基于Qt的在QGraphicsView中绘制带有可动拐点的连线的一种方法
摘要:本文详细介绍了基于Qt框架在`QGraphicsView`中实现带有可动拐点连线的绘制方法。通过自定义`CustomItem`和`CustomPath`类,结合`QGraphicsItem`的几何变化事件与`QPainterPath`的路径绘制功能,实现了动态连线的基本框架。进一步探讨了平行线偏移规则的设计与拐点交叉问题的解决方案,通过角平分线计算和交叉检测优化路径连接效果。最终提出了一种支持用户拖拽拐点、自动刷新连线的交互式图形方案,并展示了代码实现与效果演示,为复杂图形编辑工具的开发提供了参考。
关键词:QGraphicsView、QGraphicsItem、QPainterPath、可动拐点、平行线偏移、角平分线、交叉检测、Qt图形框架
完整代码见最后。
1、QGraphicsItem和QPainterPath的基础使用
做一点准备工作,先用一个简单的案例,创建代码基本框架。
问题描述:
已知起点和终点,如何绘制过两点的线段?
要求:点图形可动,连线图形可刷新
解决思路:
1、准备工作,需要创建可动的图形类CustomItem和连线类CustomPath,以便观察各种情况。
2、使用QPainterPath的moveTo()和lineTo()绘制连线。
3、在图形类CustomItem的itemChange函数中刷新连线。
代码如下:
class CustomPath;
// 图形类,描述起点和终点
class CustomItem : public QGraphicsRectItem
{
public:
CustomItem(QGraphicsItem *parent = nullptr);
void addPath(CustomPath *path);
protected:
QVariant itemChange(QGraphicsItem::GraphicsItemChange change, const QVariant &value) override;
private:
QList<CustomPath *> mPathList; // 连线列表
};
CustomItem::CustomItem(QGraphicsItem *parent) : QGraphicsRectItem(parent)
{
// 设置形状
setRect(-5, -5, 10, 10);
// 设置颜色
setBrush(Qt::black);
// 设置可移动
setFlag(QGraphicsItem::ItemIsMovable, true);
// 设置可发送几何变动,可在itemChange中进行检测
setFlag(QGraphicsItem::ItemSendsGeometryChanges, true);
}
// 添加连线
void CustomItem::addPath(CustomPath *path)
{
mPathList.append(path);
}
QVariant CustomItem::itemChange(QGraphicsItem::GraphicsItemChange change, const QVariant &value)
{
switch (change) {
// 当位置变动时,刷新连线
case QGraphicsItem::ItemPositionHasChanged:
{
for (int i = 0, size = mPathList.size(); i < size; ++i) {
mPathList.at(i)->updatePosition();
}
}
default:
break;
}
return QGraphicsItem::itemChange(change, value);
}
在这段代码中,创建了图形类CustomItem,设置图形可移动,同时在移动时刷新与图形相连的连线。
// 连线类,描述连线
class CustomPath : public QGraphicsPathItem
{
public:
CustomPath(QGraphicsItem *start, QGraphicsItem *end, QGraphicsItem *parent = nullptr);
void updatePosition(); // 刷新连线
private:
QGraphicsItem *mStartItem = nullptr; // 起点
QGraphicsItem *mEndItem = nullptr; // 终点
};
CustomPath::CustomPath(QGraphicsItem *start, QGraphicsItem *end, QGraphicsItem *parent)
: QGraphicsPathItem(parent), mStartItem(start), mEndItem(end)
{
// 设置绘制画笔,颜色黑色,笔宽为1
setPen(QPen(Qt::black, 1));
}
// 刷新连线
void CustomPath::updatePosition()
{
// 获取两端的位置
QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
// 绘制连线
QPainterPath path;
path.moveTo(start_pos);
path.lineTo(end_pos);
// 设置连线
setPath(path);
}
在这段代码中,创建了连线类CustomPath,主要作用是刷新连线updatePosition函数。
// 创建画布
QGraphicsScene *scene = new QGraphicsScene(this);
ui->graphicsView->setScene(scene);
// 创建起点
CustomItem *item_start = new CustomItem;
item_start->setPos(100, 100);
scene->addItem(item_start);
// 创建终点
CustomItem *item_end = new CustomItem;
item_end->setPos(200, 200);
scene->addItem(item_end);
// 创建连线
CustomPath *path = new CustomPath(item_start, item_end);
item_start->addPath(path);
