小垃圾myl的课后实践
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int y,m,d,ans=,flag=;
printf("请输入年月日,并用逗号隔开\n");
scanf("%d,%d,%d",&y,&m,&d);
if((y%==)||((y%!=)&&(y%==)))flag=;//判断是否为闰年
m--;
switch(m){
case :ans+=;
case :ans+=;
case :ans+=;
case :ans+=;
case :ans+=;
case :ans+=;
case :ans+=;
case :ans+=;
case :ans+=;
case :ans=ans+flag+;
case :ans+=;
}
ans+=d;
printf("这一天是这一年的第%d天\n",ans);
return ;
}
计算某一天是这一年的第几天
模板类
//
// Created by Ma_Yiling on 2020/5/15.
// #ifndef CLION_ARRAY_H
#define CLION_ARRAY_H
template<typename T>
class Array{
public:
Array(int s);
virtual ~Array();
virtual const T &Entry(int index)const;
virtual void Enter(int index,const T & value);
protected:
int size;
T *element;
};
template<typename T>
Array<T>::Array(int s){
if(s>)size=s;
else size=;
element=new T[size];
} template<typename T>
Array<T>::~Array(){
delete []element;
} template<typename T>
const T& Array<T>::Entry(int index)const{
return element[index];
} template<typename T>
void Array<T>::Enter(int index,const T &value){
element[index]=value;
}
#endif //CLION_ARRAY_H
array.h
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include"Array.h"
int main(){
Array<int>IntAry();
for(int i=;i<;i++)IntAry.Enter(i,i);
cout<<"Integer Array:\n";
for(int i=;i<;i++)cout<<IntAry.Entry(i)<<'\t';
cout<<endl;
Array<double>DouAry();
for(int i=;i<;i++)DouAry.Enter(i,(i+)*0.35);
cout<<"Double Array:\n";
for(int i=;i<;i++)cout<<DouAry.Entry(i)<<'\t';
cout<<endl;
return ;
}
模板类
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class Complex{
public:
Complex(T r=,T i=):Real(r),Image(i){};
private:
T Real,Image;
template<typename U>
friend Complex<U> operator + (const Complex<U>&c1,const Complex<U>&c2); template<typename U>
friend Complex<U> operator - (const Complex<U>&c1,const Complex<U>&c2); template<typename U>
friend Complex<U> operator - (const Complex<U>&c); template<typename U>
friend ostream & operator << (ostream & output,const Complex<U>&c);
};
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
template<typename T>
Complex<T> operator + (const Complex<T>&c1,const Complex<T>&c2){
T r=c1.Real+c2.Real;
T i=c1.Image+c2.Image;
return Complex<T>(r,i);
} template<typename T>
Complex<T> operator - (const Complex<T>&c1,const Complex<T>&c2){
T r=c1.Real-c2.Real;
T i=c1.Image-c2.Image;
return Complex<T>(r,i);
} template<typename T>
Complex<T> operator - (const Complex<T>&c){
return Complex<T>(-c.Real,-c.Image);
} template<typename T>
ostream & operator << (ostream & output,const Complex<T>&c){
output<<"("<<c.Real<<","<<c.Image<<")\n";
return output;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main(){
Complex<double>c1(2.5,3.7),c2(4.2,6.5);
cout<<"c1 = "<<c1<<"c2 = "<<c2;
cout<<"c1 + c2 = "<<c1+c2;
cout<<"c1 - c2 = "<<c1-c2;
cout<<"-c1 = "<<-c1;
return ;
}
复数类用模板定义重载运算符 友元函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const double pi=3.14159;
template<typename T>class Circle{
private:
T radius;
static int total;
public:
Circle(T r=){radius = r;total++;}
void Set_Radius(T r){radius = r;}
double Get_Radius(){return radius;}
double Get_Girth(){return *radius*pi;}
double Get_Area(){return pi*radius*radius;}
static int ShowTotal(){
return total;
}
};
template<typename T>int Circle<T>::total=;
//template<typename T>
//int Circle<T>::ShowTotal(){return total;}
int main(){
return ;
}
静态数据成员
模板函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename ElementType>
void SortBubble(ElementType *a,int size){
int work;
ElementType temp;
for(int pass=;pass<size;pass++){
work=;
for(int i=;i<size-pass;i++){
if(a[i]>a[i+]){
