61 72 65 6E 74:SerialTest, the name of the class0E DB D2 BD 85 EE 63 7A:SerialVersionUID, the serial version identifier of this class.0x02: Various flags. This flag notes that the object supports serialization.00 01: Number of fields in this class.
Now the algorithm will write the field description for the parentclass. parent has one field, int parentVersion = 100;.
0x49: Field type code. 49 represents "I", which stands forInt.00 0D: Length of the field name.70 61 72 65 6E 74 56 65 72 73 69 6F 6E:parentVersion, the name of the field.0x78:TC_ENDBLOCKDATA, the end of block data for this object.0x70:TC_NULL, which represents the fact that there are no more superclasses because we have reached the top of the class hierarchy.
So far, the serialization algorithm has written the description of the class associated with the instance and all its superclasses. Next, it will write the actual data associated with the instance. It writes the parent class members first:
00 00 00 0A: 10, the value ofparentVersion.
Then it moves on to SerialTest.
00 00 00 42: 66, the value ofversion.
The next few bytes are interesting. The algorithm needs to write the information about the contain object, shown in Listing 8.
Listing 8. The contain object
contain con =new contain();
Remember, the serialization algorithm hasn't written the class description for the contain class yet. This is the opportunity to write this description.
0x73:TC_OBJECT, designating a new object.0x72:TC_CLASSDESC.00 07: Length of the class name.63 6F 6E 74 61 69 6E:contain, the name of the class.FC BB E6 0E FB CB 60 C7:SerialVersionUID, the serial version identifier of this class.0x02: Various flags. This flag indicates that this class supports serialization.00 01: Number of fields in this class.
Next, the algorithm must write the description for contain's only field, int containVersion = 11;.
0x49: Field type code. 49 represents "I", which stands forInt.00 0E: Length of the field name.63 6F 6E 74 61 69 6E 56 65 72 73 69 6F 6E:containVersion, the name of the field.0x78:TC_ENDBLOCKDATA.
Next, the serialization algorithm checks to see if contain has any parent classes. If it did, the algorithm would start writing that class; but in this case there is no superclass for contain, so the algorithm writes TC_NULL.
0x70:TC_NULL.
Finally, the algorithm writes the actual data associated with contain.
00 00 00 0B: 11, the value ofcontainVersion.
Conclusion
In this tip, you have seen how to serialize an object, and learned how the serialization algorithm works in detail. I hope this article gives you more detail on what happens when you actually serialize an object.
About the author
Sathiskumar Palaniappan has more than four years of experience in the IT industry, and has been working with Java-related technologies for more than three years. Currently, he is working as a system software engineer at the Java Technology Center, IBM Labs. He also has experience in the telecom industry.
Resources
- Read the Java object serialization specification. (Spec is a PDF.)
- "Flatten your objects: Discover the secrets of the Java Serialization API" (Todd M. Greanier, JavaWorld, July 2000) offers a look into the nuts and bolts of the serialization process.
- Chapter 10 of Java RMI (William Grosso, O'Reilly, October 2001) is also a useful reference.
reference address:http://www.javaworld.com/article/2072752/the-java-serialization-algorithm-revealed.html
The Java serialization algorithm revealed---reference的更多相关文章
- 自己挖坑自己跳 之JsonMappingException: (was java.lang.NullPointerException) (through reference chain:)
在Web项目中,我们经常会设计一些与界面相对应的JavaBean作为Entity,而为了兼容前台传入的空值,有些字段我们会用包装类型而不是基本类型.可是往往我的Entity已经设计完成,很多时候我们会 ...
- java Serialization and Deserializaton
This article from JavaTuturial Java provides a mechanism, called object serialization where an objec ...
- JAVA Serialization 序列化
最近在做Android 项目时用到了WebView,可悲的是,在html上有无数用户的操作,而这些操作被JS返回给了Android的内存中,当深层的Activity开启时,之前的Activity很可能 ...
- Java密码体系结构简介:Java Cryptography Architecture (JCA) Reference Guide
来自Java官方的文档,作备忘使用. 简介: Java平台非常强调安全性,包括语言安全,密码学,公钥基础设施,认证,安全通信和访问控制. JCA是平台的一个主要部分,包含一个“提供者”体系结构和一组用 ...
- JAVA-基础(六) Java.serialization 序列化
序 列 化 序列化(serialization)是把一个对象的状态写入一个字节流的过程. Serializable接口 只有一个实现Serializable接口的对象可以被序列化工具存储和恢复.Ser ...
- Java中各种引用(Reference)解析
目录 1,引用类型 2, FinalReference 2.1, Finalizer 3, SoftReference 4, WeakReference 5, PhantomReference 6, ...
- java 方法引用(method reference)
it -> it != null等价于Objects::nonNull
- J2EE相关总结
Java Commons The Java™ Tutorials: http://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/index.html Java Platform, E ...
- 关键字transient是干啥的
百度百科的解释: Java语言的关键字,变量修饰符,如果用transient声明一个实例变量,当对象存储时,它的值不需要维持.换句话来说就是,用transient关键字标记的成员变量不参与序列化过程. ...
随机推荐
- angular 重定向路由
const routes: Routes = [ { path: '', redirectTo: '/home', pathMatch: 'full' }, { path: 'home', compo ...
- WinForm中DataGridView的使用(三) - 各种事件
CellMouseDown/CellMouseUp 可获得行.列号 可用if (rowIndex >= 0 && e.Y > 4 && e.Y < ( ...
- 20165219 《Java程序设计》实验一(Java开发环境的熟悉)实验报告
20165219 <Java程序设计>实验一(Java开发环境的熟悉)实验报告 一.实验报告封面 课程:Java程序设计 班级:1652班 姓名:王彦博 学号:20165219 成绩: 指 ...
- scrapy中通过set()方法进行数据过滤去重
我们经常在抓取数据是碰到 数据重复的问题,除了radis数据库去重功能外,还有一种简便的过滤方法, 来来 我们直接上代码: pipelines.py中: from scrapy.exceptions ...
- 【ARC083E】Bichrome Tree 树形dp
Description 有一颗N个节点的树,其中1号节点是整棵树的根节点,而对于第ii个点(2≤i≤N)(2≤i≤N),其父节点为PiPi 对于这棵树上每一个节点Snuke将会钦定一种颜色(黑或白), ...
- opencv学习笔记2
import cv2 as cvimport numpy as np"""#图像加法运算 即像素加法 (结果图=图1+图二) (两个图像必须是等大等类型的)image = ...
- 两种unix网络编程线程池的设计方法
unp27章节中的27.12中,我们的子线程是通过操作共享任务缓冲区,得到task的,也就是通过线程间共享的clifd[]数组,这个数组其实就是我们的任务数组,得到其中的connfd资源. 我们对这个 ...
- linux opencv版本查询
查看opencv安装路径: sudo find / -iname "*opencv*" 查看opencv版本: pkg-config opencv --modversion 查看o ...
- 【转】idea新建项目文件名为红色的解决办法
idea如果当前project用了版本控制器,其下面新建的所有的项目默认都是加入到版本控制里面,所以项目名称和文件都是红色的. 解决办法: ctrl + alt + s 进入设置界面,–>ver ...
- ubuntu画面延迟问题解决
新配的电脑,安装ubuntu16.04以后,出现画面延迟的问题,尤其浏览网页的时候画面十分卡顿.用free命令查看过可用内存6.多G,经过询问大概是显卡问题,然后在https://ubuntuforu ...