item_end->addPath(path);
path->updatePosition();
scene->addItem(path);
在这段代码中,创建了点A和点B,设置它们的位置,创建了连线并刷新。
效果如下:
2、如何创建平行线
现在要在同一个连线类CustomPath中绘制两条连线,引出偏移规则的确定方法。
问题描述:
现有点A和点B,分别在其周围找两点(点A1A2,点B1B2),如何绘制两条平行线?
解决思路:
只需确定偏移规则。比如这两点分别位于点的左右或者上下两侧。这里设置为左右偏移5个像素点。
代码如下:
void CustomPath::updatePosition()
{
QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
// 起点左右偏移
QPointF start_p1 = start_pos + QPointF(-5, 0);
QPointF start_p2 = start_pos + QPointF(5, 0);
// 终点左右偏移
QPointF end_p1 = end_pos + QPointF(-5, 0);
QPointF end_p2 = end_pos + QPointF(5, 0);
// 两次连线
QPainterPath path;
path.moveTo(start_p1);
path.lineTo(end_p1);
path.moveTo(start_p2);
path.lineTo(end_p2);
setPath(path);
}
这段代码中,将起点和终点分别左右偏移五个像素,然后连线,使用两次moveTo()和lineTo()。
效果如下:
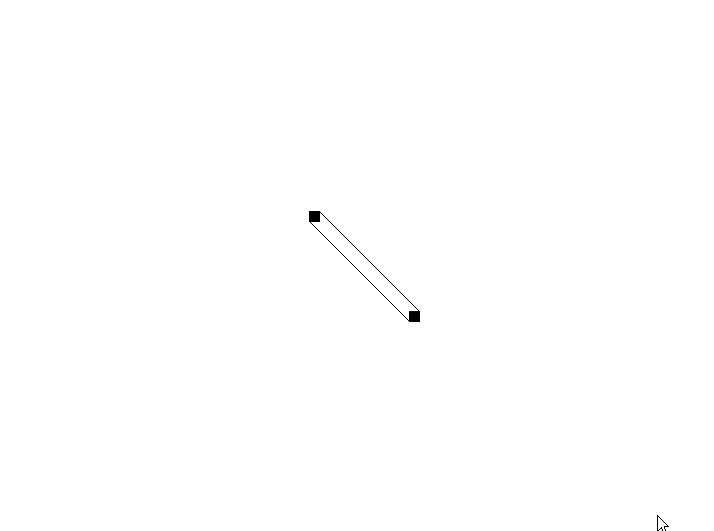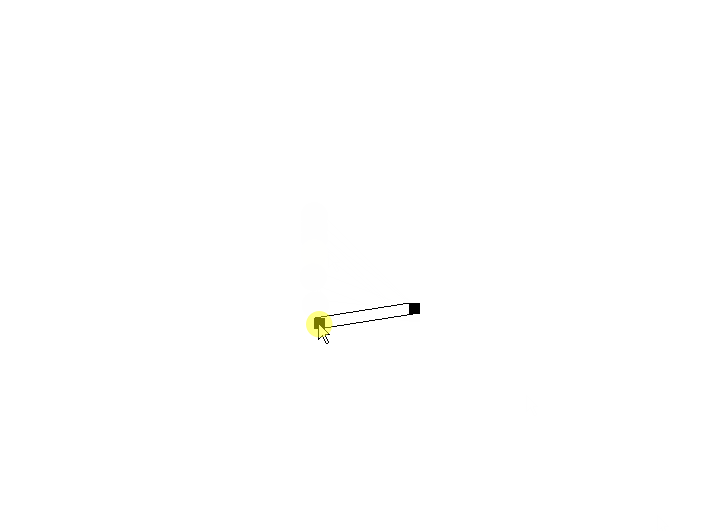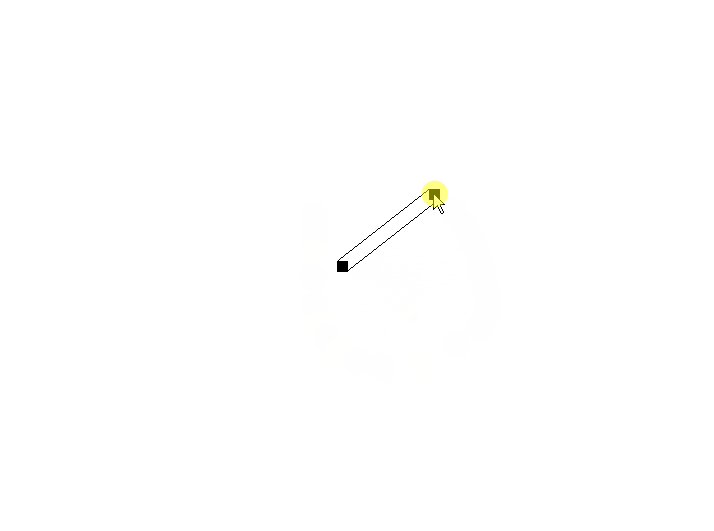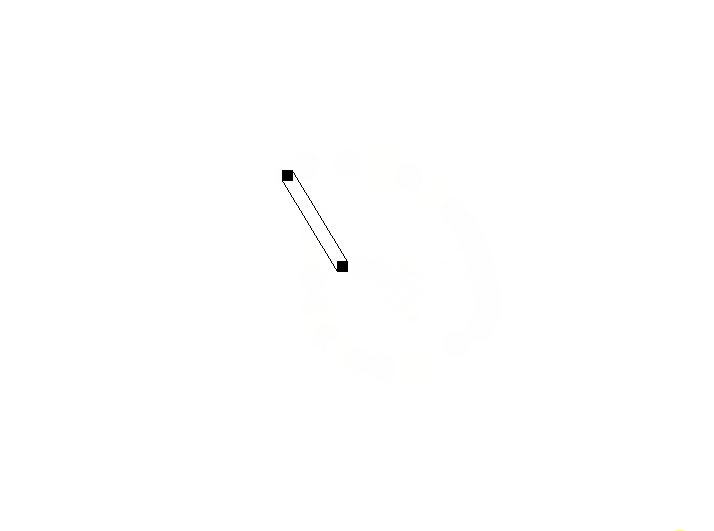
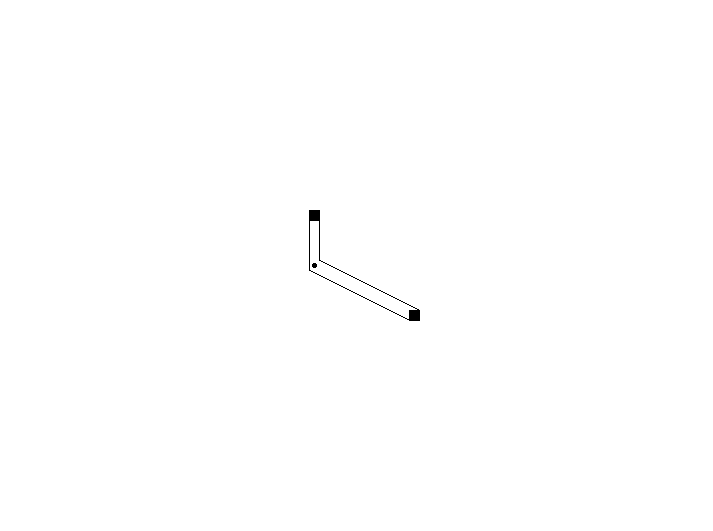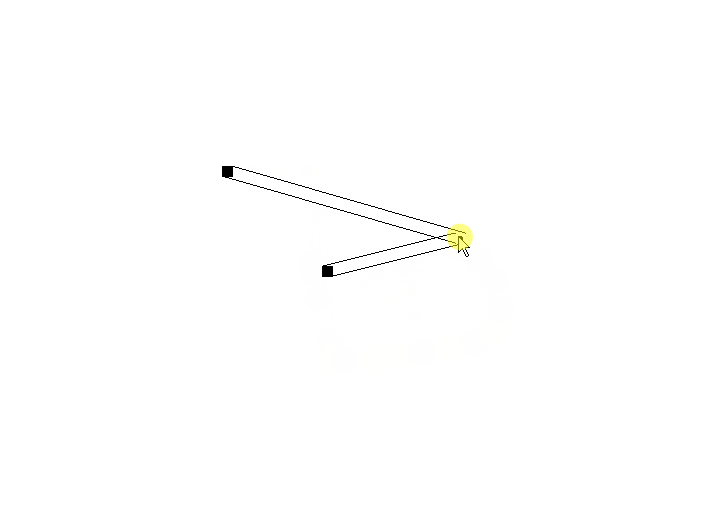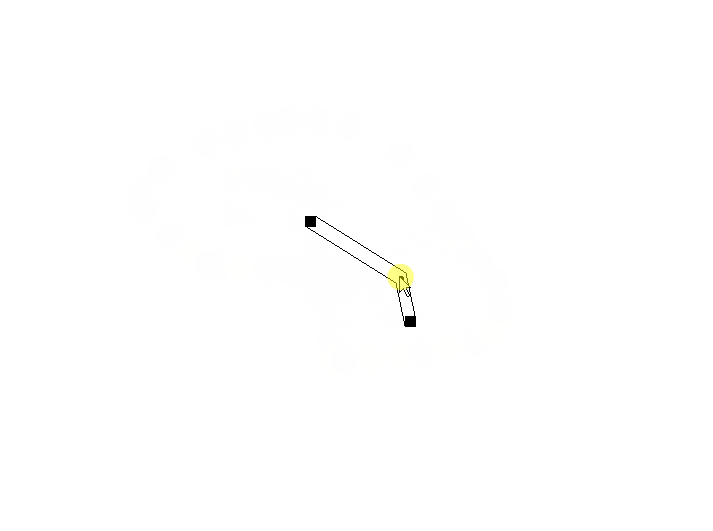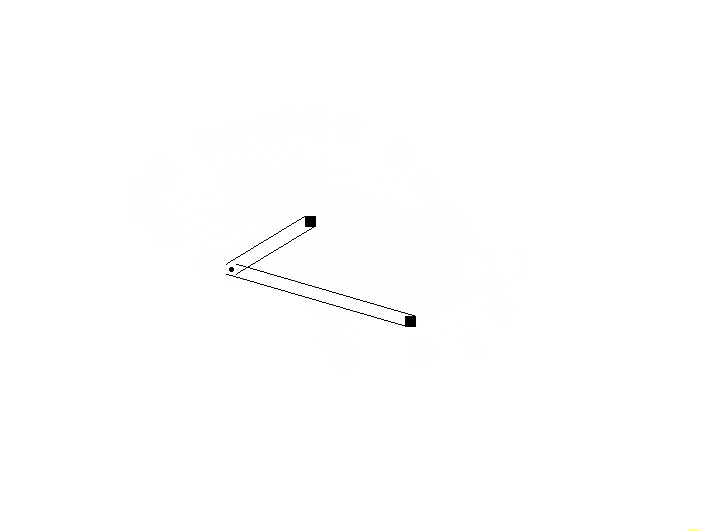
3、偏移规则的问题
问题描述:
可以发现(如图),当移动两个点位于同一水平线时,连线会发生重叠。
解决思路:
这是由于偏移规则的缺陷。无论是上下偏移还是左右偏移或者其他的偏移,都会产生这种情况。
那么,这两个偏移点必须根据情况发生变化。
确定新的偏移规则:斜向偏移,直线如果斜向右上(或者斜向左下),则偏移点为(5,5)和(-5,-5);直线如果斜向左上(或者斜向右下),则偏移点为(5,-5)和(-5,5)。
代码如下:
// 偏移规则
QPointF CustomPath::getOffset(const QPointF &p1, const QPointF &p2)
{
QPointF dp = p1 - p2;
QPointF offset;
// 根据差值判断
if (dp.x() * dp.y() >= 0) {
// 设置偏移量
offset = QPointF(-5, 5);
} else {
offset = QPointF(5, 5);
}
return offset;
}
void CustomPath::updatePosition()
{
QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
QPointF offset = getOffset(start_pos, end_pos);
// 起点和终点偏移
QPointF start_p1 = start_pos + offset;
QPointF start_p2 = start_pos - offset;
QPointF end_p1 = end_pos + offset;
QPointF end_p2 = end_pos - offset;
QPainterPath path;
path.moveTo(start_p1);
path.lineTo(end_p1);
path.moveTo(start_p2);
path.lineTo(end_p2);
setPath(path);
}
在这段代码中,使用了两点xy轴的差值进行判断斜向方向,同时设置了偏移量。
效果如下:
4、带有拐点的连线
问题描述:
重新从解决简单的问题开始:现在有点X,需要创建从A->X->B的单条连线,如何实现?
解决思路:
确定拐点位置,插入使用lineTo()即可。
代码如下:
// 拐点类
class CustomPoint : public QGraphicsEllipseItem
{
public:
CustomPoint(QGraphicsItem *parent = nullptr);
void setPathItem(CustomPath *pathItem);
protected:
QVariant itemChange(QGraphicsItem::GraphicsItemChange change, const QVariant &value) override;
private:
CustomPath *mPathItem = nullptr; // 拐点所属连线
};
CustomPoint::CustomPoint(QGraphicsItem *parent)
: QGraphicsEllipseItem(parent)
{
// 设置图形为圆形
setRect(-2, -2, 4, 4);
setBrush(Qt::black);
setFlag(QGraphicsItem::ItemIsMovable, true);
setFlag(QGraphicsItem::ItemSendsGeometryChanges, true);
}
QVariant CustomPoint::itemChange(QGraphicsItem::GraphicsItemChange change, const QVariant &value)
{
switch (change) {
case QGraphicsItem::ItemPositionHasChanged:
{
// 当拐点位置发生变化,刷新连线
if (mPathItem) {