temp=a[i];
a[i]=a[i+];
a[i+]=temp;
work=;
}
}
if(work)break;
}
} template <typename ElementType>
void Print(ElementType *x,int n){
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
printf("%d ",x[i]);
puts("");
} int main() {
int n,a[];
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
SortBubble(a,n);
Print(a,n);
}
冒泡排序
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
T Max(const T a,const T b){return a>b?a:b;}
template<typename T>
T Max(const T a,const T b,const T c)
{T t=Max(a,b);return Max(t,c);}
int Max(const int a,const char b){return a>b?a:b;}
int main(){
cout<<"Max(3,'a')is "<<Max(,'a')<<endl;
cout<<"Max(9.3,0.5)is "<<Max(9.3,0.5)<<endl;
cout<<"Max(9,5,23)is "<<Max(,,)<<endl;
return ;
}
模板函数的重载
重载运算符
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
class Complex{
private:
double real,image;
public:
Complex(){real=;image=;}
Complex(double x){real=x;image=;}
Complex(double x,double y){real=x;image=y;}
friend Complex operator -(const Complex & x);
friend Complex operator +(const Complex & x,const Complex & y);
friend Complex operator -(const Complex & x,const Complex & y);
void show(){
printf("( %.3f , %.3f )\n",real,image);
}
};
Complex operator -(const Complex & x){
Complex res;
res.real=-x.real;
res.image=-x.image;
return res;
}
Complex operator -(const Complex & x,const Complex & y){
Complex res;
res.real=x.real-y.real;
res.image=x.image-y.image;
return res;
}
Complex operator +(const Complex & x,const Complex & y){
Complex res;
res.real=x.real+y.real;
res.image=x.image+y.image;
return res;
}
int main(){
Complex a(,),b(),c(,);
Complex ans=-a+b-c-c;
ans.show();
}
用友元函数重载运算符
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
class point{
private:
int x,y;
public:
point(int xx,int yy){x=xx;y=yy;}
point(){x=;y=;}
point operator ++();
point operator ++(int);
void show(){
printf("( %d , %d )\n",x,y);
}
};
point point::operator ++(){
this->x++;
this->y++;
return *this;
}
point point::operator ++(int){
this->x++;
this->y++;
return *this;
}
int main(){
point a(,);
++a;a.show();
a++;a.show();
}
成员函数自增
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
class point{
private:
int x,y;
public:
point(int xx,int yy){x=xx;y=yy;}
point(){x=;y=;}
friend point operator ++(point &);
friend point operator ++(point &,int);//int为伪参数,目的是将前置式和后置式区分开来
void show(){
printf("( %d , %d )\n",x,y);
}
};
point operator ++(point &a){
a.x++;
a.y++;
return a;
}
point operator ++(point &a,int){
a.x++;
a.y++;
return a;
}
int main(){
point a(,);
++a;a.show();
a++;a.show();
}
友元函数自增
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
class Name{
private:
char *pName;
int size;
public:
Name(char *pN);
Name(const Name &);
Name& operator=(const Name &);
void show(){
printf("%s\n",pName);
}
};
Name::Name(char *pN){
pName=new char[strlen(pN)+];
if(pName!=)strcpy(pName,pN);
size=strlen(pN);
}
Name::Name(const Name & obj){
pName=new char[strlen(obj.pName)+];
if(pName!=)strcpy(pName,obj.pName);
size=obj.size;
}
Name & Name::operator=(const Name & obj){
delete []pName;
pName=new char[strlen(obj.pName)+];
if(pName!=)strcpy(pName,obj.pName);
size=obj.size;
return *this;
}
int main(){
Name Obj1("zhangsan");
Name Obj2=Obj1;
Obj2.show();
Name Obj3("NoName");
Obj3.show();
Obj3=Obj2=Obj1;
Obj3.show();
}
重载赋值运算符(只能用成员函数)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
class vector{
private:
int *v;
int size;
public:
vector(int n){v=new int[n];size=n;}
~vector(){delete []v;size=;}
int & operator [] (int i){return v[i];}
};
int main(){
vector a();
a[]=;
cout<<a[]<<endl;
cout<<a.operator[]()<<endl;
}
重载下标运算符[]
