Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2)
A. Elections
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
The country of Byalechinsk is running elections involving n candidates. The country consists of m cities. We know how many people in each city voted for each candidate.
The electoral system in the country is pretty unusual. At the first stage of elections the votes are counted for each city: it is assumed that in each city won the candidate who got the highest number of votes in this city, and if several candidates got the maximum number of votes, then the winner is the one with a smaller index.
At the second stage of elections the winner is determined by the same principle over the cities: the winner of the elections is the candidate who won in the maximum number of cities, and among those who got the maximum number of cities the winner is the one with a smaller index.
Determine who will win the elections.
The first line of the input contains two integers n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100) — the number of candidates and of cities, respectively.
Each of the next m lines contains n non-negative integers, the j-th number in the i-th line aij (1 ≤ j ≤ n, 1 ≤ i ≤ m, 0 ≤ aij ≤ 109) denotes the number of votes for candidate j in city i.
It is guaranteed that the total number of people in all the cities does not exceed 109.
Print a single number — the index of the candidate who won the elections. The candidates are indexed starting from one.
3 3
1 2 3
2 3 1
1 2 1
2
3 4
10 10 3
5 1 6
2 2 2
1 5 7
1
Note to the first sample test. At the first stage city 1 chosen candidate 3, city 2 chosen candidate 2, city 3 chosen candidate 2. The winner is candidate 2, he gained 2 votes.
Note to the second sample test. At the first stage in city 1 candidates 1 and 2 got the same maximum number of votes, but candidate 1 has a smaller index, so the city chose candidate 1. City 2 chosen candidate 3. City 3 chosen candidate 1, due to the fact that everyone has the same number of votes, and 1 has the smallest index. City 4 chosen the candidate 3. On the second stage the same number of cities chose candidates 1 and 3. The winner is candidate 1, the one with the smaller index.
题解:O(n+m)模拟
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#define PAU putchar(' ')
#define ENT putchar('\n')
using namespace std;
const int maxn=+;
int A[maxn][maxn],n,m,mx[maxn],cnt[maxn];
inline int read(){
int x=;bool sig=;char ch=getchar();
for(;!isdigit(ch);ch=getchar())if(ch=='-')sig=;
for(;isdigit(ch);ch=getchar())x=*x+ch-'';
return sig?x:-x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x==){putchar('');return;}if(x<)putchar('-'),x=-x;
int len=,buf[];while(x)buf[len++]=x%,x/=;
for(int i=len-;i>=;i--)putchar(buf[i]+'');return;
}
int main(){
n=read();m=read();
for(int i=;i<=m;i++){
for(int j=;j<=n;j++){
A[i][j]=read();
}
}
for(int i=;i<=m;i++){
mx[i]=;
for(int j=;j<=n;j++){
if(A[i][j]>A[i][mx[i]])mx[i]=j;
}
cnt[mx[i]]++;
}
int winer=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)if(cnt[i]>cnt[winer])winer=i;write(winer);
return ;
}
B. Simple Game
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
One day Misha and Andrew were playing a very simple game. First, each player chooses an integer in the range from 1 to n. Let's assume that Misha chose number m, and Andrew chose number a.
Then, by using a random generator they choose a random integer c in the range between 1 and n (any integer from 1 to n is chosen with the same probability), after which the winner is the player, whose number was closer to c. The boys agreed that if m and a are located on the same distance from c, Misha wins.
Andrew wants to win very much, so he asks you to help him. You know the number selected by Misha, and number n. You need to determine which value of a Andrew must choose, so that the probability of his victory is the highest possible.
More formally, you need to find such integer a (1 ≤ a ≤ n), that the probability that 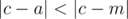 is maximal, where c is the equiprobably chosen integer from 1 to n (inclusive).
is maximal, where c is the equiprobably chosen integer from 1 to n (inclusive).
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 109) — the range of numbers in the game, and the number selected by Misha respectively.
Print a single number — such value a, that probability that Andrew wins is the highest. If there are multiple such values, print the minimum of them.
3 1
2
4 3
2
In the first sample test: Andrew wins if c is equal to 2 or 3. The probability that Andrew wins is 2 / 3. If Andrew chooses a = 3, the probability of winning will be 1 / 3. If a = 1, the probability of winning is 0.
In the second sample test: Andrew wins if c is equal to 1 and 2. The probability that Andrew wins is 1 / 2. For other choices of a the probability of winning is less.