mPathItem->updatePosition();
}
}
default:
break;
}
return QGraphicsItem::itemChange(change, value);
}
void CustomPoint::setPathItem(CustomPath *pathItem)
{
mPathItem = pathItem;
}
在这段代码中,创建了拐点类CustomPoint,设置它的形状、笔刷、可移动属性;当拐点位置发生变化时,刷线连线。
// 对部分代码进行修改
class CustomPath : public QGraphicsPathItem
{
public:
CustomPath(QGraphicsItem *start, QGraphicsItem *end, QGraphicsItem *parent = nullptr);
void updatePosition();
void setPoint(CustomPoint *point); // 设置拐点
private:
QGraphicsItem *mStartItem = nullptr;
QGraphicsItem *mEndItem = nullptr;
CustomPoint *mPoint = nullptr; // 拐点
};
void CustomPath::setPoint(CustomPoint *point)
{
mPoint = point;
}
void CustomPath::updatePosition()
{
QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
QPointF point_pos = mPoint->pos();
QPainterPath path;
path.moveTo(start_pos);
path.lineTo(point_pos); // 从起点->拐点->终点
path.lineTo(end_pos);
setPath(path);
}
// 修改使用代码
QGraphicsScene *scene = new QGraphicsScene(this);
ui->graphicsView->setScene(scene);
// 创建起点
CustomItem *item_start = new CustomItem;
item_start->setPos(100, 100);
scene->addItem(item_start);
// 创建终点
CustomItem *item_end = new CustomItem;
item_end->setPos(200, 200);
scene->addItem(item_end);
// 创建连线
CustomPath *path = new CustomPath(item_start, item_end);
item_start->addPath(path);
item_end->addPath(path);
scene->addItem(path);
// 添加拐点图形
CustomPoint *point = new CustomPoint(path);
point->setPos(100, 150);
path->setPoint(point); // 设置拐点
point->setPathItem(path); // 设置连线
path->updatePosition();
在这段代码中,对部分代码进行修改:在连线类中添加了拐点成员,在刷新连线函数中连线到拐点,在实际使用代码中添加了拐点图形,在最后刷新图形连线。
效果如下:
5、带有拐点的两条平行线
问题描述:
那么如何绘制带有拐点的两条连线呢?
解决思路:
直接将偏移规则应用到拐点位置,根据起点和拐点位置(或者拐点和终点位置)确定偏移,会如何?
代码如下:
void CustomPath::updatePosition()
{
QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
QPointF point_pos = mPoint->pos();
// 计算偏移
QPointF offset_sp = getOffset(start_pos, point_pos);
QPointF offset_pe = getOffset(point_pos, end_pos);
// 起点偏移
QPointF start_p1 = start_pos + offset_sp;
QPointF start_p2 = start_pos - offset_sp;
// 拐点对起点偏移
QPointF point_ps1 = point_pos + offset_sp;
QPointF point_ps2 = point_pos - offset_sp;
// 拐点对终点偏移
// QPointF point_pe1 = point_pos + offset_pe;
// QPointF point_pe2 = point_pos - offset_pe;
// 终点偏移
QPointF end_p1 = end_pos + offset_pe;
QPointF end_p2 = end_pos - offset_pe;
// 使用两个
QPainterPath path;
path.moveTo(start_p1);
path.lineTo(point_ps1);
// path.lineTo(point_pe1);
path.lineTo(end_p1);
path.moveTo(start_p2);
path.lineTo(point_ps2);
// path.lineTo(point_pe2);
path.lineTo(end_p2);
// 使用四个
// {
// path.moveTo(start_p1);
// path.lineTo(point_ps1);
// path.moveTo(point_pe1);
// path.lineTo(end_p1);
// path.moveTo(start_p2);
// path.lineTo(point_ps2);
// path.moveTo(point_pe2);
// path.lineTo(end_p2);
// }
setPath(path);
}
在调整代码的过程中,就会发现,在拐点对起点和拐点对终点应用偏移规则时,会产生四个偏移点。
只使用其中两个会发生什么情况?使用四个会发生什么情况?