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class F{
public:
double operator ()(double x,double y);
};
double F::operator ()(double x,double y){
return x*x+y*y;
}
int main(){
F f;
cout<<f(5.2,2.5)<<endl;
return ;
}
重载函数调用符()
istream和ostream是C++的预定义流类
cin是istream的对象,cout是ostream的对象
运算符<<由ostream重载为插入操作,用于输出基本类型数据
运算符>>由istream重载为提取操作,用于输入基本类型数据
用友元函数重载<<和>>,输出和输入用户自定义的数据类型
重载的时候,形参作为实参的别名,而实参是cout,cout是类ostream的对象;同理,cin是istream的对象。
流插入和流提取运算符的重载返回的是流类引用,以符合原语义
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class vector{
public:
vector(int size=);
~vector();
int & operator[](int i);
friend ostream & operator<<(ostream & output,vector &);
friend istream & operator>>(istream & input,vector &);
private:
int *v;
int len;
};
vector::vector(int size){
if(size<=||size>){
cout<<"The size of "<<size<<" is null!\n";
exit();
}
v=new int[size];
len=size;
}
vector::~vector(){
delete[]v;
len=;
}
int & vector::operator[](int i){
if(i>=&&i<len)return v[i];
cout<<"The subscript "<<i<<" is outside !\n";exit();
}
ostream & operator << (ostream & output,vector & ary){//output是cout的别名
for(int i=;i<ary.len;i++)output<<ary[i]<<" ";
output<<endl;
return output;
}
istream & operator >> (istream & input,vector & ary){
for(int i=;i<ary.len;i++)input>>ary[i];
return input;
}
int main(){
int k;
cout<<"Input the length of vector A:\n";
cin>>k;
vector A(k);
cout<<"Input the elements of vector A:\n";
cin>>A;
cout<<"Output the elements of vector A:\n";
cout<<A;
return ;
}
重载<<和>>
类对象的类型转换可以由两种方式实现:构造函数、转换函数
称为用户定义的类型转换或类类型转换,有隐式调用和显式调用方式

带参数的构造函数不能把一个类类型转换成基本类型
类类型转换函数是一种特殊的成员函数,提供类对象之间显式类型转换的机制

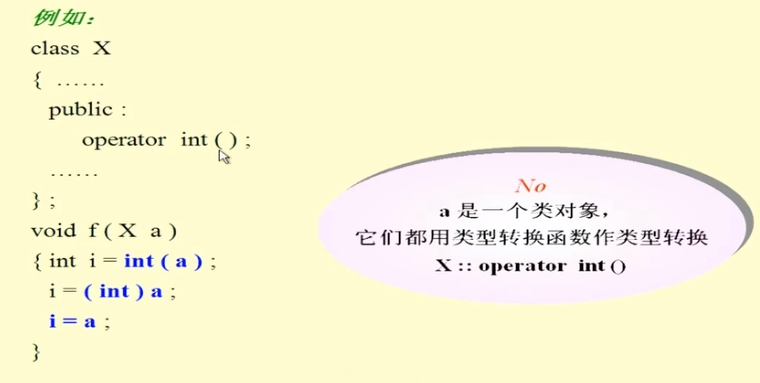

类型转换函数有两种使用方式:
隐式使用 i=a
显示使用 i=a.operator int()
使用不同函数作类型转换函数:
int i=a;//用类型转换函数进行转换
X i=a;//用构造函数进行转换
重载指针转换运算符
注意函数没有指定返回值的类型,这是语法的要求,跟其他重载函数不一样的地方,要注意
operator T * ();
Array<T>::operator T *(){
return list;
}
继承
静态成员在派生类中的调用:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class B{
public:
static void Add(){i++;}
static int i;
void out(){cout<<"static i="<<i<<endl;}
};
int B::i=;
class D: private B{
public:
void f(){
i=;
Add();
B::i++;
B::Add();
}
};
int main(){
B x;D y;
x.Add();
x.out();
y.f();
cout<<"static i="<<B::i<<endl;
cout<<"static i="<<x.i<<endl;
// cout<<"static i="<<y.i<<endl;
return ;
}
派生类的初始化
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
class parent_class{
private:
int data1,data2;
public:
parent_class(int p1,int p2){data1=p1;data2=p2;}
int inc1(){return ++data1;}
int inc2(){return ++data2;}
void display(){cout<<"data1="<<data1<<",data2="<<data2<<endl;}
};
class derived_class:private parent_class{
private:
int data3;
parent_class data4;
public:
derived_class(int p1,int p2,int p3,int p4,int p5):
parent_class(p1,p2),data4(p3,p4),data3(p5){}
int inc1(){return parent_class::inc1();}
int inc3(){return ++data3;}
void display(){
parent_class::display();
data4.display();
cout<<"data3="<<data3<<endl;
}
};
int main(){
derived_class d1(,,,,-);
d1.inc1();
d1.display();
return ;
}
派生类的初始化
排序
/*
题目:选择排序
作者:thmyl
日期:2019-10-17
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#define maxn 1010
using namespace std;
int n,a[maxn];
int main(){
printf("请输入数字的个数:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("请输入需要排序的数字:\n");
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=i+;j<=n;j++){
if(a[i]>a[j])swap(a[i],a[j]);
}
}
printf("排好序后的数列为:\n");
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)printf("%d ",a[i]);
puts("");
return ;
}
选择排序
/*
题目:冒泡排序
作者:thmyl
日期:2019-10-17
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#define maxn 1010