题解:还是很简单的啊?窝萌的最优策略YY一下肯定是贴着那个人呗,那么分情况讨论一下就好喽。注意n==1的情况。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#define PAU putchar(' ')
#define ENT putchar('\n')
using namespace std;
inline int read(){
int x=;bool sig=;char ch=getchar();
for(;!isdigit(ch);ch=getchar())if(ch=='-')sig=;
for(;isdigit(ch);ch=getchar())x=*x+ch-'';
return sig?x:-x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x==){putchar('');return;}if(x<)putchar('-'),x=-x;
int len=,buf[];while(x)buf[len++]=x%,x/=;
for(int i=len-;i>=;i--)putchar(buf[i]+'');return;
}
double n,m;
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;double mid=(n+)*0.5;
if(n==){
write();
return ;
}
if(n==){
write(-m);
return ;
}
if(m>=mid)write(m-);
else write(m+);
return ;
}
C. Replacement
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Daniel has a string s, consisting of lowercase English letters and period signs (characters '.'). Let's define the operation of replacementas the following sequence of steps: find a substring ".." (two consecutive periods) in string s, of all occurrences of the substring let's choose the first one, and replace this substring with string ".". In other words, during the replacement operation, the first two consecutive periods are replaced by one. If string s contains no two consecutive periods, then nothing happens.
Let's define f(s) as the minimum number of operations of replacement to perform, so that the string does not have any two consecutive periods left.
You need to process m queries, the i-th results in that the character at position xi (1 ≤ xi ≤ n) of string s is assigned value ci. After each operation you have to calculate and output the value of f(s).
Help Daniel to process all queries.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 300 000) the length of the string and the number of queries.
The second line contains string s, consisting of n lowercase English letters and period signs.
The following m lines contain the descriptions of queries. The i-th line contains integer xi and ci (1 ≤ xi ≤ n, ci — a lowercas English letter or a period sign), describing the query of assigning symbol ci to position xi.
Print m numbers, one per line, the i-th of these numbers must be equal to the value of f(s) after performing the i-th assignment.
10 3
.b..bz....
1 h
3 c
9 f
4
3
1
4 4
.cc.
2 .
3 .
2 a
1 a
1
3
1
1
Note to the first sample test (replaced periods are enclosed in square brackets).
The original string is ".b..bz....".
- after the first query f(hb..bz....) = 4 ("hb[..]bz...." → "hb.bz[..].." → "hb.bz[..]." → "hb.bz[..]" → "hb.bz.")
- after the second query f(hbс.bz....) = 3 ("hbс.bz[..].." → "hbс.bz[..]." → "hbс.bz[..]" → "hbс.bz.")
- after the third query f(hbс.bz..f.) = 1 ("hbс.bz[..]f." → "hbс.bz.f.")
Note to the second sample test.
The original string is ".cc.".
- after the first query: f(..c.) = 1 ("[..]c." → ".c.")
- after the second query: f(....) = 3 ("[..].." → "[..]." → "[..]" → ".")
- after the third query: f(.a..) = 1 (".a[..]" → ".a.")
- after the fourth query: f(aa..) = 1 ("aa[..]" → "aa.")
题解:好囧的题。。。比赛的时候就想起来那道序列的题了。。。于是开始敲分块啊。。。各种讨论啊。。。伤不起啊。。。
早晨起来这么一想,窝萌为啥要维护块啊哥哥。。。修改操作的影响是很小的啊。。。一开始统计完了不就行了嘛。。。呜呜呜~~~~(>_<)~~~~
于是来一发计算贡献就水过了。。。。。。。。。。。有个细节:窝萌不需要讨论完整,无意义的变换(比如点换点之类的。。。)可以让程序自己抵消哦。。。
比赛的时候代码能力喂狗了。。。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#define PAU putchar(' ')
#define ENT putchar('\n')
using namespace std;
const int maxn=+;
char s[maxn];
char str[];
inline int read(){
int x=;bool sig=;char ch=getchar();
for(;!isdigit(ch);ch=getchar())if(ch=='-')sig=;
for(;isdigit(ch);ch=getchar())x=*x+ch-'';
return sig?x:-x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x==){putchar('');return;}if(x<)putchar('-'),x=-x;
int len=,buf[];while(x)buf[len++]=x%,x/=;
for(int i=len-;i>=;i--)putchar(buf[i]+'');return;
}
int main(){
int n,m; cin >> n >> m; scanf("%s",s); int res = ; for (int i = ; i < n - ; i++) if (s[i] == s[i + ] && s[i] == '.') {
res++;
} while(m--) {
int pos; scanf("%d%s",&pos,str); --pos;
if (pos > && s[pos] == s[pos - ] && s[pos] == '.') res--;
if (pos + < n && s[pos] == s[pos + ] && s[pos] == '.') res--;
s[pos] = str[];
if (pos > && s[pos] == s[pos - ] && s[pos] == '.') res++;
if (pos + < n && s[pos] == s[pos + ] && s[pos] == '.') res++;
printf("%d\n",res);
}
return ;
}
D. Tree Requests
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Roman planted a tree consisting of n vertices. Each vertex contains a lowercase English letter. Vertex 1 is the root of the tree, each of the n - 1 remaining vertices has a parent in the tree. Vertex is connected with its parent by an edge. The parent of vertex i is vertex pi, the parent index is always less than the index of the vertex (i.e., pi < i).