效果如下:
使用两个的情况:可以看到连线产生了交错,并且某些角度情况下发生重合。
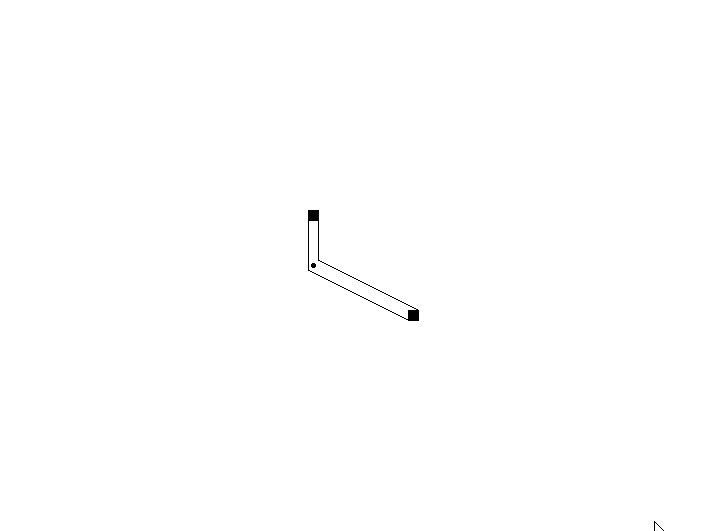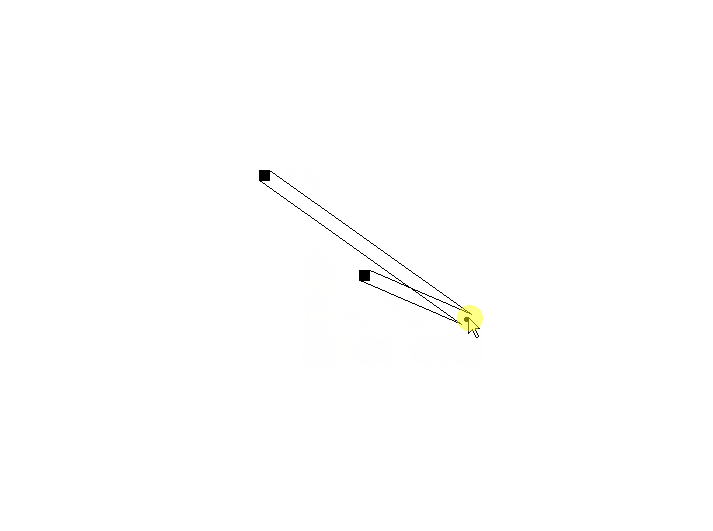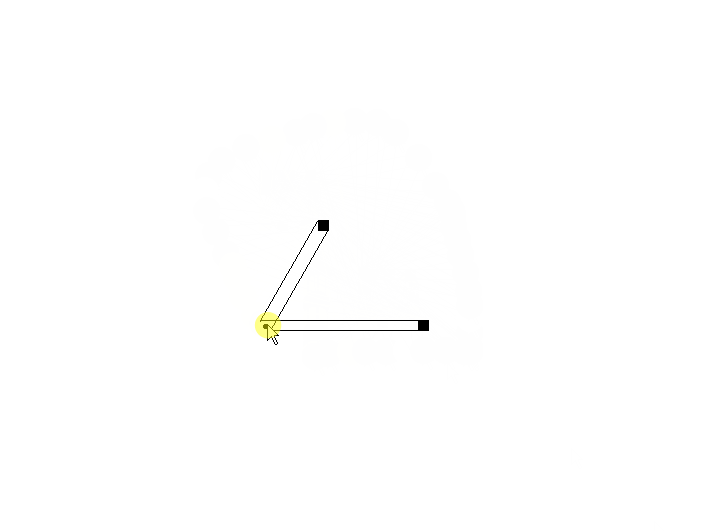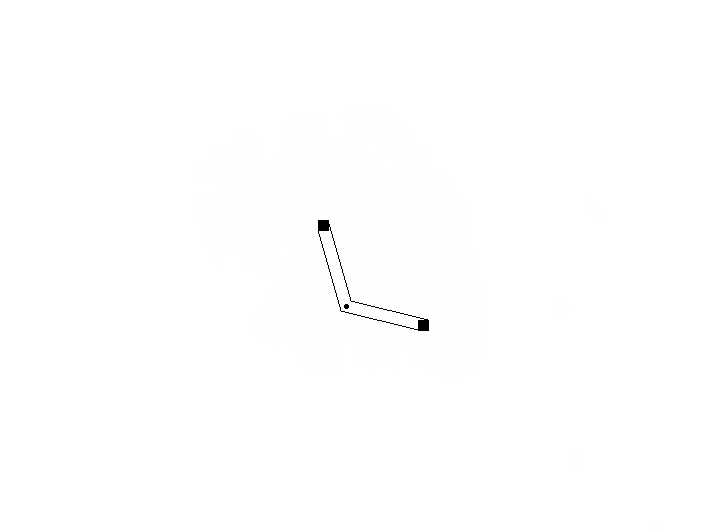
使用四个的情况:可以看到连线产生交错,并且某些角度下连接点错开。
6、拐点处的偏移问题
问题描述:
如果对拐点也应用偏移规则,使用两个点,会产生交错的情况;使用四个点,不仅会产生交错,而且会断开。
解决思路:
拐点处的偏移点应该只可以有两个;其偏移点只对一个点应用;考虑使用角平分线。
方案就是:起点-拐点-终点,形成一个角度,计算出角平分线;过起点的两个偏移点,作起点和拐点连线的两条平行线;这两条平行线和角平分线的交点,作为拐点处的偏移点;然后连接拐点处偏移点和终点偏移点,形成连线。
代码如下:
// 计算角平分线
QLineF CustomPath::calculateAngleBisector(const QPointF &start, const QPointF &mid, const QPointF &end)
{
// 计算向量A和B
QPointF vectorA = start - mid;
QPointF vectorB = end - mid;
// 归一化向量A和B
qreal lengthA = std::hypot(vectorA.x(), vectorA.y());
qreal lengthB = std::hypot(vectorB.x(), vectorB.y());
QPointF unitA = vectorA / lengthA;
QPointF unitB = vectorB / lengthB;
// 计算角平分线向量
QPointF bisector = unitA + unitB;
// 如果共线则向量为零,需要使用垂线
if (bisector.isNull()) {
bisector = QPointF(-unitA.y(), unitA.x());
}
// 归一化角平分线向量
qreal lengthBisector = std::hypot(bisector.x(), bisector.y());
QPointF unitBisector = bisector / lengthBisector;
// 从中点出发,沿角平分线方向绘制一条直线
QPointF bisectorEnd = mid + unitBisector * 100; // 100为长度,可根据需要调整
QPointF bisectorEnd_n = mid - unitBisector * 100;
return QLineF(bisectorEnd_n, bisectorEnd);
// return unitBisector;
}
// 计算过p点的l1的平行线与bisector_line的交点
QPointF CustomPath::calculateBisectorPoint(const QLineF &l1, const QLineF &bisector_line, const QPointF &p)
{
// 起点到拐点连线的向量
QPointF lp(l1.p2() - l1.p1());
qreal length = std::hypot(lp.x(), lp.y());
QPointF unit = lp / length;
// 过偏移点的平行线
QLineF line(p, p+unit*100);
// 计算交点
QPointF intersection;
QLineF::IntersectType type = line.intersects(bisector_line, &intersection);
return intersection;
}
void CustomPath::updatePosition()
{
QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
QPointF point_pos = mPoint->pos();
// 计算偏移
QPointF offset_sp = getOffset(start_pos, point_pos);
QPointF offset_pe = getOffset(point_pos, end_pos);
// 起点偏移
QPointF start_p1 = start_pos + offset_sp;
QPointF start_p2 = start_pos - offset_sp;
// 终点偏移
QPointF end_p1 = end_pos + offset_pe;
QPointF end_p2 = end_pos - offset_pe;
// 计算角平分线
QLineF bisector_line = calculateAngleBisector(start_pos, point_pos, end_pos);
QLineF start_line(start_pos, point_pos);
// 计算交点
QPointF p1_bst_itst = calculateBisectorPoint(start_line, bisector_line, start_p1);
QPointF p2_bst_itst = calculateBisectorPoint(start_line, bisector_line, start_p2);
// 连线
QPainterPath path;
path.moveTo(start_p1);
path.lineTo(p1_bst_itst);
path.lineTo(end_p1);
path.moveTo(start_p2);
path.lineTo(p2_bst_itst);
path.lineTo(end_p2);
setPath(path);
}
在这段代码中,计算起点-拐点-终点形成角度的角平分线,考虑三点共线情况下,使用垂线向量;然后有起点到拐点的连线,过两起点偏移点,作平行线,并得到和角平分线的交点;从交点连线到终点偏移点。
效果如图:
可见在拐点和终点的两条连线发生了交叉,继续完善。
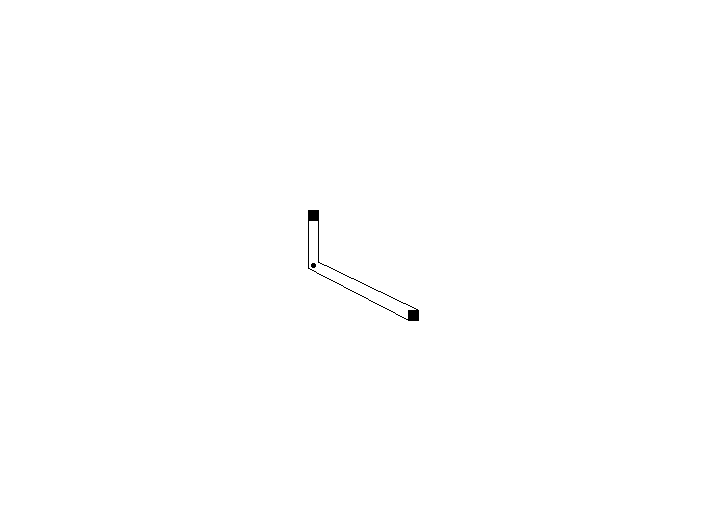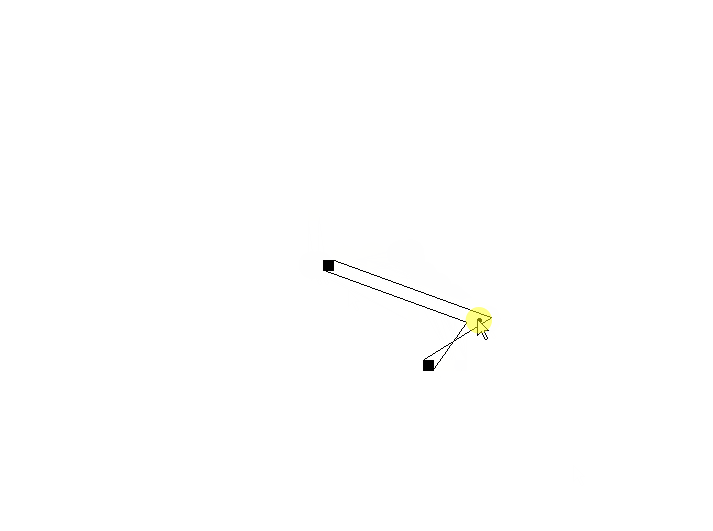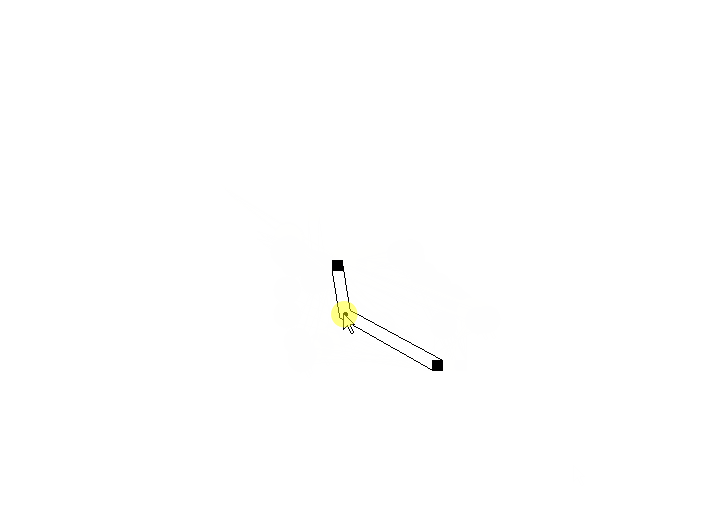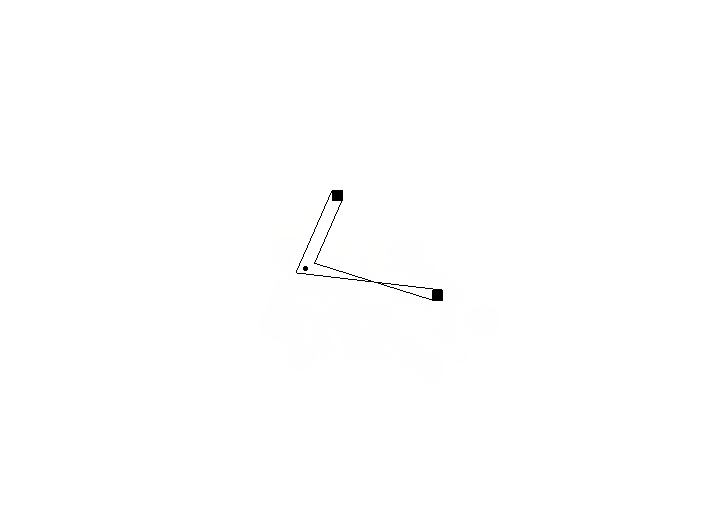
7、后半段交叉问题
问题描述:
偏移点并不总是对应的,拐点到终点的连线发生了交叉。
解决思路:
判断后半段是否交叉,如果交叉,则互换偏移点。
代码如下:
// 判断是否交叉
bool CustomPath::calculateLineIsIntersect(const QPointF &start1, const QPointF &end1,
const QPointF &start2, const QPointF &end2)
{
QLineF line1(start1, end1);
QLineF line2(start2, end2);
QPointF intersection;
QLineF::IntersectType type = line1.intersects(line2, &intersection);
if (type == QLineF::BoundedIntersection && ! intersection.isNull()) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
void CustomPath::updatePosition()
{
QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
QPointF point_pos = mPoint->pos();
QPointF offset_sp = getOffset(start_pos, point_pos);
QPointF offset_pe = getOffset(point_pos, end_pos);
QPointF start_p1 = start_pos + offset_sp;
QPointF start_p2 = start_pos - offset_sp;
QPointF end_p1 = end_pos + offset_pe;
QPointF end_p2 = end_pos - offset_pe;
// 计算角平分线
QLineF bisector_line = calculateAngleBisector(start_pos, point_pos, end_pos);
QLineF start_line(start_pos, point_pos);