using namespace std;
int n,a[maxn];
int main(){
printf("请输入数字的个数:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("请输入需要排序的数字:\n");
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=n;j>i;j--)//从后向前浮动
if(a[j]<a[j-])swap(a[j],a[j-]);
printf("排好序后的数列为:\n");
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)printf("%d ",a[i]);
puts("");
return ;
}
冒泡排序
/*
ìa??:2???±??-DòáDμ??3Dò£?ê?3???óDDòêyáD
×÷??:thmyl
è??ú:2019-10-18
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#define maxn 1010
using namespace std;
int a[maxn],n,mn,mark;
int *p[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
int main(){
printf("请输入数字的个数:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("请输入需要排序的数字:\n");
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){//?°?òμúi′óμ?êy
mn=0x7fffffff;
for(int j=;j<=n;j++)
if(a[j]<mn&&!vis[j])
mn=a[j],mark=j;
p[i]=&a[mark];
vis[mark]=;
}
printf("排好序后的数列为:\n");
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)printf("%d ",*p[i]);
puts("");
return ;
}
用指针排序
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#define maxn 100010
using namespace std;
int n,a[maxn],b[maxn];
void Sort(int l,int r){
if(l==r)return;
int mid=(l+r)>>;
Sort(l,mid);
Sort(mid+,r);
int i=l,j=mid+;
int cnt=l-;
while(i<=mid&&j<=r){
if(a[i]<=a[j]){
b[++cnt]=a[i++];
}
else b[++cnt]=a[j++];
}
while(i<=mid)b[++cnt]=a[i++];
while(j<=r)b[++cnt]=a[j++];
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++)a[i]=b[i];
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
Sort(,n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)printf("%d ",a[i]);
puts("");
return ;
}
归并排序
指针
int *a[10]:定义了10个指向整型元素的指针
int (*a)[10]:定义了一个指针,指向一个有10个整型元素的数组

#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int b[][];
int (*a)[];
int main(){
int cnt=;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
for(int j=;j<;j++){
b[i][j]=cnt;
cnt++;
}
a=b;
for(int i=;i<;i++,a++){
for(int *p=*a,j=;j<;j++,p++){
printf("%d ",*p);
}
puts("");
}
return ;
}
用(*a)[10]指向二维数组的用法
(2019.10.24)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N=;
void input(int *a,int N){//事实上没有定义数组,而是传递了数组的地址,设a[]或*a都可以,用法相同
for(int i=;i<N;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
void index(int *a,int N){
for(int i=;i<N;i++)
for(int j=i+;j<N;j++)
if(a[i]>a[j])swap(a[i],a[j]);
}
void output(int *a,int N){
for(int i=;i<N;i++)printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
int main(){
freopen("Cola.txt","r",stdin);
int a[N];
input(a,N);
index(a,N);
output(a,N);
return ;
}
函数的参数传递(数组)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N=;
int main(){
int a[N];
void input(int *a,int N);
void index(int *a,int N);
void output(int *a,int N);
input(a,N);
index(a,N);
output(a,N);
return ;
}
void input(int *a,int N){//事实上没有定义数组,而是传递了数组的地址,设a[]或*a都可以,用法相同
for(int i=;i<N;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
void index(int *a,int N){
for(int i=;i<N;i++)
for(int j=i+;j<N;j++)
if(a[i]>a[j])swap(a[i],a[j]);
}
void output(int *a,int N){
for(int i=;i<N;i++)printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
事先声明函数
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#define N 10
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b,c;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
#ifdef N
c=a+b;
#else
c=a-b;
#endif
printf("%d",c);
return ;
}
#ifdef
//这里的if后面的条件必须宏定义
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int a,b;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&a);
#if(a>0)//Error
b=a;
#else
b=-a;
#endif
printf("%d\n",b);
return ;
}
#if
//不要输出一个一个的数,要先组成一个数然后再输出。
//据说某sp考试能检测你的输出方式,嗯哼哼?