The depth of the vertex is the number of nodes on the path from the root to v along the edges. In particular, the depth of the root is equal to 1.
We say that vertex u is in the subtree of vertex v, if we can get from u to v, moving from the vertex to the parent. In particular, vertex v is in its subtree.
Roma gives you m queries, the i-th of which consists of two numbers vi, hi. Let's consider the vertices in the subtree vi located at depthhi. Determine whether you can use the letters written at these vertices to make a string that is a palindrome. The letters that are written in the vertexes, can be rearranged in any order to make a palindrome, but all letters should be used.
The first line contains two integers n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 500 000) — the number of nodes in the tree and queries, respectively.
The following line contains n - 1 integers p2, p3, ..., pn — the parents of vertices from the second to the n-th (1 ≤ pi < i).
The next line contains n lowercase English letters, the i-th of these letters is written on vertex i.
Next m lines describe the queries, the i-th line contains two numbers vi, hi (1 ≤ vi, hi ≤ n) — the vertex and the depth that appear in thei-th query.
Print m lines. In the i-th line print "Yes" (without the quotes), if in the i-th query you can make a palindrome from the letters written on the vertices, otherwise print "No" (without the quotes).
6 5
1 1 1 3 3
zacccd
1 1
3 3
4 1
6 1
1 2
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
String s is a palindrome if reads the same from left to right and from right to left. In particular, an empty string is a palindrome.
Clarification for the sample test.
In the first query there exists only a vertex 1 satisfying all the conditions, we can form a palindrome "z".
In the second query vertices 5 and 6 satisfy condititions, they contain letters "с" and "d" respectively. It is impossible to form a palindrome of them.
In the third query there exist no vertices at depth 1 and in subtree of 4. We may form an empty palindrome.
In the fourth query there exist no vertices in subtree of 6 at depth 1. We may form an empty palindrome.
In the fifth query there vertices 2, 3 and 4 satisfying all conditions above, they contain letters "a", "c" and "c". We may form a palindrome "cac".
题解:dfs一遍,把东西扔到vector里,维护一下括号序,询问时二分vector。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define scan(x) do{while((x=getchar())<'0'); for(x-='0'; '0'<=(_=getchar()); x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+_-'0');}while(0)
char _;
using namespace std;
int N, M;
char S[];
vector<int> occ[][];
int in[], out[], now;
struct ted{int x,y;ted*nxt;}adj[+],*fch[+],*ms=adj;
void add(int x,int y){
*ms=(ted){x,y,fch[x]};fch[x]=ms++;
}
void dfs(int u, int depth)
{
occ[depth][S[u]-'a'].push_back(++now);
in[u]=now;
for(ted*e=fch[u];e;e=e->nxt)
dfs(e->y, depth+);
out[u]=now;
}
int main()
{
scan(N);
scan(M);
for(int i=; i<=N; i++)
{
int a;
scan(a);add(a,i);
}
scanf("%s", S+);
dfs(, );
while(M--)
{
int v, h;
scan(v);
scan(h);
int odd=;
for(int i=; i<; i++)
{
int cnt=upper_bound(occ[h][i].begin(), occ[h][i].end(), out[v])-
upper_bound(occ[h][i].begin(), occ[h][i].end(), in[v]);
if(cnt%==)
{
odd++;
if(odd>)
break;
}
}
if(odd>)
printf("No\n");
else
printf("Yes\n");
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) C. Replacement set
C. Replacement Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/570/proble ...
- Codeforces Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) C. Replacement 线段树
C. ReplacementTime Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/570/problem ...
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) C. Replacement
题意:给定一个字符串,里面有各种小写字母和' . ' ,无论是什么字母,都是一样的,假设遇到' . . ' ,就要合并成一个' .',有m个询问,每次都在字符串某个位置上将原来的字符改成题目给的字符, ...