// 计算交点
QPointF p1_bst_itst = calculateBisectorPoint(start_line, bisector_line, start_p1);
QPointF p2_bst_itst = calculateBisectorPoint(start_line, bisector_line, start_p2);
QPainterPath path;
// 前半段
path.moveTo(start_p1);
path.lineTo(p1_bst_itst);
path.moveTo(start_p2);
path.lineTo(p2_bst_itst);
// 后半段,判断是否交叉
if (calculateLineIsIntersect(end_p1, p1_bst_itst, end_p2, p2_bst_itst)) {
// 如果交叉
path.moveTo(p1_bst_itst);
path.lineTo(end_p2);
path.moveTo(p2_bst_itst);
path.lineTo(end_p1);
} else {
path.moveTo(p1_bst_itst);
path.lineTo(end_p1);
path.moveTo(p2_bst_itst);
path.lineTo(end_p2);
}
setPath(path);
}
在这段代码中,修改了绘制连线的顺序,先绘制前半段,再绘制后半段;如果后半段发生交叉,则互换最后的终点偏移点。
效果如下:
可见当形成的角度极小的时候,拐点处会极度尖锐,对这个问题我没有很好的办法。还好拐点是可以移动的。如果你有想法,欢迎共同讨论。
总结:
本文系统性地解决了在Qt图形视图中绘制动态连线的技术难点。首先,通过继承QGraphicsItem实现可拖拽的图形项CustomItem,利用itemChange事件触发连线刷新,确保了图形与路径的实时联动。其次,引入CustomPath类管理路径绘制,通过QPainterPath灵活构建线段与拐点连接逻辑。针对平行线偏移问题,提出基于斜向偏移与角平分线的动态调整策略,有效避免了路径重叠与错位。然而,在极端角度下拐点处仍可能因偏移计算产生尖锐连接,需进一步优化算法或引入平滑曲线处理。
完整代码:
- mainwindow.h
点击折叠或展开代码
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H
#include <QMainWindow>
#include <QtWidgets>
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui { class MainWindow; }
QT_END_NAMESPACE
class CustomPath;
class CustomPoint;
// 图形类,描述起点和终点
class CustomItem : public QGraphicsRectItem
{
public:
CustomItem(QGraphicsItem *parent = nullptr);
void addPath(CustomPath *path);
protected:
QVariant itemChange(QGraphicsItem::GraphicsItemChange change, const QVariant &value) override;
private:
QList<CustomPath *> mPathList; // 连线列表
};
// 连线类,描述连线
class CustomPath : public QGraphicsPathItem
{
public:
CustomPath(QGraphicsItem *start, QGraphicsItem *end, QGraphicsItem *parent = nullptr);
void updatePosition(); // 刷新连线
void setPoint(CustomPoint *point); // 设置拐点
private:
QGraphicsItem *mStartItem = nullptr; // 起点
QGraphicsItem *mEndItem = nullptr; // 终点
CustomPoint *mPoint = nullptr; // 拐点
QPointF getOffset(const QPointF &p1, const QPointF &p2);
QLineF calculateAngleBisector(const QPointF& start, const QPointF& mid, const QPointF& end);
QPointF calculateBisectorPoint(const QLineF &l1, const QLineF &bisector_line, const QPointF &p);
bool calculateLineIsIntersect(const QPointF &start1, const QPointF &end1, const QPointF &start2, const QPointF &end2);
};
// 拐点类
class CustomPoint : public QGraphicsEllipseItem
{
public:
CustomPoint(QGraphicsItem *parent = nullptr);
void setPathItem(CustomPath *pathItem);
protected:
QVariant itemChange(QGraphicsItem::GraphicsItemChange change, const QVariant &value) override;
private:
CustomPath *mPathItem = nullptr; // 拐点所属连线
};
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
MainWindow(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~MainWindow();
private:
Ui::MainWindow *ui;
void initGraphics();
};
#endif // MAINWINDOW_H
- mainwindow.cpp
点击折叠或展开代码
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)
, ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
initGraphics();
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
// 问题1、2、3
//void MainWindow::initGraphics()
//{
// // 创建画布
// QGraphicsScene *scene = new QGraphicsScene(this);
// ui->graphicsView->setScene(scene);
// // 创建起点
// CustomItem *item_start = new CustomItem;
// item_start->setPos(100, 100);
// scene->addItem(item_start);
// // 创建终点
// CustomItem *item_end = new CustomItem;
// item_end->setPos(200, 200);
// scene->addItem(item_end);
// // 创建连线
// CustomPath *path = new CustomPath(item_start, item_end);
// item_start->addPath(path);
// item_end->addPath(path);
// scene->addItem(path);
// path->updatePosition();
//}
// 问题4、5
void MainWindow::initGraphics()
{
QGraphicsScene *scene = new QGraphicsScene(this);
ui->graphicsView->setScene(scene);
CustomItem *item_start = new CustomItem;
item_start->setPos(100, 100);
scene->addItem(item_start);
CustomItem *item_end = new CustomItem;
item_end->setPos(200, 200);
scene->addItem(item_end);