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int i=,n,a[],sum=;
printf("Please input a number in 5 single numbers:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n){
a[i]=n%;
n/=;
i++;
}
for(int i=;i<;i++)
for(int j=i+;j<;j++)
if(a[j]>a[i])swap(a[i],a[j]);
printf("The largest number is:");
for(int i=;i<;i++){
sum=sum*+a[i];
}
printf("%d\n",sum);
printf("The smallest number is:");
i=;
while(a[i]==)i--;
swap(a[],a[i]);
sum=;
for(int i=;i>=;i--){
sum=sum*+a[i];
}
printf("%d\n",sum);
return ;
}
输入一个5位数,输出其组合的最大数和最小数
(2019.10.25)
标准输入输出
/*scanf*/
%f float
%lf double
%Lf long double /*printf*/
%f float/double
%Lf long double
浮点数
malloc和free函数
malloc:
int *p;
p=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*100);
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int *p,n;
int main(){
freopen("Cola.txt","r",stdin);
scanf("%d",&n);
p=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(n+));
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&p[i]);
sort(p+,p+n+);
// free(p);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)printf("%d ",p[i]);
puts("");
free(p);
return ;
}
malloc&free
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
struct node{
int data;
node *next;
};
int main(){
int i,j,k,m,n;
node *h,*p,*q;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
h=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
h->data=;
h->next=h;
p=h;
for(i=;i<=n;i++){
q=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
q->data=i;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
}
p=h;
k=;//µ±Ç°Ëù±¨µÄÊý
while(p->next!=p){
if(k<m-){
k++;
p=p->next;
}
else if(k==m-){
q=p->next;
p->next=p->next->next;
printf("%d--",q->data);
free(q);
k=;
p=p->next;
}
}
printf("%d\n",p->data);
return ;
}
malloc、结构体和指针实现约瑟夫环
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<malloc.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
struct Tree{
int data,v;
Tree *lson;
Tree *rson;
};
Tree *p,*root;
void Insert(int x){
Tree *q;
// q=(Tree*)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
q=root;
while(){
if((p->v)>=(q->v)){
if(q->rson==NULL){
q->rson=p;
return;
}
else {
q=q->rson;
}
}
else {
if(q->lson==NULL){
q->lson=p;
return;
}
else {
q=q->lson;
}
}
}
}
void dfs(Tree *q){
printf("%d ",q->v);
if(q->lson!=NULL)
dfs(q->lson);
if(q->rson!=NULL)
dfs(q->rson);
}
int main(){
freopen("Cola.txt","r",stdin);
int x;
scanf("%d",&n);
root=(Tree*)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
scanf("%d",&x);
root->data=;
root->v=x;
root->lson=NULL;
root->rson=NULL;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&x);
p=(Tree*)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
p->data=i;
p->v=x;
p->lson=NULL;
p->rson=NULL;
Insert(x);
}
dfs(root);
return ;
}
malloc、结构体和指针实现二叉排序树
(2019.11.21)
链表
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<malloc.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int data;
node* next;
};
node* head=NULL;
bool creat_node_list(){
head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(NULL==head)return false;
else {
head->data=;
head->next=NULL;
return ;
}
}
bool Insert(node* point){
if(NULL==head)return ;
node* p=head->next;
node* q=head;
while(p!=NULL){
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
q->next=point;
point->next=NULL;
return ;
}
void reverse_list(){
if(head==NULL)return;
if(head->next==NULL)return;
node* p=head->next;
node* q=p->next;
node* t=NULL;
while(q!=NULL){
t=q->next;
q->next=p;
p=q;
q=t;
}
head->next->next=NULL;
head->next=p;
}
void sort(){
node* Head=head;