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) B. Simple Game
思路:把n分成[1,n/2],[n/2+1,n],假设m在左区间.a=m+1,假设m在右区间,a=m-1.可是我居然忘了处理1,1这个特殊数据.被人hack了. 总结:下次一定要注意了,提交前一定要看 ...
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) D计算在一棵子树内某高度的节点
题:https://codeforces.com/contest/570/problem/D 题意:给定一个以11为根的n个节点的树,每个点上有一个字母(a~z),每个点的深度定义为该节点到11号节点 ...
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) D. Tree Requests dfs序
D. Tree Requests time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard in ...
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) D、E
Problem D: 题意:给定一棵n个点树,每个点有一个字母,有m个询问,每次询问某个节点x的子树中所有深度为k的点能否组成一个回文串 分析:一堆点能组成回文串当且仅当数量为奇数的字母不多于1个,显 ...
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2C) 570C Replacement
题目:Click here 题意:看一下题目下面的Note就会明白的. 分析:一开始想的麻烦了,用了树状数组(第一次用)优化,可惜没用. 直接判断: #include <bits/stdc++. ...
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2B) 570B Simple Game 贪心
题目:Click here #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int IN ...
随机推荐
- [转] git config命令使用第一篇——介绍,基本操作,增删改查
平时我们在使用git的时候,很少去关注其配置是如何,而在实际开发中,对git config这个命令的使用也并不是很多,但是配置对一个程序和项目来说都是很重要的,我们今天来看看git的配置以及git c ...
- Java中Date各种相关用法
Java中Date各种相关用法(一) 1.计算某一月份的最大天数 Java代码 Calendar time=Calendar.getInstance(); time.clear(); time.set ...
- 9.22 noip模拟试题
水灾(sliker.cpp/c/pas) 1000MS 64MB 大雨应经下了几天雨,却还是没有停的样子.土豪CCY刚从外地赚完1e元回来,知道不久除了自己别墅,其他的地方都将会被洪水淹没. CCY ...
- KineticJS教程(1-2)
1.基本结构 KineticJS首先是要绑定到HTML页面上的一个DOM容器元素上,比如最常用的<div>标签.KineticJS在此容器中创建一个称之为舞台(stage)的结构,这个舞台 ...
- 如何配置visual studio 2013进行负载测试-万事开头难
声明:工作比较忙,文章写得不好,有时间再整理. 起因:最近众包平台因迁移到azure之后一直有网站慢的情况,让老板挨批了,但是测试环境一切正常,而且生产环境也没发现有卡顿和慢的情况,所以干脆来一次负载 ...
- tomcat发布项目时,空文件夹未发布成功
问题背景: 项目发布到服务器时,缺少文件夹,到时向此文件夹写数据时发生错误. 后来经查,缺少这个文件夹,项目部署发布时,并不会把空文件夹发布上去 解决: 1.在空文件中加入,一个文件.就可以发布成功 ...
- sqlserver触发器如何将一个库中的数据插入到另外一个库中
需求:实现的功能就是,查询当前表的所有信息,插入到另外一个库中(同一台机器,同一个SqlServer) 解决:insert into dB2.dbo.TB2 select * from db1.dbo ...
- oracle 10g 恢复dmp文件。
1. 在winxp下,安装10g,默认选择,一路ok.(安装前自检出现dhcp警告,可直接忽略) 2.命令行,在xp下,输入sqlplus,即可启动,登陆用 sqlplus / as sysdba 用 ...
- 十、C# 异常处理
1.多异常类型 2.捕捉异常 3.常规catch块 4.异常处理的指导原则 5.定义自定义异常 1.多异常类型 代码要引发任何异常,只需为要引发的异常实例实例附加关键字throw作为前缀.具体选择 ...
- 【BZOJ2653】【主席树+二分】middle
Description 一个长度为n的序列a,设其排过序之后为b,其中位数定义为b[n/2],其中a,b从0开始标号,除法取下整. 给你一个长度为n的序列s. 回答Q个这样的询问:s的左端点在[a,b ...