CustomPath *path = new CustomPath(item_start, item_end);
item_start->addPath(path);
item_end->addPath(path);
scene->addItem(path);
// 添加拐点图形
CustomPoint *point = new CustomPoint(path);
point->setPos(100, 150);
path->setPoint(point);
point->setPathItem(path);
path->updatePosition();
}
CustomItem::CustomItem(QGraphicsItem *parent) : QGraphicsRectItem(parent)
{
// 设置形状
setRect(-5, -5, 10, 10);
// 设置颜色
setBrush(Qt::black);
// 设置可移动
setFlag(QGraphicsItem::ItemIsMovable, true);
// 设置可发送几何变动,可在itemChange中进行检测
setFlag(QGraphicsItem::ItemSendsGeometryChanges, true);
}
// 添加连线
void CustomItem::addPath(CustomPath *path)
{
mPathList.append(path);
}
QVariant CustomItem::itemChange(QGraphicsItem::GraphicsItemChange change, const QVariant &value)
{
switch (change) {
// 当位置变动时,刷新连线
case QGraphicsItem::ItemPositionHasChanged:
{
for (int i = 0, size = mPathList.size(); i < size; ++i) {
mPathList.at(i)->updatePosition();
}
}
default:
break;
}
return QGraphicsItem::itemChange(change, value);
}
CustomPath::CustomPath(QGraphicsItem *start, QGraphicsItem *end, QGraphicsItem *parent)
: QGraphicsPathItem(parent), mStartItem(start), mEndItem(end)
{
// 设置绘制画笔,颜色黑色,笔宽为1
setPen(QPen(Qt::black, 1));
}
// 问题1
//void CustomPath::updatePosition()
//{
// // 获取两端的位置
// QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
// QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
// // 绘制连线
// QPainterPath path;
// path.moveTo(start_pos);
// path.lineTo(end_pos);
// // 设置连线
// setPath(path);
//}
// 问题2
//void CustomPath::updatePosition()
//{
// QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
// QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
// // 起点左右偏移
// QPointF start_p1 = start_pos + QPointF(-5, 0);
// QPointF start_p2 = start_pos + QPointF(5, 0);
// // 终点左右偏移
// QPointF end_p1 = end_pos + QPointF(-5, 0);
// QPointF end_p2 = end_pos + QPointF(5, 0);
// // 两次连线
// QPainterPath path;
// path.moveTo(start_p1);
// path.lineTo(end_p1);
// path.moveTo(start_p2);
// path.lineTo(end_p2);
// setPath(path);
//}
QPointF CustomPath::getOffset(const QPointF &p1, const QPointF &p2)
{
QPointF dp = p1 - p2;
QPointF offset;
// 根据差值判断
if (dp.x() * dp.y() >= 0) {
// 设置偏移量
offset = QPointF(-5, 5);
} else {
offset = QPointF(5, 5);
}
return offset;
}
// 问题3
//void CustomPath::updatePosition()
//{
// QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
// QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
// QPointF offset = getOffset(start_pos, end_pos);
// // 起点和终点偏移
// QPointF start_p1 = start_pos + offset;
// QPointF start_p2 = start_pos - offset;
// QPointF end_p1 = end_pos + offset;
// QPointF end_p2 = end_pos - offset;
// QPainterPath path;
// path.moveTo(start_p1);
// path.lineTo(end_p1);
// path.moveTo(start_p2);
// path.lineTo(end_p2);
// setPath(path);
//}
// 问题4
//void CustomPath::updatePosition()
//{
// QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
// QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
// QPointF point_pos = mPoint->pos();
// QPainterPath path;
// path.moveTo(start_pos);
// path.lineTo(point_pos); // 从起点->拐点->终点
// path.lineTo(end_pos);
// setPath(path);
//}
// 问题5
//void CustomPath::updatePosition()
//{
// QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
// QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
// QPointF point_pos = mPoint->pos();
// // 计算偏移
// QPointF offset_sp = getOffset(start_pos, point_pos);
// QPointF offset_pe = getOffset(point_pos, end_pos);
// // 起点偏移
// QPointF start_p1 = start_pos + offset_sp;
// QPointF start_p2 = start_pos - offset_sp;
// // 拐点对起点偏移
// QPointF point_ps1 = point_pos + offset_sp;
// QPointF point_ps2 = point_pos - offset_sp;
// // 拐点对终点偏移
// QPointF point_pe1 = point_pos + offset_pe;
// QPointF point_pe2 = point_pos - offset_pe;
// // 终点偏移
// QPointF end_p1 = end_pos + offset_pe;
// QPointF end_p2 = end_pos - offset_pe;
// // 使用两个
// QPainterPath path;
// path.moveTo(start_p1);
// path.lineTo(point_ps1);