if(head==NULL)return;
if(Head->next==NULL)return;
node* pi=Head->next;
node* pj=pi->next;
for(;pi!=NULL;pi=pi->next){
for(pj=pi->next;pj!=NULL;pj=pj->next){
if(pj->data>pi->data)
swap(pj->data,pi->data);
}
}
}
bool deletenode(int id){
if(head==NULL)return ;
node* p=head->next;
int len=;
while(p!=NULL){
len++;
p=p->next;
}
if(len<id)return ;
else {
node* q=head;
p=head;
for(int i=;i<id;i++){
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
node* t=p->next;
q->next=t;
free(p);
return ;
}
}
void destorylist(){
if(head==NULL)return;
if(head->next==NULL){
free(head);
head=NULL;
return;
}
node* p=head->next;
while(NULL!=p){
node* tmp=p;
p=p->next;
free(tmp);
}
free(head);
head=NULL;
}
void check(){
if(head==NULL){
puts("序列中没有任何元素");
return;
}
else if(head->next==NULL){
printf("%d\n",head->data);
return;
}
else {
node* p=head;
node* q=p->next;
while(p->next!=NULL){
printf("%d ",p->data);
p=q;
q=q->next;
}
printf("%d ",p->data);
puts("");
} }
int main(){
creat_node_list();
printf("%d\n",head->data);
node* node1=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
node1->data=;
node1->next=NULL; node* node2=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
node2->data=;
node2->next=NULL; Insert(node1);
Insert(node2);
check(); reverse_list();
check(); node* node3=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
node3->data=;
node3->next=NULL; Insert(node3);
sort();
check();
deletenode();
check();
destorylist(); return ;
}
链表基本操作
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<malloc.h>
using namespace std;
struct list{
int data;
list* next;
};
list* head=NULL;
void creat_list(){
head=(list*)malloc(sizeof(list));
if(head==NULL)return;
else {
head->data=;
head->next=NULL;
}
}
list* Insert(list* h,int x){
if(h==NULL||h->next==NULL){
list* p;
p=(list*)malloc(sizeof(list));
p->data=x;
p->next=NULL;
h->next=p;
return h;
}
if(head->next->data>=x){//x插到第一个位置
list* p;
p=(list*)malloc(sizeof(list));
p->data=x;
p->next=h->next;
h->next=p;
return h;
}
else {
list* q=h->next;
list* p=q->next;
list* t;
bool flag=;//标记是否插入成功
while(p!=NULL){
if(p->data>=x&&q->data<x){
flag=;
t=(list*)malloc(sizeof(list));
t->data=x;
t->next=p;
q->next=t;
break;
}
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
if(!flag){
t=(list*)malloc(sizeof(list));
t->data=x;
t->next=NULL;
q->next=t;
}
return h;
}
}
list* remove(list* h,int x){
list* q=head->next;
if(q->data==x){
h->next=q->next;
free(q);
return h;
}
if(q->next==NULL){
free(q);
head->next=NULL;
return h;
}
list* p=q->next;
while(p!=NULL){
if(p->data==x){
q->next=p->next;
free(p);
return h;
}
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
}
void check(){
list* p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL){
printf("%d ",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
puts("");
}
int main(){
freopen("Cola.txt","r",stdin);
int n,x;
puts("请输入整数的个数:");
scanf("%d",&n);
creat_list();
puts("请输入要排序的数列:");
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&x);
Insert(head,x);
check();
}
puts("请输入要删除的数的个数:");
scanf("%d",&n);
puts("请依次输入要删除的数");
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&x);
remove(head,x);
check();
}
return ;
}
指针链表实现序列插入、删除
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<malloc.h>
#define Abs(x) ((x)>=0?(x):(-x))
using namespace std;
struct node{
int a,b;//系数为a,指数为b
node* next;
};
node *head[];
void creat_node(node* &h){
h=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(h==NULL)return;
else{
h->a=;
h->b=;
h->next=NULL;
return;
}
}
void Insert(node* &h,int x,int y){