//// path.lineTo(point_pe1);
// path.lineTo(end_p1);
// path.moveTo(start_p2);
// path.lineTo(point_ps2);
//// path.lineTo(point_pe2);
// path.lineTo(end_p2);
// // 使用四个
//// {
//// path.moveTo(start_p1);
//// path.lineTo(point_ps1);
//// path.moveTo(point_pe1);
//// path.lineTo(end_p1);
//// path.moveTo(start_p2);
//// path.lineTo(point_ps2);
//// path.moveTo(point_pe2);
//// path.lineTo(end_p2);
//// }
// setPath(path);
//}
// 问题6
//void CustomPath::updatePosition()
//{
// QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
// QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
// QPointF point_pos = mPoint->pos();
// QPointF offset_sp = getOffset(start_pos, point_pos);
// QPointF offset_pe = getOffset(point_pos, end_pos);
// QPointF start_p1 = start_pos + offset_sp;
// QPointF start_p2 = start_pos - offset_sp;
// QPointF end_p1 = end_pos + offset_pe;
// QPointF end_p2 = end_pos - offset_pe;
// // 计算角平分线
// QLineF bisector_line = calculateAngleBisector(start_pos, point_pos, end_pos);
// QLineF start_line(start_pos, point_pos);
// // 计算交点
// QPointF p1_bst_itst = calculateBisectorPoint(start_line, bisector_line, start_p1);
// QPointF p2_bst_itst = calculateBisectorPoint(start_line, bisector_line, start_p2);
// QPainterPath path;
// path.moveTo(start_p1);
// path.lineTo(p1_bst_itst);
// path.lineTo(end_p1);
// path.moveTo(start_p2);
// path.lineTo(p2_bst_itst);
// path.lineTo(end_p2);
// setPath(path);
//}
// 问题7
void CustomPath::updatePosition()
{
QPointF start_pos = mStartItem->pos();
QPointF end_pos = mEndItem->pos();
QPointF point_pos = mPoint->pos();
QPointF offset_sp = getOffset(start_pos, point_pos);
QPointF offset_pe = getOffset(point_pos, end_pos);
QPointF start_p1 = start_pos + offset_sp;
QPointF start_p2 = start_pos - offset_sp;
QPointF end_p1 = end_pos + offset_pe;
QPointF end_p2 = end_pos - offset_pe;
// 计算角平分线
QLineF bisector_line = calculateAngleBisector(start_pos, point_pos, end_pos);
QLineF start_line(start_pos, point_pos);
// 计算交点
QPointF p1_bst_itst = calculateBisectorPoint(start_line, bisector_line, start_p1);
QPointF p2_bst_itst = calculateBisectorPoint(start_line, bisector_line, start_p2);
QPainterPath path;
// 前半段
path.moveTo(start_p1);
path.lineTo(p1_bst_itst);
path.moveTo(start_p2);
path.lineTo(p2_bst_itst);
// 后半段,判断是否交叉
if (calculateLineIsIntersect(end_p1, p1_bst_itst, end_p2, p2_bst_itst)) {
// 如果交叉
path.moveTo(p1_bst_itst);
path.lineTo(end_p2);
path.moveTo(p2_bst_itst);
path.lineTo(end_p1);
} else {
path.moveTo(p1_bst_itst);
path.lineTo(end_p1);
path.moveTo(p2_bst_itst);
path.lineTo(end_p2);
}
setPath(path);
}
// 计算角平分线
QLineF CustomPath::calculateAngleBisector(const QPointF &start, const QPointF &mid, const QPointF &end)
{
// 计算向量A和B
QPointF vectorA = start - mid;
QPointF vectorB = end - mid;
// 归一化向量A和B
qreal lengthA = std::hypot(vectorA.x(), vectorA.y());
qreal lengthB = std::hypot(vectorB.x(), vectorB.y());
QPointF unitA = vectorA / lengthA;
QPointF unitB = vectorB / lengthB;
// 计算角平分线向量
QPointF bisector = unitA + unitB;
// 如果共线则向量为零,需要使用垂线
if (bisector.isNull()) {
bisector = QPointF(-unitA.y(), unitA.x());
}
// 归一化角平分线向量
qreal lengthBisector = std::hypot(bisector.x(), bisector.y());
QPointF unitBisector = bisector / lengthBisector;
// 从中点出发,沿角平分线方向绘制一条直线
QPointF bisectorEnd = mid + unitBisector * 100; // 100为长度,可根据需要调整
QPointF bisectorEnd_n = mid - unitBisector * 100;
return QLineF(bisectorEnd_n, bisectorEnd);
// return unitBisector;
}
// 计算过p点的l1的平行线与bisector_line的交点
QPointF CustomPath::calculateBisectorPoint(const QLineF &l1, const QLineF &bisector_line, const QPointF &p)
{
// 起点到拐点连线的向量
QPointF lp(l1.p2() - l1.p1());
qreal length = std::hypot(lp.x(), lp.y());
QPointF unit = lp / length;
// 过偏移点的平行线
QLineF line(p, p+unit*100);
// 计算交点
QPointF intersection;
QLineF::IntersectType type = line.intersects(bisector_line, &intersection);
return intersection;
}
// 判断是否交叉
bool CustomPath::calculateLineIsIntersect(const QPointF &start1, const QPointF &end1,
const QPointF &start2, const QPointF &end2)
{
QLineF line1(start1, end1);
QLineF line2(start2, end2);
QPointF intersection;
QLineF::IntersectType type = line1.intersects(line2, &intersection);
if (type == QLineF::BoundedIntersection && ! intersection.isNull()) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
void CustomPath::setPoint(CustomPoint *point)
{
mPoint = point;
}
CustomPoint::CustomPoint(QGraphicsItem *parent)
: QGraphicsEllipseItem(parent)
{
// 设置图形为圆形
setRect(-2, -2, 4, 4);
setBrush(Qt::black);
setFlag(QGraphicsItem::ItemIsMovable, true);
setFlag(QGraphicsItem::ItemSendsGeometryChanges, true);
}
QVariant CustomPoint::itemChange(QGraphicsItem::GraphicsItemChange change, const QVariant &value)
{
switch (change) {
case QGraphicsItem::ItemPositionHasChanged:
{
// 当拐点位置发生变化,刷新连线
if (mPathItem) {
mPathItem->updatePosition();
}
}
default:
break;
}
return QGraphicsItem::itemChange(change, value);
}
void CustomPoint::setPathItem(CustomPath *pathItem)
{
mPathItem = pathItem;
}
基于Qt的在QGraphicsView中绘制带有可动拐点的连线的一种方法的更多相关文章
- MATLAB中绘制质点轨迹动图并保存成GIF
工作需要在MATLAB中绘制质点轨迹并保存成GIF以便展示. 绘制质点轨迹动图可用comet和comet3命令,使用例子如下: t = 0:.01:2*pi;x = cos(2*t).*(cos(t) ...
- 在Activity中响应ListView内部按钮的点击事件的两种方法!!!
在Activity中响应ListView内部按钮的点击事件的两种方法 转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/ivan-xu/p/4124967.html 最近交流群里面有人问到一个问题: ...
- C#中得到程序当前工作目录和执行目录的五种方法
string str="";str += "\r\n" + System.Diagnostics.Process.GetCurrentProcess().Mai ...
- (网页)angular中实现li或者某个元素点击变色的两种方法(转)
转自脚本之家: 本篇文章主要介绍了angular中实现li或者某个元素点击变色的两种方法,非常具有实用价值,需要的朋友可以参考下 本文介绍了angular中实现li或者某个元素点击变色的两种方法,分享 ...
- SQL Server中灾难时备份结尾日志(Tail of log)的两种方法
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/CareySon/archive/2012/02/23/2365006.html SQL Server中灾难时备份结尾日志(Tail of log) ...
- C#统计给定的文本中字符出现的次数,使用循环和递归两种方法
前几天看了一个.net程序员面试题目,题目是”统计给定的文本中字符出现的次数,使用循环和递归两种方法“. 下面是我对这个题目的解法: 1.使用循环: /// <summary> /// 使 ...
- java中把文件拷贝到指定目录下最简单几种方法
java中把文件拷贝到指定目录下最简单几种方法 String savePath = "D:/file";// 文件保存到d盘的file目录下 File savefile = n ...
- Mac 中显示资源库(Library)文件夹目录的几种方法
Mac中Library目录在10.6.7系统之后默认隐藏的,要想找到此文件夹有如下几种方法: 1. 用命令可以使其显示: 在终端中执行命令: chflags nohidden ~/Library ...
- 解决在onCreate()过程中获取View的width和Height为0的4种方法
很经常当我们动态创建某些View时,需要通过获取他们的width和height来确定别的view的布局,但是在onCreate()获取view的width和height会得到0.view.getWid ...
- 简析Geoserver中获取图层列表以及各图层描述信息的三种方法
文章版权由作者李晓晖和博客园共有,若转载请于明显处标明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/naaoveGIS/. 1.背景 实际项目中需要获取到Geoserver中的图层组织以及各图层 ...
随机推荐
- 【前端】【Vue】Vue3自适应瀑布流解决方案
Vue3自适应瀑布流解决方案 效果如上图所示. 说明:Vue3.[vue-masonry插件](vue-masonry - npm (npmjs.com)) 建议查看官方文档vue-masonry ( ...
- 解决:pip is configured with locations that require TLS/SSL
解决: mkdir -p ~/.pipvim ~/.pip/pip.conf然后输入内容: [global]index-url = http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/sim ...
- 龙哥量化:代写技术指标,通达信ZIG函数优化改进之字转向,高点用最高价,低点用最低价
如果您需要代写技术指标公式, 请联系我. 龙哥QQ:591438821 龙哥微信:Long622889 N:=50; A1:ZIG(3,N/10); 代码只有两行,参数是50,表示涨幅5%,在调参数时 ...
- findHomography()函数详解
indHomography: 计算多个二维点对之间的最优单映射变换矩阵 H(3行x3列) ,使用最小均方误差或者RANSAC方法 函数功能:找到两个平面之间的转换矩阵. Mat cv::findHom ...
- 用领域驱动DDD的方式实现购物车-基于abp一代6.2
废话 之前七七八八看了些DDD相关概念,充血模型.领域事件.领域服务.应用服务等,大致能理解但从未实践.最近在用ABP做个电商模块,尝试用DDD方式来实现购物车功能,感觉还行,下面做个记录. 业务分析 ...
- MySQL的7种JOIN
原文链接:https://blog.liuzijian.com/post/61e35b3c-fae7-4e0b-aaa2-1d1f2896d9b1.html -- 创建数据库 CREATE DATAB ...
- 包装类(Wrapper) 的使用
package com.ch.java2; import org.junit.Test; /* * 包装类的使用: * 1.java提供了8种基本数据类型对应的包装类,使得基本数据类型的变量具有类的特 ...
- 0511-FileWrite字符输出流和JDK7中try..finally新的特性
package A10_IOStream; import java.io.*; /* java.io.Writer:字符输出流,是所有字符数出流的最顶层抽象父类 共性方法 void write(int ...
- 微信小程序slot(一)
在我们封装组件的时候,有些时候,我们需要使用类似于vue中的slot插槽: 小程序借鉴了这个优秀的想法: 在小程序中,组件模板中可以提供一个 <slot> 节点,用于承载组件引用时提供的子 ...
- oracle11gRAC升级到19C
升级oracle11g集群到19.3 前述环境检查: [root@qhdb1 ~]# crsctl status res -t ------------------------------------ ...