if(h==NULL||h->next==NULL){
node *q;
q=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
q->a=x;
q->b=y;
q->next=NULL;
h->next=q;
return;
}
else {
node* p=h->next;
node* q=h;
node* t;
t=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
t->a=x;
t->b=y;
t->next=NULL;
while(p!=NULL){
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
q->next=t;
return;
}
}
void reverse(node* &h){//把链表反转
if(h==NULL||h->next==NULL)return;
node* p=h->next;
node* q=h;
node* t;
bool flag=;//判断是否是链表的第一个元素
while(p!=NULL){
t=p->next;
if(!flag)p->next=NULL,flag=;
else p->next=q;
q=p;
p=t;
}
h->next=q;
}
void calc1(node* &h1,node* &h2,node* &h3){
creat_node(h3);
node* p1=h1->next;
node* p2=h2->next;
node* p3;
node* q=h3;
while(p1!=NULL&&p2!=NULL){
int x=(p1->a)+(p2->a);
if(x!=){
p3=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p3->a=x;
p3->b=p1->b;
p3->next=NULL;
q->next=p3;
q=p3;
}
p1=p1->next;
p2=p2->next;
}
while(p1!=NULL){//易错!不能把p1直接赋值给q,否则head[3]链表会有一部分指向head[2]链表,链表之间失去独立性
p3=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p3->a=p1->a;
p3->b=p1->b;
p3->next=p1->next;
q->next=p3;
q=q->next;
p1=p1->next;
}
while(p2!=NULL){
p3=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p3->a=p2->a;
p3->b=p2->b;
p3->next=p2->next;
q->next=p3;
q=q->next;
p2=p2->next;
}
}
void calc2(node* &h1,node* &h2,node* &h3){
creat_node(h3);
node* p1=h1->next;
node* p2=h2->next;
node* p3;
node* q=h3;
while(p1!=NULL&&p2!=NULL){
int x=(p1->a)-(p2->a);
if(x!=){
p3=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p3->a=x;
p3->b=p1->b;
p3->next=NULL;
q->next=p3;
q=p3;
}
p1=p1->next;
p2=p2->next;
}
while(p1!=NULL){
p3=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p3->a=p1->a;
p3->b=p1->b;
p3->next=p1->next;
q->next=p3;
q=q->next;
p1=p1->next;
}
while(p2!=NULL){
p3=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p3->a=-(p2->a);
p3->b=p2->b;
p3->next=p2->next;
q->next=p3;
q=q->next;
p2=p2->next;
}
}
void check(node* &h){
if(h==NULL||h->next==NULL)return;
node* q=h->next;
bool flag=;
while(q->next!=NULL){
if(!flag)printf("%d*x^%d",q->a,q->b),flag=;
else printf("%d*x^%d",Abs(q->a),q->b);
if(q->next->a>)printf(" + ");
else printf(" - ");
q=q->next;
}
if(q!=NULL)printf("%d*x^%d\n",Abs(q->a),q->b);
}
int main(){
freopen("Cola.txt","r",stdin);
int n,x;
creat_node(head[]);
creat_node(head[]);
//-------------------------------------------------
puts("请输入第一个多项式的项数:");
scanf("%d",&n);
puts("请依次输入每一项的系数:");
// creat_node(head[1]);
for(int i=n-;i>=;i--){
scanf("%d",&x);
Insert(head[],x,i);
}
// check(head[1]);
reverse(head[]);
// check(head[1]);
//--------------------------------------------------
puts("请输入第二个多项式的项数:");
scanf("%d",&n);
puts("请依次输入每一项的系数:");
// creat_node(head[2]);
for(int i=n-;i>=;i--){
scanf("%d",&x);
Insert(head[],x,i);
}
// check(head[2]);
reverse(head[]);
// check(head[2]);
//----------------------------------------------------
puts("两多项式之和为:");
calc1(head[],head[],head[]);//加法运算
reverse(head[]);
check(head[]);
free(head[]);
//-----------------------------------------------------
puts("两多项式之差为:");
calc2(head[],head[],head[]);//减法运算
reverse(head[]);
check(head[]); return ;
}
链表实现多项式加减法
小垃圾myl的课后实践的更多相关文章
- 课后实践之mybash20155314
课后实践之mybash 实践要求 加分题-mybash的实现 使用fork,exec,wait实现mybash 写出伪代码,产品代码和测试代码 发表知识理解,实现过程和问题解决的博客(包含代码托管链接 ...
- 小鹏汽车技术中台实践 :微服务篇 InfoQ 今天 以下文章来源于InfoQ Pro
小鹏汽车技术中台实践 :微服务篇 InfoQ 今天 以下文章来源于InfoQ Pro
- Go 的垃圾回收机制在实践中有哪些需要注意的地方(转)
在网上看到一篇非常好的文章http://www.zhihu.com/question/21615032,转载如下: go的gc还不完善但也不算不靠谱,关键看怎么用,尽量不要创建大量对象,也尽量不要频繁 ...
- 微信小程序开发入门与实践
基础知识---- MINA 框架 为方便微信小程序开发,微信为小程序提供了 MINA 框架,这套框架集成了大量的原生组件以及 API.通过这套框架,我们可以方便快捷的完成相关的小程序开发工作. MIN ...
- 前端小微团队的Gitlab实践
疫情期间我感觉整个人懒散了不少,慢慢有意识要振作起来了,恢复到正常的节奏.最近团队代码库从Gerrit迁移到了Gitlab,为了让前端团队日常开发工作有条不紊,高效运转,开发历史可追溯,我也查阅和学习 ...
- 京东购物小程序 | Taro3 项目分包实践
背景 京东购物小程序作为京东小程序业务流量的主要入口,承载着许多的活动和页面,而很多的活动在小程序开展的同时,也会在京东 APP 端进行同步的 H5 端页面的投放.这时候,一个相同的活动,需要同时开发 ...
- 微信小程序从入门到实践(一)-设置底部导航栏
微信小程序最多能加5个导航图标.因为我们只有两个默认页面,这里我们就添加两个导航图标 先看我们要达到的就是这么一个效果 接下来开始实践: (1)准备工作 找几个图标,将上述起好名字的图标 保存到 小程 ...
- 海量小文件存储与Ceph实践
海量小文件存储(简称LOSF,lots of small files)出现后,就一直是业界的难题,众多博文(如[1])对此问题进行了阐述与分析,许多互联网公司也针对自己的具体场景研发了自己的存储方案( ...
- 一个小团队TDD游戏及实践
介绍的这个游戏是自己根据目前带的团队的实际情况来制定的, 在游戏实践过程中,收到了较好的效果,故打算把这个游戏分享出来,一是分享一下实践,而是集思广益,不断完善,更好的利用游戏来锻炼队伍.下面就将游戏 ...
随机推荐
- jenkins报错:Problem accessing /jenkins/. Reason: HTTP ERROR 404
这是一个Jenkins的Bug.临时解决方法是:在浏览器中手工输入:http://<ip>:<port>.不要访问"/jenkins"这个路径.
- 用vbs和ADSI管理Windows账户
ADSI (Active Directory Services Interface)是Microsoft新推出的一项技术,它统一了许多底层服务的编程接口,程序员可以使用一致的对象技术来访问这些底层服务 ...
- vb.net 带有一个参数的线程
For Each _row As DataGridViewRow In datagridview.Rows 'searchRecords_refreshRow(_row) ' 上面以前,直接运行函数, ...
- zabbix--完整安装攻略
zabbix:是一个基于WEB界面的提供分布式系统监视以及网络监视功能的企业级的开源解决方案. zabbix能监视各种网络参数,保证服务器系统的安全运营:并提供灵活的通知机制以让系统管理员快速定位/解 ...
- React: React的复合组件
一.介绍 不论Web界面是多么的复杂,它都是由一个个简单的组件组合起来实现的,既然会创建一个简单的组件,那么复杂的组件就有了下手的切入点了.现在来实现一个简单的复合组件.一个颜色面板,一共三部分组成. ...
- IT兄弟连 Java语法教程 数组 深入数组 内存中的数组
数组是一种引用数据类型,数组引用变量只是一个引用,数组元素和数组变量在内存里是分开存放的.下面将深入介绍数组在内存中的运行机制. 内存中的数组 数组引用变量只是一个引用,这个引用变量可以指向任何有效的 ...
- ABP开发框架前后端开发系列---(6)ABP基础接口处理和省份城市行政区管理模块的开发
最近没有更新ABP框架的相关文章,一直在研究和封装相关的接口,总算告一段落,开始继续整理下开发心得.上次我在随笔<ABP开发框架前后端开发系列---(5)Web API调用类在Winform项目 ...
- oracle学习笔记(二十一) 程序包
程序包 之前我们调用的dbms_output.put_line(''),dbms_output就是一个程序包 程序包创建语法 1. 声明程序包 --声明程序包中的过程,函数,自定义的类型 --程序包里 ...
- 练手WPF(二)——2048游戏的简易实现(上)
1.创建游戏界面编辑MainWindow.xaml,修改代码如下: <Window.Resources> <Style TargetType="Label"> ...
- go-家庭收支记账软件例子
家庭收支记账软件项目 项目需求说明 1) 模拟实现基于文本界面的<家庭记账软件> 2) 该软件能够记录家庭的收入.支出,并能够打印收支明细表 项目的界面 看代码效果 项目代码实现 实现基本 ...
